Renin–angiotensin system/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "これらの作用は直接的に血圧を上昇させるように作用し、心房性ナトリウム利尿ペプチド(ANP)によって対抗される。" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "==胎児レニン-アンジオテンシン系== {{Anchor|Fetal renin–angiotensin system}} 胎児では、レニン-アンジオテンシン系は主にナトリウム喪失系であり、アンジオテンシンIIはアルドステロンレベルにほとんど影響を及ぼさない。胎児ではレニンレベルは高いが、アンジオテンシンIIレベルは有意に低い。これは、肺血流が限られているため、ACE(肺循環に..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
これらの作用は直接的に血圧を上昇させるように作用し、[[atrial natriuretic peptide/ja|心房性ナトリウム利尿ペプチド]](ANP)によって対抗される。 | これらの作用は直接的に血圧を上昇させるように作用し、[[atrial natriuretic peptide/ja|心房性ナトリウム利尿ペプチド]](ANP)によって対抗される。 | ||
==局所レニン-アンジオテンシン系== | |||
==Local renin–angiotensin systems | {{Anchor|Local renin–angiotensin systems}} | ||
局所的に発現するレニン-アンジオテンシン系は、[[kidney/ja|腎臓]]、[[adrenal gland/ja|副腎]]、[[heart/ja|心臓]]、[[vasculature/ja|血管系]]、[[nervous system/ja|神経系]]などの多くの組織で見つかっており、全身性のレニン-アンジオテンシン系と関連して、あるいは独立して、[[Local blood flow regulation/ja|局所的な心血管系の調節]]や非心血管系の機能など、様々な機能を持っている。腎臓以外では、レニンは主に循環から回収されるが、一部の組織では局所的に分泌されることがある。その前駆体であるプロレニンは組織で高発現しており、循環プロレニンの半分以上は腎臓外由来であるが、レニンの前駆体としての役割以外の生理学的役割はまだ不明である。レニンとともにアンジオテンシンIを形成し、局所に発現している[[angiotensin-converting enzyme/ja|アンジオテンシン変換酵素]]、[[chymase/ja|キマーゼ]]または他の酵素によってアンジオテンシンIIに変換される。この過程は細胞内でも間質でも起こりうる。 | |||
副腎では、[[aldosterone/ja|アルドステロン]]分泌の[[paracrine/ja|パラクリン]]制御に関与している可能性が高く、心臓と血管系では、リモデリングまたは血管緊張に関与している可能性があり、循環系RASからほとんど独立している[[脳]]では、局所血圧調節に関与している可能性がある。さらに、[[central nervous system/ja|中枢性]]と[[peripheral nervous system/ja|末梢性]]の両方の神経系が交感神経伝達のためにアンジオテンシンを使用することができる。その他の発現場所としては、生殖器系、皮膚、消化器などがある。全身系を対象とした医薬品は、これらの局所系の発現に、有益または不利に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。 | |||
==胎児レニン-アンジオテンシン系== | |||
==Fetal renin–angiotensin system | {{Anchor|Fetal renin–angiotensin system}} | ||
[[fetus/ja|胎児]]では、レニン-アンジオテンシン系は主にナトリウム喪失系であり、アンジオテンシンIIはアルドステロンレベルにほとんど影響を及ぼさない。胎児ではレニンレベルは高いが、アンジオテンシンIIレベルは有意に低い。これは、肺血流が限られているため、ACE(肺循環に主に存在する)が最大限の効果を発揮できないためである。 | |||
== 臨床的意義 == | == 臨床的意義 == | ||
Latest revision as of 09:29, 28 March 2024

レニン-アンジオテンシン系(RAS)、またはレニン-アンジオテンシン-アルドステロン系(RAAS)は、血圧、体液バランス、電解質バランス、および全身の血管抵抗を調節するホルモン系である。
腎血流が減少すると、腎臓の次糸球体細胞は前駆体であるプロレニン(すでに血液中に存在する)をレニンに変換し、直接体循環に分泌する。血漿レニンは次に、肝臓から放出されたアンジオテンシノーゲンをアンジオテンシンIと呼ばれるデカペプチドに変換する。アンジオテンシンIはその後、主に肺の血管内皮細胞表面に存在するアンジオテンシン変換酵素(ACE)によってアンジオテンシンII(オクタペプチド)に変換される。アンジオテンシンIIの寿命は約1~2分と短い。その後、多くの組織の赤血球や血管床に存在するアンジオテンシナーゼによって、アンジオテンシンIIIと呼ばれるヘプタペプチドに急速に分解される。
アンジオテンシンIIIは血圧を上昇させ、副腎皮質からのアルドステロン分泌を刺激する。副腎皮質刺激活性は100%で、血管圧迫活性はアンジオテンシンIIの40%である。
アンジオテンシンIVはまた、副腎皮質作用と血管圧制御作用を持つ。
アンジオテンシンIIは強力な血管収縮ペプチドであり、血管を狭窄させて血圧を上昇させる。アンジオテンシンIIはまた、副腎皮質からのホルモンアルドステロンの分泌を刺激する。アルドステロンは腎尿細管のナトリウムの再吸収を増加させ、その結果、血液中への水分の再吸収を引き起こすと同時に、(電解質バランスを維持するために)カリウムの排泄を引き起こす。これにより体内の細胞外液の体積が増加し、血圧も上昇する。
RASが異常に活性化すると血圧が高くなりすぎる。ACE阻害薬、アンジオテンシンⅡ受容体拮抗薬(ARB)、レニン阻害薬など、血圧を改善するためにこのシステムのさまざまな段階を阻害する薬物がいくつかある。これらの薬物は、高血圧、心不全、腎不全、および糖尿病の有害な影響を制御するための主要な方法の1つである。
活性化
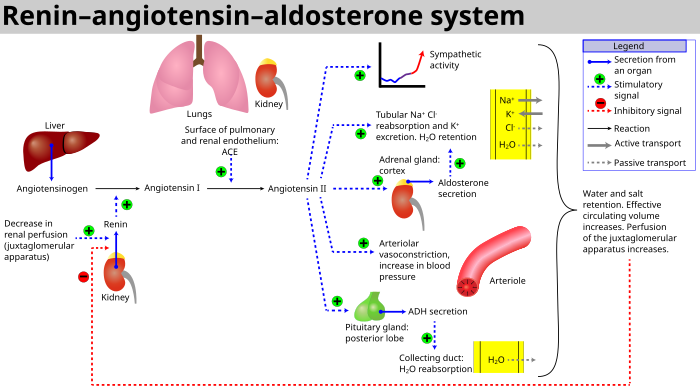
この系は、血液量の減少や血圧の低下(出血や脱水など)があると活性化する。この圧力の低下は頸動脈洞の圧受容器によって解釈される。また、濾液塩化ナトリウム(NaCl)濃度の低下や濾液流量の低下によっても活性化され、黄斑円錐体を刺激して次糸球体細胞にレニンを放出するように信号を送る。
- 腎臓の黄斑部にある傍糸球体装置の灌流が低下すると、傍糸球体細胞(糸球体毛細血管にある顆粒細胞、変化した周皮細胞)が酵素レニンを放出する。
- レニンは、球状タンパク質であるアンジオテンシノーゲンからデカペプチドを分解する。このデカペプチドはアンジオテンシンIとして知られている。
- アンジオテンシンIはその後、アンジオテンシン変換酵素(ACE)によってオクタペプチドであるアンジオテンシンIIに変換されるが、ACEは主に全身の毛細血管の内皮細胞、肺、腎臓の上皮細胞に存在すると考えられている。1992年のある研究では、すべての血管内皮細胞にACEが存在することが発見された。
- アンジオテンシンIIは、レニン-アンジオテンシン系の主要な生理活性産物であり、糸球体内メサンギウム細胞上の受容体に結合し、これらの細胞を周囲の血管とともに収縮させる;また糸球体座細胞上の受容体に結合し、副腎皮質の糸球体座からアルドステロンの放出を引き起こす。アンジオテンシンIIは、内分泌、オートクリン/パラクリン、イントラクリンホルモンとして作用する。
心血管系への影響

アンジオテンシンIはわずかな活性を持つかもしれないが、アンジオテンシンIIが主要な生理活性産物である。アンジオテンシンIIは身体に様々な作用を及ぼす:
- 全身において、アンジオテンシンIIは細動脈の強力な血管収縮薬である。
- 腎臓では、アンジオテンシンIIは糸球体細動脈を収縮させ、求心性細動脈よりも遠心性細動脈に大きな影響を及ぼす。体内の他のほとんどの毛細血管床と同様に、求心性細動脈の収縮は細動脈抵抗を増加させ、|全身を上昇させる。動脈血圧を上昇させ、血流量を減少させる。しかし、腎臓はこの血流低下にもかかわらず十分な血液を濾過し続けなければならないため、糸球体の血圧を維持するメカニズムが必要となる。そのために、アンジオテンシンIIは遠心性細動脈を収縮させ、糸球体に血液を溜めて糸球体圧を上昇させる。こうして糸球体濾過量(GFR)が維持され、腎臓全体の血流量が低下しても血液濾過を継続することができる。糸球体濾過量(GFR)と腎血漿流量(RPF)の比である濾過分画が増加しているため、下流の尿細管周囲毛細血管内の血漿液は少なくなっている。その結果、尿細管周囲毛細血管の静水圧が低下し、オンコティック圧が上昇する(未濾過の血漿タンパク質による)。尿細管周囲毛細血管における静水圧低下とオンコティック圧上昇の効果により、尿細管液の再吸収が促進される。
- アンジオテンシンIIは直細動脈を通る髄質血流を減少させる。これにより、腎髄質腔におけるNaClと尿素の洗い流しが減少する。したがって、髄質におけるNaClと尿素の濃度が高くなると、尿細管液の吸収が促進される。さらに、髄質への体液の再吸収が増加すると、ヘンレループの太い上行辺縁に沿ったナトリウムの受動的再吸収が増加する。
- アンジオテンシンIIは、集合管のNa+
チャネルに加えて、ヘンレループの近位尿細管と太い上行枝の細胞の先端膜(尿細管内腔に面している)にあるNa+
/H+
交換体を刺激する。これは最終的にナトリウムの再吸収を増加させる。 - アンジオテンシンIIは腎尿細管細胞の肥大を刺激し、さらなるナトリウム再吸収をもたらす。
- 副腎皮質では、アンジオテンシンIIはアルドステロンの放出を引き起こすように作用する。アルドステロンは尿細管(例えば、遠位尿細管および皮質)に作用する。腎臓の集合管など)に作用し、尿からナトリウムと水分をより多く再吸収させる。これは血液量を増加させ、したがって血圧を上昇させる。ナトリウムの血液への再吸収と引き換えに、カリウムが尿細管に分泌され、尿の一部となって排泄される。
- アンジオテンシンIIは、バソプレシンとも呼ばれる抗利尿ホルモン(ADH)の分泌を引き起こす - ADHは視床下部で作られ、後下垂体から放出される。その名が示すように血管収縮作用も示すが、主な作用は腎臓での水分の再吸収を促すことである。ADHはまた、中枢神経系に作用して食塩に対する食欲を増進させ、口渇の感覚を刺激する。
これらの作用は直接的に血圧を上昇させるように作用し、心房性ナトリウム利尿ペプチド(ANP)によって対抗される。
局所レニン-アンジオテンシン系
局所的に発現するレニン-アンジオテンシン系は、腎臓、副腎、心臓、血管系、神経系などの多くの組織で見つかっており、全身性のレニン-アンジオテンシン系と関連して、あるいは独立して、局所的な心血管系の調節や非心血管系の機能など、様々な機能を持っている。腎臓以外では、レニンは主に循環から回収されるが、一部の組織では局所的に分泌されることがある。その前駆体であるプロレニンは組織で高発現しており、循環プロレニンの半分以上は腎臓外由来であるが、レニンの前駆体としての役割以外の生理学的役割はまだ不明である。レニンとともにアンジオテンシンIを形成し、局所に発現しているアンジオテンシン変換酵素、キマーゼまたは他の酵素によってアンジオテンシンIIに変換される。この過程は細胞内でも間質でも起こりうる。
副腎では、アルドステロン分泌のパラクリン制御に関与している可能性が高く、心臓と血管系では、リモデリングまたは血管緊張に関与している可能性があり、循環系RASからほとんど独立している脳では、局所血圧調節に関与している可能性がある。さらに、中枢性と末梢性の両方の神経系が交感神経伝達のためにアンジオテンシンを使用することができる。その他の発現場所としては、生殖器系、皮膚、消化器などがある。全身系を対象とした医薬品は、これらの局所系の発現に、有益または不利に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。
胎児レニン-アンジオテンシン系
胎児では、レニン-アンジオテンシン系は主にナトリウム喪失系であり、アンジオテンシンIIはアルドステロンレベルにほとんど影響を及ぼさない。胎児ではレニンレベルは高いが、アンジオテンシンIIレベルは有意に低い。これは、肺血流が限られているため、ACE(肺循環に主に存在する)が最大限の効果を発揮できないためである。
臨床的意義

- アンジオテンシン変換酵素阻害薬のACE阻害薬は、より強力なアンジオテンシンⅡの生成を抑えるためによく使われる。カプトプリルはACE阻害薬の一例である。ACEは他の多くのペプチドを切断し、この能力においてキニン・カリクレイン系の重要な調節因子であり、ACEを阻害することは副作用につながる可能性がある。
- アンジオテンシンII受容体拮抗薬は、アンジオテンシン受容体遮断薬としても知られ、アンジオテンシンIIが受容体に作用するのを防ぐために使用できる。
- 直接的なレニン阻害薬も高血圧に使用できる。レニンを阻害する薬物にはアリスキレンと治験中のレミキレンがある。
- アンジオテンシンIIに対するワクチン、例えばCYT006-AngQbが研究されている。
こちらも参照
さらに読む
外部リンク
- Renin-Angiotensin+System at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)