Losartan/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "<!-- Chemical and physical data --> | IUPAC_name = (2-butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2'-(2''H''-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-1''H''-imidazol-5-yl)methanol | C=22 | H=23 | Cl=1 | N=6 | O=1 | SMILES = CCCCc1nc(Cl)c(CO)n1Cc1ccc(-c2ccccc2-c2nn[nH]n2)cc1 | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | StdInChI = 1S/C22H23ClN6O/c1-2-3-8-20-24-21(23)19(14-30)29(20)13-15-9-11-16(12-10-15)17-6-4-5-7-18(17)22-25-27-28-26-22/h4-7,9-12,30H,2-3,8,13-14H2,1H3,(H,25,26,27,28) | StdIn..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "== 薬物動態 == {{Anchor|Pharmacokinetics}} ロサルタンは経口投与後よく吸収され、有意な初回通過代謝を受けてEXP3174として指定されている5-カルボン酸代謝物を生成する。経口投与量の約14%がこの代謝物に変換され、この代謝物は長時間作用性(6~8時間)であり、AT<sub>1</sub>受容体の非競合的拮抗薬であり、ロサルタンの薬理作用に寄与する..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!-- Definition and medical uses --> | <!-- Definition and medical uses --> | ||
'''Losartan''' | '''ロサルタン'''('''Losartan''')は、商品名'''コザール(Cozaar)'''として販売されており、[[high blood pressure/ja|高血圧]](高血圧症)の治療に用いられる[[medication/ja|医薬品]]である。[[angiotensin II receptor antagonist/ja|アンジオテンシン受容体拮抗薬(ARB)]]系の医薬品であり、腎臓を保護すると考えられている。高血圧のほか、[[diabetic kidney disease/ja|糖尿病性腎臓病]]、[[heart failure/ja|心不全]]、[[left ventricular enlargement/ja|左室肥大]]にも用いられる。錠剤で[[Oral administration/ja|口から]]服用する。単独で使用することも、他の[[blood pressure medication/ja|血圧治療薬]]に追加して使用することもできる。十分な効果が現れるまで最大6週間を要することがある。 | ||
<!-- Side effects and mechanism --> | <!-- Side effects and mechanism --> | ||
一般的な副作用には、筋肉のけいれん、鼻づまり、めまい、咳、[[hyperkalemia/ja|高血中カリウム]]、[[anemia/ja|貧血]]などがある。重篤な副作用には、[[angioedema/ja|血管浮腫]]、[[low blood pressure/ja|低血圧]]、[[kidney problems/ja|腎障害]]などがある。[[pregnancy/ja|妊娠]]中の使用は赤ちゃんに害を及ぼす可能性がある。[[breastfeeding/ja|授乳中]]の使用は推奨されない。[[angiotensin II/ja|アンジオテンシンII]]を遮断することで作用する。 | |||
<!-- History and culture --> | <!-- History and culture --> | ||
ロサルタンは1986年に特許を取得し、1995年に米国で医薬品として承認された。[[WHO Model List of Essential Medicines/ja|世界保健機関の必須医薬品リスト]]に掲載されている。[[generic medication/ja|ジェネリック医薬品]]としても販売されている。2021年には55{{nbsp}}万件以上の処方で、米国で8番目に多く処方された医薬品であった。[[hydrochlorothiazide/ja|ヒドロクロロチアジド]]と組み合わせたバージョンもあり、2021年には米国で87番目に多く処方され、8{{nbsp}}万件以上の医薬品であった。 | |||
==化学== | |||
ロサルタンカリウムは化学的には2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium salt と表記される。化学式は{{Format molecular formula|C22H23CIKN6O}}で、分子量は422.9である。 | |||
ロサルタンは一般に、''ロサルタンカリウム''と呼ばれる、芳香族化した負電荷を持つ[[tetrazole/ja|テトラゾール]]の(塩基性)カリウム塩として販売されている。この分子は、カルボン酸の代わりに[[bioisostere/ja|バイオイソステア]]として使用されているテトラゾールとの拡張ビフェニル基を有する。 | |||
==医療用途== | |||
{{Anchor|Medical uses}} | |||
ロサルタンは、[[left ventricular hypertrophy/ja|左室肥大症]](心筋肥大)の患者を含む[[hypertension/ja|高血圧症]]、および2型糖尿病患者の腎機能障害に用いられる。また、[[diabetic nephropathy/ja|糖尿病性腎症]]の進行を遅らせることもある。2型糖尿病、高血圧、および微量アルブミン尿(>30 mg/24時間)または蛋白尿(>900 mg/24時間)を有する患者における腎疾患の進行抑制に適した薬理学的薬剤である。 | |||
[[calcium channel blockers/ja|カルシウム拮抗薬]]と[[thiazide diuretic/ja|サイアザイド系利尿薬]]が(有効性とコストの両面から)ほとんどの人にとって望ましい第一選択薬であるというエビデンスがあるが、[[ACE inhibitor/ja|ACE阻害薬]]に耐えられない55歳未満の人には、ロサルタンなどのアンジオテンシンII受容体拮抗薬が第一選択薬として推奨されている。ある研究では,有害心血管イベント(心筋梗塞または脳卒中)の一次予防において,ロサルタンは[[atenolol/ja|アテノロール]]よりも優れており,同等の血圧低下で心血管系の罹患率と死亡率が低下することが示された。血圧に対する最大の効果は、通常ロサルタン投与開始後3~6週間以内に現れる。 | |||
==副作用== | |||
{{Anchor|Adverse effects}} | |||
成人におけるロサルタンの最も一般的な副作用は、上部[[respiratory infection/ja|呼吸器感染症]]、[[dizziness/ja|めまい]]、[[back pain/ja|背部痛]]である。[[type 2 diabetes/ja|2型糖尿病]]や[[kidney disease/ja|腎臓病]]の患者は、[[diarrhea/ja|下痢]]、疲労、低血圧、低血糖、カリウム上昇、胸痛、または[[allergic reaction/ja|アレルギー反応]]を経験することがある。糖尿病で[[aliskiren/ja|アリスキレン]]を服用している人はロサルタンを服用してはならない。レニン-アンジオテンシン系の阻害により、[[anemia/ja|貧血]]が起こることがある。他のアンジオテンシン受容体拮抗薬と同様に、ロサルタンは肝臓を傷害することがあるが、この影響はまれであるようだ。腎臓に問題のある人がロサルタンを服用すると、電解質の不均衡が起こることがある。有害な転帰は性別、年齢、人種による差はない。 | |||
===妊娠=== | |||
2014年10月、米国[[Food and Drug Administration/ja|食品医薬品局]](FDA)は、ロサルタンは[[fetus/ja|胎児]][[toxicity/ja|毒性]]を引き起こす可能性があるという黒枠警告を出した。妊娠が判明次第中止すべきである。妊娠中にロサルタンを使用すると、胎児が傷害を受けたり死亡したりする可能性がある。 | |||
===過剰摂取=== | |||
=== | |||
過剰摂取は、血圧の低下、心拍数の増加、めまい、ふらつき、意識消失として現れる可能性が高い。マウスの研究では、マウスの体重を考慮した後、推奨最大用量の約44倍から170倍で致死が起こることが示された。 | |||
=== 相互作用=== | |||
ロサルタンは[[phenobarbital/ja|フェノバルビタール]]、[[rifampin/ja|リファンピン]]、または[[fluconazole/ja|フルコナゾール]]と有害な[[drug interaction/ja|相互作用]]を起こす可能性があり、おそらく血圧低下作用を阻害する。 | |||
===汚染=== | |||
{{See also/ja|Valsartan/ja#recalls|Angiotensin II receptor blocker/ja#recalls}} | |||
{{See also|Valsartan#recalls|Angiotensin II receptor blocker#recalls}} | |||
2018年11月から2019年9月にかけて、FDAは[[Wikipedia:Sandoz|Sandoz]]、[[Wikipedia:Torrent Pharmaceuticals|Torrent Pharmaceuticals]]、[[:en:Hetero Drugs|Hetero Labs]]、Camber Pharmaceuticals、Legacy Pharmaceutical Packaging、[[Teva Pharmaceutical Industries|Teva Pharmaceuticals]]によるロサルタンを含む錠剤の複数のリコールを発表した、 [[:en:Vivimed Labs|Vivimed Life Sciences]]、およびMacleods Pharmaceutical Limitedは、[[Active ingredient/ja|医薬品有効成分]](API)から発がん性物質である可能性のある[[N-nitrosodiethylamine/ja|N-ニトロソジエチルアミン]]、N-メチルニトロソ酪酸、N-ニトロソ-N-メチル-4-アミノ酪酸のいずれかが検出されたためである。 | |||
==作用機序== | |||
{{Anchor|Mechanism of action}} | |||
[[File:Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.svg|thumb| | [[File:Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.svg|thumb|レニン-アンジオテンシン-アルドステロン系(RAAS)|alt=|612x612px]] | ||
ロサルタンは選択的、競合的[[angiotensin II receptor type 1/ja|アンジオテンシンⅡ受容体1型]](AT<sub>1</sub>)拮抗薬であり、アンジオテンシンⅡに対する末端臓器の反応を低下させる。ロサルタンを投与すると、全末梢抵抗(後負荷)と心臓静脈還流(前負荷)が減少する。ロサルタン存在下では、[[aldosterone/ja|アルドステロン]]の放出を含むアンジオテンシンⅡの生理学的作用はすべて拮抗する。血圧の低下は[[renin–angiotensin system/ja|レニン-アンジオテンシン系]]の状態とは無関係に起こる。ロサルタン投与の結果、血漿[[renin/ja|レニン]]活性はアンジオテンシンIIフィードバックの除去により増加する。レニンは、腎動脈圧の低下、交感神経の活性化、または遠位腎尿細管へのナトリウム供給量の増加があると、腎臓から放出される。アンジオテンシン変換酵素(ACE)はアンジオテンシンIをアンジオテンシンIIに変換し、アンジオテンシンIIは血管収縮とアルドステロンの放出を引き起こす。アルドステロンは遠位腎尿細管からナトリウムを保持する役割を果たす。ナトリウムの貯留は最終的に血圧上昇をもたらす。したがって、ロサルタンのようなアンジオテンシンII受容体拮抗薬の使用は、レニンの下流作用であるアンジオテンシンIIを阻害し、最終的に血圧を低下させることになる。 | |||
アンジオテンシンII受容体拮抗薬には、ロサルタン、[[valsartan/ja|バルサルタン]]、[[azilsartan/ja|アジルサルタン]]、[[candesartan/ja|カンデサルタン]]、[[eprosartan/ja|エプロサルタン]]、[[irbesartan/ja|イルベサルタン]]、[[olmesartan/ja|オルメサルタン]]、[[telmisartan/ja|テルミサルタン]]などがある。これらはすべて同じ作用機序を持ち、[[lisinopril/ja|リシノプリル]]などの[[ACE inhibitors/ja|ACE阻害薬]]よりもアンジオテンシンの作用を阻害する可能性がある。 | |||
ロサルタンは[[uricosuric/ja|尿酸排泄薬]]である。尿酸トランスポーター1([[SLC22A12/ja|SLC22A12]]、URAT1)の特異的阻害剤として、ロサルタンは細胞内への尿酸の取り込みを阻害するため、腎臓で濾過・排泄される血液中の尿酸の量が多くなる。ロサルタンは[[hyperkalemia/ja|高カリウム血症]]を引き起こす可能性があるため、医師による適切な監視なしにカリウムを含む[[potassium/ja|カリウム]]サプリメントや代用塩を使用すべきではない。 | |||
== 薬物動態 == | |||
{{Anchor|Pharmacokinetics}} | |||
ロサルタンは経口投与後よく吸収され、有意な初回通過代謝を受けてEXP3174として指定されている5-[[carboxylic acid/ja|カルボン酸]]代謝物を生成する。経口投与量の約14%がこの代謝物に変換され、この代謝物は長時間作用性(6~8時間)であり、AT<sub>1</sub>受容体の非競合的拮抗薬であり、ロサルタンの薬理作用に寄与する。EXP3174はロサルタンの10〜40倍のAT<sub>1</sub>受容体遮断作用を有する。さらに、標的酵素への結合はpH感受性であり、陰性カルボン酸誘導体と同様の大きさの陰性荷電テトラゾール環が薬物の活性に寄与していると考えられる。 | |||
ロサルタンの[[bioavailability/ja|生物学的利用能]]は約33%である。 | |||
代謝は主に[[cytochrome P450/ja|チトクロームP450]]によって行われる。[[isoenzyme/ja|アイソザイム]]の[[CYP2C9/ja|CYP2C9]]および[[CYP3A4/ja|CYP3A4]]によって代謝される。ロサルタンおよびEXP3174の血漿中濃度のピークは、それぞれ経口投与後約1時間および3~4時間後に発現する。ロサルタンとEXP3174はともに血漿蛋白と98%以上結合している。ロサルタンは未変化体および代謝物として尿中および胆汁を介して糞中に排泄される。経口投与量の約4%が未変化体のまま尿中に排泄され、約6%が活性代謝物として尿中に排泄される。ロサルタンの終末半減期は約1.5~2.5時間、EXP3174の終末半減期は約3~9時間である。 | |||
ロサルタンをはじめとするアンジオテンシン受容体拮抗薬は胎児毒性を示すため、妊娠中、特に妊娠第2期と第3期は避けるべきである。 | |||
== 歴史 == | |||
{{Anchor|History}} | |||
{{main|Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers}} | {{main/ja|Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers/ja}} | ||
== さらに読む == | |||
* {{cite journal |vauthors=Al-Majed AR, Assiri E, Khalil NY, Abdel-Aziz HA |title=Losartan: Comprehensive Profile |journal=Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol |volume=40 |pages=159–94 |date=2015 |pmid=26051686 |doi=10.1016/bs.podrm.2015.02.003 }} | * {{cite journal |vauthors=Al-Majed AR, Assiri E, Khalil NY, Abdel-Aziz HA |title=Losartan: Comprehensive Profile |journal=Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol |volume=40 |pages=159–94 |date=2015 |pmid=26051686 |doi=10.1016/bs.podrm.2015.02.003 }} | ||
* {{cite journal |vauthors=Sica DA, Gehr TW, Ghosh S |title=Clinical pharmacokinetics of losartan |journal=Clin Pharmacokinet |volume=44 |issue=8 |pages=797–814 |date=2005 |pmid=16029066 |doi=10.2165/00003088-200544080-00003 |s2cid=41326620 }} | * {{cite journal |vauthors=Sica DA, Gehr TW, Ghosh S |title=Clinical pharmacokinetics of losartan |journal=Clin Pharmacokinet |volume=44 |issue=8 |pages=797–814 |date=2005 |pmid=16029066 |doi=10.2165/00003088-200544080-00003 |s2cid=41326620 }} | ||
== 外部リンク == | |||
{{Commons category|Metformin}} | |||
* {{cite web | title=Nitrosamine impurities in medications: Guidance | website=Health Canada | date=4 April 2022 | url=https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/compliance-enforcement/information-health-product/drugs/nitrosamine-impurities/medications-guidance.html }} | * {{cite web | title=Nitrosamine impurities in medications: Guidance | website=Health Canada | date=4 April 2022 | url=https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/compliance-enforcement/information-health-product/drugs/nitrosamine-impurities/medications-guidance.html }} | ||
{{Merck&Co}} | {{Merck&Co}} | ||
{{Angiotensin II receptor antagonists}} | {{Angiotensin II receptor antagonists/ja}} | ||
{{Angiotensin receptor modulators}} | {{Angiotensin receptor modulators/ja}} | ||
{{Portal bar | Medicine}} | {{Portal bar | Medicine}} | ||
[[Category:Angiotensin II receptor antagonists]] | [[Category:Angiotensin II receptor antagonists]] | ||
[[Category:Biphenyls]] | [[Category:Biphenyls]] | ||
| Line 235: | Line 187: | ||
[[Category:Orphan drugs]] | [[Category:Orphan drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Butyl compounds]] | [[Category:Butyl compounds]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:52, 15 March 2024
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /loʊˈsɑːrtən/ |
| Trade names | コザール、その他 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a695008 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | 経口 |
| Drug class | Angiotensin II receptor antagonist/ja |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25–35% |
| Protein binding | 99.7% (主にアルブミン) |
| Metabolism | Liver/ja (CYP2C9/ja, CYP3A4/ja) |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5–2時間 |
| Excretion | Kidney/ja 13–25%, bile duct/ja 50–60% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
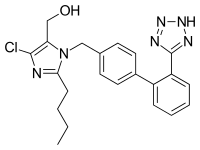
| Formula | C22H23ClN6O |
| Molar mass | 422.92 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
ロサルタン(Losartan)は、商品名コザール(Cozaar)として販売されており、高血圧(高血圧症)の治療に用いられる医薬品である。アンジオテンシン受容体拮抗薬(ARB)系の医薬品であり、腎臓を保護すると考えられている。高血圧のほか、糖尿病性腎臓病、心不全、左室肥大にも用いられる。錠剤で口から服用する。単独で使用することも、他の血圧治療薬に追加して使用することもできる。十分な効果が現れるまで最大6週間を要することがある。
一般的な副作用には、筋肉のけいれん、鼻づまり、めまい、咳、高血中カリウム、貧血などがある。重篤な副作用には、血管浮腫、低血圧、腎障害などがある。妊娠中の使用は赤ちゃんに害を及ぼす可能性がある。授乳中の使用は推奨されない。アンジオテンシンIIを遮断することで作用する。
ロサルタンは1986年に特許を取得し、1995年に米国で医薬品として承認された。世界保健機関の必須医薬品リストに掲載されている。ジェネリック医薬品としても販売されている。2021年には55 万件以上の処方で、米国で8番目に多く処方された医薬品であった。ヒドロクロロチアジドと組み合わせたバージョンもあり、2021年には米国で87番目に多く処方され、8 万件以上の医薬品であった。
化学
ロサルタンカリウムは化学的には2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium salt と表記される。化学式はC22H23CIKN6O で、分子量は422.9である。
ロサルタンは一般に、ロサルタンカリウムと呼ばれる、芳香族化した負電荷を持つテトラゾールの(塩基性)カリウム塩として販売されている。この分子は、カルボン酸の代わりにバイオイソステアとして使用されているテトラゾールとの拡張ビフェニル基を有する。
医療用途
ロサルタンは、左室肥大症(心筋肥大)の患者を含む高血圧症、および2型糖尿病患者の腎機能障害に用いられる。また、糖尿病性腎症の進行を遅らせることもある。2型糖尿病、高血圧、および微量アルブミン尿(>30 mg/24時間)または蛋白尿(>900 mg/24時間)を有する患者における腎疾患の進行抑制に適した薬理学的薬剤である。
カルシウム拮抗薬とサイアザイド系利尿薬が(有効性とコストの両面から)ほとんどの人にとって望ましい第一選択薬であるというエビデンスがあるが、ACE阻害薬に耐えられない55歳未満の人には、ロサルタンなどのアンジオテンシンII受容体拮抗薬が第一選択薬として推奨されている。ある研究では,有害心血管イベント(心筋梗塞または脳卒中)の一次予防において,ロサルタンはアテノロールよりも優れており,同等の血圧低下で心血管系の罹患率と死亡率が低下することが示された。血圧に対する最大の効果は、通常ロサルタン投与開始後3~6週間以内に現れる。
副作用
成人におけるロサルタンの最も一般的な副作用は、上部呼吸器感染症、めまい、背部痛である。2型糖尿病や腎臓病の患者は、下痢、疲労、低血圧、低血糖、カリウム上昇、胸痛、またはアレルギー反応を経験することがある。糖尿病でアリスキレンを服用している人はロサルタンを服用してはならない。レニン-アンジオテンシン系の阻害により、貧血が起こることがある。他のアンジオテンシン受容体拮抗薬と同様に、ロサルタンは肝臓を傷害することがあるが、この影響はまれであるようだ。腎臓に問題のある人がロサルタンを服用すると、電解質の不均衡が起こることがある。有害な転帰は性別、年齢、人種による差はない。
妊娠
2014年10月、米国食品医薬品局(FDA)は、ロサルタンは胎児毒性を引き起こす可能性があるという黒枠警告を出した。妊娠が判明次第中止すべきである。妊娠中にロサルタンを使用すると、胎児が傷害を受けたり死亡したりする可能性がある。
過剰摂取
過剰摂取は、血圧の低下、心拍数の増加、めまい、ふらつき、意識消失として現れる可能性が高い。マウスの研究では、マウスの体重を考慮した後、推奨最大用量の約44倍から170倍で致死が起こることが示された。
相互作用
ロサルタンはフェノバルビタール、リファンピン、またはフルコナゾールと有害な相互作用を起こす可能性があり、おそらく血圧低下作用を阻害する。
汚染
2018年11月から2019年9月にかけて、FDAはSandoz、Torrent Pharmaceuticals、Hetero Labs、Camber Pharmaceuticals、Legacy Pharmaceutical Packaging、Teva Pharmaceuticalsによるロサルタンを含む錠剤の複数のリコールを発表した、 Vivimed Life Sciences、およびMacleods Pharmaceutical Limitedは、医薬品有効成分(API)から発がん性物質である可能性のあるN-ニトロソジエチルアミン、N-メチルニトロソ酪酸、N-ニトロソ-N-メチル-4-アミノ酪酸のいずれかが検出されたためである。
作用機序

ロサルタンは選択的、競合的アンジオテンシンⅡ受容体1型(AT1)拮抗薬であり、アンジオテンシンⅡに対する末端臓器の反応を低下させる。ロサルタンを投与すると、全末梢抵抗(後負荷)と心臓静脈還流(前負荷)が減少する。ロサルタン存在下では、アルドステロンの放出を含むアンジオテンシンⅡの生理学的作用はすべて拮抗する。血圧の低下はレニン-アンジオテンシン系の状態とは無関係に起こる。ロサルタン投与の結果、血漿レニン活性はアンジオテンシンIIフィードバックの除去により増加する。レニンは、腎動脈圧の低下、交感神経の活性化、または遠位腎尿細管へのナトリウム供給量の増加があると、腎臓から放出される。アンジオテンシン変換酵素(ACE)はアンジオテンシンIをアンジオテンシンIIに変換し、アンジオテンシンIIは血管収縮とアルドステロンの放出を引き起こす。アルドステロンは遠位腎尿細管からナトリウムを保持する役割を果たす。ナトリウムの貯留は最終的に血圧上昇をもたらす。したがって、ロサルタンのようなアンジオテンシンII受容体拮抗薬の使用は、レニンの下流作用であるアンジオテンシンIIを阻害し、最終的に血圧を低下させることになる。
アンジオテンシンII受容体拮抗薬には、ロサルタン、バルサルタン、アジルサルタン、カンデサルタン、エプロサルタン、イルベサルタン、オルメサルタン、テルミサルタンなどがある。これらはすべて同じ作用機序を持ち、リシノプリルなどのACE阻害薬よりもアンジオテンシンの作用を阻害する可能性がある。
ロサルタンは尿酸排泄薬である。尿酸トランスポーター1(SLC22A12、URAT1)の特異的阻害剤として、ロサルタンは細胞内への尿酸の取り込みを阻害するため、腎臓で濾過・排泄される血液中の尿酸の量が多くなる。ロサルタンは高カリウム血症を引き起こす可能性があるため、医師による適切な監視なしにカリウムを含むカリウムサプリメントや代用塩を使用すべきではない。
薬物動態
ロサルタンは経口投与後よく吸収され、有意な初回通過代謝を受けてEXP3174として指定されている5-カルボン酸代謝物を生成する。経口投与量の約14%がこの代謝物に変換され、この代謝物は長時間作用性(6~8時間)であり、AT1受容体の非競合的拮抗薬であり、ロサルタンの薬理作用に寄与する。EXP3174はロサルタンの10〜40倍のAT1受容体遮断作用を有する。さらに、標的酵素への結合はpH感受性であり、陰性カルボン酸誘導体と同様の大きさの陰性荷電テトラゾール環が薬物の活性に寄与していると考えられる。
ロサルタンの生物学的利用能は約33%である。
代謝は主にチトクロームP450によって行われる。アイソザイムのCYP2C9およびCYP3A4によって代謝される。ロサルタンおよびEXP3174の血漿中濃度のピークは、それぞれ経口投与後約1時間および3~4時間後に発現する。ロサルタンとEXP3174はともに血漿蛋白と98%以上結合している。ロサルタンは未変化体および代謝物として尿中および胆汁を介して糞中に排泄される。経口投与量の約4%が未変化体のまま尿中に排泄され、約6%が活性代謝物として尿中に排泄される。ロサルタンの終末半減期は約1.5~2.5時間、EXP3174の終末半減期は約3~9時間である。
ロサルタンをはじめとするアンジオテンシン受容体拮抗薬は胎児毒性を示すため、妊娠中、特に妊娠第2期と第3期は避けるべきである。
歴史
さらに読む
- Al-Majed AR, Assiri E, Khalil NY, Abdel-Aziz HA (2015). "Losartan: Comprehensive Profile". Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol. 40: 159–94. doi:10.1016/bs.podrm.2015.02.003. PMID 26051686.
- Sica DA, Gehr TW, Ghosh S (2005). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of losartan". Clin Pharmacokinet. 44 (8): 797–814. doi:10.2165/00003088-200544080-00003. PMID 16029066. S2CID 41326620.
外部リンク
- "Nitrosamine impurities in medications: Guidance". Health Canada. 4 April 2022.