Metabolism/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "==生物の熱力学== {{Anchor|Thermodynamics of living organisms}} {{further/ja|Biological thermodynamics/ja}} 生物は熱力学の法則に従わなければならないが、それは熱の伝達とワークを記述するものである。熱力学の第二法則は、どのような孤立系でもエントロピー(無秩序)の量は減少しないと..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "==調節と制御== {{Anchor|Regulation and control}} {{further/ja|Metabolic pathway/ja|Metabolic control analysis/ja|Hormone|Regulatory enzymes/ja|Cell signaling/ja}} ほとんどの生物の環境は常に変化しているため、細胞内の状態を一定に保つためには、代謝反応を細かく制御する必要がある。代謝調節はまた、生物がシグナルに反応し、環境と積極的に相互作用することを可..." |
||
| Line 209: | Line 209: | ||
細胞の代謝は、異化の[[:en:spontaneous process|自発的過程]]を同化の非自発的過程と結合させることでこれを実現している。[[:en:non-equilibrium thermodynamics|熱力学]]の用語では、代謝は無秩序を作り出すことによって秩序を維持する。 | 細胞の代謝は、異化の[[:en:spontaneous process|自発的過程]]を同化の非自発的過程と結合させることでこれを実現している。[[:en:non-equilibrium thermodynamics|熱力学]]の用語では、代謝は無秩序を作り出すことによって秩序を維持する。 | ||
==調節と制御== | |||
{{Anchor|Regulation and control}} | |||
{{further|Metabolic pathway|Metabolic control analysis|Hormone|Regulatory enzymes|Cell signaling}} | {{further/ja|Metabolic pathway/ja|Metabolic control analysis/ja|Hormone|Regulatory enzymes/ja|Cell signaling/ja}} | ||
ほとんどの生物の環境は常に変化しているため、細胞内の状態を一定に保つためには、代謝反応を細かく[[:en:Control theory|制御]]する必要がある。代謝調節はまた、生物がシグナルに反応し、環境と積極的に相互作用することを可能にする。代謝経路がどのように制御されているかを理解するためには、密接に結びついた2つの概念が重要である。第一に、経路中の酵素の''制御''とは、シグナルに応答してその活性がどのように増減するかということである。第二に、この酵素が及ぼす''制御''とは、その活性の変化が経路全体の速度(経路を通る[[flux/ja|フラックス]])に及ぼす影響である。例えば、ある酵素が活性に大きな変化を示しても(すなわち、その酵素は高度に制御されている)、その変化が代謝経路のフラックスにほとんど影響しなければ、その酵素は経路の制御には関与していないことになる。 | |||
[[File:Insulin glucose metabolism ZP.svg|thumb|right|upright=1.35|''' | [[File:Insulin glucose metabolism ZP.svg|thumb|right|upright=1.35|'''グルコースの取り込みと代謝に対するインスリンの効果''' インスリンはレセプターに結合し(1)、多くのタンパク質の活性化カスケードを開始する(2)。これらには、Glut-4トランスポーターの[[plasma membrane/ja|細胞膜]]への転位とグルコースの流入(3)、[[glycogen/ja|グリコーゲン]]合成(4)、[[glycolysis/ja|解糖]](5)、[[fatty acid/ja|脂肪酸]]合成(6)などが含まれる。]] | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 12:55, 2 February 2024


| Part of a series on |
| Biochemistry/ja |
|---|
 |
代謝(/məˈtæbəlɪzəm/, from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, "change")とは、生物における生命を維持するための一連の化学反応のことである。代謝の3つの主な機能は、食物中のエネルギーを細胞プロセスを実行するために利用可能なエネルギーに変換すること、食物をタンパク質、脂質、核酸、および一部の炭水化物の構成要素に変換すること、および代謝廃棄物を除去することである。 これらの酵素触媒反応により、生物は成長・繁殖し、構造を維持し、環境に対応することができる、 また、代謝という言葉は、消化を含む生物で起こる全ての化学反応の総体を指すこともある、 この場合、上記の細胞内の一連の反応は中間(または中間代謝)と呼ばれる。
代謝反応は、異化-化合物の分解(例えば、細胞呼吸によるグルコースからピルビン酸への分解)と、同化-化合物(タンパク質、炭水化物、脂質、核酸など)の構築(合成)に分類される。通常、異化はエネルギーを放出し、同化はエネルギーを消費する。
代謝の化学反応は代謝経路に組織化されており、そこではある化学物質が一連のステップを経て別の化学物質に変換され、各ステップは特定の酵素によって促進される。酵素は、エネルギーを放出する自発的反応に結合させることによって、エネルギーを必要とし、それ自体では起こらないような望ましい反応を生物が推進することを可能にするので、代謝にとって極めて重要である。酵素は触媒として機能し、反応をより速く進行させる。また、例えばセルの環境の変化や他の細胞からのシグナルに応答して、代謝反応の速度を調節することもできる。
特定の生物の代謝システムは、どの物質を栄養とし、どの物質を毒とするかを決定する。例えば、いくつかの原核生物は硫化水素を栄養としているが、このガスは動物にとっては毒である。生物の基礎代謝量は、これらすべての化学反応によって消費されるエネルギー量の尺度である。
代謝の顕著な特徴は、大きく異なる種の間で基本的な代謝経路が類似していることである。例えば、クエン酸サイクルの中間体として最もよく知られているカルボン酸のセットは、すべての既知の生物に存在し、単細胞細菌の大腸菌やゾウのような巨大な多細胞生物などの多様な種に見られる。このような代謝経路の類似性は、進化史において早くから出現していたためと考えられ、その保持はその効能によるものと考えられる。2型糖尿病、メタボリックシンドローム、がんなどの様々な疾患では、正常な代謝が破綻している。がん細胞の代謝もまた正常細胞の代謝とは異なっており、こうした違いを利用してがんの治療介入のターゲットを見つけることができる。
主要な性化学物質


動物、植物、微生物を構成する構造のほとんどは、4つの基本的なクラスの分子からできている: アミノ酸、炭水化物、核酸、脂質(しばしば脂肪と呼ばれる)である。これらの分子は生命維持に不可欠であるため、代謝反応は細胞や組織を作る際にこれらの分子を作ることに集中するか、消化によって分解してエネルギーを得るために使用することに集中する。これらの生化学物質は結合して、DNAやタンパク質といった生命に必須な高分子のポリマーを作ることができる。
| 分子の種類 | モノマーの形態名 | ポリマーの形態名 | ポリマー形態の例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| アミノ酸 | アミノ酸 | プロテイン (ポリペプチドでできている) | 繊維状タンパク質 と 球状タンパク質 |
| 炭水化物 | 単糖類 | 多糖類 | スターチ, グリコーゲン, セルロース |
| 核酸 | ヌクレオチド | ポリヌクレオチド | DNA と RNA |
アミノ酸とタンパク質
タンパク質はアミノ酸がペプチド結合で結合した直鎖状に配列したものである。多くのタンパク質は酵素であり、代謝における化学反応を触媒する。 他のタンパク質は、細胞の形状を維持する足場のシステムである細胞骨格を形成するものなど、構造的または機械的な機能を持つ。 タンパク質はまた、細胞シグナル伝達、免疫応答、細胞接着、膜を介した活性輸送、および細胞周期において重要である。 アミノ酸はまた、クエン酸サイクル(トリカルボン酸サイクル)に入るための炭素源を提供することで、細胞のエネルギー代謝にも寄与する、 特に、グルコースのような主要なエネルギー源が不足しているときや、細胞が代謝ストレスを受けているときには、この役割を果たす。
脂質
脂質は生化学物質の中で最も多様なグループである。その主な構造的用途は、細胞膜のような内外の生体膜の一部としての利用である。その化学エネルギーを利用することもできる。脂質は、酸素を含む小さな極性領域を持つ長い非極性炭化水素鎖を含む脂肪酸のポリマーである。脂質は通常疎水性または両親媒性の生体分子と定義されるが、エタノール、ベンゼン、クロロホルムなどの有機溶媒に溶解する。脂肪は脂肪酸とグリセロールを含む化合物の大きなグループであり、エステル結合によって3つの脂肪酸に結合したグリセロール分子はトリアシルグリセリドと呼ばれる。この基本構造にはいくつかのバリエーションがあり、スフィンゴミエリンのsphingosine/jaスフィンゴシンのような骨格や、リン脂質のようなリン酸のような親水性|親水性基がある。ステロールなどのステロイドも脂質の主要な分類である。
炭水化物
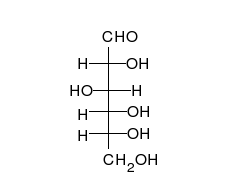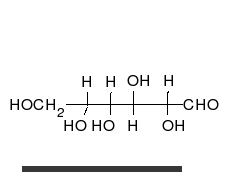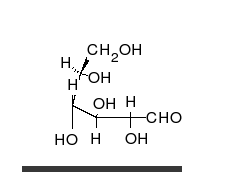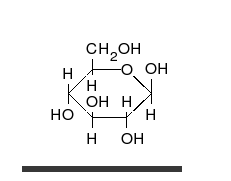
炭水化物は、多くの水酸基が結合したアルデヒドまたはケトンであり、直鎖または環として存在することができる。炭水化物は最も豊富な生体分子であり、エネルギーの貯蔵や輸送(デンプン、グリコーゲン)、構造成分(植物のセルロース、動物のキチン)など、多くの役割を担っている。基本的な炭水化物単位は単糖と呼ばれ、ガラクトース、フルクトース、そして最も重要なグルコースが含まれる。単糖類は連結してほとんど無限の方法で多糖類を形成することができる。
核酸
DNAとRNAという2つの核酸は、核酸のポリマーである。各核酸は、リボースまたはデオキシリボースの糖基に結合したリン酸から構成され、窒素塩基に結合している。核酸は、遺伝情報の保存と利用、および転写とタンパク質生合成の過程を通してのその解釈に重要である。この情報はDNA修復機構によって保護され、DNA複製によって伝播する。多くのウイルスはRNAゲノムを持っており、例えばHIVは逆転写を用いてそのウイルスRNAゲノムからDNAテンプレートを作り出す。スプライソソームやリボソームなどのリボザイムに含まれるRNAは、化学反応を触媒できるので酵素に似ている。個々の核酸はリボース糖に核酸塩基を結合させて作られる。これらの塩基は窒素を含む複素環であり、プリンまたはピリミジンに分類される。ヌクレオチドはまた、代謝基転移反応における補酵素としても働く。
補酵素(コエンザイム)

代謝には膨大な数の化学反応が含まれるが、そのほとんどは、分子内の原子の官能基とその結合の移動を伴う、いくつかの基本的なタイプの反応に分類される。この一般的な化学反応によって、細胞は小さな代謝中間体のセットを使って、異なる反応間で化学基を運ぶことができる。これらの基転移中間体は補酵素と呼ばれる。各クラスの基転移反応は、特定の補酵素によって行われる。補酵素は、それを生成する一連の酵素の基質であり、それを消費する一連の酵素の基質でもある。 したがって、これらの補酵素は絶えず作られ、消費され、そして再利用される。
中心的な補酵素のひとつが、細胞のエネルギー通貨であるアデノシン三リン酸(ATP)である。このヌクレオチドは、異なる化学反応間で化学エネルギーを伝達するために使われる。細胞内に存在するATPの量はわずかだが、絶えず再生されるため、人体は1日に自分の体重ほどのATPを使うことができる。ATPは異化作用と同化作用の橋渡しをする。異化作用によって分子が分解され、同化作用によって分子が組み合わされる。異化反応はATPを生成し、同化反応はATPを消費する。また、リン酸化反応ではリン酸基の運搬役としても働く。
ビタミンは細胞内で作ることができない、少量で必要とされる有機化合物である。ヒトの栄養学では、ほとんどのビタミンは修飾後に補酵素として機能する。例えば、全ての水溶性ビタミンは細胞内で使用される際にリン酸化されるか、ヌクレオチドと結合する。ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド(NAD+)は、ビタミンB3の誘導体(ナイアシン)であり、水素受容体として働く重要な補酵素である。何百種類ものデヒドロゲナーゼが基質から電子を除去し、NAD+をNADHに還元する。この還元型補酵素は、水素原子を基質に移動させる必要のある細胞内の還元酵素の基質となる。ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチドは、細胞内でNADHとNADPHという2つの関連した形で存在する。NAD+/NADH型は異化反応においてより重要であり、NADP+/NADPHは同化反応において使用される。

ミネラルと補酵素
無機元素は代謝において重要な役割を果たす。豊富に含まれるものもあれば(例えばナトリウムやカリウム)、微量で機能するものもある。人間の体重の約99%は炭素、窒素、カルシウム、ナトリウム、塩素、カリウム、水素、リン、酸素、硫黄の元素で構成されている。有機化合物(タンパク質、脂質、炭水化物)は炭素と窒素の大部分を含み、酸素と水素の大部分は水として存在する。
豊富な無機元素は電解質として機能する。最も重要なイオンはナトリウム、カリウム、カルシウム、マグネシウム、塩化物、リン酸塩および有機イオン重炭酸塩である。細胞膜を横切る正確なイオン勾配の維持は、浸透圧とpHを維持する。これらの組織における活動電位は、細胞外液と細胞の体液である細胞質との間の電解質の交換によって生成されるため、イオンは神経や筋肉の機能にとっても重要である。電解質はイオンチャネルと呼ばれる細胞膜のタンパク質を通して細胞に出入りする。例えば、筋収縮は、細胞膜とT管にあるイオンチャネルを介したカルシウム、ナトリウム、カリウムの移動に依存している。
遷移金属は通常微量元素として生体内に存在するが、その中でも亜鉛と鉄が最も多く含まれている。金属補因子はタンパク質の特定の部位に強固に結合している。酵素補因子は触媒反応中に修飾されることがあるが、触媒された反応の終了時には必ず元の状態に戻る。金属微量栄養素は、特定の輸送体によって生体内に取り込まれ、使用されないときはフェリチンやメタロチオネインなどの貯蔵タンパク質に結合する。
異化
異化とは、大きな分子を分解する一連の代謝過程のことである。これには食物分子の分解と酸化が含まれる。異化反応の目的は、分子を構築する同化反応に必要なエネルギーと成分を供給することである。これらの異化反応の正確な性質は生物によって異なり、生物はエネルギー、水素、炭素の供給源(一次栄養群)に基づいて下表のように分類することができる。有機栄養生物は水素原子や電子の供給源として有機分子を利用し、岩石栄養生物は無機基質を利用する。光栄養生物が太陽光を化学エネルギーに変換するのに対し、化学栄養生物は還元されたドナー分子、例えば有機分子、水素、硫化水素、鉄イオンから酸素、硝酸塩、硫酸塩への電子の移動を含む酸化還元反応に依存する。動物では、これらの反応には複雑な有機分子が関与しており、それらは二酸化炭素や水などのより単純な分子に分解される。植物やシアノバクテリアなどの光合成生物は、太陽光から吸収したエネルギーを蓄えるために同様の電子伝達反応を用いる。
| エネルギー源 | 日光 | photo- | -troph | ||
| 分子 | chemo- | ||||
| 水素または電子供与体 | 有機化合物 | organo- | |||
| 無機化合物 | litho- | ||||
| 炭素供給源 | 有機化合物 | hetero- | |||
| 無機化合物 | auto- | ||||
動物における最も一般的な一連の異化反応は、主に3つの段階に分けることができる。第一段階では、タンパク質、多糖類、脂質などの大きな有機分子が、細胞外で消化されて小さな成分になる。次に、これらの小さな分子は細胞に取り込まれ、より小さな分子、通常はアセチルコエンザイムA(アセチル-CoA)に変換され、エネルギーを放出する。最後に、アセチル-CoA上のアセチル基はクエン酸サイクルと電子伝達系で水と二酸化炭素に酸化され、補酵素ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド(NAD+)をNADHに還元しながらさらにエネルギーを放出する。
消化
高分子は細胞で直接処理することができない。高分子は細胞の代謝に使われる前に、より小さな単位に分解されなければならない。これらの高分子を消化するために、様々な種類の酵素が使われる。これらの消化酵素には、タンパク質をアミノ酸に消化するプロテアーゼや、多糖類を単糖類として知られる単純な糖に消化するグリコシドヒドロラーゼが含まれる。
微生物は単純に消化酵素を周囲に分泌するが、動物は胃や膵臓などの内蔵や唾液腺などの特殊な細胞からのみ分泌する。これらの細胞外酵素によって放出されたアミノ酸や糖は、次に能動輸送タンパク質によって細胞内に送り込まれる。

有機化合物からのエネルギー
炭水化物の異化とは、炭水化物をより小さな単位に分解することである。糖質は通常、単糖に消化された後に細胞内に取り込まれる。細胞内に取り込まれると、主な分解経路は解糖であり、グルコースやフルクトースなどの糖がピルビン酸に変換され、いくらかのATPが生成される。ピルビン酸はいくつかの代謝経路の中間体であるが、大部分は好気的(酸素を用いる)解糖によってアセチル-CoAに変換され、クエン酸サイクルに供給される。クエン酸サイクルではさらにいくらかのATPが生成されるが、最も重要な生成物はNADHであり、アセチル-CoAが酸化される際にNAD+から作られる。この酸化は、廃棄物として二酸化炭素を放出する。嫌気的条件下では、解糖は乳酸を生成し、酵素乳酸デヒドロゲナーゼがNADHをNAD+に再酸化して解糖で再利用する。

脂肪は加水分解によって遊離脂肪酸とグリセロールに異化される。グリセロールは解糖に入り、脂肪酸はβ酸化によって分解されてアセチル-CoAを放出し、クエン酸サイクルに供給される。脂肪酸は糖質よりも酸化時に多くのエネルギーを放出する。ステロイドもまた、いくつかの細菌によってβ酸化に似たプロセスで分解され、この分解プロセスでは、大量のアセチル-CoA、プロピオニル-CoA、ピルビン酸が放出される。また、M. tuberculosisは脂質コレステロールを唯一の炭素源として増殖することができ、コレステロール利用経路に関与する遺伝子はM. tuberculosisの感染ライフサイクルの様々な段階において重要であることが確認されている。
アミノ酸は、タンパク質や他の生体分子を合成するために使われるか、エネルギーを生産するために尿素と二酸化炭素に酸化される。酸化経路は、トランスアミナーゼによるアミノ基の除去から始まる。アミノ基は尿素サイクルに供給され、脱アミノ化された炭素骨格がケト酸の形で残る。これらのケト酸のいくつかはクエン酸サイクルの中間体であり、例えばα-ケトグルタル酸はグルタミン酸の脱アミノ化によって形成される。また、糖原性アミノ酸は糖新生によってグルコースに変換されることもある(後述)。
エネルギー変換
酸化的リン酸化
酸化的リン酸化では、クエン酸サイクルのような領域で有機分子から取り除かれた電子が酸素に移動し、放出されたエネルギーを使ってATPが作られる。これは真核生物では電子伝達鎖と呼ばれるミトコンドリアの膜にある一連のタンパク質によって行われる。原核生物では、これらのタンパク質は細胞の内膜に存在する。これらのタンパク質は、NADHのような被還元分子のエネルギーを使って、膜を横切ってプロトンを送り出す。
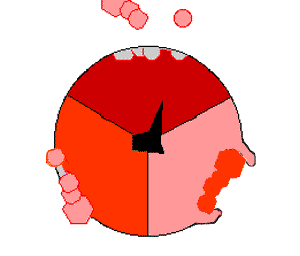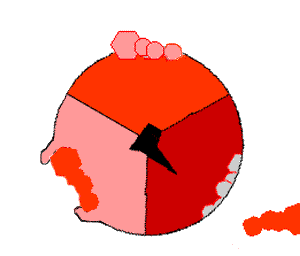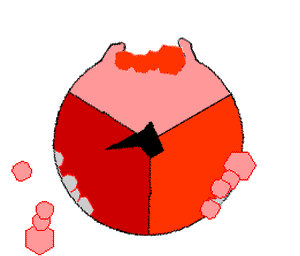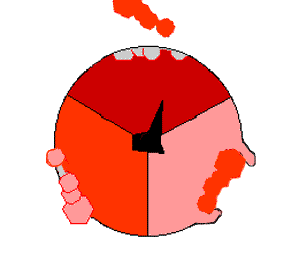
ミトコンドリアからプロトンを送り出すと、膜を横切ってプロトンの濃度差が生じ、電気化学的勾配が発生する。この力によって、プロトンはATP合成酵素と呼ばれる酵素の基部を通ってミトコンドリア内に戻る。プロトンの流れは茎サブユニットを回転させ、合成酵素ドメインの活性部位の形状を変化させ、アデノシン二リン酸 をリン酸化させ、ATPに変える。
無機化合物からのエネルギー
ケモリソトロフは原核生物に見られる代謝の一種で、無機化合物の酸化からエネルギーを得る。これらの生物は還元力の源として水素、還元された硫黄化合物(硫化物、硫化水素、チオ硫酸など)、鉄(Fe(II))、またはアンモニアを用いることができ、これらの化合物の酸化からエネルギーを得る。これらの微生物プロセスは、酢酸生成、硝化、脱窒などの地球規模の生物地球化学サイクルにおいて重要であり、土壌肥沃度にとって重要である。
光からのエネルギー
太陽光のエネルギーは、植物、シアノバクテリア、細菌、緑色硫黄細菌、およびいくつかの原生生物によって取り込まれる。このプロセスは、後述する光合成の一部として、二酸化炭素の有機化合物への変換と結合していることが多い。しかし、原核生物ではエネルギー捕捉系と炭素固定系は別々に作動することもある。紫色細菌や緑色硫黄細菌は、炭素固定と有機化合物の発酵を切り替えながら、エネルギー源として太陽光を利用することができるからである。
多くの生物において、太陽エネルギーの取り込みは、プロトン濃度勾配としてのエネルギー貯蔵を伴うため、原理的には酸化的リン酸化と似ている。このプロトン原動力が、ATP合成の原動力となる。この電子輸送鎖の駆動に必要な電子は、光合成反応センターと呼ばれる光を集めるタンパク質から供給される。反応中心は存在する光合成色素の性質によって2種類に分類され、ほとんどの光合成細菌は1種類しか持たないが、植物やシアノバクテリアは2種類持っている。
植物、藻類、シアノバクテリアでは、光化学系IIが光エネルギーを使って水から電子を取り出し、廃棄物として酸素を放出する。電子は次にシトクロムb6f複合体に流れ、そのエネルギーを使って葉緑体のチラコイド膜を横切ってプロトンを送り出す。これらのプロトンは、先ほどと同じようにATP合成酵素を駆動しながら、膜を通って再び移動する。その後、電子は光化学系Iを流れ、補酵素NADP+を還元するのに使われる。
同化
同化作用とは、異化作用によって放出されたエネルギーが複雑な分子を合成するために使われる一連の建設的な代謝過程のことである。一般に、細胞構造を構成する複雑な分子は、より小さく単純な前駆体から段階的に構築される。同化作用には3つの基本段階がある。第一に、アミノ酸、単糖類、イソプレノイド、ヌクレオチドなどの前駆体の生産、第二に、ATPからのエネルギーを用いて反応性形態への活性化、第三に、これらの前駆体をタンパク質、多糖類、脂質、核酸などの複雑な分子に組み立てることである。
生物の同化作用は、細胞内で構築される分子の供給源によって異なることがある。植物のような独立栄養生物は、二酸化炭素や水のような単純な分子から、多糖類やタンパク質のような細胞内の複雑な有機分子を構築することができる。一方、従属栄養生物は、これらの複雑な分子を作り出すために、単糖類やアミノ酸など、より複雑な物質の供給源を必要とする。光独立栄養生物と光従属栄養生物は光からエネルギーを得るが、化学独立栄養生物と化学従属栄養生物は酸化反応からエネルギーを得る。
炭素固定

光合成とは、太陽光と二酸化炭素(CO2)から炭水化物を合成することである。植物、シアノバクテリア、藻類では、酸素光合成は水を分解し、酸素は廃棄物として生成される。この過程では、前述のように光合成反応センターで生成されたATPとNADPHを用いてCO2をグリセリン酸3-リン酸に変換し、これをグルコースに変換することができる。この炭素固定反応は、カルビン - ベンソン サイクルの一部として、酵素RuBisCOによって行われる。植物ではC3炭素固定、C4炭素固定、CAM光合成の3種類の光合成が行われる。C3光合成はCO2を直接固定するが、C4光合成とCAM光合成は、強い日差しと乾燥条件に対処するための適応として、CO2をまず他の化合物に組み込む。
光合成原核生物では、炭素固定機構はより多様である。ここでは、二酸化炭素はカルビン-ベンソンサイクル、逆クエン酸サイクル、またはアセチル-CoAのカルボキシル化によって固定される。原核生物の化学的独立栄養生物もカルビン・ベンソンサイクルによってCO2を固定するが、反応の駆動には無機化合物からのエネルギーを用いる。
炭水化物と糖鎖
炭水化物の同化において、単純な有機酸はグルコースのような単糖に変換され、次にデンプンのような多糖を組み立てるのに使われる。ピルビン酸、乳酸、グリセロール、グリセリン酸3-リン酸、アミノ酸などの化合物からグルコースを生成することを糖新生という。糖新生は一連の中間体を介してピルビン酸をグルコース-6-リン酸に変換するが、その多くは解糖と共通している。しかしながら、この経路は単に解糖を逆に実行したものではなく、いくつかのステップが非解糖系酵素によって触媒されている。このことは、グルコースの生成と分解を別々に制御することを可能にし、両方の経路が同時に無駄なサイクルで走ることを防ぐという意味で重要である。
脂肪はエネルギーを貯蔵する一般的な方法であるが、ヒトのような脊椎動物ではアセチル-CoAをピルビン酸に変換することができないため、貯蔵されている脂肪酸を糖新生によってグルコースに変換することができない。植物は必要な酵素機構を持っているが、動物は持っていない。その結果、脊椎動物は長期間の飢餓の後、脂肪酸を代謝できない脳などの組織でグルコースの代わりに脂肪酸からケトン体を生成する必要がある。植物や細菌などの他の生物では、この代謝の問題はグリオキシル酸サイクルを用いて解決される。このサイクルはクエン酸サイクルの脱炭酸段階をバイパスし、アセチル-CoAからオキサロ酢酸への変換を可能にし、グルコースの生産に利用できる。 脂肪以外のグルコースは、通常血中グルコースレベルを維持するために使用されていた糖新生を通じて組織内で利用可能なエネルギー資源として、ほとんどの組織に貯蔵されている。
多糖類や糖鎖は、ウリジン二リン酸グルコース(UDP-Glc)のような反応性の糖-リン酸供与体から、糖転移酵素によって、成長する多糖類上の受容体水酸基に単糖が順次付加されることによって作られる。基質の環上の水酸基はいずれもアクセプターとなりうるので、生成する多糖は直鎖構造でも分岐構造でもよい。産生された多糖は、それ自体が構造的あるいは代謝的機能を持つこともあれば、オリゴ糖転移酵素と呼ばれる酵素によって脂質やタンパク質に転移されることもある。
脂肪酸、イソプレノイド、ステロール

脂肪酸は脂肪酸合成酵素がアセチル-CoA単位を重合し、還元することで作られる。脂肪酸のアシル鎖は、アシル基を付加し、アルコールに還元し、脱水してアルケン基にし、再び還元してアルカン基にする反応のサイクルによって延長される。脂肪酸生合成の酵素は2つのグループに分けられる。動物や菌類では、これらの脂肪酸合成酵素反応はすべて1つの多機能型I型タンパク質によって行われるが、植物のプラスチドや細菌では別々のII型酵素が経路の各段階を行う。
テルペン類およびイソプレノイドは、カロテノイド類を含む脂質の大きな分類であり、植物の天然物の最大の分類を形成している。これらの化合物は、反応性前駆体であるイソペンテニルピロホスフェートとジメチルアリルピロホスフェートから供与されたイソプレン単位の集合と修飾によって作られる。これらの前駆体はさまざまな方法で作ることができる。動物や古細菌ではメバロン酸経路がアセチル-CoAからこれらの化合物を生成するが、植物や細菌では非メバロン酸経路がピルビン酸とグリセルアルデヒド3-リン酸を基質として使用する。これらの活性化イソプレン供与体を用いる重要な反応の一つがステロール生合成である。ここでは、イソプレン単位が結合してスクアレンを作り、さらに折り重なって一連の環を形成してラノステロールを作る。ラノステロールはその後、コレステロールやエルゴステロールなどの他のステロールに変換される。
タンパク質
生物は、20種類の一般的なアミノ酸を合成する能力に差がある。ほとんどの細菌や植物は20種類すべてを合成できるが、哺乳類は11種類の非必須アミノ酸しか合成できないため、9種類の必須アミノ酸は食物から摂取しなければならない。細菌肺炎マイコプラズマのような一部の単純な寄生虫は全てのアミノ酸合成を欠き、宿主から直接アミノ酸を摂取する。すべてのアミノ酸は解糖、クエン酸サイクル、またはペントースリン酸経路の中間体から合成される。窒素はグルタミン酸とグルタミンから供給される。非必須アミノ酸合成は、適切なα-ケト酸の形成に依存し、それがトランスアミナーゼされてアミノ酸を形成する。
アミノ酸はペプチド結合の鎖で結合することでタンパク質になる。異なるタンパク質は、それぞれ固有のアミノ酸残基の配列を持っている:これがその一次構造である。アルファベットを組み合わせてほとんど無限の単語を作ることができるように、アミノ酸も様々な配列で結合して多種多様なタンパク質を作ることができる。タンパク質は、転移RNA分子にエステル結合で結合して活性化されたアミノ酸から作られる。このアミノアシルtRNA前駆体は、アミノアシルtRNA合成酵素によって行われるATP依存的反応で生成される。このアミノアシルtRNAは次にリボソームの基質となり、メッセンジャーRNAの配列情報を利用して、伸長するタンパク質鎖にアミノ酸を結合させる。
ヌクレオチドの合成とサルベージ
ヌクレオチドは、大量の代謝エネルギーを必要とする経路で、アミノ酸、二酸化炭素、ギ酸から作られる。その結果、ほとんどの生物はあらかじめ形成されたヌクレオチドを回収する効率的なシステムを持っている。プリン類はヌクレオシド(リボースに結合した塩基)として合成される。アデニンもグアニンも、アミノ酸グリシン、グルタミン、アスパラギン酸の原子と、補酵素から移動したギ酸を用いて合成される前駆体ヌクレオシドイノシン一リン酸から作られる。テトラヒドロ葉酸から移行する。一方、ピリミジンは、グルタミンとアスパラギン酸から形成される塩基オロチン酸から合成される。
ゼノバイオティクスと酸化還元代謝
すべての生物は、食物として利用できず、代謝機能を持たないため細胞内に蓄積すると有害な化合物に常にさらされている。これらの潜在的に有害な化合物はゼノバイオティクスと呼ばれる。合成薬物、自然毒、抗生物質などのゼノバイオティクスは、一連のゼノバイオティクス代謝酵素によって解毒される。ヒトでは、シトクロムP450オキシダーゼ、UDP-グルクロノシルトランスフェラーゼ、グルタチオンS-トランスフェラーゼが含まれる。この酵素系は3段階で作用し、まず異種物質を酸化し(第I相)、次に水溶性基を分子に結合させる(第II相)。その後、修飾された水溶性異種生物は細胞外に排出され、多細胞生物ではさらに代謝されてから排泄される(第III相)。生態学では、これらの反応は微生物による汚染物質の生分解や、汚染された土地や流出油のバイオレメディエーションにおいて特に重要である。これらの微生物反応の多くは多細胞生物と共通であるが、微生物の種類が驚くほど多様であるため、これらの生物は多細胞生物よりもはるかに幅広い種類の異生物に対処することができ、有機塩化物化合物のような難分解性有機汚染物質さえも分解することができる。
好気性生物にとって関連する問題は酸化ストレスである。ここでは、酸化的リン酸化やタンパク質折り畳みの際のジスルフィド結合の形成などの過程で、過酸化水素などの活性酸素種が生成される。これらの有害な酸化物質は、グルタチオンなどの抗酸化物質の代謝産物や、カタラーゼやペルオキシダーゼなどの酵素によって除去される。
生物の熱力学
生物は熱力学の法則に従わなければならないが、それは熱の伝達とワークを記述するものである。熱力学の第二法則は、どのような孤立系でもエントロピー(無秩序)の量は減少しないと述べている。生物の驚くべき複雑さはこの法則に反しているように見えるが、すべての生物は周囲と物質とエネルギーを交換するオープンシステムであるため、生命は可能である。生命システムは均衡にあるわけではない、 しかしその代わりに、環境のエントロピーをより大きく増大させることによって、複雑性の高い状態を維持する散逸系である。 細胞の代謝は、異化の自発的過程を同化の非自発的過程と結合させることでこれを実現している。熱力学の用語では、代謝は無秩序を作り出すことによって秩序を維持する。
調節と制御
ほとんどの生物の環境は常に変化しているため、細胞内の状態を一定に保つためには、代謝反応を細かく制御する必要がある。代謝調節はまた、生物がシグナルに反応し、環境と積極的に相互作用することを可能にする。代謝経路がどのように制御されているかを理解するためには、密接に結びついた2つの概念が重要である。第一に、経路中の酵素の制御とは、シグナルに応答してその活性がどのように増減するかということである。第二に、この酵素が及ぼす制御とは、その活性の変化が経路全体の速度(経路を通るフラックス)に及ぼす影響である。例えば、ある酵素が活性に大きな変化を示しても(すなわち、その酵素は高度に制御されている)、その変化が代謝経路のフラックスにほとんど影響しなければ、その酵素は経路の制御には関与していないことになる。

There are multiple levels of metabolic regulation. In intrinsic regulation, the metabolic pathway self-regulates to respond to changes in the levels of substrates or products; for example, a decrease in the amount of product can increase the flux through the pathway to compensate. This type of regulation often involves allosteric regulation of the activities of multiple enzymes in the pathway. Extrinsic control involves a cell in a multicellular organism changing its metabolism in response to signals from other cells. These signals are usually in the form of water-soluble messengers such as hormones and growth factors and are detected by specific receptors on the cell surface. These signals are then transmitted inside the cell by second messenger systems that often involved the phosphorylation of proteins.
A very well understood example of extrinsic control is the regulation of glucose metabolism by the hormone insulin. Insulin is produced in response to rises in blood glucose levels. Binding of the hormone to insulin receptors on cells then activates a cascade of protein kinases that cause the cells to take up glucose and convert it into storage molecules such as fatty acids and glycogen. The metabolism of glycogen is controlled by activity of phosphorylase, the enzyme that breaks down glycogen, and glycogen synthase, the enzyme that makes it. These enzymes are regulated in a reciprocal fashion, with phosphorylation inhibiting glycogen synthase, but activating phosphorylase. Insulin causes glycogen synthesis by activating protein phosphatases and producing a decrease in the phosphorylation of these enzymes.
Evolution

The central pathways of metabolism described above, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, are present in all three domains of living things and were present in the last universal common ancestor. This universal ancestral cell was prokaryotic and probably a methanogen that had extensive amino acid, nucleotide, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. The retention of these ancient pathways during later evolution may be the result of these reactions having been an optimal solution to their particular metabolic problems, with pathways such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle producing their end products highly efficiently and in a minimal number of steps. The first pathways of enzyme-based metabolism may have been parts of purine nucleotide metabolism, while previous metabolic pathways were a part of the ancient RNA world.
Many models have been proposed to describe the mechanisms by which novel metabolic pathways evolve. These include the sequential addition of novel enzymes to a short ancestral pathway, the duplication and then divergence of entire pathways as well as the recruitment of pre-existing enzymes and their assembly into a novel reaction pathway. The relative importance of these mechanisms is unclear, but genomic studies have shown that enzymes in a pathway are likely to have a shared ancestry, suggesting that many pathways have evolved in a step-by-step fashion with novel functions created from pre-existing steps in the pathway. An alternative model comes from studies that trace the evolution of proteins' structures in metabolic networks, this has suggested that enzymes are pervasively recruited, borrowing enzymes to perform similar functions in different metabolic pathways (evident in the MANET database) A third possibility is that some parts of metabolism might exist as "modules" that can be reused in different pathways and perform similar functions on different molecules.
As well as the evolution of new metabolic pathways, evolution can also cause the loss of metabolic functions. For example, in some parasites metabolic processes that are not essential for survival are lost and preformed amino acids, nucleotides and carbohydrates may instead be scavenged from the host. Similar reduced metabolic capabilities are seen in endosymbiotic organisms.
Investigation and manipulation

Classically, metabolism is studied by a reductionist approach that focuses on a single metabolic pathway. Particularly valuable is the use of radioactive tracers at the whole-organism, tissue and cellular levels, which define the paths from precursors to final products by identifying radioactively labelled intermediates and products. The enzymes that catalyze these chemical reactions can then be purified and their kinetics and responses to inhibitors investigated. A parallel approach is to identify the small molecules in a cell or tissue; the complete set of these molecules is called the metabolome. Overall, these studies give a good view of the structure and function of simple metabolic pathways, but are inadequate when applied to more complex systems such as the metabolism of a complete cell.
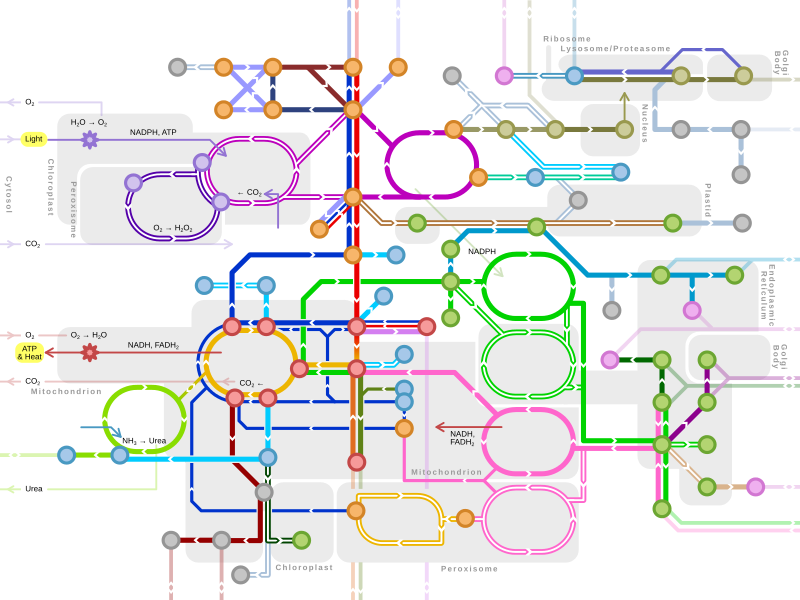
An idea of the complexity of the metabolic networks in cells that contain thousands of different enzymes is given by the figure showing the interactions between just 43 proteins and 40 metabolites to the right: the sequences of genomes provide lists containing anything up to 26.500 genes. However, it is now possible to use this genomic data to reconstruct complete networks of biochemical reactions and produce more holistic mathematical models that may explain and predict their behavior. These models are especially powerful when used to integrate the pathway and metabolite data obtained through classical methods with data on gene expression from proteomic and DNA microarray studies. Using these techniques, a model of human metabolism has now been produced, which will guide future drug discovery and biochemical research. These models are now used in network analysis, to classify human diseases into groups that share common proteins or metabolites.
Bacterial metabolic networks are a striking example of bow-tie organization, an architecture able to input a wide range of nutrients and produce a large variety of products and complex macromolecules using a relatively few intermediate common currencies.
A major technological application of this information is metabolic engineering. Here, organisms such as yeast, plants or bacteria are genetically modified to make them more useful in biotechnology and aid the production of drugs such as antibiotics or industrial chemicals such as 1,3-propanediol and shikimic acid. These genetic modifications usually aim to reduce the amount of energy used to produce the product, increase yields and reduce the production of wastes.
History
The term metabolism is derived from the Ancient Greek word μεταβολή – "Metabole" for "a change" which derived from μεταβάλλ –"Metaballein" means "To change"

Greek philosophy
Aristotle's The Parts of Animals sets out enough details of his views on metabolism for an open flow model to be made. He believed that at each stage of the process, materials from food were transformed, with heat being released as the classical element of fire, and residual materials being excreted as urine, bile, or faeces.
Ibn al-Nafis described metabolism in his 1260 AD work titled Al-Risalah al-Kamiliyyah fil Siera al-Nabawiyyah (The Treatise of Kamil on the Prophet's Biography) which included the following phrase "Both the body and its parts are in a continuous state of dissolution and nourishment, so they are inevitably undergoing permanent change."
Application of the scientific method and Modern metabolic theories
The history of the scientific study of metabolism spans several centuries and has moved from examining whole animals in early studies, to examining individual metabolic reactions in modern biochemistry. The first controlled experiments in human metabolism were published by Santorio Santorio in 1614 in his book Ars de statica medicina. He described how he weighed himself before and after eating, sleep, working, sex, fasting, drinking, and excreting. He found that most of the food he took in was lost through what he called "insensible perspiration".

In these early studies, the mechanisms of these metabolic processes had not been identified and a vital force was thought to animate living tissue. In the 19th century, when studying the fermentation of sugar to alcohol by yeast, Louis Pasteur concluded that fermentation was catalyzed by substances within the yeast cells he called "ferments". He wrote that "alcoholic fermentation is an act correlated with the life and organization of the yeast cells, not with the death or putrefaction of the cells." This discovery, along with the publication by Friedrich Wöhler in 1828 of a paper on the chemical synthesis of urea, and is notable for being the first organic compound prepared from wholly inorganic precursors. This proved that the organic compounds and chemical reactions found in cells were no different in principle than any other part of chemistry.
It was the discovery of enzymes at the beginning of the 20th century by Eduard Buchner that separated the study of the chemical reactions of metabolism from the biological study of cells, and marked the beginnings of biochemistry. The mass of biochemical knowledge grew rapidly throughout the early 20th century. One of the most prolific of these modern biochemists was Hans Krebs who made huge contributions to the study of metabolism. He discovered the urea cycle and later, working with Hans Kornberg, the citric acid cycle and the glyoxylate cycle.
See also
- Anthropogenic metabolism
- Antimetabolite
- Calorimetry
- Isothermal microcalorimetry
- Inborn errors of metabolism
- Iron–sulfur world hypothesis, a "metabolism first" theory of the origin of life
- Metabolic disorder
- Microphysiometry
- Primary nutritional groups
- Proto-metabolism
- Respirometry
- Stream metabolism
- Sulfur metabolism
- Thermic effect of food
- Urban metabolism
- Water metabolism
- Overflow metabolism
- Oncometabolism
- Reactome
- KEGG – Collection of bioinformatics databases
References
Further reading
| Library resources about Metabolism |
Introductory
- Rose S, Mileusnic R (1999). The Chemistry of Life. Penguin Press Science. ISBN 0-14-027273-9.
- Schneider EC, Sagan D (2005). Into the Cool: Energy Flow, Thermodynamics, and Life. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-73936-8.
- Lane N (2004). Oxygen: The Molecule that Made the World. USA: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-860783-0.
Advanced
- Price N, Stevens L (1999). Fundamentals of Enzymology: Cell and Molecular Biology of Catalytic Proteins. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-850229-X.
- Berg J, Tymoczko J, Stryer L (2002). Biochemistry. W. H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 0-7167-4955-6.
- Cox M, Nelson DL (2004). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 0-7167-4339-6.
- Brock TD, Madigan MR, Martinko J, Parker J (2002). Brock's Biology of Microorganisms. Benjamin Cummings. ISBN 0-13-066271-2.
- Da Silva JJ, Williams RJ (1991). The Biological Chemistry of the Elements: The Inorganic Chemistry of Life. Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855598-9.
- Nicholls DG, Ferguson SJ (2002). Bioenergetics. Academic Press Inc. ISBN 0-12-518121-3.
- Wood HG (February 1991). "Life with CO or CO2 and H2 as a source of carbon and energy". FASEB Journal. 5 (2): 156–63. doi:10.1096/fasebj.5.2.1900793. PMID 1900793. S2CID 45967404.
External links
General information
- The Biochemistry of Metabolism (archived 8 March 2005)
- Sparknotes SAT biochemistry Overview of biochemistry. School level.
- MIT Biology Hypertextbook Undergraduate-level guide to molecular biology.
Human metabolism
- Topics in Medical Biochemistry Guide to human metabolic pathways. School level.
- THE Medical Biochemistry Page Comprehensive resource on human metabolism.
Databases
Metabolic pathways
- Metabolism reference Pathway Archived 23 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- The Nitrogen cycle and Nitrogen fixation at the Wayback Machine (archive index)