Thiamine/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "==定義== {{Anchor|Definition}} チアミンはビタミンB群の一つであり、ビタミンB<sub>1</sub>としても知られている。陽イオンであり、通常は塩化物として供給される。塩として供給される。水、メタノール、グリセロールには可溶性であるが、極性の低いorganic solvent/ja|有..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "化学構造はアミノピリミジンとチアゾリウム環がメチレン架橋で結合したものである。チアゾールはメチルおよびヒドロキシエチル側鎖で置換されている。チアミンは酸性のpHでは安定であるが、アルカリ溶液や熱にさらされると不安定になる。Maillard reaction/ja|メイラー..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
チアミンは[[B vitamins/ja|ビタミンB群]]の一つであり、ビタミンB<sub>1</sub>としても知られている。[[cation/ja|陽イオン]]であり、通常は[[chloride/ja|塩化物]]として供給される。[[salt (chemistry)/ja|塩]]として供給される。水、[[methanol/ja|メタノール]]、[[glycerol/ja|グリセロール]]には[[Solubility/ja|可溶性]]であるが、極性の低い[[organic solvent/ja|有機溶媒]]には実質的に溶解しない。体内ではチアミンは[[Derivative (chemistry)/ja|誘導体]]を形成することができる;その中で最もよく特徴付けられるのは[[thiamine pyrophosphate/ja|チアミンピロリン酸]](TPP)であり、糖とアミノ酸の[[catabolism/ja|異化]]における[[coenzyme/ja|補酵素]]である。 | チアミンは[[B vitamins/ja|ビタミンB群]]の一つであり、ビタミンB<sub>1</sub>としても知られている。[[cation/ja|陽イオン]]であり、通常は[[chloride/ja|塩化物]]として供給される。[[salt (chemistry)/ja|塩]]として供給される。水、[[methanol/ja|メタノール]]、[[glycerol/ja|グリセロール]]には[[Solubility/ja|可溶性]]であるが、極性の低い[[organic solvent/ja|有機溶媒]]には実質的に溶解しない。体内ではチアミンは[[Derivative (chemistry)/ja|誘導体]]を形成することができる;その中で最もよく特徴付けられるのは[[thiamine pyrophosphate/ja|チアミンピロリン酸]](TPP)であり、糖とアミノ酸の[[catabolism/ja|異化]]における[[coenzyme/ja|補酵素]]である。 | ||
化学構造は[[pyrimidine/ja|アミノピリミジン]]と[[thiazolium/ja|チアゾリウム]]環が[[methylene bridge/ja|メチレン架橋]]で結合したものである。チアゾールはメチルおよび[[Ethanol/ja|ヒドロキシエチル側鎖]]で置換されている。チアミンは酸性の[[pH/ja|pH]]では安定であるが、[[Alkali/ja|アルカリ溶液]]や[[heat/ja|熱]]にさらされると不安定になる。[[Maillard reaction/ja|メイラード型反応]]では強く反応する。[[Redox/ja|酸化]]により蛍光誘導体[[thiochrome/ja|チオクロム]]を生成し、生体試料中のビタミン量を測定することができる。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 19 February 2024
 | |
 チアミン陽イオンの骨格式とボール&スティックモデル | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈθaɪ.əmɪn/ THY-ə-min |
| Other names | ビタミンB1, アノイリン, チアミン |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | by mouth, IV, IM |
| Drug class | vitamin/ja |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 3.7% to 5.3% (チアミン塩酸塩) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H17N4OS+ |
| Molar mass | 265.36 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
チアミン(thiamin、vitamin B1)は、ビタミンの一種で、必須微量栄養素の一つである。食品中に含まれるほか、栄養補助食品や医薬品として商業的に合成されている。チアミンのリン酸化型は、グルコースやアミノ酸の分解など、いくつかの代謝反応に必要である。
チアミンの食物源としては、全粒穀物、豆類、肉や魚がある。穀物加工はビタミン含有量の多くを除去するため、多くの国では穀物や小麦粉はチアミンで強化されている。サプリメントや医薬品は、チアミン欠乏症やそれに起因する脚気やウェルニッケ脳症などの障害を治療・予防するために利用できる。また、メープルシロップ尿症やリー症候群の治療にも用いられる。サプリメントや医薬品は通常口から摂取されるが、点滴や筋肉注射で投与されることもある。
チアミンサプリメントは一般的に忍容性が高い。注射で反復投与する場合、アナフィラキシーを含むアレルギー反応が起こることがある。チアミンは世界保健機関(WHO)の必須医薬品リストに掲載されている。チアミンはジェネリック医薬品として、また一部の国では非処方の栄養補助食品として入手可能である。
定義
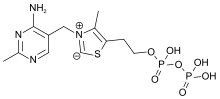
チアミンはビタミンB群の一つであり、ビタミンB1としても知られている。陽イオンであり、通常は塩化物として供給される。塩として供給される。水、メタノール、グリセロールには可溶性であるが、極性の低い有機溶媒には実質的に溶解しない。体内ではチアミンは誘導体を形成することができる;その中で最もよく特徴付けられるのはチアミンピロリン酸(TPP)であり、糖とアミノ酸の異化における補酵素である。
化学構造はアミノピリミジンとチアゾリウム環がメチレン架橋で結合したものである。チアゾールはメチルおよびヒドロキシエチル側鎖で置換されている。チアミンは酸性のpHでは安定であるが、アルカリ溶液や熱にさらされると不安定になる。メイラード型反応では強く反応する。酸化により蛍光誘導体チオクロムを生成し、生体試料中のビタミン量を測定することができる。
Deficiency
Well-known disorders caused by thiamine deficiency include beriberi, Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome, optic neuropathy, Leigh's disease, African seasonal ataxia (or Nigerian seasonal ataxia), and central pontine myelinolysis. Symptoms include malaise, weight loss, irritability and confusion.
In Western countries, chronic alcoholism is a risk factor for deficiency. Also at risk are older adults, persons with HIV/AIDS or diabetes, and those who have had bariatric surgery. Varying degrees of thiamine insufficiency have been associated with the long-term use of diuretics.
Biological functions

Five natural thiamine phosphate derivatives are known: thiamine monophosphate (ThMP), thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), thiamine triphosphate (ThTP), adenosine thiamine diphosphate (AThDP) and adenosine thiamine triphosphate (AThTP). They are involved in many cellular processes. The best-characterized form is TPP, a coenzyme in the catabolism of sugars and amino acids. While its role is well-known, the non-coenzyme action of thiamine and derivatives may be realized through binding to proteins which do not use that mechanism. No physiological role is known for the monophosphate except as an intermediate in cellular conversion of thiamine to the di- and triphosphates.
Thiamine pyrophosphate
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), also called thiamine diphosphate (ThDP), participates as a coenzyme in metabolic reactions, including those in which polarity inversion takes place. Its synthesis is catalyzed by the enzyme thiamine diphosphokinase according to the reaction thiamine + ATP → TPP + AMP (EC 2.7.6.2). TPP is a coenzyme for several enzymes that catalyze the transfer of two-carbon units and in particular the dehydrogenation (decarboxylation and subsequent conjugation with coenzyme A) of 2-oxoacids (alpha-keto acids). The mechanism of action of TPP as a coenzyme relies on its ability to form an ylide. Examples include:
- Present in most species
- Present in some species:
- pyruvate decarboxylase (in yeast)
- several additional bacterial enzymes
The enzymes transketolase, pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH) are important in carbohydrate metabolism. PDH links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. OGDH catalyzes the overall conversion of 2-oxoglutarate (alpha-ketoglutarate) to succinyl-CoA and CO2 during the citric acid cycle. The reaction catalyzed by OGDH is a rate-limiting step in the citric acid cycle. The cytosolic enzyme transketolase is central to the pentose phosphate pathway, a major route for the biosynthesis of the pentose sugars deoxyribose and ribose. The mitochondrial PDH and OGDH are part of biochemical pathways that result in the generation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the main energy transfer molecule for the cell. In the nervous system, PDH is also involved in the synthesis of myelin and the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Thiamine triphosphate

ThTP is implicated in chloride channel activation in the neurons of mammals and other animals, although its role is not well understood. ThTP has been found in bacteria, fungi and plants, suggesting that it has other cellular roles. In Escherichia coli, it is implicated in the response to amino acid starvation.
Adenosine derivatives
AThDP exists in small amounts in vertebrate liver, but its role remains unknown.
AThTP is present in E. coli, where it accumulates as a result of carbon starvation. In this bacterium, AThTP may account for up to 20% of total thiamine. It also exists in lesser amounts in yeast, roots of higher plants and animal tissue.
Medical uses
During pregnancy, thiamine is sent to the fetus via the placenta. Pregnant women have a greater requirement for the vitamin than other adults, especially during the third trimester. Pregnant women with hyperemesis gravidarum are at an increased risk of thiamine deficiency due to losses when vomiting. In lactating women, thiamine is delivered in breast milk even if it results in thiamine deficiency in the mother.
Thiamine is important not only for mitochondrial membrane development, but also for synaptic membrane function. It has also been suggested that a deficiency hinders brain development in infants and may be a cause of sudden infant death syndrome.
Dietary recommendations
| US National Academy of Medicine | |
| Age group | RDA (mg/day) |
|---|---|
| Infants 0–6 months | 0.2* |
| Infants 6–12 months | 0.3* |
| 1–3 years | 0.5 |
| 4–8 years | 0.6 |
| 9–13 years | 0.9 |
| Females 14–18 years | 1.0 |
| Males 14+ years | 1.2 |
| Females 19+ years | 1.1 |
| Pregnant/lactating females 14–50 | 1.4 |
| * Adequate intake for infants, as an RDA has yet to be established | |
| European Food Safety Authority | |
| Age group | Adequate intake (mg/MJ) |
| All persons 7 months+ | 0.1 |
| Neither the US National Academy of Medicine nor the European Food Safety Authority have determined the tolerable upper intake level for thiamine | |
The US National Academy of Medicine updated the Estimated Average Requirements (EARs) and Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for thiamine in 1998. The EARs for thiamine for women and men aged 14 and over are 0.9 mg/day and 1.1 mg/day, respectively; the RDAs are 1.1 and 1.2 mg/day, respectively. RDAs are higher than EARs to provide adequate intake levels for individuals with higher than average requirements. The RDA during pregnancy and for lactating females is 1.4 mg/day. For infants up to the age of 12 months, the Adequate Intake (AI) is 0.2–0.3 mg/day and for children aged 1–13 years the RDA increases with age from 0.5 to 0.9 mg/day.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) refers to the collective set of information as Dietary Reference Values, with Population Reference Intakes (PRIs) instead of RDAs, and Average Requirements instead of EARs. For women (including those pregnant or lactating), men and children the PRI is 0.1 mg thiamine per megajoule (MJ) of energy in their diet. As the conversion is 1 MJ = 239 kcal, an adult consuming 2390 kilocalories ought to be consuming 1.0 mg thiamine. This is slightly lower than the US RDA.
Neither the National Academy of Medicine nor EFSA have set an upper intake level for thiamine, as there is no human data for adverse effects from high doses.
Safety
Thiamine is generally well tolerated and non-toxic when administered orally. There are rare reports of adverse side effects when thiamine is given intravenously, including allergic reactions, nausea, lethargy, and impaired coordination.
Labeling
For US food and dietary supplement labeling purposes, the amount in a serving is expressed as a percent of Daily Value. Since May 27, 2016, the Daily Value has been 1.2 mg, in line with the RDA.
Sources
Thiamine is found in a wide variety of processed and whole foods, including lentils, peas, whole grains, pork, and nuts. A typical daily prenatal vitamin product contains around 1.5 mg of thiamine.
Food fortification
Some countries require or recommend fortification of grain foods such as wheat, rice or maize (corn) because processing lowers vitamin content. As of February 2022, 59 countries, mostly in North and Sub-Saharan Africa, require food fortification of wheat, rice or maize with thiamine or thiamine mononitrate. The amounts stipulated range from 2.0 to 10.0 mg/kg. An additional 18 countries have a voluntary fortification program. For example, the Indian government recommends 3.5 mg/kg for "maida" (white) and "atta" (whole wheat) flour.
Synthesis
Biosynthesis
Thiamine biosynthesis occurs in bacteria, some protozoans, plants, and fungi. The thiazole and pyrimidine moieties are biosynthesized separately and are then combined to form ThMP by the action of thiamine-phosphate synthase.
The pyrimidine ring system is formed in a reaction catalysed by phosphomethylpyrimidine synthase (ThiC), an enzyme in the radical SAM superfamily of iron–sulfur proteins, which use S-adenosyl methionine as a cofactor.
The starting material is 5-aminoimidazole ribotide, which undergoes a rearrangement reaction via radical intermediates which incorporate the blue, green and red fragments shown into the product.
The thiazole ring is formed in a reaction catalysed by thiazole synthase (EC 2.8.1.10). The ultimate precursors are 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate, 2-iminoacetate and a sulfur carrier protein called ThiS. An additional protein, ThiG, is also required to bring together all the components of the ring at the enzyme active site.

The final step to form ThMP involves decarboxylation of the thiazole intermediate, which reacts with the pyrophosphate derivative of phosphomethylpyrimidine, itself a product of a kinase, phosphomethylpyrimidine kinase.
The biosynthetic pathways differ among organisms. In E. coli and other enterobacteriaceae, ThMP is phosphorylated to the cofactor TPP by a thiamine-phosphate kinase (ThMP + ATP → TPP + ADP). In most bacteria and in eukaryotes, ThMP is hydrolyzed to thiamine and then pyrophosphorylated to TPP by thiamine diphosphokinase (thiamine + ATP → TPP + AMP).
The biosynthetic pathways are regulated by riboswitches. If there is sufficient thiamine present in the cell then the thiamine binds to the mRNAs for the enzymes that are required in the pathway and prevents their translation. If there is no thiamine present then there is no inhibition, and the enzymes required for the biosynthesis are produced. The specific riboswitch, the TPP riboswitch, is the only known riboswitch found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms.
Laboratory synthesis
In the first total synthesis in 1936, ethyl 3-ethoxypropanoate was treated with ethyl formate to give an intermediate dicarbonyl compound which when reacted with acetamidine formed a substituted pyrimidine. Conversion of its hydroxyl group to an amino group was carried out by nucleophilic aromatic substitution, first to the chloride derivative using phosphorus oxychloride, followed by treatment with ammonia. The ethoxy group was then converted to a bromo derivative using hydrobromic acid. In the final stage, thiamine (as its dibromide salt) was formed in an alkylation reaction using 4-methyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)thiazole.
Industrial synthesis

Merck & Co. adapted the 1936 laboratory-scale synthesis, allowing them to manufacture thiamine in Rahway in 1937. However, an alternative route using the intermediate Grewe diamine (5-(aminomethyl)-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinamine), first published in 1937, was investigated by Hoffman La Roche and competitive manufacturing processes followed. Efficient routes to the diamine have continued to be of interest. In the European Economic Area, thiamine is registered under REACH regulation and between 100 and 1,000 tonnes per annum are manufactured or imported there.
Synthetic analogues
Many vitamin B1 analogues, such as Benfotiamine, fursultiamine, and sulbutiamine, are synthetic derivatives of thiamine. Most were developed in Japan in the 1950s and 1960s as forms that were intended to improve absorption compared to thiamine. Some are approved for use in some countries as a drug or non-prescription dietary supplement for treatment of diabetic neuropathy or other health conditions.
Absorption, metabolism and excretion
In the upper small intestine, thiamine phosphate esters present in food are hydrolyzed by alkaline phosphatase enzymes. At low concentrations, the absorption process is carrier-mediated. At higher concentrations, absorption also occurs via passive diffusion. Active transport can be inhibited by alcohol consumption or by folate deficiency.
The majority of thiamine in serum is bound to proteins, mainly albumin. Approximately 90% of total thiamine in blood is in erythrocytes. A specific binding protein called thiamine-binding protein has been identified in rat serum and is believed to be a hormone-regulated carrier protein important for tissue distribution of thiamine. Uptake of thiamine by cells of the blood and other tissues occurs via active transport and passive diffusion. Two members of the family of transporter proteins encoded by the genes SLC19A2 and SLC19A3 are capable of thiamine transport. In some tissues, thiamine uptake and secretion appear to be mediated by a Na+-dependent transporter and a transcellular proton gradient.
Human storage of thiamine is about 25 to 30 mg, with the greatest concentrations in skeletal muscle, heart, brain, liver, and kidneys. ThMP and free (unphosphorylated) thiamine are present in plasma, milk, cerebrospinal fluid, and, it is presumed, all extracellular fluid. Unlike the highly phosphorylated forms of thiamine, ThMP and free thiamine are capable of crossing cell membranes. Calcium and magnesium have been shown to affect the distribution of thiamine in the body and magnesium deficiency has been shown to aggravate thiamine deficiency. Thiamine contents in human tissues are less than those of other species.
Thiamine and its metabolites (2-methyl-4-amino-5-pyrimidine carboxylic acid, 4-methyl-thiazole-5-acetic acid, and others) are excreted principally in the urine.
Interference
The bioavailability of thiamine in foods can be interfered with in a variety of ways. Sulfites, added to foods as a preservative, will attack thiamine at the methylene bridge, cleaving the pyrimidine ring from the thiazole ring. The rate of this reaction is increased under acidic conditions. Thiamine is degraded by thermolabile thiaminases present in some species of fish, shellfish and other foods. The pupae of an African silk worm, Anaphe venata, is a traditional food in Nigeria. Consumption leads to thiamine deficiency. Older literature reported that in Thailand, consumption of fermented, uncooked fish caused thiamine deficiency, but either abstaining from eating the fish or heating it first reversed the deficiency. In ruminants, intestinal bacteria synthesize thiamine and thiaminases. The bacterial thiaminases are cell surface enzymes that must dissociate from the cell membrane before being activated; the dissociation can occur in ruminants under acidotic conditions. In dairy cows, over-feeding with grain causes subacute ruminal acidosis and increased ruminal bacteria thiaminase release, resulting in thiamine deficiency.
From reports on two small studies conducted in Thailand, chewing slices of areca nut wrapped in betel leaves and chewing tea leaves reduced food thiamine bioavailability by a mechanism that may involve tannins.
Bariatric surgery for weight loss is known to interfere with vitamin absorption. A meta-analysis reported that 27% of people who underwent bariatric surgeries experience vitamin B1 deficiency.
History
Thiamine was the first of the water-soluble vitamins to be isolated. The earliest observations in humans and in chickens had shown that diets of primarily polished white rice caused beriberi, but did not attribute it to the absence of a previously unknown essential nutrient.
In 1884, Takaki Kanehiro, a surgeon general in the Imperial Japanese Navy, rejected the previous germ theory for beriberi and suggested instead that the disease was due to insufficiencies in the diet. Switching diets on a navy ship, he discovered that replacing a diet of white rice only with one also containing barley, meat, milk, bread, and vegetables, nearly eliminated beriberi on a nine-month sea voyage. However, Takaki had added many foods to the successful diet and he incorrectly attributed the benefit to increased protein intake, as vitamins were unknown at the time. The Navy was not convinced of the need for such an expensive program of dietary improvement, and many men continued to die of beriberi, even during the Russo-Japanese war of 1904–5. Not until 1905, after the anti-beriberi factor had been discovered in rice bran (removed by polishing into white rice) and in barley bran, was Takaki's experiment rewarded. He was made a baron in the Japanese peerage system, after which he was affectionately called "Barley Baron".
The specific connection to grain was made in 1897 by Christiaan Eijkman, a military doctor in the Dutch East Indies, who discovered that fowl fed on a diet of cooked, polished rice developed paralysis that could be reversed by discontinuing rice polishing. He attributed beriberi to the high levels of starch in rice being toxic. He believed that the toxicity was countered in a compound present in the rice polishings. An associate, Gerrit Grijns, correctly interpreted the connection between excessive consumption of polished rice and beriberi in 1901: He concluded that rice contains an essential nutrient in the outer layers of the grain that is removed by polishing. Eijkman was eventually awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1929, because his observations led to the discovery of vitamins.
In 1910, a Japanese agricultural chemist of Tokyo Imperial University, Umetaro Suzuki, isolated a water-soluble thiamine compound from rice bran, which he named aberic acid. (He later renamed it Orizanin.) He described the compound as not only an anti-beriberi factor, but also as being essential to human nutrition; however, this finding failed to gain publicity outside of Japan, because a claim that the compound was a new finding was omitted in translation of his publication from Japanese to German. In 1911 a Polish biochemist Casimir Funk isolated the antineuritic substance from rice bran (the modern thiamine) that he called a "vitamine" (on account of its containing an amino group). However, Funk did not completely characterize its chemical structure. Dutch chemists, Barend Coenraad Petrus Jansen and his closest collaborator Willem Frederik Donath, went on to isolate and crystallize the active agent in 1926, whose structure was determined by Robert Runnels Williams, in 1934. Thiamine was named by the Williams team as a portmanteau of "thio" (meaning sulfur-containing) and "vitamin". The term "vitamin" coming indirectly, by way of Funk, from the amine group of thiamine itself (although by this time, vitamins were known to not always be amines, for example, vitamin C). Thiamine was also synthesized by the Williams group in 1936.
Sir Rudolph Peters, in Oxford, used pigeons to understand how thiamine deficiency results in the pathological-physiological symptoms of beriberi. Pigeons fed exclusively on polished rice developed opisthotonos, a condition characterized by head retraction. If not treated, the animals died after a few days. Administration of thiamine after opisthotonos was observed led to a complete cure within 30 minutes. As no morphological modifications were seen in the brain of the pigeons before and after treatment with thiamine, Peters introduced the concept of a biochemical-induced injury. In 1937, Lohmann and Schuster showed that the diphosphorylated thiamine derivative, TPP, was a cofactor required for the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate.
- Some contributors to the discovery of thiamine
External links
- "Thiamine". Drug Information Portal. US National Library of Medicine.
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Thiamine/ja(11 January 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Lua error in Module:Itemnumber at line 91: attempt to concatenate local 'qid' (a nil value). |