Blood/ja: Difference between revisions
| Line 202: | Line 202: | ||
** 血液組成、心臓のポンプ作用、または血管の狭窄に問題があると、供給される組織の低酸素症(酸素欠乏)など、多くの結果をもたらす可能性がある。虚血''という用語は、血液の灌流が不十分な組織を指し、梗塞''という用語は、血液供給が遮断された(または非常に不十分である)場合に起こりうる組織の死([[necrosis/ja|壊死]])を指す。 | ** 血液組成、心臓のポンプ作用、または血管の狭窄に問題があると、供給される組織の低酸素症(酸素欠乏)など、多くの結果をもたらす可能性がある。虚血''という用語は、血液の灌流が不十分な組織を指し、梗塞''という用語は、血液供給が遮断された(または非常に不十分である)場合に起こりうる組織の死([[necrosis/ja|壊死]])を指す。 | ||
===血液=== | |||
{{see also/ja|Hematology/ja}} | |||
{{see also|Hematology}} | * 貧血 | ||
* | ** 赤血球量の不足([[anemia/ja|貧血]])は、出血、[[thalassemia/ja|サラセミア]]のような血液疾患、または[[Illnesses related to poor nutrition/ja|栄養欠乏]]の結果である可能性があり、1回以上の[[blood transfusion/ja|輸血]]を必要とすることがある。貧血はまた、赤血球が効果的に機能しない[[genetic disorder/ja|遺伝子疾患]]に起因することもある。貧血は、[[blood test/ja|血液検査]]でヘモグロビン値が男性で13.5 gm/dl未満、女性で12.0 gm/dl未満であれば確認できる。輸血可能な血液の需要を満たすために、いくつかの国には[[blood bank/ja|血液バンク]]がある。輸血を受ける人は、ドナーの血液型と適合する[[blood type/ja|血液型]]を持っていなければならない。 | ||
** | ** [[Sickle-cell anemia/ja|鎌状赤血球貧血]] | ||
** [[Sickle-cell anemia]] | * 細胞増殖の障害 | ||
* | ** [[Leukemia/ja|白血病]]は、造血組織および造血細胞の[[cancer (medicine)/ja|がん]]の一群である。 | ||
** [[Leukemia]] | ** 赤血球([[polycythemia vera/ja|真性多血症]])または血小板([[essential thrombocytosis/ja|本態性血小板増多症]])のがん以外の過剰産生は、[[Premalignant condition/ja||前悪性腫瘍]]である可能性がある。 | ||
** | **[[Myelodysplastic syndrome/ja|骨髄異形成症候群]]は、1つまたは複数の細胞系列の非有効な産生を伴う。 | ||
** [[Myelodysplastic syndrome]] | * 凝固障害 | ||
* | ** [[Hemophilia/ja|血友病]]は、血液の[[coagulation/ja|凝固機構]]の1つに機能障害を引き起こす[[Genetic disorder/ja|遺伝性疾患]]である。これにより、本来ならば取るに足らない傷が命に関わるようになることもあるが、より一般的なのは関節腔への出血、つまり[[hemarthrosis/ja|ヘモアルトロシス]]となり、歩行障害や障害をもたらす可能性がある。 | ||
** [[Hemophilia]] | ** 血小板が効果的でなかったり不十分であったりすると、[[coagulopathy/ja|凝固障害]](出血性疾患)になることもある。 | ||
** | ** 凝固能亢進状態([[thrombophilia/ja|血栓症]])は、血小板または凝固因子の機能調節の欠陥に起因し、血栓症を引き起こす。 | ||
** | * 血液の感染症 | ||
* | ** 血液は重要な感染経路である。エイズの原因ウイルスであるHIVは、感染者の血液、精液、その他の体内分泌物との接触によって感染する。[[Hepatitis B/ja|B型肝炎]]と[[Hepatitis C/ja|C]]は、主に血液の接触によって感染する。[[blood-borne infection/ja|血液媒介感染症]]のため、血液の付着した物体は[[Biological hazard/ja|バイオハザード]]として扱われる。 | ||
** | ** 血液の細菌感染は[[bacteremia/ja|菌血症]]または[[sepsis/ja|敗血症]]である。ウイルス感染はウイルス血症である。[[Malaria/ja|マラリア]]や[[trypanosomiasis/ja|トリパノソーマ症]]は血液を媒介とする寄生虫感染症である。 | ||
** | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 09:03, 22 February 2024
| 血液 | |
|---|---|
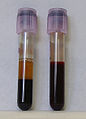
 静脈血(濃い色)と動脈血(明るい色) | |
| Anatomical terminology |
血液は、ヒトをはじめとする脊椎動物の循環系にある体液であり、栄養や酸素などの必要な物質を細胞に送り、同じ細胞から代謝廃棄物を運び出す。
血液は血漿中に浮遊する血球で構成される。血漿は血液液の55%を占め、その大部分は水分(体積比92%)であり、タンパク質、グルコース、ミネラルイオン、ホルモンを含む。血液細胞は主に赤血球(赤血球)、白血球(白血球)、(哺乳類では)血小板(血小板)である。最も豊富な細胞は赤血球である。これらはヘモグロビンを含んでおり、ヘモグロビンは酸素と可逆的に結合することで酸素の溶解度を高め、酸素輸送を促進する。顎脚脊椎動物は、主に白血球に基づく適応免疫系を持っている。白血球は感染症や寄生虫に抵抗するのに役立つ。血小板は血液の血液凝固に重要である。
血液は心臓のポンプ作用によって血管を通って全身を循環する。肺を持つ動物では、動脈血液は吸入した空気から体内の組織に酸素を運び、静脈血液は細胞から産生される代謝の老廃物である二酸化炭素を組織から肺に運び、吐き出す。血液は、ヘモグロビンが酸素化されると鮮やかな赤色になり、脱酸素化されると暗赤色になる。
血液に関する医療用語は、ギリシャ語のαἷμαに由来するhemo-、hemato-、haemo-、haemato-で始まることが多い。(ギリシャ語で「血液」を意味するhaima(haima)に由来する。解剖学や組織学の観点からは、血液は骨に由来し、フィブリノーゲンの形で潜在的な分子繊維が存在することから、特殊な形態の結合組織と考えられている。
機能
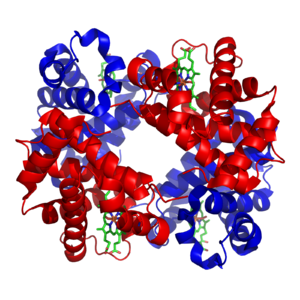
緑色=ヘム(またはヘム基)
赤と青=タンパク質サブユニット
血液は、体内で以下のような多くの重要な機能を果たしている:
- 組織への酸素の供給(赤血球に含まれるヘモグロビンと結合している)
- グルコース、アミノ酸、脂肪酸などの栄養素の供給(血液中に溶けているか、血漿タンパク質(血中脂質など)に結合している)。
- 二酸化炭素、尿素、乳酸などの老廃物を除去する。
- 白血球の循環、抗体による異物の検出を含む免疫学的機能。
- 凝固は、血管が破れたときの反応で、出血を止めるために血液を液体から半固体のゲルに変えることである。
- ホルモンの輸送や組織損傷のシグナル伝達を含むメッセンジャー機能。
- コア体温の調節
- 水圧機能
成分
哺乳類の場合
血液は人間の体重の7%を占め、平均密度は約1060 kg/m3で、純水の密度1000 kg/m3に非常に近い。平均的な成人の血液量はおよそ5 litres (11 US pt)または1.3ガロンで、血漿と形成元素で構成されている。形成要素とは、赤血球と白血球の2種類の血球または体細胞、および凝固に関与する血小板と呼ばれる細胞片である。体積では、赤血球が全血の約45%、血漿が約54.3%、白血球が約0.7%を占める。
-
遠心分離により分画されたヒト血液: 血漿(上、黄色の層)、バフィーコート(中央、薄い白色の層)、赤血球層(下、赤色の層)が見える。
-
血液循環: 赤=酸素供給、青=酸素欠乏
-
血液の構成要素を描いたイラスト
-
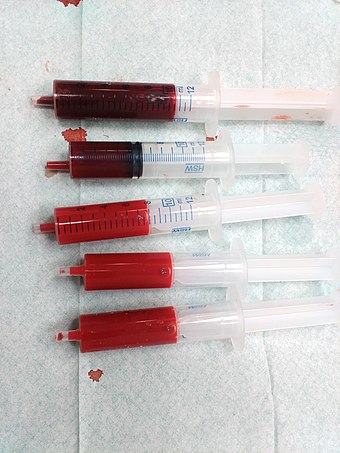
左のチューブ:静置後、赤血球はチューブの底に沈殿している。
右のチューブ: 採りたての血液
細胞
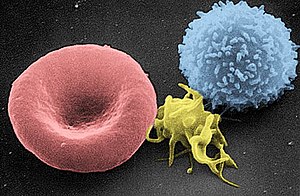
血液1マイクロリットルに含まれる成分である:
- 4.7~6.1 万個(男性)、4.2~5.4 万個(女性)赤血球: 赤血球は血液のヘモグロビンを含み、酸素を分配する。成熟した赤血球には、哺乳類では核とオルガネラがない。赤血球は(内皮血管細胞やその他の細胞とともに)、異なる血液型を規定する糖タンパク質によっても特徴づけられる。赤血球が占める血液の割合はヘマトクリットと呼ばれ、通常は約45%である。人体のすべての赤血球の表面積を合わせると、人体の外表面のおよそ2,000倍になる。
- 4,000~11,000個の白血球: 白血球は身体の免疫系の一部であり、古くなった細胞や異常な細胞、細胞の残骸を破壊・除去し、感染因子(病原体)や異物を攻撃する。白血球のがんは白血病と呼ばれる。
- 20万~50万個の血小板: 血小板とも呼ばれ、血液凝固(凝固)に関与する。凝固カスケードからのフィブリンが血小板栓の上に網目を作る。
| パラメーター | 値 | 参照 |
|---|---|---|
| Hematocrit/ja |
45 ± 7 (38–52%) 男性 |
|
| pH/ja | 7.35–7.45 | |
| base excess/ja | −3 to +3 | |
| PO2 | 10–13 kPa (80–100 mm Hg) | |
| PCO2 | 4.8–5.8 kPa (35–45 mm Hg) | |
| HCO3− | 21–27 mM | |
| Oxygen saturation/ja |
酸素含有: 98–99% |
血漿
血液の約55%は血漿であり、血液の液体媒体である液体で、それ自体は麦わら色をしている。血漿量は平均的な人間で合計2.7~3.0リットル(2.8~3.2クォート)である。血漿は本質的に、92%の水、8%の血漿タンパク質、および微量の他の物質を含む水溶液である。血漿は、グルコース、アミノ酸、脂肪酸などの溶存栄養素(血液中に溶けているか、血漿タンパク質に結合している)を循環させ、二酸化炭素、尿素、乳酸などの老廃物を除去する。
その他の重要な成分には以下のものがある:
血清という用語は、凝固タンパク質が除去された血漿を指す。残ったタンパク質のほとんどはアルブミンと免疫グロブリンである。
酸度
血液のpHは7.35~7.45の狭い範囲に収まるように調節されており、わずかに塩基性になっている(補正)。pHが7.35未満の血液中の細胞外液は酸性過ぎであり、7.45以上の血液中のpHは塩基性過ぎである。6.9以下または7.8以上のpHは通常致死的である。血中pH、酸素分圧(pO2)、二酸化炭素分圧(pCO2)、重炭酸塩(HCO3-)は、多くの恒常性維持機構によって注意深く調節されている、 これらは主に呼吸器系と泌尿器系を通じて影響を及ぼし、酸塩基平衡と呼吸を制御する。動脈血ガス検査はこれらを測定する。血漿はまた、さまざまな組織にメッセージを伝えるホルモンを循環させている。さまざまな血液電解質の正常基準範囲のリストは広範囲にわたる。
哺乳類以外の動物の場合




細胞の数、大きさ、タンパク質の構造などに関する正確な詳細は、種によって多少異なるが、ヒトの血液は哺乳類の血液の典型である。しかし、哺乳類以外の脊椎動物では、いくつかの重要な違いがある:
- 哺乳類以外の脊椎動物の赤血球は扁平な卵形をしており、細胞核を保持している。
- 例えば、好酸球は一般的にヒトよりも多い。
- 他の脊椎動物では、代わりに血小板凝集細胞と呼ばれる小さな有核紡錘形細胞が血液凝固を担っている。
生理学
循環器
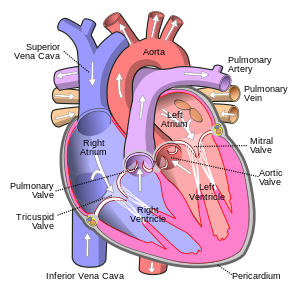
血液は心臓のポンプ作用によって血管を通って全身を循環する。ヒトの場合、血液は心臓の強い左心室から動脈を通って末梢の組織に送り出され、静脈を通って右の心房に戻る。その後、血液は右心室に入り、肺動脈を通って肺に送られ、肺静脈を通って左心房に戻る。その後、血液は再び循環するために左心室に入る。動脈血は吸入した空気から全身の細胞に酸素を運び、静脈血は細胞による代謝の老廃物である二酸化炭素を肺に運んで吐き出す。ただし、例外として肺動脈があり、肺動脈には体内で最も脱酸素化された血液が流れ、肺静脈には酸素化された血液が流れている。
追加の還流は骨格筋の動きによって生じることがあり、静脈を圧迫し、静脈の弁を通して血液を右心房に押し出すことができる。
血液循環は、1628年にウィリアム・ハーヴェイによって記述されたことで有名である。
細胞の生産と分解
脊椎動物では、血液のさまざまな細胞は造血と呼ばれるプロセスで骨髄で作られる。このプロセスには、赤血球を産生する赤血球形成と、白血球と血小板を産生する骨髄形成がある。小児期には、ヒトのほぼすべての骨が赤血球を産生するが、成人になると、赤血球の産生はより大きな骨、すなわち椎骨体、胸骨(胸骨)、胸郭、骨盤骨、および上腕と下肢の骨に限定される。さらに小児期には、縦隔にある胸腺がTリンパ球の重要な供給源となる。 血液の蛋白質成分(凝固蛋白質を含む)は主に肝臓で産生され、ホルモンは内分泌腺で産生され、水分画分は視床下部で調節され、腎臓で維持される。
健康な赤血球は、脾臓と肝臓のクッパー細胞によって分解されるまでの血漿寿命が約120日である。肝臓はまた、いくつかのタンパク質、脂質、アミノ酸を除去する。腎臓は老廃物を積極的に尿に分泌する。
酸素輸送

海面気圧で空気を吸っている健康な人間の動脈血サンプル中の酸素の約98.5%はヘモグロビンと化学的に結合している。約1.5%は物理的に他の血液液に溶けており、ヘモグロビンとは結びついていない。ヘモグロビン分子は、哺乳類や他の多くの種における酸素の主要な輸送体である。ヘモグロビンはヘモグロビン1gあたり1.36~1.40mlのO2と酸素結合能を持ち、酸素分圧1mm Hg(動脈では約100 mm Hg)あたり血液1リットルあたり0.03 mlのO2の溶解力だけで酸素を運搬する場合に比べて、血中酸素容量の合計は70倍になる。
肺動脈と臍帯動脈およびそれらに対応する静脈を除き、動脈は心臓から酸素化血液を運び、細動脈と毛細血管を介して体内に送り、そこで酸素が消費される。その後、細静脈と静脈は脱酸素化血液を心臓に戻す。
成人の安静時の正常な状態では、肺から出る血液中のヘモグロビンは約98~99%酸素飽和度であり、体への酸素供給量は950~1150ml/分である。安静時の健康な成人の酸素消費量は約200~250ml/分(70~78%)である。持続的な運動中に酸素消費量が増加すると、静脈血の酸素飽和度が低下し、訓練された運動選手では15%未満に達することがある。これを補うために呼吸数と血流量が増加するが、このような条件下では動脈血の酸素飽和度は95%以下に低下することがある。安静時(例えば麻酔下での手術中)には、これほど低い酸素飽和度は危険であると考えられている。持続的な低酸素状態(酸素飽和度90%以下)は健康にとって危険であり、重度の低酸素状態(酸素飽和度30%以下)は急速に致命的になる可能性がある。
胎盤を介して酸素を受け取る胎児は、はるかに低い酸素圧(成人の肺で見られるレベルの約21%)にさらされるため、胎児はこのような条件下で機能するために、酸素に対する親和性がはるかに高い別の形態のヘモグロビン(ヘモグロビンF)を産生する。
二酸化炭素の輸送=
CO2は血液中で3つの異なる方法で運ばれる。(正確な割合は動脈血か静脈血かによって異なる)。その大部分(約70%)は、赤血球中の酵素炭酸脱水酵素によって、反応CO
2 + H
2O → H
2CO
3 → H+
+ HCO−
3によって重炭酸イオンHCO−
3に変換され、約7%は血漿中に溶解し、約23%はカルバミノ化合物としてヘモグロビンに結合する。
ヘモグロビンは赤血球の中で酸素を運搬する主要な分子であり、酸素と二酸化炭素の両方を運搬する。しかし、ヘモグロビンに結合したCO2は、酸素と同じ部位には結合しない。代わりに、4本のグロビン鎖のN末端基と結合する。しかし、ヘモグロビン分子に対するアロステリック効果のため、CO2の結合は、与えられた酸素分圧に対して結合する酸素の量を減少させる。酸素濃度の上昇による血液中の二酸化炭素との結合の減少はハルデン効果として知られ、組織から肺への二酸化炭素の輸送において重要である。CO2分圧の上昇またはpHの低下は、ヘモグロビンからの酸素の脱荷を引き起こすが、これはボーア効果として知られている。
水素イオンの運搬
オキシヘモグロビンの一部は酸素を失い、デオキシヘモグロビンとなる。デオキシヘモグロビンは、オキシヘモグロビンよりも水素との親和性が高いため、水素イオンのほとんどを結合する。
リンパ系
哺乳類では、血液はリンパと平衡状態にあり、リンパは毛細血管による限外濾過によって血液から組織内で連続的に形成される。リンパは小リンパ管系によって集められ、胸管に導かれ、左鎖骨下静脈に排出され、そこで再び体循環に加わる。
体温調節
血液循環は全身に熱を運ぶが、この流れの調節は体温調節の重要な部分である。表面への血流を増加させると(例:温暖な気候や激しい運動時)、皮膚が温かくなり、その結果、熱損失が速くなる。対照的に、外気温が低いときは、四肢や皮膚表面への血流が減少し、熱損失を防ぐために、身体の重要な臓器に優先的に血液が循環する。
血流速度
血流速度は臓器によって大きく異なる。肝臓は最も血液供給量が多く、おおよそ1350ml/分である。腎臓は1100ml/分、脳は~700ml/分であり、2番目と3番目に血液供給量の多い臓器である。
組織100gあたりの血流量は相対的に異なっており、腎臓、副腎、甲状腺はそれぞれ1位、2位、3位と最も供給量の多い組織である。
水力学的機能
血流の制限はまた、特殊な組織において、その組織の勃起をもたらす充血を引き起こすために利用することができる;陰茎やクリトリスの勃起組織がその例である。
水力学的機能のもう一つの例はジャンピング・クモであり、圧力下で脚に押し込まれた血液が、かさばる筋肉質の脚を必要とせずに、強力なジャンプのために脚をまっすぐにする。
色

ヘモグロビンは血液の色を決定する主要な物質である(ヘモクロム)。各分子には4つのヘム基があり、様々な分子との相互作用によって正確な色が変化する。動脈血や毛細血管血は、酸素がヘム基に強い赤色を与えるため、鮮やかな赤色をしている。これは静脈に存在し、献血や静脈採血の際に見ることができる。これは、ヘモグロビンが吸収する光のスペクトルが、酸素化状態と脱酸素化状態で異なるためである。
一酸化炭素中毒の血液は真っ赤であるが、これは一酸化炭素がカルボキシヘモグロビンの生成を引き起こすためである。シアン化合物中毒では、身体は酸素を利用できないため、静脈血は酸素を含んだままとなり、赤みが増す。ヘモグロビンに存在するヘム基に影響を及ぼすいくつかの病態があり、それによって皮膚が青く見えることがある--チアノーゼと呼ばれる症状である。ヘムが酸化されると、より褐色で酸素を運搬できないメトヘモグロビンが形成される。まれな病態である硫黄ヘモグロビン血症では、動脈ヘモグロビンが部分的に酸素化され、青みがかった暗赤色に見える。
皮膚表面に近い静脈が青く見えるのは、さまざまな理由がある。しかし、この色知覚の変化の要因は、静脈血の実際の色というよりも、皮膚の光散乱特性と視覚野による視覚入力の処理に関係している。
プラシノヘウマ属のスキンクは老廃物ビリベルジンの蓄積により緑色の血液を持つ。
障害
- 体積の障害
- 循環障害
- ショックとは組織の灌流がうまくいかないことであり、失血、感染、心拍出量低下など様々な状態によって引き起こされる。
- 動脈硬化は、粥腫が動脈に並んで動脈を狭めるため、動脈を通る血液の流れを減少させる。アテロームは加齢とともに増加する傾向があり、その進行は喫煙、高血圧、過剰な循環脂質(高脂血症)、糖尿病などの多くの原因によって悪化する。
- 凝固は血栓症を形成し、血管を閉塞させることがある。
- 血液組成、心臓のポンプ作用、または血管の狭窄に問題があると、供給される組織の低酸素症(酸素欠乏)など、多くの結果をもたらす可能性がある。虚血という用語は、血液の灌流が不十分な組織を指し、梗塞という用語は、血液供給が遮断された(または非常に不十分である)場合に起こりうる組織の死(壊死)を指す。
血液
- 貧血
- 細胞増殖の障害
- 凝固障害
- 血液の感染症
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Substances other than oxygen can bind to hemoglobin; in some cases, this can cause irreversible damage to the body. Carbon monoxide, for example, is extremely dangerous when carried to the blood via the lungs by inhalation, because carbon monoxide irreversibly binds to hemoglobin to form carboxyhemoglobin, so that less hemoglobin is free to bind oxygen, and fewer oxygen molecules can be transported throughout the blood. This can cause suffocation insidiously. A fire burning in an enclosed room with poor ventilation presents a very dangerous hazard, since it can create a build-up of carbon monoxide in the air. Some carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin when smoking tobacco.
Treatments
Transfusion

Blood for transfusion is obtained from human donors by blood donation and stored in a blood bank. There are many different blood types in humans, the ABO blood group system, and the Rhesus blood group system being the most important. Transfusion of blood of an incompatible blood group may cause severe, often fatal, complications, so crossmatching is done to ensure that a compatible blood product is transfused.
Other blood products administered intravenously are platelets, blood plasma, cryoprecipitate, and specific coagulation factor concentrates.
Intravenous administration
Many forms of medication (from antibiotics to chemotherapy) are administered intravenously, as they are not readily or adequately absorbed by the digestive tract.
After severe acute blood loss, liquid preparations, generically known as plasma expanders, can be given intravenously, either solutions of salts (NaCl, KCl, CaCl2 etc.) at physiological concentrations, or colloidal solutions, such as dextrans, human serum albumin, or fresh frozen plasma. In these emergency situations, a plasma expander is a more effective life-saving procedure than a blood transfusion, because the metabolism of transfused red blood cells does not restart immediately after a transfusion.
Letting
In modern evidence-based medicine, bloodletting is used in management of a few rare diseases, including hemochromatosis and polycythemia. However, bloodletting and leeching were common unvalidated interventions used until the 19th century, as many diseases were incorrectly thought to be due to an excess of blood, according to Hippocratic medicine.
Etymology

English blood (Old English blod) derives from Germanic and has cognates with a similar range of meanings in all other Germanic languages (e.g. German Blut, Swedish blod, Gothic blōþ). There is no accepted Indo-European etymology.
History
Classical Greek medicine
Robin Fåhræus (a Swedish physician who devised the erythrocyte sedimentation rate) suggested that the Ancient Greek system of humorism, wherein the body was thought to contain four distinct bodily fluids (associated with different temperaments), were based upon the observation of blood clotting in a transparent container. When blood is drawn in a glass container and left undisturbed for about an hour, four different layers can be seen. A dark clot forms at the bottom (the "black bile"). Above the clot is a layer of red blood cells (the "blood"). Above this is a whitish layer of white blood cells (the "phlegm"). The top layer is clear yellow serum (the "yellow bile").
Types
The ABO blood group system was discovered in the year 1900 by Karl Landsteiner. Jan Janský is credited with the first classification of blood into the four types (A, B, AB, and O) in 1907, which remains in use today. In 1907 the first blood transfusion was performed that used the ABO system to predict compatibility. The first non-direct transfusion was performed on 27 March 1914. The Rhesus factor was discovered in 1937.
Culture and religion
Due to its importance to life, blood is associated with a large number of beliefs. One of the most basic is the use of blood as a symbol for family relationships through birth/parentage; to be "related by blood" is to be related by ancestry or descendence, rather than marriage. This bears closely to bloodlines, and sayings such as "blood is thicker than water" and "bad blood", as well as "Blood brother".
Blood is given particular emphasis in the Islamic, Jewish, and Christian religions, because Leviticus 17:11 says "the life of a creature is in the blood." This phrase is part of the Levitical law forbidding the drinking of blood or eating meat with the blood still intact instead of being poured off.
Mythic references to blood can sometimes be connected to the life-giving nature of blood, seen in such events as childbirth, as contrasted with the blood of injury or death.
Indigenous Australians
In many indigenous Australian Aboriginal peoples' traditions, ochre (particularly red) and blood, both high in iron content and considered Maban, are applied to the bodies of dancers for ritual. As Lawlor states:Lawlor comments that blood employed in this fashion is held by these peoples to attune the dancers to the invisible energetic realm of the Dreamtime. Lawlor then connects these invisible energetic realms and magnetic fields, because iron is magnetic.In many Aboriginal rituals and ceremonies, red ochre is rubbed all over the naked bodies of the dancers. In secret, sacred male ceremonies, blood extracted from the veins of the participant's arms is exchanged and rubbed on their bodies. Red ochre is used in similar ways in less-secret ceremonies. Blood is also used to fasten the feathers of birds onto people's bodies. Bird feathers contain a protein that is highly magnetically sensitive.
European paganism
Among the Germanic tribes, blood was used during their sacrifices; the Blóts. The blood was considered to have the power of its originator, and, after the butchering, the blood was sprinkled on the walls, on the statues of the gods, and on the participants themselves. This act of sprinkling blood was called blóedsian in Old English, and the terminology was borrowed by the Roman Catholic Church becoming to bless and blessing. The Hittite word for blood, ishar was a cognate to words for "oath" and "bond", see Ishara. The Ancient Greeks believed that the blood of the gods, ichor, was a substance that was poisonous to mortals.
As a relic of Germanic Law, the cruentation, an ordeal where the corpse of the victim was supposed to start bleeding in the presence of the murderer, was used until the early 17th century.
Christianity
In Genesis 9:4, God prohibited Noah and his sons from eating blood (see Noahide Law). This command continued to be observed by the Eastern Orthodox Church.
It is also found in the Bible that when the Angel of Death came around to the Hebrew house that the first-born child would not die if the angel saw lamb's blood wiped across the doorway.
At the Council of Jerusalem, the apostles prohibited certain Christians from consuming blood – this is documented in Acts 15:20 and 29. This chapter specifies a reason (especially in verses 19–21): It was to avoid offending Jews who had become Christians, because the Mosaic Law Code prohibited the practice.
Christ's blood is the means for the atonement of sins. Also, "... the blood of Jesus Christ his [God] Son cleanseth us from all sin." (1 John 1:7), "... Unto him [God] that loved us, and washed us from our sins in his own blood." (Revelation 1:5), and "And they overcame him (Satan) by the blood of the Lamb [Jesus the Christ], and by the word of their testimony ..." (Revelation 12:11).
Some Christian churches, including Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, and the Assyrian Church of the East teach that, when consecrated, the Eucharistic wine actually becomes the blood of Jesus for worshippers to drink. Thus in the consecrated wine, Jesus becomes spiritually and physically present. This teaching is rooted in the Last Supper, as written in the four gospels of the Bible, in which Jesus stated to his disciples that the bread that they ate was his body, and the wine was his blood. "This cup is the new testament in my blood, which is shed for you." (Luke 22:20).
Most forms of Protestantism, especially those of a Methodist or Presbyterian lineage, teach that the wine is no more than a symbol of the blood of Christ, who is spiritually but not physically present. Lutheran theology teaches that the body and blood is present together "in, with, and under" the bread and wine of the Eucharistic feast.
Judaism
In Judaism, animal blood may not be consumed even in the smallest quantity (Leviticus 3:17 and elsewhere); this is reflected in Jewish dietary laws (Kashrut). Blood is purged from meat by rinsing and soaking in water (to loosen clots), salting and then rinsing with water again several times. Eggs must also be checked and any blood spots removed before consumption. Although blood from fish is biblically kosher, it is rabbinically forbidden to consume fish blood to avoid the appearance of breaking the Biblical prohibition.
Another ritual involving blood involves the covering of the blood of fowl and game after slaughtering (Leviticus 17:13); the reason given by the Torah is: "Because the life of the animal is [in] its blood" (ibid 17:14). In relation to human beings, Kabbalah expounds on this verse that the animal soul of a person is in the blood, and that physical desires stem from it.
Likewise, the mystical reason for salting temple sacrifices and slaughtered meat is to remove the blood of animal-like passions from the person. By removing the animal's blood, the animal energies and life-force contained in the blood are removed, making the meat fit for human consumption.
Islam
Consumption of food containing blood is forbidden by Islamic dietary laws. This is derived from the statement in the Qur'an, sura Al-Ma'ida (5:3): "Forbidden to you (for food) are: dead meat, blood, the flesh of swine, and that on which has been invoked the name of other than Allah."
Blood is considered unclean, hence there are specific methods to obtain physical and ritual status of cleanliness once bleeding has occurred. Specific rules and prohibitions apply to menstruation, postnatal bleeding and irregular vaginal bleeding. When an animal has been slaughtered, the animal's neck is cut in a way to ensure that the spine is not severed, hence the brain may send commands to the heart to pump blood to it for oxygen. In this way, blood is removed from the body, and the meat is generally now safe to cook and eat. In modern times, blood transfusions are generally not considered against the rules.
Jehovah's Witnesses
Based on their interpretation of scriptures such as Acts 15:28, 29 ("Keep abstaining...from blood."), many Jehovah's Witnesses neither consume blood nor accept transfusions of whole blood or its major components: red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets (thrombocytes), and plasma. Members may personally decide whether they will accept medical procedures that involve their own blood or substances that are further fractionated from the four major components.
Vampirism
Vampires are mythical creatures that drink blood directly for sustenance, usually with a preference for human blood. Cultures all over the world have myths of this kind; for example the 'Nosferatu' legend, a human who achieves damnation and immortality by drinking the blood of others, originates from Eastern European folklore. Ticks, leeches, female mosquitoes, vampire bats, and an assortment of other natural creatures do consume the blood of other animals, but only bats are associated with vampires. This has no relation to vampire bats, which are New World creatures discovered well after the origins of the European myths.
Invertebrates
In invertebrates, a body fluid analogous to blood called hemolymph is found, the main difference being that hemolymph is not contained in a closed circulatory system. Hemolymph may function to carry oxygen, although hemoglobin is not necessarily used. Crustaceans and mollusks use hemocyanin instead of hemoglobin. In most insects, their hemolymph does not contain oxygen-carrying molecules because their bodies are small enough for their tracheal system to suffice for supplying oxygen.
Other uses
Forensic and archaeological
Blood residue can help forensic investigators identify weapons, reconstruct a criminal action, and link suspects to the crime. Through bloodstain pattern analysis, forensic information can also be gained from the spatial distribution of bloodstains.
Blood residue analysis is also a technique used in archeology.
Artistic
Blood is one of the body fluids that has been used in art. In particular, the performances of Viennese Actionist Hermann Nitsch, Istvan Kantor, Franko B, Lennie Lee, Ron Athey, Yang Zhichao, Lucas Abela and Kira O'Reilly, along with the photography of Andres Serrano, have incorporated blood as a prominent visual element. Marc Quinn has made sculptures using frozen blood, including a cast of his own head made using his own blood.
系譜学的
系図学界では、血統という言葉のように、先祖、起源、民族的背景を指して血という言葉が使われる。また、青い血、王家の血筋、混血、親族関係などがある。
こちらも参照
- Autotransfusion/ja
- Blood as food/ja
- Blood pressure/ja
- Blood substitutes/ja ("人工血液")
- Blood test/ja
- Hematology/ja
- 血液恐怖症
- Luminol/ja, 犯罪現場に残された血液の目視検査
- Oct-1-en-3-one/ja (血の"匂い")
- タブーとされる飲食物: 血液