Nicotinamide/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "== 食品源 == {{Anchor|Food sources}} ナイアシンアミドは、主に肉類、魚類、ナッツ類、キノコ類に微量に含まれる。ナイアシンアミドは、一般的にシリアルなどに添加されている。多くのマルチビタミンには20~30{{nbsp}}mgのビタミンB<sub>3</sub>が含まれており、より高用量のものもある。" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "=== 生化学 === thumb|upright=1.3|NAD<sup>+</sup>分子上の活性ニコチンアミド基は、多くの代謝経路で酸化を受ける。 ニコチンアミドは、補酵素ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド(NADH / NAD<sup>+</sup>)の一部として、生命維持に不可欠である。細胞内では、ニコチンアミドはNAD<sup>+</sup>とnicotinami..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
[[nicotinonitrile/ja|ニコチノニトリル]]の加水分解は、''[[Rhodococcus rhodochrous/ja|ロドコッカス]]''J1由来の酵素[[nitrile hydratase/ja|ニトリルヒドラターゼ]]によって触媒される。動物飼料用に年間3500トンのニコチンアミドが生産される。この酵素により、アミドから[[nicotinic acid/ja|ニコチン酸]]へのさらなる加水分解が避けられるため、より選択的な合成が可能になる。ニコチン酸からニコチンアミドを作ることもできる。''[[:en:Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry|ウルマン工業化学百科事典]]''によると、2014年には世界で31,000トンのニコチンアミドが販売された。 | [[nicotinonitrile/ja|ニコチノニトリル]]の加水分解は、''[[Rhodococcus rhodochrous/ja|ロドコッカス]]''J1由来の酵素[[nitrile hydratase/ja|ニトリルヒドラターゼ]]によって触媒される。動物飼料用に年間3500トンのニコチンアミドが生産される。この酵素により、アミドから[[nicotinic acid/ja|ニコチン酸]]へのさらなる加水分解が避けられるため、より選択的な合成が可能になる。ニコチン酸からニコチンアミドを作ることもできる。''[[:en:Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry|ウルマン工業化学百科事典]]''によると、2014年には世界で31,000トンのニコチンアミドが販売された。 | ||
=== 生化学 === | |||
=== | [[File:NAD+ Oxidation and Reduction.png|thumb|upright=1.3|NAD<sup>+</sup>分子上の活性ニコチンアミド基は、多くの代謝経路で酸化を受ける。]] | ||
[[File:NAD+ Oxidation and Reduction.png|thumb|upright=1.3| | ニコチンアミドは、補酵素[[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide/ja|ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド]](NADH / NAD<sup>+</sup>)の一部として、生命維持に不可欠である。細胞内では、ニコチンアミドはNAD<sup>+</sup>と[[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate/ja|ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチドリン酸]](NADP<sup>+</sup>)に取り込まれる。NAD<sup>+</sup>とNADP<sup>+</sup>は、多種多様な酵素的[[redox/ja|酸化還元]]反応、特に[[glycolysis/ja|解糖]]、[[citric acid cycle/ja|クエン酸サイクル]]、[[electron transport chain/ja|電子伝達系]]の[[Cofactor (biochemistry)/ja|補要素]]である。ヒトがニコチンアミドを摂取した場合、おそらくそれをNADに変換する一連の反応を経て、NADP<sup>+</sup>を形成する変換を受けることができる。このNAD<sup>+</sup>の生成方法は、[[Salvage Pathway/ja|サルベージ経路]]と呼ばれている。しかし、人体はニコチンアミドを摂取しなくても、アミノ酸[[tryptophan/ja|トリプトファン]]とナイアシンからNAD<sup>+</sup>を作り出すことができる。 | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 13:14, 3 April 2024
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌnaɪəˈsɪnəmaɪd/, /ˌnɪkəˈtɪnəmaɪd/ |
| Other names | NAM, 3-pyridinecarboxamide niacinamide nicotinic acid amide vitamin PP nicotinic amide vitamin B3 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6H6N2O |
| Molar mass | 122.127 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.40 g/cm3 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 129.5 °C (265.1 °F) |
| Boiling point | 334 °C (633 °F) |
| |
| |
ナイアシンアミド(Niacinamide)またはニコチンアミド(nicotinamide)は、食品に含まれるビタミンB3の一種であり、栄養補助食品や医薬品として用いられる。サプリメントとしては、ペラグラ(ナイアシン欠乏症)を予防・治療するために経口で使用される。この目的にはニコチン酸(ナイアシン)が使用されることもあるが、ナイアシンアミドは皮膚潮紅を引き起こさないという利点がある。クリームとしてはにきびの治療に使用され、臨床研究では色素沈着や赤みを抑えることで老化した肌の見た目を改善することが確認されている。水溶性ビタミンである。ナイアシンアミドはサプリメント名であり、ニコチンアミドは学名である。
副作用はほとんどない。高用量では肝障害が起こることがある。通常量は妊娠中の使用にも安全である。ナイアシンアミドはビタミンB系列の医薬品、特にビタミンB3複合体に属する。ニコチン酸のアミドである。ナイアシンアミドを含む食品には、酵母、肉、牛乳、緑黄色野菜などがある。
ナイアシンアミドは1935年から1937年にかけて発見された。世界保健機関の必須医薬品リストに掲載されている。ナイアシンアミドはジェネリック医薬品および市販薬として入手可能である。商業的には、ナイアシンアミドはニコチン酸(ナイアシン)またはニコチノニトリルから作られる。一部の国では、穀類にナイアシンアミドが添加されている。
医療用途
ナイアシン欠乏症
ナイアシンアミドは、ナイアシン欠乏によって引き起こされるペラグラの治療薬として好まれている。
にきび
ナイアシンアミドは、試験管内ではヒトケラチノサイトにおけるセラミドの生合成を増加させ、生体内では表皮透過性バリアを改善する。2%と4週間のナイアシンアミド局所塗布は、皮脂排泄率の低下に有効であることが判明している。ナイアシンアミドは、アクネ菌によるトール様受容体2の活性化を防ぎ、その結果、炎症性インターロイキン8産生を抑制することが示されている。
皮膚がん
ナイアシンアミドは1日500~1000 mgの用量で、メラノーマ以外の皮膚がんのリスクが高い人のリスクを低下させる。
副作用
ナイアシンアミドは副作用が少ない。3g/日を超える超高用量では、急性肝毒性が少なくとも1例記録されている。通常量は妊娠中にも安全である。
化学
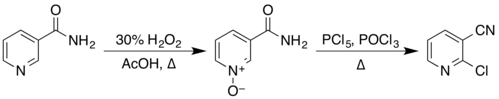
ニコチンアミドの構造は、ピリジン環に一級アミド基がメタ位に結合したものである。ニコチン酸のアミドである。芳香族化合物であるため、求電子芳香族置換反応を起こし、2つの官能基の変換を受ける。有機合成で報告されているこれらの反応の例には、N-オキシドを経由する2段階プロセスによる2-クロロニコチノニトリルの調製が含まれる、
ニコチノニトリルからは五酸化リンとの反応によって、3-アミノピリジンからは臭素と水酸化ナトリウムからその場で調製した次亜臭素酸ナトリウムの溶液との反応によって得られる。

工業生産
ニコチノニトリルの加水分解は、ロドコッカスJ1由来の酵素ニトリルヒドラターゼによって触媒される。動物飼料用に年間3500トンのニコチンアミドが生産される。この酵素により、アミドからニコチン酸へのさらなる加水分解が避けられるため、より選択的な合成が可能になる。ニコチン酸からニコチンアミドを作ることもできる。ウルマン工業化学百科事典によると、2014年には世界で31,000トンのニコチンアミドが販売された。
生化学

ニコチンアミドは、補酵素ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド(NADH / NAD+)の一部として、生命維持に不可欠である。細胞内では、ニコチンアミドはNAD+とニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチドリン酸(NADP+)に取り込まれる。NAD+とNADP+は、多種多様な酵素的酸化還元反応、特に解糖、クエン酸サイクル、電子伝達系の補要素である。ヒトがニコチンアミドを摂取した場合、おそらくそれをNADに変換する一連の反応を経て、NADP+を形成する変換を受けることができる。このNAD+の生成方法は、サルベージ経路と呼ばれている。しかし、人体はニコチンアミドを摂取しなくても、アミノ酸トリプトファンとナイアシンからNAD+を作り出すことができる。
NAD+ acts as an electron carrier that mediates the interconversion of energy between nutrients and the cell's energy currency, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In oxidation-reduction reactions, the active part of the cofactor is the nicotinamide. In NAD+, the nitrogen in the aromatic nicotinamide ring is covalently bonded to adenine dinucleotide. The formal charge on the nitrogen is stabilized by the shared electrons of the other carbon atoms in the aromatic ring. When a hydride atom is added onto NAD+ to form NADH, the molecule loses its aromaticity, and therefore a good amount of stability. This higher energy product later releases its energy with the release of a hydride, and in the case of the electron transport chain, it assists in forming adenosine triphosphate.
When one mole of NADH is oxidized, 158.2 kJ of energy will be released.
Biological role
Nicotinamide occurs as a component of a variety of biological systems, including within the vitamin B family and specifically the vitamin B3 complex. It is also a critically important part of the structures of NADH and NAD+, where the N-substituted aromatic ring in the oxidised NAD+ form undergoes reduction with hydride attack to form NADH. The NADPH/NADP+ structures have the same ring, and are involved in similar biochemical reactions.
Nicotinamide can be methylated in the liver to biologically active 1-Methylnicotinamide when there are sufficient methyl donors.
食品源
ナイアシンアミドは、主に肉類、魚類、ナッツ類、キノコ類に微量に含まれる。ナイアシンアミドは、一般的にシリアルなどに添加されている。多くのマルチビタミンには20~30 mgのビタミンB3が含まれており、より高用量のものもある。
公定書収載状況
研究
2015年の試験で、ナイアシンアミドは非黒色腫皮膚癌と光線性角化症の新規発生率を減少させることが明らかになった。
ナイアシンアミドは、水疱性類天疱瘡非メラノーマ皮膚がんの治療など、さらに多くの疾患に対して研究されている。
ナイアシンアミドは乾癬の治療に有効かもしれない。
にきび、酒さ、自己免疫性水疱症、老化皮膚、アトピー性皮膚炎の治療にナイアシンアミドの役割が期待できるという暫定的な証拠がある。ナイアシンアミドはまた、放射線や化学療法によって誘発されたDNA鎖切断の再結合に関与する酵素であるポリ(ADP-リボース)ポリメラーゼ(PARP-1)を阻害する。ARCON(加速放射線療法+カルボゲン吸入+ニコチンアミド)は、がんにおいて研究されている。
研究では、ナイアシンアミドがHIVの治療に一役買う可能性が示唆されている。