Metformin/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "DPP-4阻害薬とメトホルミンの併用には、シタグリプチン/メトホルミン配合剤(ジャヌメット)、サキサグリプチン/メトホルミン配合剤(コンビグライゼXR、コンビグライゼ)、アログリプチン/メトホルミン配合剤(カザーノ、ビップドメット)などがある。" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
No edit summary |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
<!-- Definition and medical uses --> | <!-- Definition and medical uses --> | ||
'''メトホルミン'''('''Metformin''')は、''' | '''メトホルミン'''('''Metformin''')は、'''グルコファージ'''('''Glucophage''')などの商品名で販売されており、特に[[overweight/ja|太りすぎ]]の[[diabetes mellitus type 2/ja|2型糖尿病]]の治療のための主要な[[first-line treatment/ja|第一選択]]医薬品である。また、[[polycystic ovary syndrome/ja|多嚢胞性卵巣症候群]]の治療にも用いられる。[[antipsychotic/ja|抗精神病薬]]を服用している人の[[metabolic syndrome/ja|メタボリックシンドローム]]のリスクを軽減するために、適応外の補助薬として使用されることもある。 | ||
<!-- Adverse effects --> | <!-- Adverse effects --> | ||
| Line 285: | Line 285: | ||
DPP-4阻害薬とメトホルミンの併用には、[[sitagliptin/metformin/ja|シタグリプチン/メトホルミン]]配合剤(ジャヌメット)、[[saxagliptin/metformin/ja|サキサグリプチン/メトホルミン]]配合剤(コンビグライゼXR、コンビグライゼ)、[[alogliptin/metformin/ja|アログリプチン/メトホルミン]]配合剤(カザーノ、ビップドメット)などがある。 | DPP-4阻害薬とメトホルミンの併用には、[[sitagliptin/metformin/ja|シタグリプチン/メトホルミン]]配合剤(ジャヌメット)、[[saxagliptin/metformin/ja|サキサグリプチン/メトホルミン]]配合剤(コンビグライゼXR、コンビグライゼ)、[[alogliptin/metformin/ja|アログリプチン/メトホルミン]]配合剤(カザーノ、ビップドメット)などがある。 | ||
[[Linagliptin/ja|リナグリプチン]]とメトホルミン塩酸塩の組み合わせは、Jentaduetoという商品名で販売されている。2021年8月現在、米国ではリナグリプチン/メトホルミンは[[generic medicine/ja|ジェネリック医薬品]]として販売されている。 | |||
[[Linagliptin]] | |||
=====SGLT-2阻害剤===== | |||
=====SGLT- | |||
メトホルミンと[[SGLT-2 inhibitor/ja|SGLT-2阻害薬]]の[[Dapagliflozin/metformin/ja|ダパグリフロジン]]、[[Empagliflozin/metformin/ja|エンパグリフロジン]]、[[Canagliflozin/metformin/ja|カナグリフロジン]]との併用がある。 | |||
===== スルホニル尿素薬 ===== | |||
===== | [[Sulfonylurea/ja|スルホニル尿素]]は、[[pancreas/ja|膵臓]]の[[beta cell/ja|β細胞]]からのインスリン放出を増加させることによって作用する。 | ||
[[Sulfonylurea]] | |||
2019年のシステマティックレビューでは、メトホルミンとスルホニル尿素の併用療法が、メトホルミンと他の血糖降下薬の併用療法と比較して、死亡率、重篤な有害事象、大血管合併症、細小血管合併症において有益か有害かのエビデンスは限られていることが示唆された。メトホルミンとスルホニル尿素の併用療法は、低血糖のリスクが高いように思われた。 | |||
メトホルミンは、スルホニル尿素の[[glipizide/ja|グリピジド]](メタグリップ)と[[glibenclamide/ja|グリベンクラミド]](米国:グリブリド)(グルコバンス)と組み合わせて使用できる。メトホルミン/グリピジドとメトホルミン/グリベンクラミドのジェネリック製剤が入手可能である(後者の方が人気がある)。 | |||
===== メグリチニド ===== | |||
== | [[Meglitinide/ja|メグリチニド]]は、膵臓のβ細胞に結合することからスルホニル尿素薬と類似しているが、目的とする受容体への結合部位と受容体に対する薬物の親和性が異なる。その結果、スルホニル尿素薬に比べて作用時間が短く、インスリンの分泌を開始するにはより高い血糖値を必要とする。ナテグリニドおよびレパングリニドとして知られる両メグリチニドは、メトホルミンと組み合わせた製剤で販売されている。[[repaglinide/ja|レパグリニド]]とメトホルミンの組み合わせは、Prandimetとして、またはそのジェネリック医薬品として販売されている。 | ||
[[Meglitinide]] | |||
===== トリプル併用療法 ===== | |||
===== | メトホルミンとダパグリフロゼンとサキサグリプチンの併用は、米国ではQternmet XRとして販売されている。 | ||
メトホルミンと[[pioglitazone/ja|ピオグリタゾン]]およびグリベンクラミドの配合剤は、インドではAccuglim-MP、Adglim MP、Alnamet-GPとして、フィリピンではTri-Senzaとして販売されている。 | |||
トルコでは、メトホルミンとピオグリタゾンおよび[[lipoic acid/ja|リポ酸]]の配合剤がPionalとして販売されている。 | |||
{{Anchor|impurities}} | {{Anchor|impurities}} | ||
=== 不純物 === | |||
{{See also/ja|Ranitidine/ja#impurities}} | |||
{{See also|Ranitidine#impurities}} | |||
2019年12月、米国FDAは、米国外で製造された一部のメトホルミン医薬品に、ヒト発がん性物質の可能性が高いと分類される[[N-nitrosodimethylamine/ja|N-ニトロソジメチルアミン]](NDMA)と呼ばれるニトロソアミン不純物が低レベルで含まれている可能性があることが分かったと発表した。カナダ保健省は、メトホルミン中のNDMA濃度を評価していると発表した。 | |||
2020年2月、FDAは検査したメトホルミンのサンプルの一部から、1日の許容摂取量を超えないNDMA濃度を検出した。 | |||
2020年2月、[[:en:Health Canada|カナダ保健省]]はアポテックス社の即時放出型メトホルミンのリコールを発表し、3月にはランバクシー社のメトホルミン、さらに3月にはジャンプ社のメトホルミンのリコールを発表した。 | |||
2020年5月、FDAは5社にメトホルミン製剤の自主回収を要請した。その5社とは、アムニール・ファーマシューティカルズ(Amneal Pharmaceuticals)、アクタヴィス・ファーマ(Actavis Pharma)、アポテックス・コーポレーション(Apotex Corp)、ルピン・ファーマ(Lupin Pharma)、マークサン・ファーマ・リミテッド(Marksans Pharma Limited)の5社であることが、市民請願書を通じてメトホルミンにこの汚染物質が含まれていることを最初にFDAに警告した薬局である[[:en:Valisure|Valisure]]に送られた書簡で明らかになった。 | |||
2020年6月、FDAは検査したメトホルミン製品のNDMA量を示す検査結果を公表した。その結果、ERメトホルミンの特定のロットからNDMAが検出され、許容摂取限界値である1日96ナノグラムを超えるNDMAが検出されたロットの回収を各社に勧告している。FDAはまた、メトホルミンの検査結果を共有するために、国際的な規制当局と協力している。 | |||
2020年7月、ルピン・ファーマシューティカルズ社は、検査したサンプルから許容できないほど高濃度のNDMAが検出されたため、すべての[[:en:Lot number|ロット]](バッチ)のメトホルミンを回収した。 | |||
2020年8月、Bayshore Pharmaceuticals社は2つのロットの錠剤を回収した。 | |||
== 研究 == | |||
{{Anchor|Research}} | |||
メトホルミンは、以下のような他の複数の疾患に対する効果について研究されている: | |||
* [[Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease]] | * [[Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/ja|非アルコール性脂肪性肝疾患]] | ||
* [[Premature puberty]] | * [[Premature puberty/ja|思春期早発症]] | ||
* [[anti-cancer| | * [[anti-cancer/ja|ガン]] | ||
* [[Cardiovascular disease]] | * 糖尿病患者における[[Cardiovascular disease/ja|心臓血管疾患]] | ||
* [[Ageing| | * [[Ageing/ja|老化]] | ||
メトホルミンは[[fragile X syndrome/ja|脆弱X症候群]]の人の体重を減らすかもしれないが、神経症状や精神症状を改善するかどうかは不明である。メトホルミンは生体内(''[[Caenorhabditis elegans/ja|線虫]]''および[[Acheta domesticus/ja|コオロギ]])で老化に対する影響について研究されている。2017年のレビューによると、メトホルミンを服用している糖尿病患者は全死亡率が低かった。また、他の治療を受けている人に比べて、がんや心血管疾患も減少していた。 | |||
また、メトホルミンは糖尿病を予防するが、がんや心血管疾患のリスクは減少させないため、糖尿病でない人の寿命は延びないことを示唆する研究もある。さらに、健康な人がメトホルミンを長期間慢性的に使用すると、[[vitamin B12 deficiency/ja|ビタミンB12欠乏症]]になる可能性を示唆する研究もある。 | |||
| | ||
Latest revision as of 16:42, 12 March 2024
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /mɛtˈfɔːrmɪn/, met-FOR-min |
| Trade names | フォルタメット, グルコファージ, グルメッツァ, その他 |
| Other names | N,N-dimethylbiguanide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a696005 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | 経口 |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50–60% |
| Protein binding | Minimal |
| Metabolism | 肝臓ではない |
| Elimination half-life | 4–8.7 時間 |
| Excretion | 尿中 (90%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
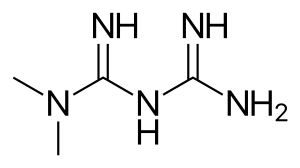
| Formula | C4H11N5 |
| Molar mass | 129.167 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| |
| |
メトホルミン(Metformin)は、グルコファージ(Glucophage)などの商品名で販売されており、特に太りすぎの2型糖尿病の治療のための主要な第一選択医薬品である。また、多嚢胞性卵巣症候群の治療にも用いられる。抗精神病薬を服用している人のメタボリックシンドロームのリスクを軽減するために、適応外の補助薬として使用されることもある。
メトホルミンは一般的に忍容性が高い。一般的な副作用には、下痢、吐き気、腹痛などがある。メトホルミンは低血糖を引き起こすリスクが小さい。高血中乳酸値(アシドーシス)は、医薬品を過度に大量に使用したり、重度の腎障害のある人に処方した場合に懸念される。
メトホルミンはビグアナイド系抗高血糖薬である。肝臓におけるグルコース産生を減少させ、体組織のインスリン感受性を高めることによって作用する。
メトホルミンは、1922年にEmil WernerとJames Bellによって初めて科学文献に記載された。フランスの医師ジャン・スターン(Jean Sterne)は1950年代にヒトでの研究を開始した。フランスでは1957年に、米国では1995年に医薬品として導入された。メトホルミンは世界保健機関の必須医薬品リストに掲載されており、口から服用する糖尿病治療薬として最も広く使用されている。ジェネリック医薬品としても販売されている。2021年には、米国で2番目に多く処方された医薬品であり、91 万以上の処方があった。
医療用途
メトホルミンは、2型糖尿病患者の血糖を低下させるために使用される。また、多嚢胞性卵巣症候群の不妊症の第二選択薬としても用いられる。
2型糖尿病
米国糖尿病学会と米国内科学会はともに、メトホルミンを2型糖尿病治療の第一選択薬として推奨している。メトホルミンはレパグリニドと同程度に有効であり、2型糖尿病に対する他のすべての経口薬物よりも有効である。
有効性
欧州糖尿病学会、欧州心臓病学会、米国糖尿病学会などの主要な専門学会の治療ガイドラインでは、メトホルミンの心血管ベネフィットに関するエビデンスは曖昧であると記述されている。2020年のコクランでは システマティックレビューでは、メトホルミン単剤療法を他の糖低下薬物、行動変容介入、プラセボ、介入なしと比較した場合、心血管死亡率、非致死的心筋梗塞、非致死的脳卒中の減少を示す十分なエビデンスは認められなかった。
メトホルミンの使用は、体重増加と関連するスルホニル尿素とは対照的に、2型糖尿病患者の体重を減少させる。メトホルミンが糖尿病がない肥満の体重減少に関連することを示す証拠もある。メトホルミンはスルホニル尿素系薬剤よりも低血糖のリスクが低いが、低血糖は激しい運動、カロリー不足、または血糖を低下させる他の薬剤との併用時に起こることがまれである。メトホルミンは、低密度リポ蛋白およびトリグリセリド値を緩やかに低下させる。
糖尿病予備軍の個人において、2019年に行われた2型糖尿病の発症リスク低下におけるメトホルミンと他の介入との効果を比較したシステマティックレビューでは、メトホルミンが食事療法や運動療法、またはプラセボと比較した場合に2型糖尿病の発症リスクを低下させるという中程度の質のエビデンスが認められた。しかし、メトホルミンと集中的な食事療法または運動療法を比較した場合、メトホルミンは2型糖尿病の発症リスクを減少させないという中等度の質のエビデンスが得られ、集中的な食事療法または運動療法にメトホルミンを追加しても、集中的な運動療法と食事療法のみと比較した場合、2型糖尿病のリスクを減少させるという利点も欠点も示さないという非常に質の低いエビデンスが得られた。同レビューでは、糖尿病予備軍における2型糖尿病発症リスクの低下におけるメトホルミンとスルホニル尿素の効果を比較した適切な試験も1件見つかったが、この試験では患者に関連するアウトカムは報告されていない。
多嚢胞性卵巣症候群
多嚢胞性卵巣症候群(PCOS)では、メトホルミンの使用により生児出生率が増加するという暫定的なエビデンスがある。これには、クロミフェンで妊娠できなかった人も含まれる。メトホルミンは流産のリスクを変化させないようである。その他にも、妊娠中および非妊娠中のPCOS女性において、多くの有益性が認められている。PCOS女性におけるIVF/ICSI前または治療中のメトホルミン対プラセボ/無治療に関するコクラン(2020年)の最新レビューでは、生児出生率の改善に関する決定的な証拠は見つかっていない。長時間のGnRHアゴニストプロトコールでは、生児出生率改善のエビデンスには不確実性があったが、臨床的妊娠率の増加はあり得た。要するに、GnRHアンタゴニストプロトコールのメトホルミンは、臨床的妊娠率への影響については不確実であるが、生児出生率を低下させる可能性がある。メトホルミンはOHSSの減少をもたらすかもしれないが、副作用の頻度が高くなる可能性がある。流産に対するメトホルミンの影響については不明確であった。エビデンスは、肥満女性の母体および乳児の転帰を改善するための妊娠中の一般的な使用を支持していない。
イギリスの米国国立医療技術評価機構は2004年に、PCOSで肥満度が25を超える女性に対して、他の治療法で効果が得られない場合に無排卵と不妊のためにメトホルミンを投与することを推奨した。英国および国際的な臨床実践ガイドラインでは、耐糖能異常のある女性を除き、メトホルミンを第一選択治療として推奨していないか、まったく推奨していない。ガイドラインでは、クロミフェンを第一選択医薬品として推奨し、内科的治療とは別に生活習慣の改善を強調している。メトホルミン治療は、ベースライン時に耐糖能障害を示したPCOS女性における2型糖尿病の発症リスクを低下させる。
胃癌
胃癌(GC)は、その高い有病率と死亡率から、世界的な健康上の大きな問題となっている。様々な治療法がある中で、2型糖尿病(T2DM)の一般的な医薬品であるメトホルミンは、その潜在的な抗がん作用が注目されている。GCに対するメトホルミンの有効性については議論の的となってきたが、最近の臨床研究では、GC患者のリスクを低減し生存率を向上させるというメトホルミンの保護作用が優勢に支持されている。メトホルミンの抗癌作用は、複数の経路、特にAMPKの活性化とIGF-1Rの調節を介すると考えられている。有望な知見にもかかわらず、GCの予防と治療におけるメトホルミンの応用に関するコンセンサスは得られていないため、その治療的役割を確認するためには、さらなる臨床的およびメカニズム的研究が必要である。
糖尿病と妊娠
妊娠中のメトホルミン使用について、インスリン単独と比較した総説では、母児ともに短期的な安全性は良好であったが、長期的な安全性は不明であった。いくつかの観察研究およびランダム化比較試験では、メトホルミンは妊娠糖尿病の管理においてインスリンと同様に有効かつ安全であることが明らかにされた。それにもかかわらず、いくつかの懸念が提起されており、母子双方に対するメトホルミンの長期安全性に関するエビデンスは不足している。インスリンと比較して、メトホルミンを投与された妊娠糖尿病の女性は体重増加が少なく、妊娠中に子癇前症を発症する可能性が低い。メトホルミンを投与された女性から生まれた赤ちゃんは内臓脂肪が少なく、そのため、その後の人生でインスリン抵抗性になりにくい可能性がある。妊娠糖尿病にメトホルミンを使用すると、インスリンによる治療と比較して赤ちゃんが小さくなる。しかし、妊娠中にメトホルミンを投与された子どもは、当初は出生体重が低かったにもかかわらず、出生後の成長が促進され、妊娠中にインスリンを投与された子どもよりも小児期半ばまでに体重が増加した。このように、出生時低体重の後、比較対照児を上回るキャッチアップ成長というパターンは、長期的な心代謝疾患と関連している。
体重の変化
メトホルミンの使用は一般的に体重減少を伴う。メトホルミンは、抗精神病薬であるオランザピンおよびクロザピンによって引き起こされる体重増加を打ち消すのに安全かつ有効であるようである。メトホルミンによりクロザピンによる体重増加の緩やかな逆転が認められるが、体重増加の一次予防の方がより価値がある。
インスリンとの併用
メトホルミンは、低血糖のリスクは増加するものの、1型糖尿病におけるインスリン必要量を減少させる可能性がある。
寿命延長
メトホルミンは、健康な人でも寿命延長に役立つ可能性があることを示す証拠がいくつかある。メトホルミンは、おそらく糖尿病治療(インスリンと糖質調節)と同様のメカニズムで老化を遅らせる薬剤として大きな関心を集めている。
アルツハイマー病
予備研究では、メトホルミンがアルツハイマー病のリスクを低下させるかどうか、2型糖尿病とアルツハイマー病のリスクに相関があるかどうかが検討されている。
禁忌事項
メトホルミンは以下の併用禁忌である:
- 重度の腎機能障害(推定糸球体濾過量(eGFR)が30 mL/分/1.73 m2未満)。
- メトホルミンに対する既知の過敏症
- 糖尿病性ケトアシドーシス(コントロールされていない糖尿病による)を含む急性または慢性の代謝性アシドーシスで、昏睡を伴うか伴わない。
副作用
メトホルミンの最も一般的な副作用は、下痢、けいれん、吐き気、嘔吐、および鼓腸の増加などの消化管刺激である。メトホルミンは、他のほとんどの抗糖尿病医薬品よりも一般的に消化器系の副作用と関連している。メトホルミンの最も重篤な潜在的副作用は乳酸アシドーシスである;この合併症はまれであり、肝機能または腎機能の低下に関連しているようである。メトホルミンは重度の腎臓病患者への使用は承認されていないが、腎臓に問題のある患者には低用量で使用することができる。
胃腸
胃腸の不調は激しい不快感を引き起こすことがある;メトホルミンの初回投与時または増量時に最もよくみられる。低用量(1.0~1.7g/日)から開始し、徐々に増量することで不快感を回避できることが多いが、低用量でも5%の人はメトホルミンに耐えられないことがある。徐放性製剤または徐放性製剤を用いると、忍容性が改善することがある。
メトホルミンの長期使用は、ホモシステイン値の上昇およびビタミンB12の吸収不良と関連している。高用量や長期間の使用はビタミンB12欠乏症の発生率の増加と関連しており、スクリーニングや予防戦略を推奨する研究者もいる。
乳酸アシドーシス
日常診療でメトホルミンに曝露しても乳酸アシドーシスが起こることはほとんどない。メトホルミンに関連した乳酸アシドーシスの発生率は、10万人/年あたり約9人であり、これは一般集団における乳酸アシドーシスの背景率と同様である。システマティックレビューでは、メトホルミンと乳酸アシドーシスを決定的に関連づけるデータは存在しないと結論づけている。
メトホルミンは一般に軽度から中等度の慢性腎臓病において安全であり、推算糸球体濾過量(eGFR)の重症度に応じてメトホルミンの投与量を比例的に減量し、腎機能を定期的に評価する(例えば、定期的な血漿クレアチニン測定)。米国食品医薬品局(FDA)は、eGFRのカットオフ値である30mL/分/1.73m2未満の、より重症の慢性腎臓病ではメトホルミンの使用を避けるよう推奨している。乳酸は肝糖新生の基質であり、メトホルミンが阻害するプロセスであるため、メトホルミンの使用により肝臓での乳酸取り込みが減少する。健常者では、このわずかな過剰は他の機序(障害のない腎臓による取り込みを含む)によって排出され、乳酸の血中濃度の有意な上昇は起こらない。腎機能が著しく低下している場合は、メトホルミンと乳酸のクリアランスが低下し、両方の濃度が上昇し、乳酸が蓄積する可能性がある。メトホルミンは乳酸の肝臓への取り込みを減少させるため、乳酸アシドーシスを誘発するような病態は禁忌である。一般的な原因としては、アルコール中毒(NAD+貯蔵量の枯渇による)、心不全、呼吸器疾患(組織の酸素化が不十分なため)などが挙げられる;最も一般的な原因は腎疾患である。
メトホルミンに伴う乳酸産生は大腸でも起こる可能性があり、危険因子を有する患者では乳酸アシドーシスの一因となる可能性がある。しかし、このことの臨床的意義は不明であり、メトホルミン関連乳酸アシドーシスのリスクは、腸での産生増加よりもむしろ肝での取り込み減少に起因することが最も一般的である。
過剰摂取
過量投与後の最も一般的な症状としては、嘔吐、下痢、腹痛、頻脈、眠気、まれに低血糖または高血糖がある。メトホルミン過剰摂取の治療は、特異的な解毒剤が知られていないため、一般に支持療法である。重度の過量投与では、体外治療が推奨される。メトホルミンは分子量が低く、血漿蛋白結合がないため、これらの手技にはメトホルミンを血漿から除去し、さらなる乳酸の過剰産生を防ぐという利点がある。
メトホルミンは、治療のモニタリング、中毒の診断の確認、または法医学的死亡調査の補助のために、血液、血漿、または血清で定量することができる。血中または血漿中のメトホルミン濃度は通常、治療用量の投与を受けている人で1~4 mg/L、急性過剰摂取の犠牲者で40~120 mg/L、死亡例で80~200 mg/Lの範囲である。クロマトグラフィー技術が一般的に採用されている。
メトホルミンに関連した乳酸アシドーシスのリスクは、メトホルミンの大量過剰投与によっても高まるが、かなり大量のメトホルミンを投与しても致命的にならないことが多い。
相互作用
H2受容体拮抗薬はメトホルミンの血漿中濃度を上昇させる。シメチジンは、腎臓によるメトホルミンのクリアランスを低下させることにより、メトホルミンの血漿中濃度の上昇を引き起こす;メトホルミンとシメチジンはどちらも尿細管分泌によって体外に排出され、両者、特にシメチジンの陽イオン(正の電荷を帯びた)型は、同じ輸送機序で競合する可能性がある。小規模な二重盲検のランダム化試験で、抗生物質である セファレキシンも同様の機序でメトホルミン濃度を上昇させることがわかった;理論的には、他の陽イオン医薬品も同じ効果をもたらす可能性がある。
メトホルミンはまた、胃運動への影響により抗コリン薬とも相互作用する。抗コリン薬は胃の運動性を低下させ、薬が消化管に留まる時間を延長させる。この障害により、抗コリン薬が存在しない場合よりもメトホルミンが多く吸収され、血漿中のメトホルミン濃度が上昇し、副作用のリスクが高まる可能性がある。
薬理学
作用機序
メトホルミンの分子メカニズムは完全には解明されていない。複数の潜在的な作用機序が提唱されている: ミトコンドリア呼吸鎖(複合体I)の阻害、AMP活性化プロテインキナーゼ(AMPK)の活性化、プロテインキナーゼA(PKA)の活性化の減少を伴うグルカゴン誘導性のgut microbiota/ja|環状アデノシン一リン酸(cAMP)の上昇の阻害、 ミトコンドリアグリセロール-3-リン酸デヒドロゲナーゼのGPD2変異体の複合体IV媒介阻害(それにより、グリセロール由来の肝グルコネシン生成を減少させる)、および腸内細菌叢への影響。
メトホルミンは、ほとんどの人に無欲作用を及ぼし、カロリー摂取を減少させる。メトホルミンは、肝臓での糖新生(グルコース産生)を減少させる。メトホルミンは、下垂体からの成長ホルモン、副腎皮質刺激ホルモン、卵胞刺激ホルモンの基礎分泌、およびプロオピオメラノコルチンの発現を阻害し、このことが、肝臓、骨格筋、内皮、脂肪組織、および卵巣を含む組織に対する複数の作用を有するインスリン感作作用の一因となっている。平均的な2型糖尿病患者は、正常の3倍の糖新生速度を持っている。メトホルミンの治療は、これを3分の1以上減少させる。
肝グルコース産生に対するメトホルミンの抑制効果には、AMPKの活性化が必要であった。AMPKは、インスリンシグナル伝達、全身のエネルギーバランス、グルコースと脂肪の代謝において重要な役割を果たす酵素である。AMPKの活性化は、スモールヘテロダイマーパートナーの発現増加に必要であり、その結果、肝グルコネーシス遺伝子ホスホエノールピルビン酸カルボキシキナーゼおよびグルコース6-ホスファターゼの発現が阻害された。メトホルミンは、AMPKアゴニストとしてAICAリボヌクレオチドとともに研究において頻繁に使用されている。メトホルミンは、細胞質のアデノシン一リン酸(AMP)濃度を上昇させる(総AMPまたは総AMP/アデノシン三リン酸の変化とは異なる)。メトホルミンは、サイクリックAMP産生を阻害し、グルカゴンの作用を阻害し、それによって空腹時グルコースレベルを低下させる。メトホルミンはまた、糖尿病マウスの糞便微生物群集プロフィールの大きな変化を誘導し、これはおそらくグルカゴン様ペプチド-1分泌への影響を通してその作用様式に寄与している可能性がある。
肝グルコース産生抑制に加えて、メトホルミンはインスリン感受性を高め、末梢でのグルコース取り込みを(GLUT4エンハンサー因子のリン酸化を誘導することによって)促進し、インスリンによる脂肪酸酸化の抑制を減少させ、消化管からのグルコースの吸収を減少させる。末梢でのグルコース利用の増加は、インスリン受容体へのインスリン結合の改善によるものと考えられる。メトホルミン治療後のインスリン結合の増加は、2型糖尿病患者においても証明されている。
メトホルミンを投与すると骨格筋のAMPK活性が上昇することから、AMPKはおそらく末梢のインスリン感受性増加にも関与していると考えられる。AMPKは、GLUT4の細胞膜への展開を引き起こし、インスリン非依存性のグルコース取り込みをもたらすことが知られている。メトホルミンの代謝作用の一部は、AMPK非依存的な機序で起こるようであるが、AMPKの全体的な作用は緩やかであり、その活性が肝臓での糖新生を直接低下させることはなさそうである。
メトホルミンは、インスリン感受性に対する有益な作用により、PCOSのようなインスリン抵抗性を有する女性において間接的な抗アンドロゲン作用を有する。メトホルミンは、そのような女性のテストステロンレベルを50%も低下させる可能性がある。しかし、あるコクラン・レビューでは、メトホルミンはPCOSの女性においてアンドロゲンレベルを減少させるのにわずかに有効であるだけであった。
メトホルミンはまた、腸内細菌によるアグマチン産生を増加させる効果など、腸内細菌叢にも大きな影響を及ぼすが、他の機序と比較してこの機序の相対的重要性は不明である。
GLUT4とAMPKに作用することから、メトホルミンは運動模倣薬と呼ばれている。
薬物動態
メトホルミンの経口生物学的利用能は、空腹条件下で50~60%であり、ゆっくりと吸収される。血漿中濃度のピーク(Cmax)は、メトホルミンの即時放出型製剤では服用後1~3時間以内に、徐放型製剤では4~8時間以内に到達する。メトホルミンの血漿タンパク質結合は、非常に高い見かけの分布容積(単回投与で300~1000 L)に反映されるように、無視できる。定常状態は通常1~2日で到達する。
メトホルミンの酸解離定数(pKa)は2.8と11.5であるため、生理的pH値では非常に大部分が親水性の陽イオン種として存在する。メトホルミンのpKa値は、血中非イオン化率0.01%未満の他のほとんどの塩基性医薬品よりも強い塩基となる。さらに、非イオン化種の脂溶性は、-1.43という低いlogP値(オクタノールと水の間の非イオン化型の分配係数のlog(10))が示すようにわずかである。これらの化学的パラメータは、親油性が低いことを示しており、その結果、メトホルミンが細胞膜を通過して急速に受動拡散する可能性は低い。脂溶性が低いため、トランスポーターが必要である。メトホルミンが細胞内に入るためには、SLC22A1が必要である。メトホルミンのlogPはフェンホルミンのlogP(-0.84)よりも小さいが、これはメトホルミンの2つのメチル置換基がフェンホルミンの大きなフェニルエチル側鎖よりも低い親油性を与えるためである。現在,メトホルミンよりも優れた経口吸収性を有するプロドラッグを製造する目的で,メトホルミンのより親油性の誘導体が研究されている。
メトホルミンは代謝されない。メトホルミンは尿細管分泌によって体外に排出され、尿中に未変化のまま排泄される;単回経口投与後24時間以内の血漿中では検出されない。血漿中の平均脱離半減期は6.2時間である。メトホルミンは赤血球に分布し(蓄積すると思われる)、消失半減期は17.6時間とはるかに長い(非糖尿病患者を対象とした単回投与試験では18.5~31.5時間であったと報告されている)。
ヒトにおけるメトホルミンの肝濃度は、経口投与における門脈吸収と肝臓による初回通過取り込みにより、血漿中濃度の2~3倍高い可能性があることを示す証拠もある。
化学
メトホルミン塩酸塩(1,1-ジメチルビグアニド塩酸塩)は、水に自由に溶け、エタノールにわずかに溶けるが、アセトン、エーテル、クロロホルムにはほとんど溶けない。メトホルミンのpKaは12.4である。1922年に記載されたメトホルミンの通常の合成は、ジメチルアミン塩酸塩と2-シアノグアニジンを加熱しながらワンポットで反応させる。

1975年のアロン特許および医薬品製造百科事典に記載された手順によると、等モル量のジメチルアミンと2-シアノグアニジンを冷却しながらトルエンに溶解して濃縮溶液とし、等モル量の塩化水素をゆっくりと加える。混合物はそれ自体で沸騰し始め、冷却後、メトホルミン塩酸塩が96%の収率で沈殿する。
誘導体
IM156としても知られる新規誘導体HL156Aは、医療用新薬の可能性がある。
歴史

抗糖尿病薬のビグアナイドクラスは、休薬中のフェンフォルミンとブフォルミンも含み、数世紀にわたって民間療法で使用されてきたフレンチライラックまたはヤギのルー(Galega officinalis)に由来する。G.officinalis自体にはこれらの医薬品は含まれていないが、イソアミレングアニジン、フェンホルミン、ブホルミン、メトホルミンは2つのグアニジン分子からなる化学合成化合物であり、植物由来の親化合物よりも親油性である。
メトホルミンは、1922年にエミール・ヴェルナーとジェームズ・ベルによって、N,N-ジメチルグアニジンの合成生成物として初めて科学文献に記載された。1929年、SlottaとTschescheはウサギでその糖低下作用を発見し、彼らが研究した中で最も強力なビグアナイド類似体であることを見出した。この結果は無視され、シンタリンのような他のグアニジン類縁体がその座を奪い、すぐにインスリンの影に隠れてしまった。
メトホルミンへの関心は1940年代の終わりに再燃した。1950年、メトホルミンは他の類似化合物とは異なり、動物において血圧と心拍数を低下させないことが判明した。その年、フィリピンの医師エウセビオ・Y・ガルシアがインフルエンザの治療にメトホルミン(彼はこれをフルアミンと命名した)を使用した。彼はこの医薬品が「血糖値を生理的な最小限度まで低下させ」、毒性はないと指摘した。ガルシアはメトホルミンが静菌作用、抗ウイルス作用、抗マラリア作用、解熱作用、鎮痛作用をもつと考えた。1954年にポーランドの薬理学者Janusz Supniewskiは一連の論文で、血糖値の低下などこれらの作用のほとんどを確認することができなかった。その代わりに、彼はヒトにおいて抗ウイルス作用を観察した。
フランスの糖尿病学者Jean Sterneは、G. officinalisから単離されたアルカロイドであるガレギンの抗高血糖特性を研究した。その後、パリのアロン研究所に勤務していた彼は、ガルシアの報告に促されて、メトホルミンといくつかのビグアナイド類縁体の血糖降下活性を再調査した。シュテルンは、メトホルミンを糖尿病治療薬として初めてヒトに投与した。彼は、この医薬品に「グルコファージ」(グルコースを食べる)という名前をつけ、1957年にその結果を発表した。
メトホルミンは1958年にBritish National Formularyで入手できるようになった。イギリスではロナという小さなアロンの子会社が販売していた。
メトホルミンに対する幅広い関心が再燃したのは、1970年代に他のビグアナイド薬が撤退してからであった。メトホルミンは1972年にカナダで承認されたが、2型糖尿病に対する米国食品医薬品局(FDA)の承認は1994年まで得られなかった。グルコファージはBristol-Myers Squibbによってライセンス生産され、1995年3月3日から米国で販売されたメトホルミンの最初のブランド製剤である。ジェネリック製剤は、いくつもの国で入手可能であり、メトホルミンは、世界で最も広く処方されている抗糖尿病医薬品になったと考えられている。
社会と文化
環境
メトホルミンとその主要な変換産物であるグアニル尿素は廃水処理場の排水中に存在し、地表水でも定期的に検出される。グアニル尿素の濃度は200 μg/Lを超え、ドイツの河川Erpeで測定されており、これは水生環境における医薬品変換産物としては最高レベルの報告である。
製剤

"メトホルミン"という名称は、この医薬品のBAN、USAN、INNであり、いくつかの商品名で販売されている。一般的な商品名には、米国ではグルコファージ、リオメット、フォルタメット、グルメッツァなどがある。世界の他の地域では、Obimet、Gluformin、Dianben、Diabex、Diaformin、Metsol、Siofor、Metfogamma、Gliforもある。市販されているメトホルミンにはいくつかの製剤があり、液剤以外はすべて同等のジェネリック医薬品がある。メトホルミンIR(即時放出)には500mg、850mg、1000mgの錠剤があり、メトホルミンXR(徐放)には500mg、750mg、1000mgの錠剤がある(米国ではFortamet、Glumetza、Glucophage XRとしても販売されている)。また、液体メトホルミン(米国ではリオメットとして販売)もあり、5 mLの溶液に500mgの錠剤と同量の薬物が含まれている。
他の医薬品との併用
2型糖尿病に用いる場合、メトホルミンはしばしば他の医薬品と併用処方される。
いくつかの薬剤は合剤として販売されており、錠剤の負担を軽減し、コストを削減し、投与を簡略化できる可能性がある。
チアゾリジン系薬剤(グリタゾン系薬剤)
ロシグリタゾン
メトホルミンとロシグリタゾンの配合剤が2002年に発売され、GlaxoSmithKlineからアバンダメットとして、またはジェネリック医薬品として販売されている。製剤は、メトホルミン/ロシグリタゾンとして500/1、500/2、500/4、1000/2、1000 mg/4 mgである。
2009年までには、最も人気のあるメトホルミン配合剤となった。
2005年、アバンダメットを製造していた工場が適正製造規範に違反していることが検査で判明したため、アバンダメットの在庫は市場から撤去された。医薬品ペアは別々に処方され続け、アバンダメットは同年末までに再び入手できるようになった。Tevaのメトホルミン/ロシグリタゾンのジェネリック製剤がFDAから暫定承認を受け、2012年初めに市場に出た。
しかし、2007年にこの医薬品の使用と心臓発作のリスク上昇を関連付けたメタアナリシスが発表された後、ロシグリタゾンを含む医薬品の安全性に対する懸念が高まった。2010年9月、欧州医薬品庁は、ロシグリタゾンのベネフィットはもはやリスクを上回らないとして、この医薬品を欧州市場から一時停止するよう勧告した。
ロシグリタゾンおよびメトホルミン・ロシグリタゾンは、処方箋なしで販売することができず、さらに、メーカーはその使用に関連するリスクを患者に通知する必要があり、薬物は指定された薬局を通じて通信販売で購入しなければならなかった。
2013年11月、FDAは2009年に実施されたRECORD臨床試験(6年間の非盲検無作為化対照試験)の結果を検討した結果、ロシグリタゾンに対する以前の制限を解除した。
ピオグリタゾン
メトホルミンとピオグリタゾンの配合剤(アクトプラスメット、ピオメット、ポリトール、グルブラバ)は、米国および欧州連合で入手可能である。
DPP-4阻害薬
ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4阻害薬は、ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4を阻害するため、グルカゴンおよび血糖値を低下させる。
DPP-4阻害薬とメトホルミンの併用には、シタグリプチン/メトホルミン配合剤(ジャヌメット)、サキサグリプチン/メトホルミン配合剤(コンビグライゼXR、コンビグライゼ)、アログリプチン/メトホルミン配合剤(カザーノ、ビップドメット)などがある。
リナグリプチンとメトホルミン塩酸塩の組み合わせは、Jentaduetoという商品名で販売されている。2021年8月現在、米国ではリナグリプチン/メトホルミンはジェネリック医薬品として販売されている。
SGLT-2阻害剤
メトホルミンとSGLT-2阻害薬のダパグリフロジン、エンパグリフロジン、カナグリフロジンとの併用がある。
スルホニル尿素薬
スルホニル尿素は、膵臓のβ細胞からのインスリン放出を増加させることによって作用する。
2019年のシステマティックレビューでは、メトホルミンとスルホニル尿素の併用療法が、メトホルミンと他の血糖降下薬の併用療法と比較して、死亡率、重篤な有害事象、大血管合併症、細小血管合併症において有益か有害かのエビデンスは限られていることが示唆された。メトホルミンとスルホニル尿素の併用療法は、低血糖のリスクが高いように思われた。
メトホルミンは、スルホニル尿素のグリピジド(メタグリップ)とグリベンクラミド(米国:グリブリド)(グルコバンス)と組み合わせて使用できる。メトホルミン/グリピジドとメトホルミン/グリベンクラミドのジェネリック製剤が入手可能である(後者の方が人気がある)。
メグリチニド
メグリチニドは、膵臓のβ細胞に結合することからスルホニル尿素薬と類似しているが、目的とする受容体への結合部位と受容体に対する薬物の親和性が異なる。その結果、スルホニル尿素薬に比べて作用時間が短く、インスリンの分泌を開始するにはより高い血糖値を必要とする。ナテグリニドおよびレパングリニドとして知られる両メグリチニドは、メトホルミンと組み合わせた製剤で販売されている。レパグリニドとメトホルミンの組み合わせは、Prandimetとして、またはそのジェネリック医薬品として販売されている。
トリプル併用療法
メトホルミンとダパグリフロゼンとサキサグリプチンの併用は、米国ではQternmet XRとして販売されている。
メトホルミンとピオグリタゾンおよびグリベンクラミドの配合剤は、インドではAccuglim-MP、Adglim MP、Alnamet-GPとして、フィリピンではTri-Senzaとして販売されている。
トルコでは、メトホルミンとピオグリタゾンおよびリポ酸の配合剤がPionalとして販売されている。
不純物
2019年12月、米国FDAは、米国外で製造された一部のメトホルミン医薬品に、ヒト発がん性物質の可能性が高いと分類されるN-ニトロソジメチルアミン(NDMA)と呼ばれるニトロソアミン不純物が低レベルで含まれている可能性があることが分かったと発表した。カナダ保健省は、メトホルミン中のNDMA濃度を評価していると発表した。
2020年2月、FDAは検査したメトホルミンのサンプルの一部から、1日の許容摂取量を超えないNDMA濃度を検出した。
2020年2月、カナダ保健省はアポテックス社の即時放出型メトホルミンのリコールを発表し、3月にはランバクシー社のメトホルミン、さらに3月にはジャンプ社のメトホルミンのリコールを発表した。
2020年5月、FDAは5社にメトホルミン製剤の自主回収を要請した。その5社とは、アムニール・ファーマシューティカルズ(Amneal Pharmaceuticals)、アクタヴィス・ファーマ(Actavis Pharma)、アポテックス・コーポレーション(Apotex Corp)、ルピン・ファーマ(Lupin Pharma)、マークサン・ファーマ・リミテッド(Marksans Pharma Limited)の5社であることが、市民請願書を通じてメトホルミンにこの汚染物質が含まれていることを最初にFDAに警告した薬局であるValisureに送られた書簡で明らかになった。
2020年6月、FDAは検査したメトホルミン製品のNDMA量を示す検査結果を公表した。その結果、ERメトホルミンの特定のロットからNDMAが検出され、許容摂取限界値である1日96ナノグラムを超えるNDMAが検出されたロットの回収を各社に勧告している。FDAはまた、メトホルミンの検査結果を共有するために、国際的な規制当局と協力している。
2020年7月、ルピン・ファーマシューティカルズ社は、検査したサンプルから許容できないほど高濃度のNDMAが検出されたため、すべてのロット(バッチ)のメトホルミンを回収した。
2020年8月、Bayshore Pharmaceuticals社は2つのロットの錠剤を回収した。
研究
メトホルミンは、以下のような他の複数の疾患に対する効果について研究されている:
- 非アルコール性脂肪性肝疾患
- 思春期早発症
- ガン
- 糖尿病患者における心臓血管疾患
- 老化
メトホルミンは脆弱X症候群の人の体重を減らすかもしれないが、神経症状や精神症状を改善するかどうかは不明である。メトホルミンは生体内(線虫およびコオロギ)で老化に対する影響について研究されている。2017年のレビューによると、メトホルミンを服用している糖尿病患者は全死亡率が低かった。また、他の治療を受けている人に比べて、がんや心血管疾患も減少していた。
また、メトホルミンは糖尿病を予防するが、がんや心血管疾患のリスクは減少させないため、糖尿病でない人の寿命は延びないことを示唆する研究もある。さらに、健康な人がメトホルミンを長期間慢性的に使用すると、ビタミンB12欠乏症になる可能性を示唆する研究もある。
さらに読む
- Markowicz-Piasecka M, Huttunen KM, Mateusiak L, Mikiciuk-Olasik E, Sikora J (2017). "Is Metformin a Perfect Drug? Updates in Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 23 (17): 2532–2550. doi:10.2174/1381612822666161201152941. PMID 27908266.
- McCreight LJ, Bailey CJ, Pearson ER (March 2016). "Metformin and the gastrointestinal tract". Diabetologia. 59 (3): 426–35. doi:10.1007/s00125-015-3844-9. PMC 4742508. PMID 26780750.
- Moin T, Schmittdiel JA, Flory JH, Yeh J, Karter AJ, Kruge LE, Schillinger D, Mangione CM, Herman WH, Walker EA (October 2018). "Review of Metformin Use for Type 2 Diabetes Prevention". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 55 (4): 565–574. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.04.038. PMC 6613947. PMID 30126667.
- Rena G, Hardie DG, Pearson ER (September 2017). "The mechanisms of action of metformin". Diabetologia. 60 (9): 1577–1585. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4342-z. PMC 5552828. PMID 28776086.
- Sanchez-Rangel E, Inzucchi SE (September 2017). "Metformin: clinical use in type 2 diabetes". Diabetologia. 60 (9): 1586–1593. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4336-x. PMID 28770321.
- Zhou J, Massey S, Story D, Li L (September 2018). "Metformin: An Old Drug with New Applications". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 19 (10): 2863. doi:10.3390/ijms19102863. PMC 6213209. PMID 30241400.
- Zhou T, Xu X, Du M, Zhao T, Wang J (October 2018). "A preclinical overview of metformin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes". Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 106: 1227–1235. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.085. PMID 30119191. S2CID 52031602.
外部リンク
- "Nitrosamine impurities in medications: Guidance". Health Canada. 4 April 2022.