Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor/ja: Difference between revisions
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "{{Oral hypoglycemics/ja}} {{Enzyme inhibition/ja}}" |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
2018年の[[meta-analysis/ja|メタアナリシス]]では、2型糖尿病患者の全死亡、心血管死亡、[[myocardial infarction/ja|心筋梗塞]]、[[stroke/ja|脳卒中]]に対するDPP-4阻害薬の好ましい効果は認められなかった。 | 2018年の[[meta-analysis/ja|メタアナリシス]]では、2型糖尿病患者の全死亡、心血管死亡、[[myocardial infarction/ja|心筋梗塞]]、[[stroke/ja|脳卒中]]に対するDPP-4阻害薬の好ましい効果は認められなかった。 | ||
==事例== | |||
{{Anchor|Examples}} | |||
このクラスに属する薬物は以下の通りである: | |||
* [[Sitagliptin]] ( | * [[Sitagliptin/ja]] (FDAは2006年に承認、[[Merck & Co.]]が[[Januvia/ja]]として販売している) | ||
* [[Vildagliptin]] | * [[Vildagliptin/ja|ビルダグリプチン]](2007年EU承認、EUでは[[Novartis]]がGalvusとして販売している) | ||
* [[Saxagliptin]] | * [[Saxagliptin/ja|サキサグリプチン]](2009年FDA承認、[[Onglyza/ja|オングリザ]]として販売されている) | ||
* [[Linagliptin]] | * [[Linagliptin/ja|リナグリプチン]](2011年FDA承認、[[Eli Lilly and Company]]と[[Boehringer Ingelheim]]によりトラジェンタとして販売されている) | ||
* [[Gemigliptin]] | * [[Gemigliptin/ja|ジェミグリプチン]](2012年に韓国で承認、[[LG Chem|LGライフサイエンス]]がゼミグロとして販売されている) | ||
* [[Anagliptin]] | * [[Anagliptin/ja|アナグリプチン]](日本では2012年にスイニーとして承認され、株式会社三和化学研究所と[[Kowa (company)|興和株式会社]]が販売している) | ||
* [[Teneligliptin]] | * [[Teneligliptin/ja|テネリグリプチン]](日本では2012年にテネリアとして承認されている) | ||
* [[Alogliptin]] | * [[Alogliptin/ja|アログリプチン]](ネシーナ/ビピディアとして2013年にFDA承認、[[Takeda Pharmaceutical Company|武田薬品工業]]が販売) | ||
* [[Trelagliptin]] | * [[Trelagliptin/ja|トレラグリプチン]](日本では2015年にザファテック/ウェディカとして承認されている) | ||
* [[Omarigliptin]] | * [[Omarigliptin/ja|オマリグリプチン]](MK-3102)(日本では2015年にマリゼブとして承認、[[Merck & Co]]が開発、オマリグリプチンは週1回の治療として使用可能であり、ベース試験および延長試験を通じて全般的に良好な忍容性が示された。) | ||
* [[Evogliptin]] | * [[Evogliptin/ja|エボグリプチン]](韓国ではスガノン/エボジンとして承認されている) | ||
* [[Gosogliptin]] | * [[Gosogliptin/ja|ゴソグリプチン]](ロシアではサテレックスとして承認されている) | ||
* [[Dutogliptin]] | * [[Dutogliptin/ja|デュトグリプチン]](PHX- 1149遊離塩基、[[Phenomix Corporation]]が開発中)、フェーズIII | ||
* [[Retagliptin]] | * [[Retagliptin/ja|レタグリプチン]](SP-2086)は中国で承認されている。 | ||
*[[Denagliptin]] | *[[Denagliptin/ja]] | ||
* [[Cofrogliptin]] (HSK- 7653, compound 2) | * [[Cofrogliptin/ja]] (HSK- 7653, compound 2) | ||
* [[Fotagliptin]] | * [[Fotagliptin/ja]] | ||
* [[Prusogliptin]] | * [[Prusogliptin/ja]] | ||
DPP-4を阻害する可能性のある他の化学物質には以下のものがある: | |||
* [[Berberine/ja|ベルベリン]]は、[[Berberis/ja|ベルベリス]]属の植物に含まれる[[alkaloid/ja|アルカロイド]]で、ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4を阻害する。 | |||
* [[Berberine]] | |||
==副作用== | |||
{{Anchor|Adverse effects}} | |||
すでに[[sulphonylurea/ja|スルホニルウレア]]を服用している場合、DPP-4薬物クラスの薬を服用すると[[hypoglycemia/ja|低血糖]]のリスクが高まる。 | |||
副作用には鼻咽頭炎、[[headache/ja|頭痛]]、[[nausea/ja|吐き気]]、[[heart failure/ja|心不全]]、過敏症、皮膚反応などがある。 | |||
米国食品医薬品局(FDA)は、2型糖尿病治療薬である[[sitagliptin/ja|シタグリプチン]]、[[saxagliptin/ja|サキサグリプチン]]、[[linagliptin/ja|リナグリプチン]]、[[alogliptin/ja|アログリプチン]]が、関節痛を引き起こし、重篤な障害を引き起こす可能性があると警告している。FDAは、ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4(DPP-4)阻害薬と呼ばれるこのクラスの薬物のラベルに、このリスクに関する警告と注意を新たに追加した。しかし、DPP-4阻害薬使用者における関節リウマチのリスクを評価した研究では、結論が出ていない。 | |||
2014年のレビューで、サキサグリプチンおよびアログリプチンによる[[heart failure/ja|心不全]]のリスク増加が発見され、FDAは2016年に関連薬物のラベルに警告を追加した。 | |||
2018年のメタ解析によると、DPP-4阻害薬の使用は、プラセボまたは無治療と比較して、急性膵炎の発症リスクを58%増加させることが示された。 | |||
2018年の観察研究では、炎症性腸疾患(具体的には潰瘍性大腸炎)の発症リスクの上昇が示唆され、3~4年の使用でピークに達し、4年以上の使用で減少した。 | |||
2020年のコクラン系統的レビューでは、2型糖尿病の治療において[[metformin/ja|メトホルミン]]単剤療法とジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4阻害薬を比較した場合、全死亡、重篤な有害事象、心血管死亡、非致死的[[myocardial infarction/ja|心筋梗塞]]、非致死的[[stroke/ja|脳卒中]]、または[[Chronic kidney disease/ja|末期腎疾患]]の減少を示す十分なエビデンスは認められなかった。 | |||
===癌=== | |||
DPP-4阻害薬シタグリプチンを投与されたラットおよび臓器提供者の膵臓に前癌性変化がみられたという報告を受けて、米国FDAと欧州医薬品庁はそれぞれ、DPP-4阻害薬と膵癌との関連の可能性に関するすべての臨床および前臨床データの独立したレビューを行った。ニューイングランド・ジャーナル・オブ・メディシン誌への共同書簡の中で、両機関はまだ因果関係の可能性に関する最終結論には至っていないと述べている。 | |||
2014年のメタアナリシスでは、DPP-4阻害薬で治療された患者における[[pancreatic cancer/ja|膵臓がん]]リスク増加のエビデンスは認められなかったが、入手可能なデータ量が少ないため、可能性のあるリスクを完全に除外することはできなかった。 | |||
==併用薬物== | |||
{{Anchor|Combination drugs}} | |||
DPP-4阻害薬の中には、[[metformin/ja|メトホルミン]]と併用することで相乗効果を発揮し、グルカゴン様ペプチド1(GLP-1)のレベルを上昇させ、[[hepatic/ja|肝]]の[[gluconeogenesis/ja||グルコース産生]]を低下させる。 | |||
== こちらも参照 == | |||
* [[Development of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors/ja]] | |||
* [[Development of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors]] | |||
{{Oral hypoglycemics/ja}} | |||
{{Oral hypoglycemics}} | {{Enzyme inhibition/ja}} | ||
{{Enzyme inhibition}} | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor}} | ||
[[Category:Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors| ]] | [[Category:Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors| ]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:57, 12 March 2024
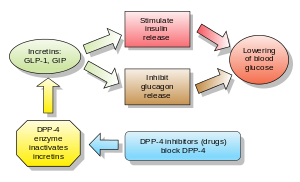
ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ4阻害薬(DPP-4 inhibitorまたはgliptins)は、経口血糖降下薬の一種であり、ブロック薬である。酵素ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4(DPP-4)を阻害する。これらは2型糖尿病の治療に使用できる。
このクラスの最初の薬物であるシタグリプチンは、2006年にFDAによって承認された。
グルカゴンは血糖値を上昇させ、DPP-4阻害薬はグルカゴンと血糖値を低下させる。DPP-4阻害薬の機序は、インクレチンレベル(GLP-1とGIP)を増加させ、グルカゴン放出を阻害し、その結果、インスリン分泌を増加させ、胃排出を減少させ、血糖値を低下させる。
2018年のメタアナリシスでは、2型糖尿病患者の全死亡、心血管死亡、心筋梗塞、脳卒中に対するDPP-4阻害薬の好ましい効果は認められなかった。
事例
このクラスに属する薬物は以下の通りである:
- シタグリプチン (FDAは2006年に承認、Merck & Co.がJanuvia/jaとして販売している)
- ビルダグリプチン(2007年EU承認、EUではNovartisがGalvusとして販売している)
- サキサグリプチン(2009年FDA承認、オングリザとして販売されている)
- リナグリプチン(2011年FDA承認、Eli Lilly and CompanyとBoehringer Ingelheimによりトラジェンタとして販売されている)
- ジェミグリプチン(2012年に韓国で承認、LGライフサイエンスがゼミグロとして販売されている)
- アナグリプチン(日本では2012年にスイニーとして承認され、株式会社三和化学研究所と興和株式会社が販売している)
- テネリグリプチン(日本では2012年にテネリアとして承認されている)
- アログリプチン(ネシーナ/ビピディアとして2013年にFDA承認、武田薬品工業が販売)
- トレラグリプチン(日本では2015年にザファテック/ウェディカとして承認されている)
- オマリグリプチン(MK-3102)(日本では2015年にマリゼブとして承認、Merck & Coが開発、オマリグリプチンは週1回の治療として使用可能であり、ベース試験および延長試験を通じて全般的に良好な忍容性が示された。)
- エボグリプチン(韓国ではスガノン/エボジンとして承認されている)
- ゴソグリプチン(ロシアではサテレックスとして承認されている)
- デュトグリプチン(PHX- 1149遊離塩基、Phenomix Corporationが開発中)、フェーズIII
- レタグリプチン(SP-2086)は中国で承認されている。
- Denagliptin/ja
- Cofrogliptin/ja (HSK- 7653, compound 2)
- Fotagliptin/ja
- Prusogliptin/ja
DPP-4を阻害する可能性のある他の化学物質には以下のものがある:
副作用
すでにスルホニルウレアを服用している場合、DPP-4薬物クラスの薬を服用すると低血糖のリスクが高まる。
副作用には鼻咽頭炎、頭痛、吐き気、心不全、過敏症、皮膚反応などがある。
米国食品医薬品局(FDA)は、2型糖尿病治療薬であるシタグリプチン、サキサグリプチン、リナグリプチン、アログリプチンが、関節痛を引き起こし、重篤な障害を引き起こす可能性があると警告している。FDAは、ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4(DPP-4)阻害薬と呼ばれるこのクラスの薬物のラベルに、このリスクに関する警告と注意を新たに追加した。しかし、DPP-4阻害薬使用者における関節リウマチのリスクを評価した研究では、結論が出ていない。
2014年のレビューで、サキサグリプチンおよびアログリプチンによる心不全のリスク増加が発見され、FDAは2016年に関連薬物のラベルに警告を追加した。
2018年のメタ解析によると、DPP-4阻害薬の使用は、プラセボまたは無治療と比較して、急性膵炎の発症リスクを58%増加させることが示された。
2018年の観察研究では、炎症性腸疾患(具体的には潰瘍性大腸炎)の発症リスクの上昇が示唆され、3~4年の使用でピークに達し、4年以上の使用で減少した。
2020年のコクラン系統的レビューでは、2型糖尿病の治療においてメトホルミン単剤療法とジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4阻害薬を比較した場合、全死亡、重篤な有害事象、心血管死亡、非致死的心筋梗塞、非致死的脳卒中、または末期腎疾患の減少を示す十分なエビデンスは認められなかった。
癌
DPP-4阻害薬シタグリプチンを投与されたラットおよび臓器提供者の膵臓に前癌性変化がみられたという報告を受けて、米国FDAと欧州医薬品庁はそれぞれ、DPP-4阻害薬と膵癌との関連の可能性に関するすべての臨床および前臨床データの独立したレビューを行った。ニューイングランド・ジャーナル・オブ・メディシン誌への共同書簡の中で、両機関はまだ因果関係の可能性に関する最終結論には至っていないと述べている。
2014年のメタアナリシスでは、DPP-4阻害薬で治療された患者における膵臓がんリスク増加のエビデンスは認められなかったが、入手可能なデータ量が少ないため、可能性のあるリスクを完全に除外することはできなかった。
併用薬物
DPP-4阻害薬の中には、メトホルミンと併用することで相乗効果を発揮し、グルカゴン様ペプチド1(GLP-1)のレベルを上昇させ、肝の|グルコース産生を低下させる。
こちらも参照