Prosultiamine
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
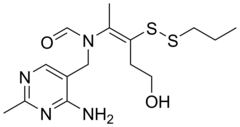
| Formula | C15H24N4O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 356.50 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Prosultiamine (INN; also known as thiamine propyl disulfide or TPD; brand name Jubedel,) is a disulfide thiamine derivative discovered in garlic in Japan in the 1950s, and is similar to allithiamine. It was developed as a treatment for vitamin B1 deficiency. It has improved lipid solubility relative to thiamine and is not rate-limited by dependency on intestinal transporters for absorption, hence the reasoning for its development.
Research
It has been studied as a potential treatment for infection with human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV), since it has been shown to reduce viral load and symptoms.
See also
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Prosultiamine(2 March 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Item:Q21701 |