Low-density lipoprotein/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "NMR分光法を含む他の''リポ蛋白サブクラス分析''測定法の継続的な研究、コストの低下、入手しやすさの向上、および広く受け入れられるようになったことで、ヒトの臨床的に明らかな心血管系イベントと定量的に測定された粒子濃度との間には、より強い相関関係があることが研究により示され続けている。" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "===酸化LDL=== 酸化LDLとは、構造成分が酸化的に変化したLDL粒子の総称である。その結果、フリーラジカル攻撃により、LDLの脂質部分とタンパク質部分の両方が血管壁中で酸化される。血管壁で起こる酸化反応の他に、LDL中の酸化脂質は酸化した食事性脂質にも由来する。 酸化LDLはアテローム性動脈硬化症の発症に関与する..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
[[NMR spectroscopy/ja|NMR分光法]]を含む他の''リポ蛋白サブクラス分析''測定法の継続的な研究、コストの低下、入手しやすさの向上、および広く受け入れられるようになったことで、ヒトの臨床的に明らかな心血管系イベントと定量的に測定された粒子濃度との間には、より強い相関関係があることが研究により示され続けている。 | [[NMR spectroscopy/ja|NMR分光法]]を含む他の''リポ蛋白サブクラス分析''測定法の継続的な研究、コストの低下、入手しやすさの向上、および広く受け入れられるようになったことで、ヒトの臨床的に明らかな心血管系イベントと定量的に測定された粒子濃度との間には、より強い相関関係があることが研究により示され続けている。 | ||
===酸化LDL=== | |||
酸化LDLとは、構造成分が酸化的に変化したLDL粒子の総称である。その結果、[[free radical/ja|フリーラジカル]]攻撃により、LDLの脂質部分とタンパク質部分の両方が血管壁中で酸化される。血管壁で起こる酸化反応の他に、LDL中の酸化脂質は酸化した食事性脂質にも由来する。 酸化LDLは[[atherosclerosis/ja|アテローム性動脈硬化症]]の発症に関与することが知られており、[[cardiovascular diseases/ja|心血管疾患]]の潜在的な危険因子として広く研究されている。酸化LDLのアテローム性は、LDLレセプターによる酸化修飾LDL構造の認識不足によって説明されており、LDL粒子の正常な代謝を妨げ、最終的にアテローム性動脈硬化斑の発生につながる。LDLに含まれる脂質のうち、様々な脂質酸化産物は究極の動脈硬化種として知られている。これらの有害分子のトランスポーターとして働くことも、LDLが動脈硬化のリスクを増大させるもう一つのメカニズムである。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 8 March 2024

低比重リポ蛋白(LDL)は、リポ蛋白の5つの主要なグループの1つであり、細胞外水中で体内のすべての脂肪分子を輸送する。これらのグループは、最も密度の低いものから順に、カイロミクロン(全体密度の命名規則では別名ULDL)、超低比重リポ蛋白(VLDL)、中比重リポ蛋白(IDL)、低比重リポ蛋白(LDL)、および高比重リポ蛋白(HDL)である。LDLは脂肪分子を細胞に送り込む。LDLは動脈の壁内で酸化される過程であるアテローム性動脈硬化症に関与している。
概要
リポタンパク質は、細胞外液中で脂質(脂肪)を体中に移動させ、脂肪を体細胞が受容体を介したエンドサイトーシスで利用できるようにする。リポ蛋白質は複数の蛋白質から成る複合粒子であり、通常1粒子あたり80~100個の蛋白質から成る(LDLおよびそれ以上の粒子では単一のアポリポ蛋白質Bによって組織化されている)。1個のLDL粒子の直径は約220~275オングストロームで、通常1粒子あたり3,000~6,000個の脂肪分子を運搬し、中に含まれる脂肪分子の数と組み合わせによって大きさが変わる。運搬される脂質には、コレステロール、リン脂質、トリグリセリドを主成分とするすべての脂肪分子が含まれるが、それぞれの量はかなり異なる。
血中脂質値に関する一般的な臨床的解釈は、LDLが高いと心血管疾患のリスクが高まるというものである。
生化学
構造
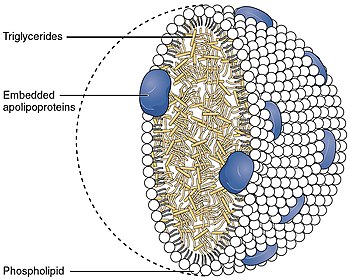
それぞれのネイティブLDL粒子は乳化を可能にし、すなわち運ばれる脂肪酸を取り囲み、これらの脂肪が細胞外の水中で体内を移動することを可能にする。各粒子には1個のアポリポ蛋白質が含まれている。B-100分子(Apo B-100、4536個のアミノ酸残基と514kDaの質量を持つ蛋白質)と80から100個の補助蛋白質が含まれている。各LDLは、リノレイン酸として知られる多価不飽和脂肪酸と、数百から数千(平均値として一般的に引用される約1500)のエステル化および非エステル化コレステロール分子から成る高度に疎水性のコアを持つ。このコアはまた、様々な数のトリグリセリドや他の脂肪を運び、リン脂質と未エステル化コレステロールの殻、およびApo B-100の単一コピーに囲まれている。LDL粒子の直径は約22~27.5nmで、質量は約300万ダルトンである。LDL粒子は脂肪酸分子の数が変化するため、LDL粒子の質量と大きさには分布がある。LDLの構造を決定することは、その不均一な構造のために困難な課題であった。しかし2011年、極低温電子顕微鏡を用いて、約16オングストロームの分解能で、ヒトの体温におけるLDLの構造が明らかにされた。
生理学
LDL粒子は、リポタンパク質リパーゼ酵素(LPL)によってVLDLからトリグリセリドが除去されると形成され、より小さく高密度(すなわち、同じタンパク質輸送シェルでより少ない脂肪分子)になり、より高い割合のコレステロールエステルを含む。
細胞内へのコレステロール輸送
細胞が(現在の内部HMGCoA産生経路を超えて)さらなるコレステロールを必要とする場合、細胞は必要なLDL受容体を合成するとともに、LDL受容体を分解のためにマークするプロテイン転換酵素であるPCSK9を合成する。LDL受容体は細胞膜に挿入され、クラスリンでコートされたピットと会合するまで自由に拡散する。LDL受容体が血流中のLDL粒子と結合すると、クラスリンでコートされたピットが細胞内にエンドサイトーシスされる。
LDLと結合したLDL受容体を含む小胞はエンドソームに送られる。エンドソームに見られるような低いpHの存在下では、LDL受容体はコンフォメーション変化を起こし、LDLを放出する。LDLはその後リソソームに送られ、そこでLDL中のコレステロールエステルが加水分解される。LDL受容体は通常細胞膜に戻され、そこでこのサイクルを繰り返す。しかし、LDL受容体がPCSK9と結合すると、LDL受容体の輸送はリソソームへと方向転換され、そこで分解される。
===自然免疫系における役割====。 LDLは、侵襲性黄色ブドウ球菌感染に必要な遺伝子をアップレギュレートするクオラムセンシングシステムを妨害する。拮抗のメカニズムとしては、アポリポタンパク質Bが黄色ブドウ球菌の自己誘導物質フェロモンに結合し、その受容体を介したシグナル伝達を阻害することが挙げられる。アポリポタンパク質Bを欠損したマウスは、侵襲性細菌感染症にかかりやすくなる。
LDLのサイズパターン
LDLはその大きさによってグループ分けすることができる。大きな低密度LDL粒子はパターンA、小さな高密度LDL粒子はパターンBと表現される。パターンBは冠動脈性心疾患のリスクが高いという報告がある。これは、粒子が小さいほど動脈壁の内皮を透過しやすいためと考えられている。パターンIは中間を意味し、ほとんどのLDL粒子が内皮の正常な隙間(26 nm)に非常に近いサイズであることを示している。ある研究によると、19.0-20.5 nmの大きさのLDLはパターンBとされ、20.6-22 nmの大きさのLDLはパターンAとされている。
パターンBと冠動脈性心疾患との相関は、標準的な脂質プロファイル検査で測定されるLDL数値との対応よりも強いことを示唆する証拠もある。これらのLDLサブタイプパターンを測定する検査は高価であり、広く普及していないため、一般的な脂質プロファイル検査がより多く用いられている。
また、トリグリセリド値が高くなると、より小さく密度の高いLDL粒子の値が高くなり、逆にトリグリセリド値が低くなると、より大きく密度の低い(「浮遊性」)LDLの値が高くなるという対応関係も指摘されている。
NMR分光法を含む他のリポ蛋白サブクラス分析測定法の継続的な研究、コストの低下、入手しやすさの向上、および広く受け入れられるようになったことで、ヒトの臨床的に明らかな心血管系イベントと定量的に測定された粒子濃度との間には、より強い相関関係があることが研究により示され続けている。
酸化LDL
酸化LDLとは、構造成分が酸化的に変化したLDL粒子の総称である。その結果、フリーラジカル攻撃により、LDLの脂質部分とタンパク質部分の両方が血管壁中で酸化される。血管壁で起こる酸化反応の他に、LDL中の酸化脂質は酸化した食事性脂質にも由来する。 酸化LDLはアテローム性動脈硬化症の発症に関与することが知られており、心血管疾患の潜在的な危険因子として広く研究されている。酸化LDLのアテローム性は、LDLレセプターによる酸化修飾LDL構造の認識不足によって説明されており、LDL粒子の正常な代謝を妨げ、最終的にアテローム性動脈硬化斑の発生につながる。LDLに含まれる脂質のうち、様々な脂質酸化産物は究極の動脈硬化種として知られている。これらの有害分子のトランスポーターとして働くことも、LDLが動脈硬化のリスクを増大させるもう一つのメカニズムである。
Testing
Blood tests commonly report LDL-C: the amount of cholesterol which is estimated to be contained with LDL particles, on average, using a formula, the Friedewald equation. In clinical context, mathematically calculated estimates of LDL-C are commonly used as an estimate of how much low density lipoproteins are driving progression of atherosclerosis. The problem with this approach is that LDL-C values are commonly discordant with both direct measurements of LDL particles and actual rates of atherosclerosis progression.
Direct LDL measurements are also available and better reveal individual issues but are less often promoted or done due to slightly higher costs and being available from only a couple of laboratories in the United States. In 2008, the ADA and ACC recognized direct LDL particle measurement by NMR as superior for assessing individual risk of cardiovascular events.
Estimation of LDL particles via cholesterol content
Chemical measures of lipid concentration have long been the most-used clinical measurement, not because they have the best correlation with individual outcome, but because these lab methods are less expensive and more widely available.
The lipid profile does not measure LDL particles. It only estimates them using the Friedewald equation by subtracting the amount of cholesterol associated with other particles, such as HDL and VLDL, assuming a prolonged fasting state, etc.:
- where H is HDL cholesterol, L is LDL cholesterol, C is total cholesterol, T are triglycerides, and k is 0.20 if the quantities are measured in mg/dL and 0.45 if in mmol/L.
There are limitations to this method, most notably that samples must be obtained after a 12 to 14 h fast and that LDL-C cannot be calculated if plasma triglyceride is >4.52 mmol/L (400 mg/dL). Even at triglyceride levels 2.5 to 4.5 mmol/L, this formula is considered inaccurate. If both total cholesterol and triglyceride levels are elevated then a modified formula, with quantities in mg/dL, may be used
This formula provides an approximation with fair accuracy for most people, assuming the blood was drawn after fasting for about 14 hours or longer, but does not reveal the actual LDL particle concentration because the percentage of fat molecules within the LDL particles which are cholesterol varies, as much as 8:1 variation. There are several formulas published addressing the inaccuracy in LDL-C estimation. The inaccuracy is based on the assumption that VLDL-C (Very low density lipoprotein cholesterol) is always one-fifth of the triglyceride concentration. A new formulae published recently addresses this issue by using an adjustable factor or by using a regression equation. There are few studies which have compared the LDL-C values derived form this recently published formula and values obtained by direct enzymatic method. Direct enzymatic method are found to be accurate and it has to be the test of choice in clinical situations. In the resource poor settings, the option of using the formula has to be considered.
However, the concentration of LDL particles, and to a lesser extent their size, has a stronger and consistent correlation with individual clinical outcome than the amount of cholesterol within LDL particles, even if the LDL-C estimation is approximately correct. There is increasing evidence and recognition of the value of more targeted and accurate measurements of LDL particles. Specifically, LDL particle number (concentration), and to a lesser extent size, have shown slightly stronger correlations with atherosclerotic progression and cardiovascular events than obtained using chemical measures of the amount of cholesterol carried by the LDL particles. It is possible that the LDL cholesterol concentration can be low, yet LDL particle number high and cardiovascular events rates are high. Correspondingly, it is possible that LDL cholesterol concentration can be relatively high, yet LDL particle number low and cardiovascular events are also low.
Normal ranges
In the US, the American Heart Association, NIH, and NCEP provide a set of guidelines for fasting LDL-Cholesterol levels, estimated or measured, and risk for heart disease. As of about 2005, these guidelines were:
| Level mg/dL | Level mmol/L | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| 25 to <50 | <1.3 | Optimal LDL cholesterol, levels in healthy young children before onset of atherosclerotic plaque in heart artery walls |
| <70 | <1.8 | Optimal LDL cholesterol, corresponding to lower rates of progression, promoted as a target option for those known to clearly have advanced symptomatic cardiovascular disease |
| <100 | <2.6 | Optimal LDL cholesterol, corresponding to lower, but not zero, rates for symptomatic cardiovascular disease events |
| 100 to 129 | 2.6 to 3.3 | Near optimal LDL level, corresponding to higher rates for developing symptomatic cardiovascular disease events |
| 130 to 159 | 3.3 to 4.1 | Borderline high LDL level, corresponding to even higher rates for developing symptomatic cardiovascular disease events |
| 160 to 199 | 4.1 to 4.9 | High LDL level, corresponding to much higher rates for developing symptomatic cardiovascular disease events |
| >200 | >4.9 | Very high LDL level, corresponding to highest increased rates of symptomatic cardiovascular disease events |
Over time, with more clinical research, these recommended levels keep being reduced because LDL reduction, including to abnormally low levels, was the most effective strategy for reducing cardiovascular death rates in one large double blind, randomized clinical trial of men with hypercholesterolemia; far more effective than coronary angioplasty/stenting or bypass surgery.
For instance, for people with known atherosclerosis diseases, the 2004 updated American Heart Association, NIH and NCEP recommendations are for LDL levels to be lowered to less than 70 mg/dL, unspecified how much lower. This low level of less than 70 mg/dL (higher than Tim Russert's value shortly prior to his heart attack) was recommended for primary prevention of 'very-high risk patients' and in secondary prevention as a 'reasonable further reduction'. Lack of evidence for such a recommendation is discussed in an article in the Annals of Internal Medicine. Statin drugs involved in such clinical trials have numerous physiological effects beyond simply the reduction of LDL levels.
It has been estimated from the results of multiple human pharmacologic LDL lowering trials that LDL should be lowered to below 30 to reduce cardiovascular event rates to near zero. For reference, from longitudinal population studies following progression of atherosclerosis-related behaviors from early childhood into adulthood, the usual LDL in childhood, before the development of fatty streaks, is about 35 mg/dL. However, all the above values refer to chemical measures of lipid/cholesterol concentration within LDL, not measured low-density lipoprotein concentrations, the accurate approach.
A study was conducted measuring the effects of guideline changes on LDL cholesterol reporting and control for diabetes visits in the US from 1995 to 2004. It was found that although LDL cholesterol reporting and control for diabetes and coronary heart disease visits improved continuously between 1995 and 2004, neither the 1998 ADA guidelines nor the 2001 ATP III guidelines increased LDL cholesterol control for diabetes relative to coronary heart disease.
Direct measurement of LDL particle concentrations
There are several competing methods for measurement of lipoprotein particle concentrations and size. The evidence is that the NMR methodology (developed, automated & greatly reduced in costs while improving accuracy as pioneered by Jim Otvos and associates) results in a 22-25% reduction in cardiovascular events within one year, contrary to the longstanding claims by many in the medical industry that the superiority over existing methods was weak, even by statements of some proponents.
Since the later 1990s, because of the development of NMR measurements, it has been possible to clinically measure lipoprotein particles at lower cost [under $80 US (including shipping) & is decreasing; versus the previous costs of >$400 to >$5,000] and higher accuracy. There are two other assays for LDL particles, however, like LDL-C, most only estimate LDL particle concentrations.
Direct LDL particle measurement by NMR was mentioned by the ADA and ACC, in a 28 March 2008 joint consensus statement, as having advantages for predicting individual risk of atherosclerosis disease events, but the statement noted that the test is less widely available, is more expensive [about $13.00 US (2015 without insurance coverage) from some labs which use the Vantera Analyzer]. Debate continues that it is "...unclear whether LDL particle size measurements add value to measurement of LDL-particle concentration", though outcomes have always tracked LDL particle, not LDL-C, concentrations.
Using NMR, the total LDL particle concentrations, in nmol/L plasma, are typically subdivided by percentiles referenced to the 5,382 men and women, not on any lipid medications, who are participating in the MESA trial.
Optimal ranges
The LDL particle concentrations are typically categorized by percentiles, <20%, 20–50%, 50th–80th%, 80th–95% and >95% groups of the people participating and being tracked in the MESA trial, a medical research study sponsored by the United States National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
| MESA Percentile | LDL particles nmol/L | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| 0–20% | <1,000 | Those with lowest rate of cardiovascular disease events & low (optimal) LDL particle concentration |
| 20–50% | 1,000–1,299 | Those with moderate rate of cardiovascular disease events & moderate LDL particle concentration |
| 50–80% | 1,300–1,599 | Those with Borderline-High rate of cardiovascular disease events & higher LDL particle concentration |
| 89–95% | 1,600–2,000 | Those with High rate of cardiovascular disease events and even higher LDL particle concentration |
| >95% | >2,000 | Those with very high rate of cardiovascular disease events and highest LDL particle concentration |
The lowest incidence of atherosclerotic events over time occurs within the <20% group, with increased rates for the higher groups. Multiple other measures, including particle sizes, small LDL particle concentrations, large total and HDL particle concentrations, along with estimations of insulin resistance pattern and standard cholesterol lipid measurements (for comparison of the plasma data with the estimation methods discussed above) are also routinely provided.
Lowering LDL-cholesterol
| Markers indicating a need for LDL-C Reduction
(Per 2004 United States Government Minimum Guidelines) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| If the patient's cardiac risk is... | then the patient should consider LDL-C reduction if the count in mg/dL is over... | and LDL-C reduction is indicated if the count in mg/dL is over... | ||
| High, meaning a 20% or greater risk of heart attack within 10 years, or an extreme risk factor | 70 | 100 | ||
| moderately high, meaning a 10-20% risk of heart attack within 10 years and more than 2 heart attack risk factors | 100 | 130 | ||
| moderate, meaning a 10% risk of heart attack within 10 years and more than 2 heart attack risk factors | 130 | 160 | ||
| low, meaning less than 10% risk of heart attack within 10 years and 1 or 0 heart attack risk factors | 160 | 190 | ||
The mevalonate pathway serves as the basis for the biosynthesis of many molecules, including cholesterol. The enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG CoA reductase) is an essential component and performs the first of 37 steps within the cholesterol production pathway, and is present in every animal cell.
LDL-C is not a measurement of actual LDL particles. LDL-C is only an estimate (not measured from the individual's blood sample) of how much cholesterol is being transported by all LDL particles, which is either a smaller concentration of large particles or a high concentration of small particles. LDL particles carry many fat molecules (typically 3,000 to 6,000 fat molecules per LDL particle); this includes cholesterol, triglycerides, phospholipids and others. Thus even if the hundreds to thousands of cholesterol molecules within an average LDL particle were measured, this does not reflect the other fat molecules or even the number of LDL particles.
Pharmaceutical
- PCSK9 inhibitors, in clinical trials, by several companies, are more effective for LDL reduction than the statins, including statins alone at high dose (though not necessarily the combination of statins plus ezetimibe).
- Statins reduce high levels of LDL particles by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase in cells, the rate-limiting step of cholesterol synthesis. To compensate for the decreased cholesterol availability, synthesis of LDL receptors (including hepatic) is increased, resulting in an increased clearance of LDL particles from the extracellular water, including of the blood.
- Ezetimibe reduces intestinal absorption of cholesterol, thus can reduce LDL particle concentrations when combined with statins.
- Niacin (B3), lowers LDL by selectively inhibiting hepatic diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2, reducing triglyceride synthesis and VLDL secretion through a receptor HM74 and HM74A or GPR109A.
- Several CETP inhibitors have been researched to improve HDL concentrations, but so far, despite dramatically increasing HDL-C, have not had a consistent track record in reducing atherosclerosis disease events. Some have increased mortality rates compared with placebo.
- Clofibrate is effective at lowering cholesterol levels, but has been associated with significantly increased cancer and stroke mortality, despite lowered cholesterol levels. Other, more recently developed and tested fibrates, e.g. fenofibric acid have had a better track record and are primarily promoted for lowering VLDL particles (triglycerides), not LDL particles, yet can help some in combination with other strategies.
- Some tocotrienols, especially delta- and gamma-tocotrienols, are being promoted as statin alternative non-prescription agents to treat high cholesterol, having been shown in vitro to have an effect. In particular, gamma-tocotrienol appears to be another HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, and can reduce cholesterol production. As with statins, this decrease in intra-hepatic (liver) LDL levels may induce hepatic LDL receptor up-regulation, also decreasing plasma LDL levels. As always, a key issue is how benefits and complications of such agents compare with statins—molecular tools that have been analyzed in large numbers of human research and clinical trials since the mid-1970s.
- Phytosterols are widely recognized as having a proven LDL cholesterol lowering efficacy' A 2018 review found a dose-response relationship for phytosterols, with intakes of 1.5 to 3 g/day lowering LDL-C by 7.5% to 12%, but reviews as of 2017 had found no data indicating that the consumption of phytosterols may reduce the risk of CVD. Current supplemental guidelines for reducing LDL recommend doses of phytosterols in the 1.6-3.0 grams per day range (Health Canada, EFSA, ATP III, FDA) with a 2009 meta-analysis demonstrating an 8.8% reduction in LDL-cholesterol at a mean dose of 2.15 gram per day.
Gene editing
In 2021, scientists demonstrated that CRISPR gene editing can decrease blood levels of LDL cholesterol in vivo in Macaca fascicularis monkeys for months by 60% via knockout of PCSK9 in the liver.
ライフスタイル
LDLコレステロールは、飽和脂肪を含む食品を制限し、トランス脂肪を含む食品を避けるという食事介入によって低下させることができる。飽和脂肪は肉製品(鶏肉を含む)、全脂肪乳製品、卵、ココナッツやパームなどの精製された熱帯油に含まれる。しかし、トランス脂肪酸は羊や牛などの反芻動物が少量生産するため、赤身肉や乳製品にも含まれることがある。LDLコレステロールは、水溶性食物繊維と植物性食品の摂取を増やすことによっても低下させることができる。
LDLコレステロールを減少させるためのもう一つのライフスタイルのアプローチは、総体脂肪、特に腹腔内に蓄積された脂肪(内臓脂肪)を最小限に抑えることである。皮下脂肪よりも代謝活性の高い内臓脂肪は、多くの酵素シグナル、例えばレジスチンを産生し、インスリン抵抗性と循環VLDL粒子濃度を増加させ、その結果LDL粒子濃度を増加させ、糖尿病の発症を促進させることがわかっている。
こちらも参照
- Catechin/ja
- Cholesterol/ja
- Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency/ja
- Cholesteryl ester storage disease/ja
- Coenzyme Q10/ja
- Flavonoid/ja
- Glutathione/ja
- Health effects of tea/ja
- High density lipoprotein/ja
- LDL receptor/ja
- Lipid profile/ja
- Lipoprotein(a)/ja
- Lipoprotein-X/ja
- Melatonin/ja
- Polyphenol antioxidant/ja
- Saturated fat/ja
- Stanol ester/ja
- Sterol ester/ja
- トリグリセリド
- Vitamin A/ja
- Vitamin C/ja
- Vitamin E/ja
外部リンク
- Fat (LDL) Degradation: PMAP The Proteolysis Map-animation
- Adult Treatment Panel III Full Report
- ATP III Update 2004
- O'Keefe JH, Cordain L, Harris WH, Moe RM, Vogel R (June 2004). "Optimal low-density lipoprotein is 50 to 70 mg/dL: lower is better and physiologically normal". Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 43 (11): 2142–6. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2004.03.046. PMID 15172426.