Biguanide/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "ビグアナイド" |
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | <languages /> | ||
{{Pathnav|Medication/ja|Diabetes medication/ja|frame=1}} | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="width:100%" | |||
|- | |||
!一般名 | |||
!先発名 | |||
!class="unsortable"| 日本 | |||
!創薬/開発 | |||
!備考 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Metformin/ja]] | |||
|[https://sumitomo-pharma.jp/product/metgluco/ メトグルコ](Metgulco) ([https://pins.japic.or.jp/pdf/newPINS/00061908.pdf PI]) ([https://sumitomo-pharma.jp/product/metgluco/attachment/interv.html IF]) | |||
|販売 | |||
|[[住友ファーマ]] | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
{{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| Watchedfields = changed | | Watchedfields = changed | ||
| Line 8: | Line 22: | ||
| ImageFile_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | | ImageFile_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | ||
| ImageSize = 160 | | ImageSize = 160 | ||
| ImageName = | | ImageName = ビグアナイドの骨格式 | ||
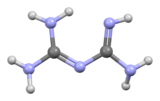
| ImageFile1 = Biguanide-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png | | ImageFile1 = Biguanide-from-xtal-3D-bs-17.png | ||
| ImageFile1_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | | ImageFile1_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | ||
| ImageSize1 = 160 | | ImageSize1 = 160 | ||
| ImageName1 = | | ImageName1 = ビグアナイドのボールとスティックのモデル | ||
| PIN = Imidodicarbonimidic diamide | | PIN = Imidodicarbonimidic diamide | ||
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| Line 43: | Line 57: | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''ビグアナイド'''('''Biguanide'''、{{IPAc-en|b|aɪ|ˈ|g|w|ɒ|n|aɪ|d}})は、式HN(C(NH)NH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>2</sub>で表される有機化合物である。 無色の固体で、水に溶けて塩基性の高い溶液を作る。 これらの溶液はゆっくりと加水分解して[[ammonia/ja|アンモニア]]と[[urea/ja|尿素]]になる。 | |||
'''Biguanide''' | |||
==合成== | |||
{{Anchor|Synthesis}} | |||
ビグアニドは[[dicyandiamide/ja|ジシアンジアミド]]と[[ammonia/ja|アンモニア]]の反応から、[[pinner reaction/ja|ピナー]]型のプロセスを経て得ることができる。 | |||
:<math>\mathrm{C_2H_4N_4 + NH_3 \longrightarrow C_2H_7N_5}</math> | :<math>\mathrm{C_2H_4N_4 + NH_3 \longrightarrow C_2H_7N_5}</math> | ||
ビグアナイドは1879年に[[:en:Bernhard Rathke|Bernhard Rathke]]によって初めて合成された。 | |||
==ビグアニジン薬物== | |||
{{Anchor|Biguanidine drugs}} | |||
ビグアニジンのさまざまな[[derivative (chemistry)/ja|誘導体]]が薬物として使用されている。 | |||
===抗高血糖薬=== | |||
=== | "ビグアニジン"という用語は、特に、[[diabetes mellitus/ja|糖尿病]]または[[prediabetes/ja|糖尿病前症]]の治療に用いられる経口抗高血糖[[drug/ja|薬物]]として機能する一群の薬物を指すことが多い。 | ||
例えば、以下のようなものがある: | |||
* [[Metformin/ja|メトホルミン]] - [[diabetes mellitus type 2/ja|2型糖尿病]]の治療に広く用いられる。 | |||
* [[Metformin]] - | * [[phenformin/ja|フェンホルミン]] - 毒性作用のため、ほとんどの国で市場から撤退した。 | ||
* [[ | * [[Buformin/ja|ブホルミン]] - 毒性により市場から撤退した。 | ||
* [[Buformin]] - | |||
<gallery caption="bioactive biguanidines" widths="180px" heights="120px" perrow="3"> | <gallery caption="bioactive biguanidines" widths="180px" heights="120px" perrow="3"> | ||
File:Metformin.svg|[[Metformin]] | File:Metformin.svg|[[Metformin/ja|メトホルミン]]は、非対称ジメチルビグアニジンとも呼ばれる。 | ||
File:Buformin.svg|[[Buformin]] | File:Buformin.svg|[[Buformin/ja|ブホルミン]]。ビグアニジンの[[butyl/ja|ブチル]]誘導体である。 | ||
File:Phenformin.svg|[[Phenformin]]. | File:Phenformin.svg|[[Phenformin/ja|フェンフォルミン]]. フェネチル化ビグアニジンである。 | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
====歴史==== | |||
==== | {{details/ja|metformin/ja#History}} | ||
{{details|metformin#History}} | ''[[:en:Galega officinalis|ガレガ・オフィシナリス]]''(フランスのライラック)は、何世紀にもわたって糖尿病治療に用いられてきた。1920年代、'''ガレガ'''の抽出物から[[guanidine/ja|グアニジン]]化合物が発見された。動物実験では、これらの化合物が血糖値を下げることが示された。毒性の低い誘導体である[[synthalin/ja|シンタリン]]も発見された。シンタリンAとシンタリンBは糖尿病治療に用いられたが、[[insulin/ja|インスリン]]の発見後、その使用は減少した。ビグアナイド薬は1950年代後半に2型[[diabetes/ja|糖尿病]]治療に再び導入された。当初は[[phenformin/ja|フェンホルミン]]が広く使用されていたが、時に致命的な[[lactic acidosis/ja|乳酸アシドーシス]]を引き起こす可能性があったため、ほとんどの薬局方から撤回された(米国では1978年)。メトホルミンは安全性プロファイルがはるかに優れており、世界中で薬物治療に使用されている主要なビグアナイド薬物である。 | ||
''[[Galega officinalis]]'' | |||
====作用機序=== | |||
=== | ビグアナイド薬の[[mechanism of action/ja|作用機序]]は完全には解明されておらず、メトホルミンについては多くの機序が提唱されている。 | ||
ビグアナイド薬は、[[sulfonylurea/ja|スルホニル尿素]]や[[meglitinide/ja|メグリチニド]]などの他の[[hypoglycemic agent/ja|血糖降下薬]]とは異なり、インスリンの分泌に影響を与えない。 したがって、ビグアナイド薬は2型糖尿病患者に有効であり、インスリン療法と併用すれば1型糖尿病にも有効である。 | |||
主にII型糖尿病に用いられるメトホルミンは、生体内でインスリン感受性を高め、血漿グルコース濃度の低下、グルコース取り込みの増加、糖新生の減少をもたらすと考えられている。 | |||
しかし、高インスリン血症では、ビグアナイド薬は血漿中のインスリンの空腹時レベルを低下させる。 ビグアナイド薬の治療的用途は、肝臓での[[gluconeogenesis/ja|糖新生]]を減少させ、その結果、血液中のグルコース濃度を低下させる傾向からきている。 ビグアナイドはまた、体内の細胞が血流中にすでに存在するグルコースを吸収しやすくする傾向があり、再び血漿中のグルコースレベルを低下させる。 | |||
ビグアナイドは銅と相互作用することが示されており、特にミトコンドリアでは、2+酸化状態の銅(Cu(II))をキレート化することによって、細胞の代謝を阻害する。 | |||
====副作用と毒性==== | |||
==== | 最も一般的な副作用は[[diarrhea/ja|下痢]]と消化不良であり、患者の最大30%に発現する。 最も重要で重篤な副作用は[[lactic acidosis/ja|乳酸アシドーシス]]であるため、メトホルミンは進行した[[chronic kidney disease/ja|慢性腎臓病]]では禁忌である。メトホルミンを開始する前に腎機能を評価すべきである。フェンホルミンとブホルミンはメトホルミンよりもアシドーシスを起こしやすいため、実質的にメトホルミンに取って代わられている。しかし、メトホルミンと他の薬物を併用する場合(併用療法)、[[hypoglycemia/ja|低血糖症]]や他の副作用の可能性がある。 | ||
===抗マラリア薬=== | |||
第二次世界大戦中、[[Frank Rose (chemist)/ja|フランク・ローズ]]が率いるイギリスのチームが、いくつかのビグアナイドが[[antimalarial drug/ja|抗マラリア薬]]として有用であることを発見した(詳細はそちらを参照)。ずっと後になって、それらは活性のある[[dihydrotriazine/ja|ジヒドロトリアジン]]誘導体に代謝されるプロドラッグであることが証明され、最近まで[[dihydrofolate reductase/ja|ジヒドロ葉酸還元酵素]]を[[Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor/ja|阻害]]することで作用すると考えられていた。その例には以下が含まれる: | |||
* [[Proguanil/ja|プログアニル]](>[[cycloguanil/ja|シクログアニル]]) | |||
* [[Proguanil]] | * [[Chlorproguanil/ja|クロルプログアニル]] | ||
* [[Chlorproguanil]] | |||
===消毒薬=== | |||
{{see also/ja|Bisbiguanide/ja}} | |||
{{see also|Bisbiguanide}} | 消毒剤[[chlorhexidine/ja|クロルヘキシジン]]、[[polyaminopropyl biguanide/ja|ポリアミノプロピルビグアニド]](PAPB)、[[polihexanide/ja|ポリヘキサニド]]、[[alexidine/ja|アレキシジン]]はビグアニド[[functional group/ja|官能基]]を特徴とする。 | ||
{{oral hypoglycemics/ja}} | |||
{{oral hypoglycemics}} | {{antimalarials/ja}} | ||
{{antimalarials}} | |||
[[Category:Biguanides| ]] | [[Category:Biguanides| ]] | ||
[[Category:Guanidines]] | [[Category:Guanidines]] | ||
[[Category:Substances discovered in the 19th century]] | [[Category:Substances discovered in the 19th century]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:05, 23 April 2024
| 一般名 | 先発名 | 日本 | 創薬/開発 | 備考 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| メトホルミン | メトグルコ(Metgulco) (PI) (IF) | 販売 | 住友ファーマ |

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Imidodicarbonimidic diamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 507183 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 240093 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H7N5 | |
| Molar mass | 101.113 g·mol−1 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.07, 13.25 |
ビグアナイド(Biguanide、/baɪˈɡwɒnaɪd/)は、式HN(C(NH)NH2)2で表される有機化合物である。 無色の固体で、水に溶けて塩基性の高い溶液を作る。 これらの溶液はゆっくりと加水分解してアンモニアと尿素になる。
合成
ビグアニドはジシアンジアミドとアンモニアの反応から、ピナー型のプロセスを経て得ることができる。
ビグアナイドは1879年にBernhard Rathkeによって初めて合成された。
ビグアニジン薬物
ビグアニジンのさまざまな誘導体が薬物として使用されている。
抗高血糖薬
"ビグアニジン"という用語は、特に、糖尿病または糖尿病前症の治療に用いられる経口抗高血糖薬物として機能する一群の薬物を指すことが多い。
例えば、以下のようなものがある:
歴史
ガレガ・オフィシナリス(フランスのライラック)は、何世紀にもわたって糖尿病治療に用いられてきた。1920年代、ガレガの抽出物からグアニジン化合物が発見された。動物実験では、これらの化合物が血糖値を下げることが示された。毒性の低い誘導体であるシンタリンも発見された。シンタリンAとシンタリンBは糖尿病治療に用いられたが、インスリンの発見後、その使用は減少した。ビグアナイド薬は1950年代後半に2型糖尿病治療に再び導入された。当初はフェンホルミンが広く使用されていたが、時に致命的な乳酸アシドーシスを引き起こす可能性があったため、ほとんどの薬局方から撤回された(米国では1978年)。メトホルミンは安全性プロファイルがはるかに優れており、世界中で薬物治療に使用されている主要なビグアナイド薬物である。
=作用機序
ビグアナイド薬の作用機序は完全には解明されておらず、メトホルミンについては多くの機序が提唱されている。
ビグアナイド薬は、スルホニル尿素やメグリチニドなどの他の血糖降下薬とは異なり、インスリンの分泌に影響を与えない。 したがって、ビグアナイド薬は2型糖尿病患者に有効であり、インスリン療法と併用すれば1型糖尿病にも有効である。
主にII型糖尿病に用いられるメトホルミンは、生体内でインスリン感受性を高め、血漿グルコース濃度の低下、グルコース取り込みの増加、糖新生の減少をもたらすと考えられている。
しかし、高インスリン血症では、ビグアナイド薬は血漿中のインスリンの空腹時レベルを低下させる。 ビグアナイド薬の治療的用途は、肝臓での糖新生を減少させ、その結果、血液中のグルコース濃度を低下させる傾向からきている。 ビグアナイドはまた、体内の細胞が血流中にすでに存在するグルコースを吸収しやすくする傾向があり、再び血漿中のグルコースレベルを低下させる。
ビグアナイドは銅と相互作用することが示されており、特にミトコンドリアでは、2+酸化状態の銅(Cu(II))をキレート化することによって、細胞の代謝を阻害する。
副作用と毒性
最も一般的な副作用は下痢と消化不良であり、患者の最大30%に発現する。 最も重要で重篤な副作用は乳酸アシドーシスであるため、メトホルミンは進行した慢性腎臓病では禁忌である。メトホルミンを開始する前に腎機能を評価すべきである。フェンホルミンとブホルミンはメトホルミンよりもアシドーシスを起こしやすいため、実質的にメトホルミンに取って代わられている。しかし、メトホルミンと他の薬物を併用する場合(併用療法)、低血糖症や他の副作用の可能性がある。
抗マラリア薬
第二次世界大戦中、フランク・ローズが率いるイギリスのチームが、いくつかのビグアナイドが抗マラリア薬として有用であることを発見した(詳細はそちらを参照)。ずっと後になって、それらは活性のあるジヒドロトリアジン誘導体に代謝されるプロドラッグであることが証明され、最近までジヒドロ葉酸還元酵素を阻害することで作用すると考えられていた。その例には以下が含まれる:
消毒薬
消毒剤クロルヘキシジン、ポリアミノプロピルビグアニド(PAPB)、ポリヘキサニド、アレキシジンはビグアニド官能基を特徴とする。