ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4阻害剤
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor/ja
ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ4阻害薬(DPP-4 inhibitorまたはgliptins)は、経口血糖降下薬の一種であり、ブロック薬である。酵素ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4(DPP-4)を阻害する。これらは2型糖尿病の治療に使用できる。
このクラスの最初の薬物であるシタグリプチンは、2006年にFDAによって承認された。
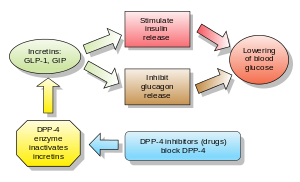
グルカゴンは血糖値を上昇させ、DPP-4阻害薬はグルカゴンと血糖値を低下させる。DPP-4阻害薬の機序は、インクレチンレベル(GLP-1とGIP)を増加させ、グルカゴン放出を阻害し、その結果、インスリン分泌を増加させ、胃排出を減少させ、血糖値を低下させる。
2018年のメタアナリシスでは、2型糖尿病患者の全死亡、心血管死亡、心筋梗塞、脳卒中に対するDPP-4阻害薬の好ましい効果は認められなかった。
事例
このクラスに属する薬物は以下の通りである:
- シタグリプチン (FDAは2006年に承認、Merck & Co.がJanuvia/jaとして販売している)
- ビルダグリプチン(2007年EU承認、EUではNovartisがGalvusとして販売している)
- サキサグリプチン(2009年FDA承認、オングリザとして販売されている)
- リナグリプチン(2011年FDA承認、Eli Lilly and CompanyとBoehringer Ingelheimによりトラジェンタとして販売されている)
- ジェミグリプチン(2012年に韓国で承認、LGライフサイエンスがゼミグロとして販売されている)
- アナグリプチン(日本では2012年にスイニーとして承認され、株式会社三和化学研究所と興和株式会社が販売している)
- テネリグリプチン(日本では2012年にテネリアとして承認されている)
- アログリプチン(ネシーナ/ビピディアとして2013年にFDA承認、武田薬品工業が販売)
- トレラグリプチン(日本では2015年にザファテック/ウェディカとして承認されている)
- オマリグリプチン(MK-3102)(日本では2015年にマリゼブとして承認、Merck & Coが開発、オマリグリプチンは週1回の治療として使用可能であり、ベース試験および延長試験を通じて全般的に良好な忍容性が示された。)
- エボグリプチン(韓国ではスガノン/エボジンとして承認されている)
- ゴソグリプチン(ロシアではサテレックスとして承認されている)
- デュトグリプチン(PHX- 1149遊離塩基、Phenomix Corporationが開発中)、フェーズIII
- レタグリプチン(SP-2086)は中国で承認されている。
- Denagliptin/ja
- Cofrogliptin/ja (HSK- 7653, compound 2)
- Fotagliptin/ja
- Prusogliptin/ja
DPP-4を阻害する可能性のある他の化学物質には以下のものがある:
副作用
すでにスルホニルウレアを服用している場合、DPP-4薬物クラスの薬を服用すると低血糖のリスクが高まる。
副作用には鼻咽頭炎、頭痛、吐き気、心不全、過敏症、皮膚反応などがある。
米国食品医薬品局(FDA)は、2型糖尿病治療薬であるシタグリプチン、サキサグリプチン、リナグリプチン、アログリプチンが、関節痛を引き起こし、重篤な障害を引き起こす可能性があると警告している。FDAは、ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4(DPP-4)阻害薬と呼ばれるこのクラスの薬物のラベルに、このリスクに関する警告と注意を新たに追加した。しかし、DPP-4阻害薬使用者における関節リウマチのリスクを評価した研究では、結論が出ていない。
2014年のレビューで、サキサグリプチンおよびアログリプチンによる心不全のリスク増加が発見され、FDAは2016年に関連薬物のラベルに警告を追加した。
A 2018 meta analysis showed that use of DPP-4 inhibitors was associated with a 58% increased risk of developing acute pancreatitis compared with placebo or no treatment.
A 2018 observational study suggested an elevated risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease (specifically, ulcerative colitis), reaching a peak after three to four years of use and decreasing after more than four years of use.
A 2020 Cochrane systematic review did not find enough evidence of reduction of all-cause mortality, serious adverse events, cardiovascular mortality, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke or end-stage renal disease when comparing metformin monotherapy to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Cancer
In response to a report of precancerous changes in the pancreases of rats and organ donors treated with the DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin, the United States FDA and the European Medicines Agency each undertook independent reviews of all clinical and preclinical data related to the possible association of DPP-4 inhibitors with pancreatic cancer. In a joint letter to the New England Journal of Medicine, the agencies stated that they had not yet reached a final conclusion regarding a possible causative relationship.
A 2014 meta-analysis found no evidence for increased pancreatic cancer risk in people treated with DPP-4 inhibitors, but owing to the modest amount of data available, was not able to completely exclude possible risk.
Combination drugs
Some DPP-4 inhibitor drugs have received approval from the FDA to be used with metformin concomitantly with additive effect to increase the level of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) which also decreases hepatic glucose production.
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor/ja(1 February 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Lua error in Module:Itemnumber at line 91: attempt to concatenate local 'qid' (a nil value). |