Chronic kidney disease/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "GFRは血清クレアチニンから算出され、1/クレアチニンに比例する。クレアチニンが高いほどGFRは低くなる。GFRは腎機能の一側面、すなわち糸球体(ろ過装置)がどれだけ効率よく働いているかを反映している。正常なGFRは90~120ml/分である。クレアチニンの単位は国によって異なるが、糸球体は腎臓の質量の5%未満であるため、GFRは腎臓の健康と機能の..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "===超音波検査=== 腎臓超音波検査は、慢性腎臓病の診断および予後判定に有用である。基礎にある病理学的変化が糸球体硬化、尿細管萎縮、間質性線維症、炎症のいずれであっても、その結果、皮質のエコー源性が増大することが多い。腎臓のエコー源性は、肝臓または脾臓のエコー源性と関連しているはずである(図22および図23)..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
GFRは血清クレアチニンから算出され、1/クレアチニンに比例する。クレアチニンが高いほどGFRは低くなる。GFRは腎機能の一側面、すなわち糸球体(ろ過装置)がどれだけ効率よく働いているかを反映している。正常なGFRは90~120ml/分である。クレアチニンの単位は国によって異なるが、糸球体は腎臓の質量の5%未満であるため、GFRは腎臓の健康と機能のすべての側面を示すわけではない。GFR値と、体液の状態、ヘモグロビン、カリウム、リン酸塩、副甲状腺ホルモンの値を含む臨床的評価とを組み合わせることで評価することができる。 | GFRは血清クレアチニンから算出され、1/クレアチニンに比例する。クレアチニンが高いほどGFRは低くなる。GFRは腎機能の一側面、すなわち糸球体(ろ過装置)がどれだけ効率よく働いているかを反映している。正常なGFRは90~120ml/分である。クレアチニンの単位は国によって異なるが、糸球体は腎臓の質量の5%未満であるため、GFRは腎臓の健康と機能のすべての側面を示すわけではない。GFR値と、体液の状態、ヘモグロビン、カリウム、リン酸塩、副甲状腺ホルモンの値を含む臨床的評価とを組み合わせることで評価することができる。 | ||
===超音波検査=== | |||
[[Renal ultrasonography/ja|腎臓超音波検査]]は、慢性腎臓病の診断および予後判定に有用である。基礎にある病理学的変化が糸球体硬化、尿細管萎縮、間質性線維症、炎症のいずれであっても、その結果、皮質のエコー源性が増大することが多い。腎臓のエコー源性は、肝臓または脾臓のエコー源性と関連しているはずである(図22および図23)。さらに、腎臓の大きさの減少や皮質の菲薄化もしばしば見られ、特に病気が進行すると顕著である(図24および図25)。しかし、腎臓の大きさは身長と相関があり、背の低い人は腎臓が小さい傾向がある。 | |||
[[Renal ultrasonography| | |||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | <gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | ||
File:Ultrasonography of chronic renal disease caused by glomerulonephritis.jpg| | File:Ultrasonography of chronic renal disease caused by glomerulonephritis.jpg|[[glomerulonephritis/ja|糸球体腎炎]]による慢性腎疾患で、エコー源性の増大と皮質の厚さの減少がみられる。超音波画像上の腎臓の長さの測定値を'+'と破線で示す。 | ||
File:Ultrasonography of kidney with nephrotic syndrome.jpg|[[Nephrotic syndrome]] | File:Ultrasonography of kidney with nephrotic syndrome.jpg|[[Nephrotic syndrome/ja|ネフローゼ症候群]]。皮質と髄質の境界のない高エコー腎。 | ||
File:Ultrasonography of chronic pyelonephritis with reduced kidney size and focal cortical thinning.jpg|[[Chronic pyelonephritis]] | File:Ultrasonography of chronic pyelonephritis with reduced kidney size and focal cortical thinning.jpg|[[Chronic pyelonephritis/ja|慢性腎盂腎炎]]で、腎臓の大きさが縮小し、局所的に皮質が菲薄化している。超音波画像上の腎臓の長さの測定値を'+'と破線で示す。 | ||
File:Ultrasonography of end-stage chronic kidney disease.jpg| | File:Ultrasonography of end-stage chronic kidney disease.jpg|慢性腎臓病末期で、エコーが亢進し、腎実質と腎洞の区別がなく、腎臓の大きさが縮小している。超音波画像上の腎臓の長さの測定値を'+'と破線で示す。 | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 12:42, 26 February 2024
| 慢性腎臓病 | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 慢性腎臓病、腎不全、腎機能障害 |
 | |
| 慢性腎不全患者の腎臓のイラスト | |
| Specialty | Nephrology/ja |
| Symptoms | 初期:なし 後期:下肢腫脹、疲労感、嘔吐、食欲不振、錯乱 |
| Complications | 心臓病, 高血圧, anemia/ja |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Causes | 糖尿病, high blood pressure/ja, glomerulonephritis/ja, polycystic kidney disease/ja |
| Diagnostic method | Blood tests/ja, urine tests/ja |
| Treatment | 血圧や血糖値を管理し、コレステロールを下げる医薬品、腎代替療法、腎移植などがある。 |
| Frequency | 753 million (2016) |
| Deaths | 1.2 million (2015) |
慢性腎臓病(CKD)は腎臓病の一種であり、数ヶ月から数年かけて徐々に腎臓の機能が低下していく。初期には一般に症状は見られないが、後に脚のむくみ、疲労感、嘔吐、食欲不振、錯乱などの症状が現れることがある。合併症は腎臓のホルモン機能障害に関係することがあり、(時系列順に)高血圧(しばしばレニン-アンジオテンシン系の活性化に関係する)、骨疾患、貧血などがある。さらに、CKD患者は死亡や入院のリスクを高める心血管系疾患合併症を著しく増加させる。
慢性腎臓病の原因には、糖尿病、高血圧、糸球体腎炎、多発性嚢胞腎などがある。危険因子には慢性腎臓病の家族歴が含まれる。診断は、推定糸球体濾過量(eGFR)を測定する血液検査と、アルブミンを測定する尿検査によって行われる。腎超音波検査または腎生検を行って、根本的な原因を特定することもある。いくつかの重症度ベースの病期分類システムが使用されている。
リスクのある人はスクリーニングを受けることが推奨される。初期治療には、血圧、血糖、コレステロールを低下させる医薬品が含まれる。アンジオテンシン変換酵素阻害薬(ACEI)またはアンジオテンシンII受容体拮抗薬(ARB)は、腎疾患の進行を遅らせ、心臓病のリスクを低下させるため、一般に血圧コントロールの第一選択薬である。ループ利尿薬は、浮腫をコントロールし、必要に応じてさらに血圧を下げるために使用される。非ステロイド性抗炎症薬(NSAIDs)は避けるべきである。その他の推奨される対策としては、活動的に過ごすこと、および塩分を控えた食事や適切な量のタンパク質摂取など、特定の食生活の改善が挙げられる。貧血や骨疾患の治療も必要となる。重症の場合は、血液透析、腹膜透析、または腎移植が必要である。
慢性腎臓病は、2016年に世界で7億5300万人(女性4億1700万人、男性3億3600万人)が罹患した。2015年には120万人が死亡し、1990年の40万9000人から増加した。最も多くの死亡に寄与している原因は高血圧で55万人、次いで糖尿病41万8000人、糸球体腎炎23万8000人である。
兆候と症状

CKDは初期には症状がなく、通常、定期的なスクリーニング血液検査で血清クレアチニンの増加、または蛋白尿のいずれかによって発見される。腎機能が低下すると、さらに不快な症状が現れることがある:
- レニン・アンジオテンシン系を介して腎臓で作られる血管作動性ホルモンの産生と体液過多により血圧が上昇し、高血圧と心不全の発症リスクが高まる。CKD患者は一般集団よりもアテローム性動脈硬化症を発症しやすく、その結果として心血管疾患を発症する可能性が高いが、この影響は少なくとも部分的には尿毒症毒素によって媒介されている可能性がある。CKDと心血管疾患の両方を有する人の予後は、心血管疾患のみを有する人よりも有意に悪い。
- 尿素が蓄積し、アゾ血症、最終的には尿毒症(嗜眠から心膜炎、脳症に至る症状)に至る。尿素は全身濃度が高いため、エクリン汗中に高濃度で排泄され、汗が蒸発する際に皮膚上で結晶化する(「尿毒症性霜」)。
- カリウムが血液中に蓄積する(倦怠感や致死的な不整脈を含む様々な症状を伴う高カリウム血症)。高カリウム血症は通常、糸球体濾過量が20~25mL/分/1.73m2未満に低下するまで発症しない。CKDにおける高カリウム血症は、酸性血症(カリウムの細胞外移行を引き起こす)やインスリンの不足によって悪化する。
- |体液過多の症状は、軽度の浮腫から生命を脅かす肺水腫まで様々である。
- 高リン血症は、腎におけるリン酸排泄不良から生じ、血管石灰化を引き起こすことによって心血管リスクの増加に寄与する。循環中の線維芽細胞増殖因子23(FGF-23)濃度は、腎臓のリン酸排泄能が低下するにつれて徐々に上昇し、CKD患者では左室肥大と死亡率上昇の一因となる可能性がある。
- 低カルシウム血症は、1,25ジヒドロキシビタミンD3の欠乏(高いFGF-23と腎量の減少によって引き起こされる)と副甲状腺ホルモンの作用に対する抵抗性から生じる。骨細胞は、酵素1-α-ヒドロキシラーゼ(25-ヒドロキシコレカルシフェロールの1,25-ジヒドロキシビタミンD3への変換を担う)の強力な阻害因子であるFGF-23の産生増加を担っている。その後、これは二次性副甲状腺機能亢進症、腎性骨異栄養症、および心機能をさらに損なう血管石灰化へと進行する。極端な結果として、石灰沈着症というまれな病態が起こる。
- 1) カルシウム、リン(リン酸)、副甲状腺ホルモン、またはビタミンDの代謝に異常を引き起こ可能性のある、ミネラルおよび骨代謝の変化。2) 骨のターンオーバー、骨のミネラル化、体積、線成長、または強度の異常(腎性骨異栄養症)3)血管または他の軟部組織の石灰化。CKD-腎・骨障害は、不良な転帰と関連している。
- 代謝性アシドーシスは、近位尿細管の細胞から十分なアンモニアを生成する能力の低下から起こる可能性がある。
- 貧血は一般的であり、特に血液透析を必要とする患者に多い。原因は多因子性であるが、炎症の亢進、エリスロポエチンの減少、骨髄抑制につながる高尿酸血症などがある。低増殖性貧血は、腎臓によるエリスロポエチンの産生が不十分なために起こる。
- 後期には悪液質が発現し、意図しない体重減少、筋肉の衰弱、脱力感、食欲不振をきたすことがある。
- CKD患者における認知機能低下は、研究文献で明らかにされている新たな症状である。現在の研究では、CKD患者では認知機能の低下や認知症の可能性が35〜40%高いことが示唆されている。この関係は各患者のCKDの重症度に依存するが、新たな文献によると、CKDのすべての段階にある患者はこれらの認知問題を発症するリスクが高い。
- 性機能障害はCKD患者では男女ともに非常に一般的である。 男性の大部分は性衝動の減退、勃起が困難、オーガズムに達することが困難であり、その問題は加齢とともに悪化する。 ほとんどの女性は性的興奮に問題があり、月経痛やセックスの実行や楽しみの問題が一般的である。
原因
2015年現在、CKDの最も一般的な3つの原因は、頻度の高い順に糖尿病、高血圧、糸球体腎炎である。高血圧の成人の約5人に1人、糖尿病の成人の3人に1人がCKDである。 原因不明の場合は特発性と呼ばれる。
解剖学的部位別
- 血管疾患には、両側腎動脈狭窄症などの大血管疾患と、虚血性腎症、溶血性尿毒症症候群、血管炎などの小血管疾患がある。
- 糸球体疾患は多様なグループからなり、以下のように分類される:
- 巣状分節性糸球体硬化症やIgA腎症(または腎炎)などの一次性糸球体疾患。
- 糖尿病性腎症やループス腎炎などの二次性糸球体疾患。
- 尿細管間質性疾患には、薬物および毒物誘発性の慢性尿細管間質性腎炎、および逆流性腎症が含まれる。
- 両側の腎結石や前立腺の前立腺肥大症に代表される閉塞性腎症;まれに、腎臓に感染した蟯虫が閉塞性腎症を引き起こすことがある。
その他
- 多発性嚢胞腎や17q12微小欠失症候群などの遺伝性先天性疾患。
- メソアメリカ腎症は「農業腎症とも呼べる新しい腎臓病」である。中米の男性労働者の間で、主にエルサルバドルとニカラグアの低地のサトウキビ畑で、メソアメリカ腎症と呼ばれるCKDの新規症例が多く、今のところ原因不明であることが指摘されている。平均気温約36 °C(96 °F)の高温下での長時間の出来高払い労働による熱ストレスが疑われ、農業化学物質も同様である。
診断

CKDの診断は、主に病歴、診察、および血清クレアチニン値の測定と組み合わせた尿検査に基づく(上記参照)。CKDと急性腎障害(AKI)の鑑別は、AKIが可逆的である可能性があるため重要である。CKDとAKIの鑑別に役立つ診断の手がかりの1つは、血清クレアチニンの急激な上昇(数日から数週間)とは対照的に、血清クレアチニンの緩やかな上昇(数ヵ月または数年間)である。多くのCKD患者では、以前に腎臓病を患っていたことや他の基礎疾患が既に知られている。原因不明のCKDも相当数存在する。
スクリーニング
CKDの症状も危険因子もない人のスクリーニングは推奨されない。スクリーニングを受けるべき人は、高血圧または心血管疾患の既往のある人、糖尿病または著しい肥満のある人、60歳以上の人、アフリカ系アメリカ人の祖先を持つ人、過去に腎臓病の既往のある人、透析を必要とする腎臓病を患った親族を持つ人などである。
スクリーニングには、血清クレアチニン値から推定GFR(eGFR)を算出すること、朝一番の尿検体で尿中アルブミン/クレアチニン比(ACR)を測定すること(これは尿中のアルブミンというタンパク質の量を反映する)、さらに尿潜血検査で血尿を調べることが含まれる。
GFRは血清クレアチニンから算出され、1/クレアチニンに比例する。クレアチニンが高いほどGFRは低くなる。GFRは腎機能の一側面、すなわち糸球体(ろ過装置)がどれだけ効率よく働いているかを反映している。正常なGFRは90~120ml/分である。クレアチニンの単位は国によって異なるが、糸球体は腎臓の質量の5%未満であるため、GFRは腎臓の健康と機能のすべての側面を示すわけではない。GFR値と、体液の状態、ヘモグロビン、カリウム、リン酸塩、副甲状腺ホルモンの値を含む臨床的評価とを組み合わせることで評価することができる。
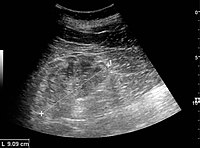
超音波検査
腎臓超音波検査は、慢性腎臓病の診断および予後判定に有用である。基礎にある病理学的変化が糸球体硬化、尿細管萎縮、間質性線維症、炎症のいずれであっても、その結果、皮質のエコー源性が増大することが多い。腎臓のエコー源性は、肝臓または脾臓のエコー源性と関連しているはずである(図22および図23)。さらに、腎臓の大きさの減少や皮質の菲薄化もしばしば見られ、特に病気が進行すると顕著である(図24および図25)。しかし、腎臓の大きさは身長と相関があり、背の低い人は腎臓が小さい傾向がある。
-
糸球体腎炎による慢性腎疾患で、エコー源性の増大と皮質の厚さの減少がみられる。超音波画像上の腎臓の長さの測定値を'+'と破線で示す。
-
ネフローゼ症候群。皮質と髄質の境界のない高エコー腎。
-
慢性腎盂腎炎で、腎臓の大きさが縮小し、局所的に皮質が菲薄化している。超音波画像上の腎臓の長さの測定値を'+'と破線で示す。
-
慢性腎臓病末期で、エコーが亢進し、腎実質と腎洞の区別がなく、腎臓の大きさが縮小している。超音波画像上の腎臓の長さの測定値を'+'と破線で示す。
Additional imaging
Additional tests may include nuclear medicine MAG3 scan to confirm blood flow and establish the differential function between the two kidneys. Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scans are also used in kidney imaging; with both MAG3 and DMSA being used chelated with the radioactive element technetium-99.
Stages
| Chronic kidney disease (CKD) staging - CKD G1-5 A1-3 glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACR | ||||||
| A1 | A2 | A3 | ||||
| Normal to mildly increased | Moderately increased | Severely increased | ||||
| <30 | 30–300 | >300 | ||||
| G F R | ||||||
| G1 | Normal | ≥ 90 | 1 if kidney damage present | 1 | 2 | |
| G2 | Mildly decreased | 60–89 | 1 if kidney damage present | 1 | 2 | |
| G3a | Mildly to moderately decreased | 45–59 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| G3b | Moderately to severely decreased | 30–44 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| G4 | Severely decreased | 15–29 | 3 | 4+ | 4+ | |
| G5 | Kidney failure | <15 | 4+ | 4+ | 4+ | |
| Numbers 1–4 indicates risk of progression as well as frequency of monitoring (number of times a year). Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes - KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease | ||||||
A glomerular filtration rate (GFR) ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 is considered normal without chronic kidney disease if there is no kidney damage present.
Kidney damage is defined signs of damage seen in blood, urine, or imaging studies which includes lab albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR) ≥ 30. All people with a GFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 for 3 months are defined as having chronic kidney disease.
Protein in the urine is regarded as an independent marker for worsening of kidney function and cardiovascular disease. Hence, British guidelines append the letter "P" to the stage of chronic kidney disease if protein loss is significant.
- Stage 1: Slightly diminished function; kidney damage with normal or relatively high GFR (≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2) and persistent albuminuria. Kidney damage is defined as pathological abnormalities or markers of damage, including abnormalities in blood or urine tests or imaging studies.
- Stage 2: Mild reduction in GFR (60–89 mL/min/1.73 m2) with kidney damage. Kidney damage is defined as pathological abnormalities or markers of damage, including abnormalities in blood or urine tests or imaging studies.
- Stage 3: Moderate reduction in GFR (30–59 mL/min/1.73 m2):. British guidelines distinguish between stage 3A (GFR 45–59) and stage 3B (GFR 30–44) for purposes of screening and referral.
- Stage 4: Severe reduction in GFR (15–29 mL/min/1.73 m2)Preparation for kidney replacement therapy.
- Stage 5: Established kidney failure (GFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m2), permanent kidney replacement therapy, or end-stage kidney disease.
The term "non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease" (NDD-CKD) is a designation used to encompass the status of those persons with an established CKD who do not yet require the life-supporting treatments for kidney failure known as kidney replacement therapy (RRT, including maintenance dialysis or kidney transplantation). The condition of individuals with CKD, who require either of the two types of kidney replacement therapy (dialysis or transplant), is referred to as the end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). Hence, the start of the ESKD is practically the irreversible conclusion of the NDD-CKD. Even though the NDD-CKD status refers to the status of persons with earlier stages of CKD (stages 1 to 4), people with advanced stage of CKD (stage 5), who have not yet started kidney replacement therapy, are also referred to as NDD-CKD.
Management
Apart from controlling other risk factors, the goal of therapy is to slow down or halt the progression of CKD. Control of blood pressure and treatment of the original disease are the broad principles of management.
Blood pressure
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs) are recommended as first-line agents since they have been found to slow the decline of kidney function, relative to a more rapid decline in those not on one of these agents. They have also been found to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, and death from cardiovascular disease when compared to placebo in individuals with CKD. ACEIs may be superior to ARBs for protection against progression to kidney failure and death from any cause in those with CKD.
Other measures
- Aggressive treatment of high blood lipids is recommended.
- A low-protein, low-salt diet may result in slower progression of CKD and reduction in proteinuria as well as controlling symptoms of advanced CKD to delay dialysis start. A tailored low-protein diet, designed for low acidity, may help prevent damage to kidneys for people with CKD. Additionally, controlling salt ingestion helps to decrease the incidence of coronary heart disease, lowering blood pressure and reducing albuminuria.
- Anemia – A target hemoglobin level of 100-120 g/L is recommended; raising hemoglobin levels to the normal range has not been found to be of benefit.
- Guidelines recommend treatment with parenteral iron prior to treatment with erythropoietin.
- Replacement of erythropoietin is often necessary in people with advanced disease.
- It is unclear if androgens improve anemia.
- Calcitriol is recommended for vitamin D deficiency and control of metabolic bone disease.
- Phosphate binders are used to control the serum phosphate levels, which are usually elevated in advanced chronic kidney disease.
- Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and zinc may improve sexual dysfunction in men.
Lifestyle interventions
Weight loss
Obesity may have a negative impact in CKD, increasing the risk of disease progression to ESKD or kidney failure compared to controls with healthy weight, and when in advanced stages also may hinder people's eligibility to kidney transplantation. For example, the consumption of high calorie and high fructose beverages can make an individual "60% more likely to develop CKD".
Weight management interventions in overweight and obese adults with CKD (of various stages) have been studied to assess its safety and efficacy. A recent systematic review collected evidence from 17 studies which evaluated lifestyle (including dietary, physical activity/exercise, or behavioural strategies used in isolation or in combination), pharmacological (used to reduce absorption or suppress appetite) and surgical interventions. The review concluded that lifestyle interventions may provide some health benefits, namely improving body weight, low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and diastolic blood pressure (DBP), when compared to usual care or controls. Whether these benefits extend to help reducing cardiovascular events, kidney function and risk of death is uncertain. These conclusions were based on very low quality of evidence, so future robust studies are needed. Thus, it is recommended that weight management interventions should be individualised, according to a thorough patients' assessment regarding clinical condition, motivations and preferences.
Dietary salt intake
High dietary sodium intake may increase the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. The effect of dietary restriction of salt in foods has been investigated in people with chronic kidney disease. A 2021 Cochrane review of controlled trials in people with CKD at any stage, including those on dialysis, found high-certainty evidence that reduced salt intake may help to lower both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, as well as albuminuria. However, there was also moderate certainty evidence that some people may experience hypotensive symptoms, such as dizziness, following sudden sodium restriction. It is unclear whether this affects the dosage required for anti-hypertensive medications. The effect of salt restriction on extracellular fluid, oedema, and total body weight reduction was also uncertain.
Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation
In people with CKD who require hemodialysis, there is a risk that vascular blockage due to clotting, may prevent dialysis therapy from being possible. Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to the production of eicosanoid molecules that reduce clotting. However, a Cochrane review in 2018 did not find clear evidence that omega-3 supplementation has any impact on the prevention of vascular blockage in people with CKD. There was also moderate certainty that supplementation did not prevent hospitalisation or death within a 12-month period.
Protein supplementation
There is moderate-certainty evidence that regular consumption of oral protein-based nutritional supplements may increase serum albumin levels slightly in people with CKD, especially among those requiring hemodialysis or who are malnourished. Pre-albumin levels and mid-arm circumference measurements may also be increased following supplementation, though the certainty of evidence is low. Despite possible improvement in these indicators of nutritional status, it is not certain that protein supplements affect quality of life, life expectancy, inflammation or body composition.
Iron supplementation
A Cochrane review of controlled trials comparing intravenous (IV) iron therapy with oral iron supplements, found low-certainty evidence that people receiving IV-iron treatment were 1.71 times as likely to reach their target hemoglobin levels. Overall, hemoglobin was 0.71g/dl higher than those treated with oral iron supplements. Iron stores in the liver, estimated by serum ferritin, were also 224.84 µg/L higher in those receiving IV-iron. However, there was also low-certainty evidence that allergic reactions were more likely following IV-iron therapy. It was unclear whether type of iron therapy administration affects the risk of death from any cause, including cardiovascular, nor whether it may alter the number of people who may require a blood transfusion or dialysis.
Sleep
People with CKD experience sleep disorders, thus not being able to get quality sleep. There are several strategies that could help, such as relaxation techniques, exercise, acupressure and medication:
- Exercise: weak evidence demonstrates that exercise may be helpful with sleep regulation. Nevertheless, exercise possibly decreases fatigue and depression in people with CKD.
- Acupressure: evidence suggests that this technique may have slight effects on latency and sleep duration, as well as on fatigue reduction, although these results are not reliable due to the diversity of conclusions in several articles.
Despite all the available options studied so far, evidence shows that none of them is effective in the treatment of sleep disorders. This means that we are not able to conclude which is the best guidance to improve sleep quality in this type of population.
eHealth interventions
There is currently limited evidence suggesting that eHealth interventions may improve dietary sodium intake and fluid management for people with chronic kidney disease (CKD). The findings are based on low certainty evidence of 43 studies. So, more large and higher quality research studies are needed to understand the impact of eHealth on the health of people with CKD.
Referral to a nephrologist
Guidelines for referral to a nephrologist vary between countries. Most agree that nephrology referral is required by Stage 4 CKD (when eGFR/1.73m2 is less than 30 mL/min; or decreasing by more than 3 mL/min/year).
It may also be useful at an earlier stage (e.g. CKD3) when urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio is more than 30 mg/mmol, when blood pressure is difficult to control, or when hematuria or other findings suggest either a primarily glomerular disorder or secondary disease amenable to specific treatment. Other benefits of early nephrology referral include proper education regarding options for kidney replacement therapy as well as pre-emptive transplantation, and timely workup and placement of an arteriovenous fistula in those people with chronic kidney disease opting for future hemodialysis.
Renal replacement therapy
At stage 5 CKD, kidney replacement therapy is usually required, in the form of either dialysis or a kidney transplant.
In CKD numerous uremic toxins accumulate in the blood. Even when ESKD (largely synonymous with CKD5) is treated with dialysis, the toxin levels do not go back to normal as dialysis is not that efficient. Similarly, after a kidney transplant, the levels may not go back to normal as the transplanted kidney may not work 100%. If it does, the creatinine level is often normal. The toxins show various cytotoxic activities in the serum and have different molecular weights, and some of them are bound to other proteins, primarily to albumin. Uremic toxins are classified into three groups as small water-soluble solutes, middle molecular-weight solutes, and protein-bound solutes. Hemodialysis with high-flux dialysis membrane, long or frequent treatment, and increased blood/dialysate flow has improved removal of water-soluble small molecular weight uremic toxins. Middle molecular weight molecules are removed more effectively with hemodialysis using a high-flux membrane, hemodiafiltration and hemofiltration. However, conventional dialysis treatment is limited in its ability to remove protein-bound uremic toxins.
Prognosis
CKD increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, and people with CKD often have other risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood lipids. The most common cause of death in people with CKD is cardiovascular disease rather than kidney failure.
Chronic kidney disease results in worse all-cause mortality (the overall death rate) which increases as kidney function decreases. The leading cause of death in chronic kidney disease is cardiovascular disease, regardless of whether there is progression to stage 5.
While kidney replacement therapies can maintain people indefinitely and prolong life, the quality of life is negatively affected. Kidney transplantation increases the survival of people with stage 5 CKD when compared to other options; however, it is associated with an increased short-term mortality due to complications of the surgery. Transplantation aside, high-intensity home hemodialysis appears to be associated with improved survival and a greater quality of life, when compared to the conventional three-times-a-week hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
People with ESKD are at increased overall risk for cancer. This risk is particularly high in younger people and gradually diminishes with age. Medical specialty professional organizations recommend that physicians do not perform routine cancer screening in people with limited life expectancies due to ESKD because evidence does not show that such tests lead to improved outcomes.
In children, growth failure is a common complication from CKD. Children with CKD will be shorter than 97% of children the same age and sex. This can be treated with additional nutritional support, or medication such as Growth hormone
Survival without dialysis
In a review from 2022 survival and quality of life was investigated in patients who had decided against dialysis treatment when reaching end-stage chronic kidney disease. 41 longitudinal studies (cohort studies) with a total of 5.102 patients were evaluated. The mean age of patients per study was 60 – 87 years. The mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) at the time of decision per study was 7 – 19 ml/min pro 1,73 m².
The median survival per study was:
- all 41 studies: 1 – 41 months
- studies from continental Europe (11 studies, 1.021 patients): 6 – 37 months
- studies from Asia (7 studies, 1.147 patients): 7 – 41 months
- age 70–79 years (9 studies, 607 patients): 7 – 41 months
- age 80+ (25 studies, 3.186 patients): 1 – 37 months
The longest survival times per study from the three studies with the highest median were 82, 79, and 75 months.
During the observation periods of 8 to 24 months mental well-being improved, and physical well-being and quality of life were largely stable until the late phase of the illness.
The authors of the review reached the following conclusion: “Our findings challenge the common misconception that the only alternative to dialysis for many patients with advanced CKD is no care or death.”
In a review from 2021 25 studies were analyzed that had compared survival times and quality of life between patients with and without dialysis. Survival was generally longer with dialysis, but from the age of 80 and in elderly patients with comorbidities this effect became uncertain. Concerning quality of life there was a trend that patients without dialysis had an advantage.
Epidemiology
About one in ten people have chronic kidney disease. In Canada 1.9 to 2.3 million people were estimated to have CKD in 2008. CKD affected an estimated 16.8% of U.S. adults aged 20 years and older in the period from 1999 to 2004. In 2007 8.8% of the population of Great Britain and Northern Ireland had symptomatic CKD.
Chronic kidney disease was the cause of 956,000 deaths globally in 2013, up from 409,000 deaths in 1990.
Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology
The cause of chronic kidney disease is in some cases not known; it is referred to as chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology (CKDu). 2020年現在[update] a rapidly progressive chronic kidney disease, unexplained by diabetes and hypertension, had increased dramatically in prevalence over a few decades in several regions in Central America and Mexico, a CKDu referred to as the Mesoamerican nephropathy (MeN). It was estimated in 2013 that at least 20,000 men had died prematurely, some in their 20s and 30s; a figure of 40,000 per year was estimated in 2020. In some affected areas CKD mortality was five times the national rate. MeN primarily affects men working as sugarcane labourers. The cause is unknown, but in 2020 the science found a clearer connection between heavy labour in high temperatures and incidence of CKDu; improvements such as regular access to water, rest and shade, can significantly decrease the potential CKDu incidence. CKDu also affects people in Sri Lanka where it is the eighth largest cause of in-hospital mortality.
Although CKDu was first documented among sugar cane workers in Costa Rica in the 1970s, it may well have affected plantation labourers since the introduction of sugar cane farming to the Caribbean in the 1600s. In colonial times the death records of slaves on sugar plantations was much higher than for slaves forced into other labour.
Race
African, Hispanics, and South Asians, particularly those from Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, and India, are at high risk of developing CKD. Africans are at greater risk due to the number of people affected with hypertension among them. As an example, 37% of ESKD cases in African Americans can be attributed to high blood pressure, compared with 19% among Caucasians. Treatment efficacy also differs between racial groups. Administration of antihypertensive drugs generally halts disease progression in white populations but has little effect in slowing kidney disease among black people, and additional treatment such as bicarbonate therapy is often required. While lower socioeconomic status contributes to the number of people affected with CKD, differences in the number of people affected by CKD are still evident between Africans and Whites when controlling for environmental factors.
Society and culture
The International Society of Nephrology is an international body representing specialists in kidney diseases.
United States
- The National Kidney Foundation is a national organization representing people with chronic kidney diseases and professionals who treat kidney diseases.
- The American Kidney Fund is a national nonprofit organization providing treatment-related financial assistance to one of every five people undergoing dialysis each year.
- The Renal Support Network is a nonprofit, patient-focused, patient-run organization that provides non-medical services to those affected by CKD.
- The American Association of Kidney Patients is a nonprofit, patient-centric group focused on improving the health and well-being of CKD and people undergoing dialysis .
- The Renal Physicians Association is an association representing nephrology professionals.
United Kingdom
It was said to be costing the National Health Service about £1.5 billion a year in 2020.
Kidney Care UK and The UK National Kidney Federation represent people with chronic kidney disease. The Renal Association represents Kidney physicians and works closely with the National Service Framework for kidney disease.
Australia
Kidney Health Australia serves that country.
Other animals
Dogs
The incidence rate of CKD in dogs was 15.8 cases per 10,000 dog years at risk. The mortality rate of CKD was 9.7 deaths per 10,000 dog years at risk. (rates developed from a population of 600,000 insured Swedish dogs; one dog year at risk is one dog at risk for one year)The breeds with the highest rates were the Bernese mountain dog, miniature schnauzer and boxer. The Swedish elkhound, Siberian husky and Finnish spitz were the breeds with the lowest rates.
Cats
Cats with chronic kidney disease may have a buildup of waste products usually removed by the kidneys. They may appear lethargic, unkempt, and lose weight, and may have hypertension. The disease can prevent appropriate concentration of urine, causing cats to urinate greater volumes and drink more water to compensate. Loss of important proteins and vitamins through urine may cause abnormal metabolism and loss of appetite. The buildup of acids within blood can result in blood acidifcation, which can lead to anemia, pink or whitish gums, and lethargy.
Research
Currently, several compounds are in development for the treatment of CKD. These include the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) olmesartan medoxomil; and sulodexide, a mixture of low molecular weight heparin and dermatan sulfate.
Unbiased research with complete reporting is required to determine the safety and effectiveness of acupuncture to treat depression, pain, sleep problems, and uraemic pruritus in people who are undergoing dialysis treatments on a regular basis.
外部リンク
- Dialysis Complications of Chronic Renal Failure at eMedicine
- Chronic Renal Failure Information Archived 2013-03-15 at the Wayback Machine from Great Ormond Street Hospital
- [./Https://www.mybestpdf.com/world-diabetes-day-2022/ How to Prevent Chronic Kidney Disease n World Diabetes Day 2022]