Discovery and development of gliflozins/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "== 導入 == {{Anchor|Introduction}}" |
Created page with "Gliflozins " Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{{Anchor|Introduction}} | {{Anchor|Introduction}} | ||
=== グルコースホメオスタシスにおける腎臓の役割 === | |||
{{Also/ja|Secondary active transport/ja}} | |||
{{Also|Secondary active transport}} | 二次活性グルコーストランスポーターであるSLC-5遺伝子ファミリーには少なくとも4つのメンバーが存在する。ナトリウムグルコーストランスポータータンパク質[[SGLT-1/ja|SGLT-1]]とSGLT-2は、このファミリーの2つの主要メンバーである。これら2つのメンバーは、他のトランスポーターの中でも[[kidneys/ja|腎臓]]に存在し、そこでは[[blood sugar/ja|血糖]]に関連する主要な共トランスポーターである。腎臓でのグルコース再吸収と腸でのグルコース吸収に関与している。 | ||
[[Blood glucose/ja|血中グルコース]]は[[Glomerulus (kidney)/ja|糸球体]]で自由に濾過され、SGLT-1とSGLT-2は腎臓でグルコースを再吸収し、循環細胞に戻す。SGLT-2は再吸収の90%を、SGLT-1は残りの10%を担っている。 | |||
[[Blood glucose]] | |||
=== SGLT-2タンパク質 === | |||
=== SGLT- | ナトリウム/グルコース共輸送体([[SGLT/ja|SGLT]])タンパク質は[[cell membrane/ja|細胞膜]]に結合しており、グルコースの[[Molecular diffusion/ja|濃度勾配]]に逆らって、グルコースを細胞膜を通して細胞内に輸送する役割を持っている。これはナトリウム/カリウム[[ATPase/ja|ATPase]]ポンプによって生じるナトリウム勾配を利用することで行われるため、グルコースが細胞内に輸送されると同時にナトリウムも輸送される。勾配に逆らっているため、働くにはエネルギーが必要である。SGLTタンパク質は、[[insulin/ja|インスリン]]とは無関係に、[[glomerular filtrate/ja|糸球体濾液]]からの[[Renal glucose reabsorption/ja|グルコース再吸収]]を引き起こす。 | ||
SGLT-2はグルコーストランスポーターファミリーの一員であり、低親和性で高容量のグルコーストランスポーターである。SGLT-2は主に[[proximal renal tubule/ja|近位腎尿細管]]のS-1およびS-2セグメントで発現しており、濾過されたグルコースの大部分が吸収される。SGLT-2はグルコースの調節に関与し、腎臓におけるグルコースの再吸収の大部分を担っている。 | |||
糖尿病では、細胞外グルコース濃度が上昇し、この高いグルコースレベルがSGLT-2の[[Downregulation and upregulation/ja|アップレギュレーション]]を引き起こし、腎臓でのグルコースの吸収を増加させる。これらの作用により、[[hyperglycemia/ja|高血糖]]が維持される。ナトリウムはSGLT-2を介してグルコースと同時に吸収されるため、SGLT-2のアップレギュレーションはおそらく[[hypertension/ja|高血圧]]の発症または維持につながる。ラットに[[ramipril/ja|ラミプリル]]または[[losartan/ja|ロサルタン]]を与えた研究では,SGLT-2タンパク質と[[mRNA/ja|mRNA]]のレベルが有意に減少した。糖尿病患者において高血圧は一般的な問題であるため、この疾患との関連性があるかもしれない。 | |||
ナトリウム/グルコース共輸送体2を阻害する薬物は、腎のグルコース再吸収を阻害し、尿中グルコース排泄を促進し、血中グルコースを低下させる。これらの薬剤はインスリンとは独立して作用し、低血糖や体重増加を引き起こすことなくグルコースレベルを低下させることができる。 | |||
== 発見 == | |||
{{Anchor|Discovery}} | |||
中世の医師たちは日常的に尿を試飲し、その観察結果を論述していた。[[diabetes mellitus/ja|糖尿病]]は[[urine/ja|尿]]中にブドウ糖が排出されることから[[renal disorder/ja|腎障害]]であると考えたのは当初どの医師であったかは、現在では歴史から失われているらしい。インスリンの発見は、やがて[[pancreas/ja|膵臓]]に焦点を当てた糖尿病管理につながった。糖尿病の治療戦略の伝統的な焦点は、内因性インスリン分泌の増強と[[insulin sensitivity/ja|インスリン感受性]]の改善であった。 | |||
過去10年間、高血糖の発症と維持における腎臓の役割が検討されてきた。腎臓の役割は、ナトリウム/グルコーストランスポーター2タンパク質を阻害する薬物の開発につながった。健康な成人では、毎日約180グラムのグルコースが[[glomeruli/ja|糸球体]]で濾過され、原尿中に失われるが、最初に濾過されたグルコースの90%以上は、近位尿細管の初期凸分節にあるSGLT-2によって制御される高容量システムによって再吸収される。残りの濾過されたグルコースはほとんどすべてナトリウム/グルコーストランスポーター1によって再吸収されるため、正常な状況下では、濾過されたグルコースはほとんどすべて再吸収され、糖尿病でない人の尿中に含まれる[[glucose/ja|グルコース]]は100 mg未満である。 | |||
=== フロリジン === | |||
[[File:Phlorhizin.svg|thumb|フロリジン]] | |||
[[File:Phlorhizin.svg|thumb| | [[Phlorizin/ja|フロリジン]]は100年以上前から知られている化合物である。天然に存在する植物性[[glucoside/ja|グルコシド]]であり、腎近位尿細管および[[small intestine/ja|小腸]]の粘膜に存在するナトリウム/グルコース[[Symporter/ja|シンポーター]]を阻害することにより、[[Renal glycosuria/ja|腎糖尿]]を生じさせ、腸のグルコース吸収を阻害する。フロリジンは1835年に初めて単離され、その後、SGLT-1とSGLT-2の両タンパク質に対して強力ではあるが非選択的な阻害剤であることが判明した。 | ||
[[Phlorizin]] | |||
フロリジンは非常に興味深い特性を持っているようで、動物実験での結果は有望で、インスリン感受性を改善し、糖尿病[[Laboratory rat/ja|ラットモデル]]では尿中のグルコース濃度を増加させ、血漿中の正常なグルコース濃度も低血糖を起こすことなく上昇させるようであった。残念なことに、これらの特性にもかかわらず、フロリジンはいくつかの理由から[[clinical development/ja|臨床開発]]には十分適していなかった。フロリジンは[[gastrointestinal tract/ja|消化管]]で分解されるため経口[[bioavailability/ja|バイオアベイラビリティ]]が非常に悪く,非経口的に投与しなければならない。フロリジンの活性代謝物である[[Phloretin/ja|フロレチン]]は[[glucose transporters/ja|グルコーストランスポーター]]の強力な阻害剤であり、フロリジンは[[diarrhea/ja|下痢]]や[[dehydration/ja|脱水]]のような消化管における重篤な有害事象を引き起こすようである。このような理由から、フロリジンはヒトで使用されることはなかった。 | |||
フロリジンはそれ以上の[[clinical trials/ja|臨床試験]]には適さなかったが、SGLT-2阻害薬の開発において重要な役割を果たした。それは、安全性と忍容性のプロファイルが改善されたSGLT阻害剤が認識される基礎となった。例えば、SGLT阻害薬は胃腸の有害事象を伴わず、バイオアベイラビリティもはるかに高い。 | |||
SGLT-2を阻害すると、グルコースレベルのコントロールが改善し、インスリン値が低下し、[[blood pressure/ja|血圧]]と[[uric acid/ja|尿酸]]値が低下し、カロリー浪費が増強する。SGLT-2阻害が直接的な腎保護作用を持つかもしれないという仮説を支持するデータもある。これには、糖尿病に伴う尿細管[[hypertrophy/ja|肥大]]および濾過亢進を抑制する作用や、グルコースの尿細管毒性を軽減する作用が含まれる。ダパグリフロジンによる治療後のSGLT-2の阻害は、尿細管グルコース再吸収能を約30~50%低下させる。 | |||
== 薬物開発 == | |||
{{Anchor|Drug development}} | |||
フロリジンはグルコース[[Moiety (chemistry)/ja|部位]]と2つの[[aromatic rings/ja|芳香環]]([[aglycone/ja|アグリコン]]部位)からなり、[[alkyl/ja|アルキル]]スペーサーによって結合されている。当初、フロリジンは発熱や感染症、特に[[malaria/ja|マラリア]]の治療のために単離された。[[:en:Michael Nauck|マイケル・ナック]]と彼のパートナーによると、1950年代にフロリジンに関する研究が行われ、腎臓、小腸、および他のいくつかの組織における糖輸送を阻害できることが示された。年代初めには、ナトリウム/グルコース共輸送体2が完全に特性決定されたので、フロリジンのメカニズムが注目されるようになった。その後の研究では、フロリジンの糖阻害作用はナトリウム/グルコース共輸送体タンパク質の阻害によるものだと言われている。 | |||
報告されているSGLT-2阻害剤のほとんどは[[glucosides/ja|グルコシド]]類縁体であり、自然界に存在するo-アリールグルコシドまで追跡することができる。SGLT-2阻害剤として[[o-glucosides/ja|o-グルコシド]]を使用する際の問題は、小腸内の[[Beta-glucosidase/ja|β-グルコシダーゼ]]による分解まで追跡できる不安定性である。そのため、経口投与されるo-グルコシドは[[prodrug/ja|プロドラッグ]]エステルでなければならない。これらのプロドラッグは体内で変化を起こし、グルコースと[[aglycone/ja|アグリコン]]部分の間に[[carbon-carbon bond/ja|炭素-炭素結合]]が生じるため、o-グルコシドから[[c-glucoside/ja|c-グルコシド]]が形成される。C-グルコシドはo-グルコシドとは異なる薬物動態プロファイル(例えば[[half-life/ja|半減期]]や作用時間)を持ち、β-グルコシダーゼでは分解されない。最初に発見されたc-グルコシドは薬物[[dapagliflozin/ja|ダパグリフロジン]]であった。ダパグリフロジンは、[[:en:European Medicines Agency|欧州医薬品庁]]によって承認された最初の高選択的SGLT-2阻害薬である。臨床開発中のSGLT-2阻害薬はすべて[[prodrugs/ja|プロドラッグ]]であり、活性を発揮するためには活性型'A'に変換する必要がある。 | |||
=== T-1095 === | === T-1095 === | ||
[[File:T-1095.svg|thumb| | [[File:T-1095.svg|thumb|T-1095の構造]]。 | ||
フロリジンは非選択的阻害剤で経口バイオアベイラビリティが低いため、フロリジン誘導体が合成され、T-1095と呼ばれるようになった。T-1095は[[methyl carbonate/ja|炭酸メチル]]プロドラッグであり、経口投与すると循環吸収され、肝臓で速やかに活性代謝物T-1095Aに変換される。[[SGLT-1/ja|SGLT-1]]および[[SGLT-2/ja|SGLT-2]]を阻害することにより、糖尿病動物の尿中グルコース排泄量を増加させた。T-1095は臨床開発が進まなかったが、これはおそらくSGLT-1を阻害するためであろうが、非選択的SGLT阻害薬は[[Glucose transporter/ja|グルコーストランスポーター1]](GLUT-1)も阻害する可能性がある。濾過されたグルコースの90%はSGLT-2を介して再吸収されるため、研究は特にSGLT-2に焦点を当てている。SGLT-1の阻害は、激しい下痢を特徴とする遺伝性疾患[[glucose-galactose malabsorption/ja|グルコース-ガラクトース吸収不良]]を引き起こす可能性もある。 | |||
=== ISIS 388626=== | |||
=== ISIS 388626 === | SGLT-2阻害の新規な方法の予備的知見によると、[[Sense (molecular biology)/ja|アンチセンス]]である。[[oligonucleotide/ja|オリゴヌクレオチド]]である。ISIS 388626は、1週間に1回投与した場合、近位腎尿細管における[[mRNA/ja|mRNA]]発現を最大80%低下させることにより、げっ歯類およびイヌの血漿グルコースを改善した。SGLT-1には影響しなかった。ISIS 388626の[[Animal testing on non-human primates/ja|非ヒト霊長類]]における長期使用に関する研究結果では、低血糖を伴うことなく[[Glycosuria/ja|糖尿]]の1000倍以上の増加が観察された。この糖尿の増加は、SGLT-2の発現の用量依存的な減少に起因すると考えられ、最高用量では75%以上の減少につながった。2011年、[[Ionis Pharmaceuticals|Ionis Pharmaceuticals社]]は12ヌクレオチドアンチセンス[[oligonucleotide/ja|オリゴヌクレオチド]]であるISIS-SGLT-2RXの[[Phases of clinical research/ja|臨床第1相試験]]を開始した。この研究の結果は2017年に発表され、この治療は「予期せぬ腎作用と関連していた」。著者らは、"ISIS 388626によるSGLT2のアンチセンスを介した遮断という概念をさらに検討する前に、さらなる検討を正当化するために、より多くの前臨床データが必要である"と結論づけた。 | ||
=== 血糖コントロールにおけるSGLT-2阻害薬の活性 === | |||
Michael Nauck氏は、2型糖尿病患者の血糖コントロールにおけるSGLT-2阻害薬の活性に関する研究の[[Meta-analysis/ja|メタ解析]]では、[[placebo/ja|プラセボ]]、[[metformin/ja|メトホルミン]]、[[sulfonylurea/ja|スルホニルウレア]]、[[thiazolidinediones/ja|チアゾリジン薬]]、インスリンなどと比較した場合、グルコースコントロールの改善が認められたと述べている。[[HbA1c/ja|HbA1c]]は、SGLT-2阻害薬を単独で(単剤療法として)投与した後と、他の糖尿病治療薬に上乗せ療法として投与した後に調べられた。使用されたSGLT-2阻害薬は、ダパグリフロジンとカナグリフロジン、および同じ薬物クラスの他の薬物であった。メタアナリシスは、数週間から100週間以上にわたる研究をまとめて行われた。 | |||
Michael | |||
その結果を要約すると、10 mgのダパグリフロジンを24週間投与した場合、プラセボよりも高い血糖コントロール効果を示した。しかし、メトホルミンの上乗せ療法としてダパグリフロジン10 mgを52週間使用した場合、[[glipizide/ja|グリピジド]]と比較して劣る有効性は示されなかった。ダパグリフロジン10 mgを[[monotherapy/ja|単剤療法]]で24週間投与した場合、メトホルミンと比較して劣る有効性は示されなかった。 | |||
カナグリフロジンを検討したメタアナリシスの結果、カナグリフロジンはプラセボと比較してHbA1cに影響を及ぼすことが示された。また、エンパグリフロジンの10 mgと25 mgは、プラセボと比較してHbA1cを改善することがメタアナリシス研究で示された。 | |||
== 構造活性相関(SAR)== | |||
{{Anchor|Structure-activity relationship (SAR)}} | |||
フロリジンおよびダパグリフロジンの[[aglycones/ja|アグリコン]]は、SGLT-1およびSGLT-2に対して弱い阻害作用を有する。阻害剤とSGLTの結合には2つの[[Synergy/ja#Drug synergy|シナジー]]力が関与している。アグリコン上の異なる糖は、アクセス前庭におけるアグリコンの向きに影響を与え、変化させる。なぜなら、結合に関与する力の一つは、グルコース部位への糖の結合だからである。もう一つの力はアグリコンとの結合であり、これは阻害剤全体の結合親和性に影響を与える。 | |||
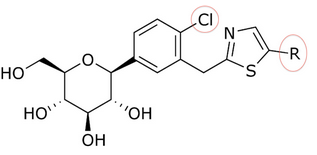
T-1095の発見を契機に、グリコシド・コアに様々な置換基を付加することにより、効力、選択性、経口バイオアベイラビリティを向上させる方法が研究されるようになった。一例として、グルコースとアグリコン部分の間に炭素-炭素結合を作ることによって、o-グリコシドをc-グリコシドに変化させることができる。C-グルコシドはo-グルコシドよりも安定性が高く、半減期や作用時間が変化する。これらの修飾はまた、SGLT-2に対する特異性の向上にもつながっている。遠位環または近位環に[[heterocyclic/ja|複素環]]を有するC-グルコシドは、抗糖尿病効果と[[Physical chemistry/ja|物理化学的]]特徴に関して、すべてにおいて優れている。カナグリフロジンの遠位環に[[thiazole/ja|チアゾール]]を有するC-グルコシドは、表1および表2に示すように、臨床開発につながる良好な物理化学的特性を示しているが、ダパグリフロジンと同等の抗糖尿病活性を有している。 | |||
ソン(Song)たちはカルボン酸からチアゾール化合物を調製した。チアゾール環を持つダパグリフロジンのような化合物を得るには、3つのステップが必要だった。化合物のSGLT-2に対する阻害作用が、ソンと彼の共同研究者らによって試験された。表1、2、3において、IC<sub>50</sub>値は、どの化合物が環の位置にあるか、近位フェニル環のC-4領域にあるか、チアゾール環がどのように関係しているかによって変化する。 | |||
Song | |||
多くの化合物が''[[in vitro/ja|試験管内]]'活性において、環の位置で異なるIC<sub>50</sub>値を示した。例えば、n-ペンチル基(IC<sub>50</sub> = 13,3 nM)、n-ブチル基(IC<sub>50</sub> = 119 nM)、2-フリル基を持つフェニル基(IC<sub>50</sub> = 0,720)または3-チオフェニル基(IC<sub>50</sub> = 0,772)には大きな違いがあった。表1に見られるように、''試験管内''活性は、(近位フェニル環のC-4領域にCl原子があることから)遠位環に結合する化合物によって増加する。 | |||
'''表1:'''遠位環に結合する化合物による'''試験管内'''活性の違い。 | |||
''' | |||
[[File:Mynd fyrir toflu1.png]] | [[File:Mynd fyrir toflu1.png]] | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! R !! IC<sub>50</sub> (nM) !! | ! R !! IC<sub>50</sub> (nM) !! 活性 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"| [[File:Bygging 1.png]] ||align="center"| 0.720 ||align="center"| '' | |align="center"| [[File:Bygging 1.png]] ||align="center"| 0.720 ||align="center"| ''試験管内''活性が向上* | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"| [[File:Bygging 2.png]] ||align="center"| 1.14 ||align="center"| '' | |align="center"| [[File:Bygging 2.png]] ||align="center"| 1.14 ||align="center"| ''試験管内''活性が向上* | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"| [[File:Bygging 3.png]] ||align="center"| 13.3 ||align="center"| | |align="center"| [[File:Bygging 3.png]] ||align="center"| 13.3 ||align="center"| 炭素数が増えるにつれて、IC-50値は変動 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"| [[File:1-Methoxy-n-butane.png]] ||align="center"| 19.6 ||align="center"| '' | |align="center"| [[File:1-Methoxy-n-butane.png]] ||align="center"| 19.6 ||align="center"| ''試験管内''での''活性が低下* | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"| [[File:Bygging 5.png]] ||align="center"| 21.2 ||align="center"| '' | |align="center"| [[File:Bygging 5.png]] ||align="center"| 21.2 ||align="center"| ''試験管内''での''活性が低下* | ||
|} | |} | ||
''* | ''*エチル基との比較対象 (IC<sub>50</sub> = 16,7)'' | ||
表2において、''試験管内''活性は、近位フェニル環(X)のC-4領域の化合物によって変化する。C-4位に小さなメチル基や他のハロゲン原子があると、IC<sub>50</sub>は0.72-36.7の範囲になった(2-フリルを持つフェニルが環の位置にあることを考慮)。 | |||
'''表2:'''近位フェニル環のC-4領域にどの化合物があるかによる'''試験管内'''活性の違い。 | |||
''' | |||
[[File:Mynd fyrir toflu2.png]] | [[File:Mynd fyrir toflu2.png]] | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 164: | Line 108: | ||
|align="center"| CN ||align="center"| 36.7 | |align="center"| CN ||align="center"| 36.7 | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''表3:'''チアゾール環の関わり方によるIC<sub>50</sub>値の違い(他の構造は何も変えていない(X = Cl, R = フェニルと2-フリル)。 | |||
''' | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! 化合物 !! IC<sub>50</sub> (nM) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"| [[File:Mynd fyrir toflu3-1.png]] ||align="center"| 0.720 | |align="center"| [[File:Mynd fyrir toflu3-1.png]] ||align="center"| 0.720 | ||
| Line 176: | Line 118: | ||
|align="center"| [[File:Mynd fyrir toflu3-2.png]] ||align="center"| 1.11 | |align="center"| [[File:Mynd fyrir toflu3-2.png]] ||align="center"| 1.11 | ||
|} | |} | ||
== こちらも参照 == | |||
* [[Sodium-glucose transport proteins/ja]] | |||
* [[Sodium-glucose transport proteins]] | * [[SLC5A2/ja]] | ||
* [[SLC5A2]] | * [[SGLT1/ja]] | ||
* [[SGLT1]] | * [[SGLT2/ja]] | ||
* [[SGLT2]] | * [[Dapagliflozin/ja]] | ||
* [[Dapagliflozin]] | * [[Empagliflozin/ja]] | ||
* [[Empagliflozin]] | * [[Canagliflozin/ja]] | ||
* [[Canagliflozin]] | * [[Ipragliflozin/ja]] | ||
* [[Ipragliflozin]] | |||
{{Drug design/ja}} | |||
{{Drug design}} | |||
[[Category:Drug discovery|Gliflozins]] | [[Category:Drug discovery|Gliflozins]] | ||
[[Category:SGLT2 inhibitors| ]] | [[Category:SGLT2 inhibitors| ]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:58, 14 February 2024
グリフロジンは、2型糖尿病(T2D)の治療薬の一種である。これらはナトリウム/グルコース共輸送体2(SGLT-2)を阻害することで作用するため、SGLT-2阻害薬とも呼ばれる。薬物の有効性は腎排泄に依存し、糖排泄を促進することでグルコースが血液循環に乗るのを防ぐ。作用機序はインスリン非依存性である。
米国では、ダパグリフロジン、カナグリフロジン、エンパグリフロジンの3つの薬物が食品医薬品局(FDA)に受け入れられている。カナグリフロジンは2013年3月にFDAに承認された最初のSGLT-2阻害薬である。ダパグリフロジンとエンパグリフロジンは2014年に承認された。
導入
グルコースホメオスタシスにおける腎臓の役割
二次活性グルコーストランスポーターであるSLC-5遺伝子ファミリーには少なくとも4つのメンバーが存在する。ナトリウムグルコーストランスポータータンパク質SGLT-1とSGLT-2は、このファミリーの2つの主要メンバーである。これら2つのメンバーは、他のトランスポーターの中でも腎臓に存在し、そこでは血糖に関連する主要な共トランスポーターである。腎臓でのグルコース再吸収と腸でのグルコース吸収に関与している。
血中グルコースは糸球体で自由に濾過され、SGLT-1とSGLT-2は腎臓でグルコースを再吸収し、循環細胞に戻す。SGLT-2は再吸収の90%を、SGLT-1は残りの10%を担っている。
SGLT-2タンパク質
ナトリウム/グルコース共輸送体(SGLT)タンパク質は細胞膜に結合しており、グルコースの濃度勾配に逆らって、グルコースを細胞膜を通して細胞内に輸送する役割を持っている。これはナトリウム/カリウムATPaseポンプによって生じるナトリウム勾配を利用することで行われるため、グルコースが細胞内に輸送されると同時にナトリウムも輸送される。勾配に逆らっているため、働くにはエネルギーが必要である。SGLTタンパク質は、インスリンとは無関係に、糸球体濾液からのグルコース再吸収を引き起こす。
SGLT-2はグルコーストランスポーターファミリーの一員であり、低親和性で高容量のグルコーストランスポーターである。SGLT-2は主に近位腎尿細管のS-1およびS-2セグメントで発現しており、濾過されたグルコースの大部分が吸収される。SGLT-2はグルコースの調節に関与し、腎臓におけるグルコースの再吸収の大部分を担っている。
糖尿病では、細胞外グルコース濃度が上昇し、この高いグルコースレベルがSGLT-2のアップレギュレーションを引き起こし、腎臓でのグルコースの吸収を増加させる。これらの作用により、高血糖が維持される。ナトリウムはSGLT-2を介してグルコースと同時に吸収されるため、SGLT-2のアップレギュレーションはおそらく高血圧の発症または維持につながる。ラットにラミプリルまたはロサルタンを与えた研究では,SGLT-2タンパク質とmRNAのレベルが有意に減少した。糖尿病患者において高血圧は一般的な問題であるため、この疾患との関連性があるかもしれない。
ナトリウム/グルコース共輸送体2を阻害する薬物は、腎のグルコース再吸収を阻害し、尿中グルコース排泄を促進し、血中グルコースを低下させる。これらの薬剤はインスリンとは独立して作用し、低血糖や体重増加を引き起こすことなくグルコースレベルを低下させることができる。
発見
中世の医師たちは日常的に尿を試飲し、その観察結果を論述していた。糖尿病は尿中にブドウ糖が排出されることから腎障害であると考えたのは当初どの医師であったかは、現在では歴史から失われているらしい。インスリンの発見は、やがて膵臓に焦点を当てた糖尿病管理につながった。糖尿病の治療戦略の伝統的な焦点は、内因性インスリン分泌の増強とインスリン感受性の改善であった。
過去10年間、高血糖の発症と維持における腎臓の役割が検討されてきた。腎臓の役割は、ナトリウム/グルコーストランスポーター2タンパク質を阻害する薬物の開発につながった。健康な成人では、毎日約180グラムのグルコースが糸球体で濾過され、原尿中に失われるが、最初に濾過されたグルコースの90%以上は、近位尿細管の初期凸分節にあるSGLT-2によって制御される高容量システムによって再吸収される。残りの濾過されたグルコースはほとんどすべてナトリウム/グルコーストランスポーター1によって再吸収されるため、正常な状況下では、濾過されたグルコースはほとんどすべて再吸収され、糖尿病でない人の尿中に含まれるグルコースは100 mg未満である。
フロリジン
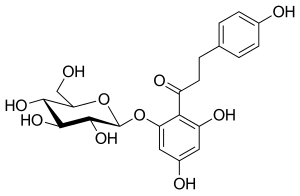
フロリジンは100年以上前から知られている化合物である。天然に存在する植物性グルコシドであり、腎近位尿細管および小腸の粘膜に存在するナトリウム/グルコースシンポーターを阻害することにより、腎糖尿を生じさせ、腸のグルコース吸収を阻害する。フロリジンは1835年に初めて単離され、その後、SGLT-1とSGLT-2の両タンパク質に対して強力ではあるが非選択的な阻害剤であることが判明した。
フロリジンは非常に興味深い特性を持っているようで、動物実験での結果は有望で、インスリン感受性を改善し、糖尿病ラットモデルでは尿中のグルコース濃度を増加させ、血漿中の正常なグルコース濃度も低血糖を起こすことなく上昇させるようであった。残念なことに、これらの特性にもかかわらず、フロリジンはいくつかの理由から臨床開発には十分適していなかった。フロリジンは消化管で分解されるため経口バイオアベイラビリティが非常に悪く,非経口的に投与しなければならない。フロリジンの活性代謝物であるフロレチンはグルコーストランスポーターの強力な阻害剤であり、フロリジンは下痢や脱水のような消化管における重篤な有害事象を引き起こすようである。このような理由から、フロリジンはヒトで使用されることはなかった。
フロリジンはそれ以上の臨床試験には適さなかったが、SGLT-2阻害薬の開発において重要な役割を果たした。それは、安全性と忍容性のプロファイルが改善されたSGLT阻害剤が認識される基礎となった。例えば、SGLT阻害薬は胃腸の有害事象を伴わず、バイオアベイラビリティもはるかに高い。
SGLT-2を阻害すると、グルコースレベルのコントロールが改善し、インスリン値が低下し、血圧と尿酸値が低下し、カロリー浪費が増強する。SGLT-2阻害が直接的な腎保護作用を持つかもしれないという仮説を支持するデータもある。これには、糖尿病に伴う尿細管肥大および濾過亢進を抑制する作用や、グルコースの尿細管毒性を軽減する作用が含まれる。ダパグリフロジンによる治療後のSGLT-2の阻害は、尿細管グルコース再吸収能を約30~50%低下させる。
薬物開発
フロリジンはグルコース部位と2つの芳香環(アグリコン部位)からなり、アルキルスペーサーによって結合されている。当初、フロリジンは発熱や感染症、特にマラリアの治療のために単離された。マイケル・ナックと彼のパートナーによると、1950年代にフロリジンに関する研究が行われ、腎臓、小腸、および他のいくつかの組織における糖輸送を阻害できることが示された。年代初めには、ナトリウム/グルコース共輸送体2が完全に特性決定されたので、フロリジンのメカニズムが注目されるようになった。その後の研究では、フロリジンの糖阻害作用はナトリウム/グルコース共輸送体タンパク質の阻害によるものだと言われている。
報告されているSGLT-2阻害剤のほとんどはグルコシド類縁体であり、自然界に存在するo-アリールグルコシドまで追跡することができる。SGLT-2阻害剤としてo-グルコシドを使用する際の問題は、小腸内のβ-グルコシダーゼによる分解まで追跡できる不安定性である。そのため、経口投与されるo-グルコシドはプロドラッグエステルでなければならない。これらのプロドラッグは体内で変化を起こし、グルコースとアグリコン部分の間に炭素-炭素結合が生じるため、o-グルコシドからc-グルコシドが形成される。C-グルコシドはo-グルコシドとは異なる薬物動態プロファイル(例えば半減期や作用時間)を持ち、β-グルコシダーゼでは分解されない。最初に発見されたc-グルコシドは薬物ダパグリフロジンであった。ダパグリフロジンは、欧州医薬品庁によって承認された最初の高選択的SGLT-2阻害薬である。臨床開発中のSGLT-2阻害薬はすべてプロドラッグであり、活性を発揮するためには活性型'A'に変換する必要がある。
T-1095

。
フロリジンは非選択的阻害剤で経口バイオアベイラビリティが低いため、フロリジン誘導体が合成され、T-1095と呼ばれるようになった。T-1095は炭酸メチルプロドラッグであり、経口投与すると循環吸収され、肝臓で速やかに活性代謝物T-1095Aに変換される。SGLT-1およびSGLT-2を阻害することにより、糖尿病動物の尿中グルコース排泄量を増加させた。T-1095は臨床開発が進まなかったが、これはおそらくSGLT-1を阻害するためであろうが、非選択的SGLT阻害薬はグルコーストランスポーター1(GLUT-1)も阻害する可能性がある。濾過されたグルコースの90%はSGLT-2を介して再吸収されるため、研究は特にSGLT-2に焦点を当てている。SGLT-1の阻害は、激しい下痢を特徴とする遺伝性疾患グルコース-ガラクトース吸収不良を引き起こす可能性もある。
ISIS 388626
SGLT-2阻害の新規な方法の予備的知見によると、アンチセンスである。オリゴヌクレオチドである。ISIS 388626は、1週間に1回投与した場合、近位腎尿細管におけるmRNA発現を最大80%低下させることにより、げっ歯類およびイヌの血漿グルコースを改善した。SGLT-1には影響しなかった。ISIS 388626の非ヒト霊長類における長期使用に関する研究結果では、低血糖を伴うことなく糖尿の1000倍以上の増加が観察された。この糖尿の増加は、SGLT-2の発現の用量依存的な減少に起因すると考えられ、最高用量では75%以上の減少につながった。2011年、Ionis Pharmaceuticals社は12ヌクレオチドアンチセンスオリゴヌクレオチドであるISIS-SGLT-2RXの臨床第1相試験を開始した。この研究の結果は2017年に発表され、この治療は「予期せぬ腎作用と関連していた」。著者らは、"ISIS 388626によるSGLT2のアンチセンスを介した遮断という概念をさらに検討する前に、さらなる検討を正当化するために、より多くの前臨床データが必要である"と結論づけた。
血糖コントロールにおけるSGLT-2阻害薬の活性
Michael Nauck氏は、2型糖尿病患者の血糖コントロールにおけるSGLT-2阻害薬の活性に関する研究のメタ解析では、プラセボ、メトホルミン、スルホニルウレア、チアゾリジン薬、インスリンなどと比較した場合、グルコースコントロールの改善が認められたと述べている。HbA1cは、SGLT-2阻害薬を単独で(単剤療法として)投与した後と、他の糖尿病治療薬に上乗せ療法として投与した後に調べられた。使用されたSGLT-2阻害薬は、ダパグリフロジンとカナグリフロジン、および同じ薬物クラスの他の薬物であった。メタアナリシスは、数週間から100週間以上にわたる研究をまとめて行われた。
その結果を要約すると、10 mgのダパグリフロジンを24週間投与した場合、プラセボよりも高い血糖コントロール効果を示した。しかし、メトホルミンの上乗せ療法としてダパグリフロジン10 mgを52週間使用した場合、グリピジドと比較して劣る有効性は示されなかった。ダパグリフロジン10 mgを単剤療法で24週間投与した場合、メトホルミンと比較して劣る有効性は示されなかった。
カナグリフロジンを検討したメタアナリシスの結果、カナグリフロジンはプラセボと比較してHbA1cに影響を及ぼすことが示された。また、エンパグリフロジンの10 mgと25 mgは、プラセボと比較してHbA1cを改善することがメタアナリシス研究で示された。
構造活性相関(SAR)
フロリジンおよびダパグリフロジンのアグリコンは、SGLT-1およびSGLT-2に対して弱い阻害作用を有する。阻害剤とSGLTの結合には2つのシナジー力が関与している。アグリコン上の異なる糖は、アクセス前庭におけるアグリコンの向きに影響を与え、変化させる。なぜなら、結合に関与する力の一つは、グルコース部位への糖の結合だからである。もう一つの力はアグリコンとの結合であり、これは阻害剤全体の結合親和性に影響を与える。
T-1095の発見を契機に、グリコシド・コアに様々な置換基を付加することにより、効力、選択性、経口バイオアベイラビリティを向上させる方法が研究されるようになった。一例として、グルコースとアグリコン部分の間に炭素-炭素結合を作ることによって、o-グリコシドをc-グリコシドに変化させることができる。C-グルコシドはo-グルコシドよりも安定性が高く、半減期や作用時間が変化する。これらの修飾はまた、SGLT-2に対する特異性の向上にもつながっている。遠位環または近位環に複素環を有するC-グルコシドは、抗糖尿病効果と物理化学的特徴に関して、すべてにおいて優れている。カナグリフロジンの遠位環にチアゾールを有するC-グルコシドは、表1および表2に示すように、臨床開発につながる良好な物理化学的特性を示しているが、ダパグリフロジンと同等の抗糖尿病活性を有している。
ソン(Song)たちはカルボン酸からチアゾール化合物を調製した。チアゾール環を持つダパグリフロジンのような化合物を得るには、3つのステップが必要だった。化合物のSGLT-2に対する阻害作用が、ソンと彼の共同研究者らによって試験された。表1、2、3において、IC50値は、どの化合物が環の位置にあるか、近位フェニル環のC-4領域にあるか、チアゾール環がどのように関係しているかによって変化する。
多くの化合物が試験管内'活性において、環の位置で異なるIC50値を示した。例えば、n-ペンチル基(IC50 = 13,3 nM)、n-ブチル基(IC50 = 119 nM)、2-フリル基を持つフェニル基(IC50 = 0,720)または3-チオフェニル基(IC50 = 0,772)には大きな違いがあった。表1に見られるように、試験管内活性は、(近位フェニル環のC-4領域にCl原子があることから)遠位環に結合する化合物によって増加する。
表1:遠位環に結合する化合物による試験管内活性の違い。
| R | IC50 (nM) | 活性 |
|---|---|---|
 |
0.720 | 試験管内活性が向上* |
 |
1.14 | 試験管内活性が向上* |
| 13.3 | 炭素数が増えるにつれて、IC-50値は変動 | |
| 19.6 | 試験管内での活性が低下* | |
 |
21.2 | 試験管内での活性が低下* |
*エチル基との比較対象 (IC50 = 16,7)
表2において、試験管内活性は、近位フェニル環(X)のC-4領域の化合物によって変化する。C-4位に小さなメチル基や他のハロゲン原子があると、IC50は0.72-36.7の範囲になった(2-フリルを持つフェニルが環の位置にあることを考慮)。
表2:近位フェニル環のC-4領域にどの化合物があるかによる試験管内活性の違い。
| X | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|
| Cl | 0.720 |
| Me | 1.43 |
| F | 6.11 |
| H | 22.6 |
| CN | 36.7 |
表3:チアゾール環の関わり方によるIC50値の違い(他の構造は何も変えていない(X = Cl, R = フェニルと2-フリル)。
| 化合物 | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|
 |
0.720 |
 |
1.11 |