Body mass index/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "===BMIプライム(指数2、正規化係数)=== BMIプライムとは、BMIシステムを改良したもので、上限至適BMI(現在25 kg/m<sup>2</sup>で定義されている)に対する実際のBMIの比率、すなわち上限至適に対する実際のBMIの割合として表したものである。BMIプライムは単位に依存しない無次元数である。BMIプライムが0.74未満の人は低体重、0.74~1.00..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 511: | Line 511: | ||
<blockquote>一般に、発育過程において、異なる年齢における体重の2乗が身長の5乗になると仮定しても、それほど間違いはない</blockquote> | <blockquote>一般に、発育過程において、異なる年齢における体重の2乗が身長の5乗になると仮定しても、それほど間違いはない</blockquote> | ||
この2.5という指数は、[[:ja:オックスフォード大学|オックスフォード大学]]の数値解析教授である[[:en:Nick Trefethen|ニック・トリーフェッセン]]によって提唱されたボディマス指数の改訂式で使用されており、従来のBMI式で2の指数を使用することによって生じる低身長者と高身長者の歪みを最小限に抑えている: | この2.5という指数は、[[:ja:オックスフォード大学|オックスフォード大学]]の数値解析教授である[[:en:Nick Trefethen|ニック・トリーフェッセン]]によって提唱されたボディマス指数の改訂式で使用されており、従来のBMI式で2の指数を使用することによって生じる低身長者と高身長者の歪みを最小限に抑えている: | ||
<math>mathrm{BMI} | :<math>\mathrm{BMI}_\text{new} = 1.3 \times \frac{\text{mass}_\text{kg}}{\text{height}_\text{m}^{2.5}}</math> | ||
1.3というスケーリング係数は、提案された新しいBMI式を、平均身長の成人に対する従来のBMI式と整合させるために決定されたものであり、2.5という指数は、従来のBMI式の指数2と、体重(密度が一定であれば、理論的には体積、すなわち身長の3乗としてスケールする)の身長に対するスケーリングに期待される指数3との妥協点である。トリーフェッセンの分析では、2.5の指数は、2または3の指数よりも歪みが少なく、より密接に経験的データに適合することが判明した。 | 1.3というスケーリング係数は、提案された新しいBMI式を、平均身長の成人に対する従来のBMI式と整合させるために決定されたものであり、2.5という指数は、従来のBMI式の指数2と、体重(密度が一定であれば、理論的には体積、すなわち身長の3乗としてスケールする)の身長に対するスケーリングに期待される指数3との妥協点である。トリーフェッセンの分析では、2.5の指数は、2または3の指数よりも歪みが少なく、より密接に経験的データに適合することが判明した。 | ||
===BMIプライム(指数2、正規化係数)=== | ===BMIプライム(指数2、正規化係数)=== | ||
BMIプライムとは、BMIシステムを改良したもので、上限至適BMI(現在25 kg/m<sup>2</sup>で定義されている)に対する実際のBMIの比率、すなわち上限至適に対する実際のBMIの割合として表したものである。BMIプライムは単位に依存しない[[:en:dimensionless number|無次元数]]である。BMIプライムが0.74未満の人は低体重、0.74~1.00の人は至適体重、1.00以上の人は過体重である。BMIプライムは、その人が至適BMIの最大値からどの程度の比率(例:1.36)または割合(例:136%、または36%以上)で逸脱しているかを示すため、臨床的に有用である。 | BMIプライムとは、BMIシステムを改良したもので、上限至適BMI(現在25 kg/m<sup>2</sup>で定義されている)に対する実際のBMIの比率、すなわち上限至適に対する実際のBMIの割合として表したものである。BMIプライムは単位に依存しない[[:en:dimensionless number|無次元数]]である。BMIプライムが0.74未満の人は低体重、0.74~1.00の人は至適体重、1.00以上の人は過体重である。BMIプライムは、その人が至適BMIの最大値からどの程度の比率(例:1.36)または割合(例:136%、または36%以上)で逸脱しているかを示すため、臨床的に有用である。 | ||
例えば、BMI 34 kg/m<sup>2</sup>の人のBMIプライムは34/25=1.36であり、上限値を36%超えている。東南アジアおよび華南の集団([[#International variations|§国際的バリエーション]]を参照)では、BMIプライムは25ではなく、分母に上限BMI 23を用いて計算すべきである。BMIプライムにより、上限最適BMI値が異なる集団間の比較が容易になる。 | |||
===ウエスト周囲径=== | |||
{{Main/ja|Waist-to-height ratio/ja|Waist-to-hip ratio/ja}} | |||
{{Main|Waist-to-height ratio|Waist-to-hip ratio}} | ウエスト周囲径は[[visceral fat/ja|内臓脂肪]]の良い指標であり、内臓脂肪は他の場所の脂肪よりも健康上のリスクが高い。米国[[:en:National Institutes of Health|国立衛生研究所]](NIH)によると、ウエスト周囲径が男性で{{cvt|1020|mm}}、(妊娠していない)女性で{{cvt|880|mm}}を超えると、2型糖尿病、[[dyslipidemia/ja|脂質異常症]]、[[hypertension/ja|高血圧]]、[[cardiovascular disease/ja|心血管疾患]]のリスクが高いと考えられている。CVDである。ウエスト周囲径は、BMIよりも肥満に関連した疾患リスクの指標となりうる。例えば、アジア系住民や高齢者ではそうである。男性では{{cvt|940|mm}}、女性では{{cvt|800|mm}}が「より高いリスク」をもたらすとされており、NIHの数値は「さらに高い」とされている。 | ||
ウエスト-ヒップ周囲径比も使用されているが、ウエスト周囲径だけより優れているわけではなく、測定がより複雑であることがわかっている。 | |||
関連する指標は、ウエスト周囲径を身長で割った値である。リスク上昇を示す値は、40歳未満で0.5以上、40~50歳で0.5~0.6、50歳以上で0.6以上である。 | |||
=== 表面ベース体型指数 === | |||
表面ベースの体型指数 (SBSI)は、[[body surface area/ja|体表面積]](BSA)、体幹垂直周囲長(VTC)、ウエスト周囲長(WC)、身長(H)である。全米健康・人間栄養調査(NHANES)1999~2004年の11,808人のデータでは、SBSIはBMI、ウエスト周囲径、BMIの代替指標である[[Body Shape Index/ja|A体型指数(ABSI)]]を上回っていた。 | |||
: <math>\mathrm{SBSI} = \frac{(\text{H}^{7/4})(\text{WC}^{5/6})}{\text{BSA VTC}}</math> | : <math>\mathrm{SBSI} = \frac{(\text{H}^{7/4})(\text{WC}^{5/6})}{\text{BSA VTC}}</math> | ||
SBSI<sup>*</sup>として知られるSBSIの簡略化された無次元形も開発されている。 | |||
: <math>\mathrm{SBSI^\star} = \frac{(\text{H}^2)(\text{WC})}{\text{BSA VTC}}</math> | : <math>\mathrm{SBSI^\star} = \frac{(\text{H}^2)(\text{WC})}{\text{BSA VTC}}</math> | ||
===修正肥満指数=== | |||
== | [[familial amyloid polyneuropathy/ja|家族性アミロイドポリニューロパチー]]などのいくつかの医学的状況では、血清アルブミンは修正肥満度指数(mBMI)を生成するために考慮される。mBMIは、BMIに[[human serum albumin/ja|血清アルブミン]]を1リットルあたりのグラム数で乗じることで得られる。 | ||
== こちらも参照 == | == こちらも参照 == | ||
Latest revision as of 21:16, 29 February 2024
| ボディマス指数 (BMI) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Synonyms | Quetelet index |
| MeSH | D015992 |
| MedlinePlus | 007196 |
| LOINC | 39156-5 |
| aシリーズの一部である。 |
| 体重 |
|---|
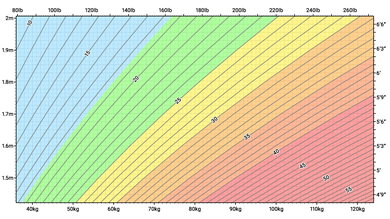
ボディマス指数(BMI)は、人の質量(体重)と身長から導き出される値である。BMIは、体重を身長の2乗で割ったものとして定義され、kg/m2の単位で表される。質量はキログラム(kg)、身長はメートル(m)である。
BMIは、まず体重計とスタジオメーターを用いてその構成要素を測定することによって決定することができる。掛け算と割り算は、手書きまたは電卓を使って直接行うこともできるし、ルックアップテーブル(またはチャート)を使って間接的に行うこともできる。表はBMIを質量と身長の関数として表示し、他の測定単位(計算のためにメートル単位に変換)を表示することができる。また、BMIのカテゴリーごとに等高線や色を表示することもできる。
BMIは、組織量(筋肉、脂肪、骨)と身長に基づいて人を大まかに分類するために用いられる便利な経験則である。成人の主なBMI分類は、低体重(18.5kg/m2未満)、標準体重(18.5~24.9)、過体重(25~29.9)、肥満(30以上)である。 集団の統計的測定値としてではなく、個人の健康状態を予測するために使用する場合、BMIには制限があり、特に腹部肥満、低身長、高筋肉量の個人に適用する場合、いくつかの代替のものよりも有用性が低くなることがある。
BMIが20未満でも25以上でも全死亡率が高く、20-25の範囲から離れるほどリスクは高くなる。
歴史

ベルギーの天文学者、数学者、統計学者、社会学者であるアドルフ・ケテレは、彼が「社会物理学」と呼ぶものを開発する中で、1830年から1850年の間にBMIの基礎を考案した。ケテレ自身は、当時ケテレ指数と呼ばれていたこの指数を、医学的評価の手段として使用するつもりはなかった。その代わり、この指数は彼のl'homme moyen(平均的人間)研究の一要素であった。ケテレは平均的な人間を社会的理想と考え、社会的に理想的な人間を発見する手段として肥満度を開発した。『Scandinavian Journal of Disability Research』誌のLars GrueとArvid Heibergによれば、ケテレの平均的人間の理想化は、10年後の優生学の発展において、フランシス・ガルトンによってさらに精緻化されることになる。
身長の2乗に対する人間の体重の比率を表す「体格指数」(BMI)という現代用語は、アンセル・キーズらによって1972年7月号の慢性疾患ジャーナルに発表された論文で作られた。この論文でキーズは、BMIと呼ばれるものが「完全に満足できるものではないにしても、少なくとも相対的な肥満の指標としては他の相対的な体重指数と同じくらい優れている」と主張した。
体脂肪を測定する指標への関心は、豊かな西欧社会で肥満が増加していることが観察されたことから生まれた。キーズは、BMIは集団の研究に適しており、個人の評価には不適切であると明確に判断した。それにもかかわらず、その単純さゆえに、予備診断に広く使われるようになった。ウエスト周囲径のような付加的な指標はより有用である。
BMIはkg/m2で表され、質量はキログラム、身長はメートルである。ポンドとインチを使う場合、換算係数は703 となる(kg/m2)/(lb/in2)。 (ポンドとフィートを使用する場合は、4.88の換算係数が使用される) BMIという用語が非公式に使用される場合、単位は通常省略される。
BMIは、人の太さまたはやせ具合を数値で簡単に表すことができるため、医療専門家が体重の問題を患者とより客観的に話し合うことができる。BMIは、平均的な体組成を持つ平均的な座りがちな(身体的に不活発な)集団を分類する単純な手段として使用するように設計された。そのような人々に対して、BMI値の推奨2014年現在は以下の通り: 18.5~24.9 kg/m2は最適体重、18.5未満は低体重、25~29.9は過体重、30以上は肥満を示す。痩せている男性アスリートは筋肉と脂肪の比率が高いことが多く、そのためBMIは体脂肪率に対して誤解を招くほど高くなる。
カテゴリー
BMIの一般的な使用法は、個人の体重がその人の身長の標準値からどの程度ずれているかを評価することである。体重の過不足は、部分的には体脂肪(脂肪組織)によって説明されるかもしれないが、筋肉質などの他の要因もBMIに大きく影響する(以下の議論および過体重を参照)。
WHOは、成人のBMIが18.5未満を低体重とみなし、栄養失調、摂食障害、またはその他の健康問題を示している可能性があるとし、BMIが25以上を過体重、30以上を肥満とみなしている。原則的で国際的なWHOのBMIカットオフポイント(16、17、18.5、25、30、35、40)に加えて、リスクのあるアジア人に対する4つのカットオフポイント(23、27.5、32.5、37.5)が特定された。これらのBMI値の範囲は、統計上のカテゴリーとしてのみ有効である。
| カテゴリ | BMI (kg/m2) | BMIプライム |
|---|---|---|
| 低体重(重度のやせ) | < 16.0 | < 0.64 |
| 低体重(中程度のやせ) | 16.0 – 16.9 | 0.64 – 0.67 |
| 低体重(軽度のやせ) | 17.0 – 18.4 | 0.68 – 0.73 |
| 正常範囲 | 18.5 – 24.9 | 0.74 – 0.99 |
| 過体重(肥満予備軍) | 25.0 – 29.9 | 1.00 – 1.19 |
| 肥満 (Class I) | 30.0 – 34.9 | 1.20 – 1.39 |
| 肥満 (Class II) | 35.0 – 39.9 | 1.40 – 1.59 |
| 肥満 (Class III) | ≥ 40.0 | ≥ 1.60 |
子供と青少年
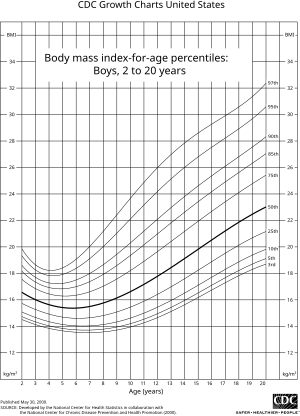

BMIは、2歳から20歳までで使用方法が異なる。BMIは成人と同じ方法で計算されるが、同じ年齢の他の子供や青少年の典型的な値と比較される。低体重と過体重の固定された基準値との比較の代わりに、BMIは同じ性別と年齢の子どものパーセンタイル値と比較される。
BMIが5パーセンタイル未満は低体重、95パーセンタイル以上は肥満とみなされる。BMIが85パーセンタイルと95パーセンタイルの間の子どもは過体重とみなされる。 2013年にイギリスで行われた調査では、12歳から16歳までの女性のBMIは、同年齢の男性よりも平均で1.0 kg/m2高かった。
国際的な差異
直線的な尺度に沿って推奨されるこれらの区別は、時代や国によって異なる可能性があり、世界的な縦断的調査を問題にしている。BMI、体脂肪率と健康リスクとの関連は、異なる集団や血統の人々によって異なっており、2型糖尿病やアテローム性動脈硬化症の心血管疾患のリスクは、WHOの過体重のカットオフポイントである25 kg/m2より低いBMIで高くなるが、観察されるリスクのカットオフは集団によって異なる。観察されたリスクのカットオフ値は、ヨーロッパ、アジア、アフリカの集団や小集団によって異なる。
====香港 香港の病院局は以下のBMI範囲の使用を推奨している:
| カテゴリ | BMI (kg/m2) |
|---|---|
| 低体重(不健康) | < 18.5 |
| 正常範囲(健康) | 18.5 – 22.9 |
| 過体重Ⅰ(リスクあり) | 23.0 – 24.9 |
| 過体重II(中等度肥満) | 25.0 – 29.9 |
| 過体重III(高度肥満) | ≥ 30.0 |
日本
日本肥満学会(JASSO)の2000年の研究によると、BMIの分類は以下のようになっている:
| カテゴリ | BMI (kg/m2) |
|---|---|
| 低体重(痩せ型) | < 18.5 |
| 標準体重 | 18.5 – 24.9 |
| 肥満(クラス1) | 25.0 – 29.9 |
| 肥満(クラス2) | 30.0 – 34.9 |
| 肥満(クラス3) | 35.0 – 39.9 |
| 肥満(クラス4) | ≥ 40.0 |
シンガポール
シンガポールでは、2005年に健康増進委員会(HPB)によってBMIカットオフ値が改訂された。これは、シンガポール人を含む多くのアジア人集団は、他国の一般的なBMI推奨値と比較して体脂肪の割合が高く、心血管疾患や糖尿病のリスクが高いという研究結果を受けたものである。BMIカットオフ値は、体重よりもむしろ健康リスクに重点を置いて提示されている。
| カテゴリ | BMI (kg/m2) | 健康リスク |
|---|---|---|
| 低体重 | < 18.5 | 栄養不足と骨粗鬆症の可能性がある。 |
| 正常 | 18.5 – 22.9 | リスクが低い(健康な範囲)。 |
| 軽度から中等度の過体重 | 23.0 – 27.4 | 心臓病、高血圧、脳卒中、糖尿病の発症リスクは中程度である。 |
| 非常に太りすぎ~肥満 | ≥ 27.5 | 心臓病、高血圧、脳卒中、糖尿病発症の高いリスク。代謝症候群。 |
イギリス
イギリスでは、NICEのガイダンスにより、2型糖尿病の予防はBMIが白人で30、アフリカ系黒人、アフリカ系カリブ人、南アジア人、中国人の集団では27.5から開始することが推奨されている。
イングランドの約150万人を対象とした大規模サンプルに基づく新たな調査によると、BMI(四捨五入)以上であれば予防の恩恵を受けられる民族グループがあることがわかった:
- 白人では30
- 黒人では28
- 英国系黒人では30をわずかに下回る
- アフリカ系黒人では29
- 黒人その他で27
- カリブ系黒人の26
- アラブ系および中国系では 27
- 南アジア系では24人
- パキスタン、インド、ネパール人で24人
- タミール人とスリランカ人で23人
- バングラデシュ人の21%である。
米国
1998年、米国国立衛生研究所は、米国の定義を世界保健機関のガイドラインに沿ったものにし、正常/過体重のカットオフをBMI 27.8(男性)および27.3(女性)からBMI 25に引き下げた。これにより、これまで健康であった約2,500万人のアメリカ人が太りすぎに再定義された。
このことは、過去20年間に太りすぎと診断されることが増加し、同時期に減量商品の売上が増加したことを部分的に説明することができる。また、WHOは、東南アジアの体型の標準/過体重の基準値をBMI23前後に引き下げることを推奨しており、さまざまな体型の臨床研究からさらなる改訂が出てくることを期待している。
2007年の調査では、アメリカ人の63%が過体重または肥満であり、26%が肥満(BMI30以上)であった。2014年には、米国の成人の37.7%が肥満で、男性は35.0%、女性は40.4%で、クラス3肥満(BMI40以上)の値は男性で7.7%、女性で9.9%だった。2015-2016年のアメリカ国民健康栄養調査によると、アメリカ人男女の71.6%がBMI25以上であった。肥満-BMI30以上-は米国成人の39.8%に見られた。
| 年齢 | パーセンテージ | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5th | 10th | 15th | 25th | 50th | 75th | 85th | 90th | 95th | |
| ≥ 20 (total) | 20.7 | 22.2 | 23.0 | 24.6 | 27.7 | 31.6 | 34.0 | 36.1 | 39.8 |
| 20–29 | 19.3 | 20.5 | 21.2 | 22.5 | 25.5 | 30.5 | 33.1 | 35.1 | 39.2 |
| 30–39 | 21.1 | 22.4 | 23.3 | 24.8 | 27.5 | 31.9 | 35.1 | 36.5 | 39.3 |
| 40–49 | 21.9 | 23.4 | 24.3 | 25.7 | 28.5 | 31.9 | 34.4 | 36.5 | 40.0 |
| 50–59 | 21.6 | 22.7 | 23.6 | 25.4 | 28.3 | 32.0 | 34.0 | 35.2 | 40.3 |
| 60–69 | 21.6 | 22.7 | 23.6 | 25.3 | 28.0 | 32.4 | 35.3 | 36.9 | 41.2 |
| 70–79 | 21.5 | 23.2 | 23.9 | 25.4 | 27.8 | 30.9 | 33.1 | 34.9 | 38.9 |
| ≥ 80 | 20.0 | 21.5 | 22.5 | 24.1 | 26.3 | 29.0 | 31.1 | 32.3 | 33.8 |
| 年齢 | パーセンテージ | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5th | 10th | 15th | 25th | 50th | 75th | 85th | 90th | 95th | |
| ≥ 20 (total) | 19.6 | 21.0 | 22.0 | 23.6 | 27.7 | 33.2 | 36.5 | 39.3 | 43.3 |
| 20–29 | 18.6 | 19.8 | 20.7 | 21.9 | 25.6 | 31.8 | 36.0 | 38.9 | 42.0 |
| 30–39 | 19.8 | 21.1 | 22.0 | 23.3 | 27.6 | 33.1 | 36.6 | 40.0 | 44.7 |
| 40–49 | 20.0 | 21.5 | 22.5 | 23.7 | 28.1 | 33.4 | 37.0 | 39.6 | 44.5 |
| 50–59 | 19.9 | 21.5 | 22.2 | 24.5 | 28.6 | 34.4 | 38.3 | 40.7 | 45.2 |
| 60–69 | 20.0 | 21.7 | 23.0 | 24.5 | 28.9 | 33.4 | 36.1 | 38.7 | 41.8 |
| 70–79 | 20.5 | 22.1 | 22.9 | 24.6 | 28.3 | 33.4 | 36.5 | 39.1 | 42.9 |
| ≥ 80 | 19.3 | 20.4 | 21.3 | 23.3 | 26.1 | 29.7 | 30.9 | 32.8 | 35.2 |
成人における高値の影響
BMIの範囲は、体重と疾病および死亡との関係に基づいている。過体重および肥満の人は、以下の疾患のリスクが高くなる:
タバコを吸ったことのない人では、体重が普通である人に比べて、過体重/肥満は死亡率を51%増加させる。
適用
公衆衛生
BMIは一般的に、一般的な質量で関連するグループ間の相関の手段として使用され、脂肪率を推定する漠然とした手段として機能することができる。BMIの二面性は、一般的な計算としては使いやすいが、そこから得られるデータがどの程度正確で適切なものであるかに限界があることである。一般に、BMIは誤差が少ないため、座りがちな人や太り過ぎの人の傾向を把握するのに適している。BMIは、WHOによって1980年代初頭以来、肥満統計を記録するための標準として使用されている。
この一般的な相関関係は、肥満やその他の様々な状態に関するコンセンサス・データとして特に有用である。というのも、このデータを使って半精密な表現を構築し、そこから解決策を規定したり、あるグループのRDAを計算したりできるからである。同様に、子どもたちの大半は座りがちであるため、これは子どもたちの成長にとってますます適切になってきている。 横断的研究では、座りがちな人がより身体的に活動的になることで、BMIを減少させることができることが示された。前向きコホート研究では、BMIのさらなる上昇を防ぐ手段として積極的な運動を支持するような、より小さな効果が見られる。
法律
フランス、イタリア、スペインでは、BMI18未満のファッションショーモデルの使用を禁止する法律が導入されている。イスラエルでは、BMI18.5未満のモデルは禁止されている。これはモデルやファッションに関心のある人々の拒食症と闘うために行われている。
健康との関係
2005年にJournal of the American Medical Association (JAMA)によって発表された研究によると、太りすぎの人の死亡率はBMIで定義された普通体重の人と同程度であり、痩せすぎや肥満の人の死亡率は高かった。
2009年にThe Lancetが発表した90万人の成人を対象とした研究によると、太りすぎの人と痩せすぎの人は、BMIで定義される標準体重の人よりも死亡率が高いことが示された。最適なBMIは22.5~25の範囲であることがわかった。アスリートの平均BMIは女性22.4、男性23.6である。
高BMIは、血清γ-グルタミルトランスペプチダーゼが高値の人においてのみ、2型糖尿病と関連する。
25万人を対象とした40の研究の分析では、BMIが「正常」な冠動脈疾患患者は、BMIが「過体重」(BMI25-29.9)の範囲にある患者よりも、心血管疾患による死亡リスクが高かった。
ある研究では、BMIは体脂肪率と一般的に良い相関関係があることを発見し、肥満は喫煙を抜いて世界第一の死因になっていることを指摘した。しかし、この研究では、体脂肪率による肥満の定義では男性の50%、女性の62%が肥満であったのに対し、BMIによる肥満の定義では男性の21%、女性の31%に過ぎず、BMIは肥満者の数を過小評価していることが判明したことも指摘している。
11,000人の被験者を最長8年間追跡調査した2010年の研究では、BMIは心臓発作、脳卒中、死亡のリスクを測る最も適切な指標ではないと結論づけられた。より適切な指標はウエスト対身長比であることが判明した。60,000人の被験者を13年間追跡した2011年の研究では、ウエスト-ヒップ比が虚血性心疾患死亡のより良い予測因子であることが判明した。
限界

医学界も統計界もBMIの限界を強調している。
人種および性別による違い
BMI尺度の統計的限界の一部は、Queteletのオリジナルのサンプリング方法の結果である。彼の主著である『人間とその諸能力の発達に関する論考』(A Treatise on Man and the Development of His Faculties)で述べられているように、Queteletが計算式を導き出したデータは、主にスコットランドの高地兵とフランスの憲兵隊から採取されたものであった。BMIは常にヨーロッパ人男性のための指標として設計された。女性や非ヨーロッパ系の人々にとって、この尺度はしばしば偏っている。社会学者サブリナ-ストリングスによって指摘されたように、BMIは、特に黒人のための大部分は不正確であり、不釣り合いに健康な個人であっても太りすぎとしてそれらをラベル付けする。
スケーリング
BMIの計算式の分母の指数は任意である。BMIは体重と身長の2乗に依存する。質量は線形寸法の3乗に増加するため、全く同じ体型と相対的な組成を持つ背の高い人のBMIは大きくなる。BMIは質量に比例し、身長の2乗に反比例する。つまり、体の寸法がすべて2倍になり、質量が身長の3乗に自然に比例すると、BMIは変わらない代わりに2倍になる。この結果、背の高い人のBMIは、実際の体脂肪レベルと比較して、特徴的でないほど高いと報告されている。それに比べて、ポンデラル指数は、身長の3乗による質量の自然なスケーリングに基づいている。
しかし、背の高い人の多くは、単に背の低い人を「スケールアップ」したのではなく、身長に比例して骨格が細い傾向がある。Carl Lavieは、「B.M.I.表は、大規模な集団における肥満や体脂肪を特定するのには優れているが、個人における太りやすさを判断するのにははるかに信頼性が低い」と書いている。
米国成人の指数推定値は、男性で1.92から1.96、女性で1.45から1.95である。
身体的特徴
BMIは、骨格が大きい(または背が高い)場合はおよそ10%過大評価し、骨格が小さい(背が低い)場合はおよそ10%過小評価する。言い換えれば、小柄な体格の人は最適な体格よりも脂肪が多いが、BMIでは普通ということになる。逆に、骨格が大きい(または背が高い)人は、かなり健康的で体脂肪率がかなり低いかもしれないが、BMIでは太りすぎに分類される。
例えば、身長/体重チャートでは、1.78-metre tall (5 ft 10 in)の男性の理想体重(BMI 21.5)は68 kilograms (150 lb)である。しかし、その男性の体格が細身(小柄)であれば、150 lb or 68 kg[convert: invalid option]で太りすぎかもしれず、およそ135 lb or 61 kg[convert: invalid option]まで10%減らすべきである。(BMI 19.4)。逆に、骨格が大きくしっかりした体格の男性は、10%増加して、およそ165 lb or 75 kg[convert: invalid option]になるはずである。(BMI 23.7)。小・中、中・大の境界線上にいる場合は、常識的な範囲で理想体重を計算すべきである。しかし、身長と体格に対して理想的な体重の範囲に入ることは、ウエスト対身長比や実際の体脂肪率ほど正確には健康リスク要因を決定できない。
正確な骨格サイズ計算機では、いくつかの測定値(手首周り、肘幅、首周りなど)を使って、ある身長がどのカテゴリーに入るかを判断する。また、BMIは加齢による身長の低下を考慮していない。このような状況では、体重が増加しなくてもBMIは増加する。
筋肉対脂肪
筋肉量と脂肪量の分布に関する仮定は不正確である。BMIは一般的に、痩せた体格の人(例えばアスリート)の脂肪率を過大評価し、太った体格の人の過剰な脂肪率を過小評価する。
2008年6月に行われたRomero-Corralらによる研究では、米国の第3回国民健康・栄養調査(NHANES III)の13,601人を対象に調査が行われ、BMIで定義される肥満(BMI≧30)は男性の21%、女性の31%に認められた。体脂肪で定義された肥満は、男性の50%、女性の62%に認められた。BMIで定義された肥満が高い特異度(男性95%、女性99%)を示したのに対し、BMIは感度(男性36%、女性49%)が悪かった。言い換えれば、BMIは、肥満であると判断する場合にはほとんど正しいが、肥満でないと判断する場合にはかなりの頻度で誤る可能性がある。このようにBMIによる肥満のカウントが過小であるにもかかわらず、BMIの中間値である20~30のBMI値は、幅広い体脂肪率と関連していることがわかった。BMI25の男性では、約20%が体脂肪率20%未満、約10%が体脂肪率30%以上である。
アスリートの体組成は、スキンフォールド測定や水中体重測定などの技術によって決定される体脂肪の測定値を用いて計算する方が良い場合が多く、手作業による測定の限界から、体積指数のような、肥満度を測定する新しい代替法も生まれている。
定義のカテゴリのばらつき
過体重および肥満の閾値をBMIスケール上でどこに設定すべきかは明確ではありません。そのため、基準は過去数十年間で異なってきました。1980年から2000年までの間、アメリカの食事ガイドラインでは、過体重をBMI 24.9から27.1までのさまざまなレベルで定義してきました。1985年には、国立衛生研究所(NIH)の合意会議が、男性の過体重BMIを27.8、女性の過体重BMIを27.3に設定することを推奨しました。
1998年、NIHの報告書はBMI25以上を過体重、30以上を肥満と結論づけた。1990年代、世界保健機関(WHO)は、NIHが設定した基準であるBMI 25〜30を過体重、BMI 30以上を肥満とみなすべきであると決定した。これは、誰かが太り過ぎかどうかを判断するための決定的なガイドとなった。
ある研究では、現在の定義に従って「過体重」や「肥満」とされた人の大多数は、実際には早期死亡のリスクを意味あるほど高めていないことがわかった。60万人以上の男女を対象としたいくつかの研究の定量的分析では、死亡率が最も低かったのはBMI23〜29の人々であった。
代替案
体格指数(指数3)
体格指数は2ではなく3の指数を使う。体格指数は非常に背の低い人や非常に背の高い人でも有効な結果をもたらすが、これはBMIの問題点である。例えば、152.4 cm (5 ft 0 in)背の高い人が48 kg (106 lb)理想体重の場合、正常なBMIは20.74、CIは13.6となる。 6、200 cm (6 ft 7 in)身長で100 kg (220 lb)体重の人のBMIは24.84で、太りすぎのBMI25に非常に近く、CIは12.4で、正常値のCI12に非常に近い。
新しいBMI(指数は2.5)
5/2の指数は19世紀にQueteletによって提案された:
一般に、発育過程において、異なる年齢における体重の2乗が身長の5乗になると仮定しても、それほど間違いはない
この2.5という指数は、オックスフォード大学の数値解析教授であるニック・トリーフェッセンによって提唱されたボディマス指数の改訂式で使用されており、従来のBMI式で2の指数を使用することによって生じる低身長者と高身長者の歪みを最小限に抑えている:
1.3というスケーリング係数は、提案された新しいBMI式を、平均身長の成人に対する従来のBMI式と整合させるために決定されたものであり、2.5という指数は、従来のBMI式の指数2と、体重(密度が一定であれば、理論的には体積、すなわち身長の3乗としてスケールする)の身長に対するスケーリングに期待される指数3との妥協点である。トリーフェッセンの分析では、2.5の指数は、2または3の指数よりも歪みが少なく、より密接に経験的データに適合することが判明した。
BMIプライム(指数2、正規化係数)
BMIプライムとは、BMIシステムを改良したもので、上限至適BMI(現在25 kg/m2で定義されている)に対する実際のBMIの比率、すなわち上限至適に対する実際のBMIの割合として表したものである。BMIプライムは単位に依存しない無次元数である。BMIプライムが0.74未満の人は低体重、0.74~1.00の人は至適体重、1.00以上の人は過体重である。BMIプライムは、その人が至適BMIの最大値からどの程度の比率(例:1.36)または割合(例:136%、または36%以上)で逸脱しているかを示すため、臨床的に有用である。
例えば、BMI 34 kg/m2の人のBMIプライムは34/25=1.36であり、上限値を36%超えている。東南アジアおよび華南の集団(§国際的バリエーションを参照)では、BMIプライムは25ではなく、分母に上限BMI 23を用いて計算すべきである。BMIプライムにより、上限最適BMI値が異なる集団間の比較が容易になる。
ウエスト周囲径
ウエスト周囲径は内臓脂肪の良い指標であり、内臓脂肪は他の場所の脂肪よりも健康上のリスクが高い。米国国立衛生研究所(NIH)によると、ウエスト周囲径が男性で1,020 mm (40 in)、(妊娠していない)女性で880 mm (35 in)を超えると、2型糖尿病、脂質異常症、高血圧、心血管疾患のリスクが高いと考えられている。CVDである。ウエスト周囲径は、BMIよりも肥満に関連した疾患リスクの指標となりうる。例えば、アジア系住民や高齢者ではそうである。男性では940 mm (37 in)、女性では800 mm (31 in)が「より高いリスク」をもたらすとされており、NIHの数値は「さらに高い」とされている。
ウエスト-ヒップ周囲径比も使用されているが、ウエスト周囲径だけより優れているわけではなく、測定がより複雑であることがわかっている。
関連する指標は、ウエスト周囲径を身長で割った値である。リスク上昇を示す値は、40歳未満で0.5以上、40~50歳で0.5~0.6、50歳以上で0.6以上である。
表面ベース体型指数
表面ベースの体型指数 (SBSI)は、体表面積(BSA)、体幹垂直周囲長(VTC)、ウエスト周囲長(WC)、身長(H)である。全米健康・人間栄養調査(NHANES)1999~2004年の11,808人のデータでは、SBSIはBMI、ウエスト周囲径、BMIの代替指標であるA体型指数(ABSI)を上回っていた。
SBSI*として知られるSBSIの簡略化された無次元形も開発されている。
修正肥満指数
家族性アミロイドポリニューロパチーなどのいくつかの医学的状況では、血清アルブミンは修正肥満度指数(mBMI)を生成するために考慮される。mBMIは、BMIに血清アルブミンを1リットルあたりのグラム数で乗じることで得られる。
こちらも参照
- Allometry/ja
- Body water/ja
- History of anthropometry/ja
- List of countries by body mass index/ja
- Obesity paradox/ja
- Relative Fat Mass/ja
- Somatotype and constitutional psychology/ja
さらに読む
- Ferrera LA, ed. (2006). Focus on Body Mass Index And Health Research. New York: Nova Science. ISBN 978-1-59454-963-2.
- Samaras TT, ed. (2007). Human Body Size and the Laws of Scaling: Physiological, Performance, Growth, Longevity and Ecological Ramifications. New York: Nova Science. ISBN 978-1-60021-408-0.
- Sothern MS, Gordon ST, von Almen TK, eds. (19 April 2016). Handbook of Pediatric Obesity: Clinical Management (Illustrated ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-1911-7.
外部リンク
- 米国国立保健統計センター:
- "BMI Growth Charts for children and young adults". US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 31 January 2019.
- "BMI calculator ages 20 and older". US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 21 July 2021.