Collagen/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "{| class="wikitable" |- |+'''コラーゲン遺伝子の遺伝子異常'''" |
No edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | <languages /> | ||
{{Pathnav|Dietary supplement/ja|protein/ja|frame=1}} | |||
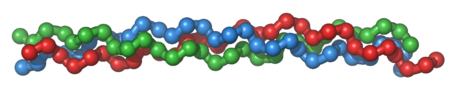
[[Image:Collagentriplehelix.png|thumb|upright=1.5|トロポコラーゲン分子:3つの左巻きプロコラーゲン(赤、緑、青)が結合し、右巻き三重らせんトロポコラーゲンを形成する。]] | [[Image:Collagentriplehelix.png|thumb|upright=1.5|トロポコラーゲン分子:3つの左巻きプロコラーゲン(赤、緑、青)が結合し、右巻き三重らせんトロポコラーゲンを形成する。]] | ||
| Line 157: | Line 158: | ||
1個のコラーゲン分子であるトロポコラーゲンは、線維のような大きなコラーゲン凝集体を構成するために使用される。長さは約300 [[:en:nanometre|nm]]、直径は1.5 nmで、3本の[[polypeptide/ja|ポリペプチド]]鎖(アルファペプチドと呼ばれる。ステップ2参照)これら3つの左巻き[[helix/ja|らせん]]は、ねじれながら右巻きの3重らせん、または「スーパーらせん」となり、多くの[[hydrogen bond/ja|水素結合]]によって安定化された協力的な[[quaternary structure/ja|4次構造]]を形成する。全てのコラーゲンではないにせよ、I型コラーゲンやおそらく全ての線維性コラーゲンでは、各三重らせんはコラーゲン・ミクロフィブリルと呼ばれる右巻きの超スーパーコイルに結合する。各ミクロフィブリルは隣接するミクロフィブリルと[[wikt:interdigitate/ja|聯絡]]しており、コラーゲン線維内では結晶と言えるほど整然と並んでいるが、個々が不安定であることを示唆する程度である。 | 1個のコラーゲン分子であるトロポコラーゲンは、線維のような大きなコラーゲン凝集体を構成するために使用される。長さは約300 [[:en:nanometre|nm]]、直径は1.5 nmで、3本の[[polypeptide/ja|ポリペプチド]]鎖(アルファペプチドと呼ばれる。ステップ2参照)これら3つの左巻き[[helix/ja|らせん]]は、ねじれながら右巻きの3重らせん、または「スーパーらせん」となり、多くの[[hydrogen bond/ja|水素結合]]によって安定化された協力的な[[quaternary structure/ja|4次構造]]を形成する。全てのコラーゲンではないにせよ、I型コラーゲンやおそらく全ての線維性コラーゲンでは、各三重らせんはコラーゲン・ミクロフィブリルと呼ばれる右巻きの超スーパーコイルに結合する。各ミクロフィブリルは隣接するミクロフィブリルと[[wikt:interdigitate/ja|聯絡]]しており、コラーゲン線維内では結晶と言えるほど整然と並んでいるが、個々が不安定であることを示唆する程度である。 | ||
[[File:Collagen biosynthesis (en).png|thumb|upright=1.3|3つの[[polypeptide/ja|ポリペプチド]]がコイル状になってトロポコラーゲンを形成する。その後、多くのトロポコラーゲンが結合してフィブリルを形成し、その多くが線維を形成する。]] | |||
[[File:Collagen biosynthesis (en).png|thumb|upright=1.3|3つの[[polypeptide/ja|ポリペプチド]] | |||
コラーゲンの特徴は、コラーゲンサブユニットの3本の鎖のそれぞれに[[amino acid/ja|アミノ酸]]が規則正しく並んでいることである。その配列はしばしば[[glycine/ja|Gly]]-[[proline/ja|Pro]]-XまたはGly-X-[[hydroxyproline/ja|Hyp]]のパターンに従う。プロリンまたはヒドロキシプロリンは全塩基配列の約1/6を占める。コラーゲン配列の1/3がグリシンであることから、コラーゲン配列の約半分はグリシン、プロリン、ヒドロキシプロリンではないことになる。コラーゲンの高いグリシン含量は、コラーゲンらせんの安定化に関して重要である。これは、分子内のコラーゲン線維の非常に密接な結合を可能にし、水素結合と分子間架橋の形成を促進するからである。このような規則的な繰り返しと高いグリシン含量は、絹[[fibroin/ja|フィブロイン]]のような数少ない繊維状タンパク質にしか見られない。 | コラーゲンの特徴は、コラーゲンサブユニットの3本の鎖のそれぞれに[[amino acid/ja|アミノ酸]]が規則正しく並んでいることである。その配列はしばしば[[glycine/ja|Gly]]-[[proline/ja|Pro]]-XまたはGly-X-[[hydroxyproline/ja|Hyp]]のパターンに従う。プロリンまたはヒドロキシプロリンは全塩基配列の約1/6を占める。コラーゲン配列の1/3がグリシンであることから、コラーゲン配列の約半分はグリシン、プロリン、ヒドロキシプロリンではないことになる。コラーゲンの高いグリシン含量は、コラーゲンらせんの安定化に関して重要である。これは、分子内のコラーゲン線維の非常に密接な結合を可能にし、水素結合と分子間架橋の形成を促進するからである。このような規則的な繰り返しと高いグリシン含量は、絹[[fibroin/ja|フィブロイン]]のような数少ない繊維状タンパク質にしか見られない。 | ||
| Line 182: | Line 181: | ||
|+'''コラーゲン遺伝子の遺伝子異常''' | |+'''コラーゲン遺伝子の遺伝子異常''' | ||
| '''タイプ''' || '''備考''' || '''遺伝子''' || '''[[Collagen disease/ja|障害]]''' | |||
| ''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Type-I collagen|I]] || | | [[Type-I collagen/ja|I]] || 人体に最も多く存在するコラーゲンである。組織が修復によって[[healing/ja|治療]]する際の最終産物である[[scar/ja|瘢痕]]組織に存在する。[[tendon/ja|腱]]、皮膚、動脈壁、角膜、筋線維を取り囲む[[endomysium/ja|内膜]]、線維軟骨、骨や歯の器質部分に存在する。 || [[COL1A1/ja]], [[COL1A2/ja]] || [[Osteogenesis imperfecta/ja]], [[Ehlers–Danlos syndrome/ja]], [[infantile cortical hyperostosis/ja]] 別名キャッフィー病 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Type-II collagen|II]] || [[Hyaline cartilage]] | | [[Type-II collagen/ja|II]] || [[Hyaline cartilage/ja|ヒアリン軟骨]]は軟骨タンパク質の50%を占める。眼球の[[vitreous humour/ja|硝子体液]] || [[COL2A1/ja]] || [[Collagenopathy, types II and XI/ja]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Type-III collagen|III]] || | | [[Type-III collagen/ja|III]] || これは[[granulation tissue/ja|肉芽組織]]のコラーゲンであり、より丈夫なI型コラーゲンが合成される前に、若い線維芽細胞によって速やかに産生される。[[reticular fiber/ja|網状線維]]。動脈壁、皮膚、腸、子宮にも見られる。 || [[COL3A1/ja]] || [[Ehlers–Danlos syndrome/ja]], [[Dupuytren's contracture/ja]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Type-IV collagen|IV]] || [[Basal lamina]] | | [[Type-IV collagen/ja|IV]] || [[Basal lamina/ja|基底膜]]、[[eye lens/ja|眼球の水晶体]]。また、[[capillaries/ja|毛細血管]]および[[kidney/ja|腎臓]]の[[nephron/ja|ネフロン]]の[[Glomerulus (kidney)/ja|糸球体]]の濾過システムの一部としても機能する。 || [[Collagen, type IV, alpha 1/ja|COL4A1]], [[COL4A2/ja]], [[COL4A3/ja]], [[COL4A4/ja]], [[COL4A5/ja]], [[COL4A6/ja]] || [[Alport syndrome/ja]], [[Goodpasture's syndrome/ja]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| V || | | V || ほとんどの間質組織は、I型と関連している。 [[placenta/ja]] || [[COL5A1/ja]], [[COL5A2/ja]], [[COL5A3/ja]] || [[Ehlers–Danlos syndrome/ja]] (classical) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| VI || | | VI || ほとんどの間質組織は、I型と関連している。 || [[COL6A1/ja]], [[COL6A2/ja]], [[COL6A3/ja]], [[COL6A5/ja]] || [[Ulrich myopathy/ja]], [[Bethlem myopathy/ja]], [[atopic dermatitis/aj]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| VII || | | VII || [[dermoepidermal junction/ja|真皮表皮接合部]]で[[anchoring fibril/ja|アンカリング線維]]を形成する。 || [[COL7A1/ja]] || [[Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica/ja]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| VIII || | | VIII || いくつかの[[endothelium/ja内皮]]細胞がある。 || [[COL8A1/ja]], [[COL8A2/ja]] || [[Posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy 2/ja]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| IX || [[FACIT collagen]], | | IX || [[FACIT collagen/ja|FACITコラーゲン]], 軟骨、II型およびXI型線維に関連する。 || [[COL9A1/ja]], [[COL9A2/ja]], [[COL9A3/ja]] || [[EDM2/ja]]と[[EDM3/ja]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| X || [[Hypertrophic]] | | X || [[Hypertrophic/ja|肥大型]]と[[Mineralization (biology)/ja|石化]]軟骨 || [[COL10A1/ja]] || [[Schmid metaphyseal dysplasia/ja]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XI || | | XI || 軟骨 || [[COL11A1/ja]], [[COL11A2/ja]] || [[Collagenopathy, types II and XI/ja]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XII || [[FACIT collagen]], | | XII || [[FACIT collagen/ja|FACITコラーゲン]], フィブリル、[[decorin/ja|デコリン]]およびグリコサミノグリカンを含むI型と相互作用する || [[COL12A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XIII || | | XIII || 膜貫通型コラーゲンで、インテグリンa1b1、[[fibronectin/ja|フィブロネクチン]]、および[[didogen/ja|ニドゲン]]や[[perlecan/ja|ペルレカン]]のような基底膜の成分と相互作用する。 || [[COL13A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XIV|| [[FACIT collagen]], | | XIV|| [[FACIT collagen/ja|FACITコラーゲン]], 別名ウンドゥリン || [[COL14A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XV || – || [[COL15A1]] || – | | XV || – || [[COL15A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XVI || [[FACIT collagen]] || [[COL16A1]] || – | | XVI || [[FACIT collagen/ja|FACITコラーゲン]] || [[COL16A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Collagen XVII|XVII]] || Transmembrane collagen, also known as BP180, a 180 kDa protein || [[COL17A1]] || [[Bullous pemphigoid]] | | [[Collagen XVII/ja|XVII]] || Transmembrane collagen, also known as BP180, a 180 kDa protein || [[COL17A1/ja]] || [[Bullous pemphigoid/ja]]および接合型[[epidermolysis bullosa/ja|表皮水疱症]]のある種の形態である。 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Type XVIII collagen|XVIII]] || | | [[Type XVIII collagen/ja|XVIII]] || [[endostatin/ja|エンドスタチン]]の生成源である。 || [[COL18A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XIX || [[FACIT collagen]] || [[COL19A1]] || – | | XIX || [[FACIT collagen/ja|FACITコラーゲン]] || [[COL19A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XX || – || [[COL20A1]] || – | | XX || – || [[COL20A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XXI || [[FACIT collagen]] || [[COL21A1]] || – | | XXI || [[FACIT collagen/ja|FACITコラーゲン]] || [[COL21A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XXII || [[FACIT collagen]] || [[COL22A1]] || – | | XXII || [[FACIT collagen/ja|FACITコラーゲン]] || [[COL22A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Collagen, type XXIII, alpha 1|XXIII]] || | | [[Collagen, type XXIII, alpha 1/ja|XXIII]] || MACITコラーゲン || [[COL23A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XXIV || – || [[COL24A1]] || – | | XXIV || – || [[COL24A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XXV || – || [[COL25A1]] || – | | XXV || – || [[COL25A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XXVI || – || [[EMID2]] || – | | XXVI || – || [[EMID2/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XXVII || – || [[COL27A1]] || – | | XXVII || – || [[COL27A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XXVIII || – || [[COL28A1]] || – | | XXVIII || – || [[COL28A1/ja]] || – | ||
|- | |- | ||
| XXIX || | | XXIX || 表皮コラーゲン || [[COL29A1/ja]] || アトピー性皮膚炎 | ||
|} | |} | ||
上記の疾患に加えて、[[scleroderma/ja|強皮症]]ではコラーゲンの過剰沈着が起こる。 | |||
==病気{{Anchor|Diseases}}== | |||
==Diseases== | 20種類以上のコラーゲンのうち12種類で1000もの変異が同定されている。これらの変異は組織レベルで様々な病気を引き起こす可能性がある。 | ||
[[Osteogenesis imperfecta/ja|骨形成不全症]] - ''1型コラーゲン''の突然変異によって引き起こされ、優性常染色体疾患であり、骨が弱く、結合組織が不規則である。軽症例では1型コラーゲンのレベルが低下しているが、重症例ではコラーゲンの構造的欠陥がある。 | |||
[[Osteogenesis imperfecta]] | |||
[[Chondrodysplasia/ja|軟骨異形成症]] - ''2型コラーゲン''の突然変異によって引き起こされると考えられている骨格障害であるが、これを確認するためにさらなる研究が行われている。 | |||
[[Chondrodysplasia]] | |||
[[Ehlers–Danlos syndrome/ja|エーラス・ダンロス症候群]] - 結合組織の変形を引き起こすこの疾患は、13の異なるタイプが知られている。まれなタイプでは、動脈が破裂する致死的なものもある。それぞれの症候群は異なる突然変異によって引き起こされる。例えば、この疾患の血管型(vEDS)は''3型コラーゲン''の突然変異によって起こる。 | |||
[[Ehlers–Danlos syndrome]] | |||
[[Alport syndrome/ja|アルポート症候群]] - 遺伝的に受け継がれる可能性があり、通常はX連鎖優性遺伝であるが、常染色体優性遺伝や常染色体劣性遺伝もある。 | |||
[[Alport syndrome]] | |||
[[Knobloch syndrome/ja|ノブロッホ症候群]] - コラーゲンXVIIIの産生をコードする[[COL18A1/ja|COL18A1]]遺伝子の変異によって引き起こされる。脳組織の突出と網膜の変性がみられる。家族にこの疾患の患者がいる場合、遺伝的な関連性があるため、自分自身が発症するリスクが高くなる。 | |||
[[Knobloch syndrome]] | |||
==特徴{{Anchor|Characteristics}}== | |||
==Characteristics== | コラーゲンは長い[[fibrous protein/ja|繊維構造タンパク質]]の一つであり、その機能は[[enzyme/ja|酵素]]などの[[globular protein/ja|球状タンパク質]]とは全く異なる。''コラーゲン線維''と呼ばれる丈夫なコラーゲンの束は、ほとんどの組織を支え、細胞に外側から構造を与える[[extracellular matrix/ja|細胞外マトリックス]]の主要な構成要素であるが、コラーゲンはある種の細胞内部にも存在する。コラーゲンは大きな[[tensile strength/ja|引っ張り強度]]を持ち、[[fascia/ja|筋膜]]、[[cartilage/ja|軟骨]]、[[ligament/ja|靭帯]]、[[tendon/ja|腱]]、[[bone/ja|骨]]、皮膚の主成分である。[[elastin/ja|エラスチン]]や柔らかい[[keratin/ja|ケラチン]]とともに皮膚の強度と弾力性を担っており、その劣化は[[aging/ja|老化]]に伴う[[wrinkle/ja|しわ]]の原因となる。[[blood vessel/ja|血管]]を強化し、[[biological tissue/ja|組織]]の発達に関与する。眼の[[cornea/ja|角膜]]や水晶体には[[crystal/ja|結晶]]線状で存在する。[[Mesozoic/ja|中生代]]や[[Paleozoic/ja|古生代]]の骨でも頻繁に化石化することから、化石記録では最も豊富なタンパク質の1つかもしれない。 | ||
===用途=== | |||
[[file:Beretta Salami and Collagen Casing .jpg|right|150px|thumb|サラミとその中に入っていたコラーゲンのケーシング(下)]] | |||
[[file:Beretta Salami and Collagen Casing .jpg|right|150px|thumb| | コラーゲンの用途は食品から医薬品まで多岐にわたる。医療業界では、[[plastic surgery/ja|美容外科]]や[[burn (injury)/ja|火傷手術]]に使用されている。食品分野では、[[casing (sausage)/ja|ソーセージ用ケーシング]]が使用例のひとつである。 | ||
コラーゲンが加熱などの十分な[[denaturation (biochemistry)/ja|変性]]を受けると、3本のトロポコラーゲン鎖は部分的または完全に分離して球状ドメインとなり、[[random coil/ja|ランダムコイル]]の通常のコラーゲン・ポリプロリンII(PPII)とは異なる二次構造を含む。このプロセスは[[gelatin/ja|ゼラチン]]の形成を説明するものであり、味付けされた[[gelatin dessert/ja|ゼラチンデザート]]を含む多くの食品に使用されている。食品以外にも、ゼラチンは製薬、化粧品、写真産業で使用されている。ゼラチンは[[dietary supplement/ja|栄養補助食品]]としても使用され、老化防止薬としても宣伝されている。 | |||
ギリシア語で糊を意味する''kolla''から、コラーゲンという言葉は「[[animal glue/ja|糊]]生産者」を意味し、糊を得るために馬や他の動物の皮膚や[[tendon/ja|筋]]を煮沸する初期のプロセスを指す。コラーゲン接着剤は約4,000年前にエジプト人によって使用され、ネイティブ・アメリカンは約1,500年前に[[:en:bow (weapon)|弓]]に使用していた。世界最古の接着剤は[[radiocarbon dating/ja|炭素年代]]で8,000年以上前のもので、コラーゲンであることが判明した-縄籠や[[:en:embroidery|刺繍]]された[[:en:Textile|ファブリック]]の保護裏地として、[[:en:list of eating utensils|食器]]をつなぎ合わせるために、また[[human skull/ja|人間の頭蓋骨]]の十字の装飾に使われていた。コラーゲンは通常ゼラチンに変化するが、乾燥状態のために生き残った。動物の接着剤は[[thermoplastic/ja|熱可塑性]]であり、再加熱すると再び軟化するため、現在でも高級バイオリンやギターなどの[[:en:musical instrument|楽器]]の製作に使われている。永久的で強靭な[[chemical synthesis/ja|合成]]プラスチック接着剤とは相容れない用途である。革を含む動物のすじや皮は、何千年もの間、有用な物品を作るために使われてきた。 | |||
ゼラチン-[[resorcinol/ja|レゾルシノール]]-[[formaldehyde/ja|ホルムアルデヒド]]接着剤(およびホルムアルデヒドを毒性の低いペンタンジアルと[[glyoxal/ja|エタンジアル]]に置き換えたもの)は、ウサギの[[lung/ja|肺]]の実験的切開の修復に用いられてきた。 | |||
=== 化粧品 | === 化粧品 | ||
Latest revision as of 18:39, 23 April 2024
コラーゲン(/ˈkɒlədʒən/)は、主に軟骨、骨、腱、靭帯、皮膚などの身体の様々な結合組織に見られる細胞外マトリックスの主要な構造タンパク質である。結合組織の主成分として、哺乳類において最も豊富なタンパク質であり、全身のタンパク質含有量の25%から35%を占める。コラーゲンはアミノ酸が結合してコラーゲンヘリックスとして知られる細長い線維の三重らせんを形成している。ビタミンCはコラーゲンの合成に不可欠であり、ビタミンEはコラーゲンの産生を改善する。

コラーゲン組織は、ミネラルミネラリゼーションの程度によって、剛直(骨)かコンプライアント(腱)、あるいは剛直からコンプライアントへの勾配(軟骨)を持つ。コラーゲンは角膜、血管、腸、椎間板、歯の象牙質にも豊富に存在する。筋肉組織では、内膜の主要な構成成分として機能する。コラーゲンは筋肉組織の1~2%を占め、骨格筋組織の重量の6%を占める。線維芽細胞はコラーゲンを作り出す最も一般的な細胞である。食品や工業用に使用されるゼラチンは、熱、塩基性溶液、弱酸を用いて不可逆的に加水分解されたコラーゲンである。
語源

コラーゲンという名称は、"接着剤"を意味するギリシャ語κόλλα(kólla)と、「生成」を表す接尾辞-γέν(-gen)に由来する。
ヒトのタイプ
人体中のコラーゲンの90%以上はI型コラーゲンである。しかし、2011年現在、28種類のヒト・コラーゲンが同定、記述され、形成する構造によっていくつかのグループに分けられている。全てのタイプが少なくとも1つの三重らせんを含んでいる。この種類の多さは、コラーゲンの多様な機能性を示している。
- 線維性(タイプI、II、III、V、XI)
- 非線維性
最も一般的な5つのタイプがある:
- I型:皮膚、腱、血管系、臓器、骨(骨の有機部分の主成分)
- |II型: 軟骨(軟骨の主なコラーゲン成分)
- III型:網状(網状繊維の主成分)、I型と並んでよく見られる。
- IV型:基底膜(基底膜の上皮分泌層)を形成する。
- V型:細胞表面、毛髪、胎盤を形成する。
心臓
4つの心臓弁リングを含むコラーゲン質の心骨格は、組織学的に、弾力的かつ特異的に心筋に結合している。心骨格には、心室間隔と房室隔という心室の隔壁も含まれる。コラーゲンの心臓性能の測定への寄与は、要約すると心臓から放出される血圧の流体力学に対抗する連続的なねじり力を表す。心臓の上室と下室を仕切るコラーゲン構造は、典型的な生理学的手段によって血液と電気インパルスの両方を排除する不透過性の膜である。コラーゲンによるサポートがあれば、心房細動が心室細動に悪化することはない。コラーゲンは、平滑筋量とともに、さまざまな密度で層になっている。コラーゲンの質量、分布、年齢、密度はすべて、血液を前後に移動させるのに必要なコンプライアンスに寄与する。個々の心臓弁膜は、可変的な圧力の下で、特殊なコラーゲンによって形状に折り畳まれる。コラーゲン内のカルシウム沈着は、老化の自然な機能として徐々に起こる。コラーゲンマトリックス内の石灰化した点は、血液と筋肉の動くディスプレイの中でコントラストを示し、心臓画像技術の方法によって、本質的に血液の流入(心臓入力)と血液の流出(心臓出力)の比率を示すことができる。心臓を支えるコラーゲンの病理は結合組織病の範疇で理解されている。
骨移植
骨格は身体の構造を形成しているため、骨折や怪我の後でも強度を維持することが不可欠である。コラーゲンは三重らせん構造を持ち、非常に強い分子であるため、骨移植に使用される。骨格の構造的完全性を損なわないので、骨に使用するのに理想的である。コラーゲンの三重らせん構造は酵素による分解を防ぎ、細胞の接着を可能にし、細胞外マトリックスの適切な組み立てに重要である。
組織再生
コラーゲン・スキャフォールドは、スポンジ、薄いシート、ファイバーなど、組織再生に用いられている。コラーゲンは、孔構造、透過性、親水性、生体内での安定性など、組織再生に有利な特性を持つ。コラーゲンの足場はまた、骨芽細胞や線維芽細胞などの細胞の沈着を支持し、一度挿入されると成長が正常に進むように促進する。
再建外科的用途=
コラーゲンは、重度の熱傷や創傷の管理に使用される人工皮膚代替物の構築に広く使用されている。これらのコラーゲンは、ウシ、ウマ、ブタ、あるいはヒト由来であり、シリコーン、グリコサミノグリカン、線維芽細胞、成長因子および他の物質と組み合わせて使用されることもある。
創傷治癒
コラーゲンは、身体の重要な天然資源のひとつであり、創傷治癒のあらゆる段階に役立つ皮膚組織の成分である。コラーゲンが創傷床で利用可能になると、創傷の閉鎖が起こる。創傷が悪化し、時には切断などの処置が必要になることもあるが、それを避けることができる。
コラーゲンは天然物であるため、天然の創傷被覆材として使用され、人工の創傷被覆材にはない特性を持っている。細菌に対する耐性があり、これは創傷被覆材にとって極めて重要である。コラーゲンには感染と闘う自然な能力があるため、傷口を無菌状態に保つのに役立つ。コラーゲンを火傷のドレッシング材として使用すると、健康な肉芽組織が火傷の上に非常に早く形成され、火傷が急速に治癒するのを助ける。
創傷治癒の4つの段階を通して、コラーゲンは以下の機能を果たす:
- ガイド機能: コラーゲン線維は線維芽細胞を誘導する役割を果たす。線維芽細胞は結合組織マトリックスに沿って移動する。
- 走化性特性: コラーゲン線維の大きな表面積は、治癒を助ける線維形成細胞を引き寄せることができる。
- 核形成: コラーゲンは、ある種の中性塩分子の存在下で、線維構造の形成を引き起こす核形成剤として働くことができる。
- 止血作用: 血液血小板はコラーゲンと相互作用して止血栓を作る。
基礎研究
コラーゲンは実験室での研究において細胞培養に使用され、細胞の挙動や細胞と細胞外環境との相互作用を研究している。コラーゲンはまた、3Dバイオプリンティングや3D組織モデルのバイオファブリケーションのためのバイオインクとしても広く使用されている。
生物学
コラーゲンタンパク質は三重らせんで構成され、一般に2本の同一鎖(α1)と化学組成がわずかに異なるもう1本の鎖(α2)からなる。コラーゲンのアミノ酸組成はタンパク質としては非定型であり、特にヒドロキシプロリンの含有量が高い。コラーゲンのアミノ酸配列で最も一般的なモチーフはグリシン-プロリン-Xとグリシン-X-ヒドロキシプロリンであり、Xはグリシン、プロリン、ヒドロキシプロリン以外のアミノ酸である。魚類と哺乳類の皮膚の平均アミノ酸組成を示す。
| アミノ酸 | 哺乳類の皮膚に多い (残基/1000) |
魚類の皮膚に多い (残基/1000) |
|---|---|---|
| Glycine/ja | 329 | 339 |
| Proline/ja | 126 | 108 |
| Alanine/ja | 109 | 114 |
| Hydroxyproline/ja | 95 | 67 |
| Glutamic acid/ja | 74 | 76 |
| Arginine/ja | 49 | 52 |
| Aspartic acid/ja | 47 | 47 |
| Serine/ja | 36 | 46 |
| Lysine/ja | 29 | 26 |
| Leucine/ja | 24 | 23 |
| Valine/ja | 22 | 21 |
| Threonine/ja | 19 | 26 |
| Phenylalanine/ja | 13 | 14 |
| Isoleucine/ja | 11 | 11 |
| Hydroxylysine/ja | 6 | 8 |
| Methionine/ja | 6 | 13 |
| Histidine/ja | 5 | 7 |
| Tyrosine/ja | 3 | 3 |
| Cysteine/ja | 1 | 1 |
| Tryptophan/ja | 0 | 0 |
合成
まず、アミノ酸のグリシンとプロリンを主成分とする三次元鎖構造が組み立てられる。これはまだコラーゲンではなく、その前駆体であるプロコラーゲンである。プロコラーゲンはその後、プロリンとリジンというアミノ酸に水酸基を付加することで修飾される。この段階は、後のグリコシル化とコラーゲンの三重らせん構造の形成に重要である。これらの反応を行う水酸化酵素は補因子としてビタミンCを必要とするため、このビタミンが長期的に欠乏するとコラーゲン合成が阻害され、壊血病になる。この反応は水酸化1回につきアスコルビン酸1分子を消費する。
コラーゲンの合成は細胞内外で起こる。ここでは、線維性コラーゲン(最も一般的な形態)をもたらすコラーゲンの形成について述べる。濾過システムの形成にしばしば関与する網目状コラーゲンは、コラーゲンの他の形態である。すべてのタイプのコラーゲンは三重らせんであり、その違いはステップ2で作られるαペプチドの構成にある。
- mRNAの転写:コラーゲン形成に関連する遺伝子は約44種類あり、それぞれが特定のmRNA配列をコードし、通常「COL」という接頭辞を持つ。コラーゲン合成の始まりは、特定のαペプチド(典型的にはα1、2、3)の形成に関連する遺伝子をオンにすることから始まる。
- プレプロペプチドの形成:最終的なmRNAが細胞核から出て細胞質に入ると、リボソームサブユニットと結びつき、翻訳のプロセスが起こる。新しいペプチドの初期/最初の部分はシグナル配列として知られている。ペプチドのN末端にあるシグナル配列は、小胞体上のシグナル認識粒子によって認識され、プレプロペプチドを小胞体に導く役割を果たす。したがって、新しいペプチドの合成が終わると、翻訳後プロセシングのために小胞体に直接入る。現在ではプレプロコラーゲンとして知られている。
- プレプロペプチドからプロコラーゲンへ:プレプロペプチドに3つの修飾が起こり、アルファペプチドが形成される:
- N末端のシグナルペプチドが除去され、プロペプチド(プロコラーゲンではない)と呼ばれるようになる。
- 酵素「プロリルヒドロキシラーゼ」と「リシルヒドロキシラーゼ」によるプロペプチド上のリジンとプロリンのヒドロキシル化(ヒドロキシプロリンとヒドロキシリジンの生成)が起こり、αペプチドの架橋を助ける。この酵素的段階は補因子としてビタミンCを必要とする。壊血病では、プロリンとリジンのヒドロキシル化が欠如しているため、三重らせん(3つのαペプチドによって形成される)が緩くなる。
- グリコシル化は、グルコースかガラクトースのモノマーを、プロリンではなくリジンの水酸基に付加することで起こる。
- 一旦これらの修飾が起こると、水酸基とグリコシル化されたプロペプチドのうち3つが三重らせん状にねじれ、プロコラーゲンを形成する。プロコラーゲンにはまだ巻かれていない末端があり、これは後で切り取られる。この時点で、プロコラーゲンはゴルジ体に向かう小胞にパッケージされる。
- ゴルジ体の修飾:細胞外に分泌される前に最後の翻訳後修飾を受ける。このステップでは、オリゴ糖(ステップ3のような単糖ではない)が付加され、プロコラーゲンは細胞外腔に向かう分泌小胞にパッケージされる。
- トロポコラーゲンの形成:細胞外に出ると、コラーゲンペプチダーゼとして知られる膜結合酵素が、プロコラーゲン分子の "ルースエンド "を除去する。残ったものがトロポコラーゲンである。このステップに欠陥があると、エーラス・ダンロス症候群として知られる多くのコラーゲン異常症のひとつが生じる。線維性コラーゲンの一種であるIII型コラーゲンを合成する際には、このステップは存在しない。
- コラーゲン線維の形成:リシルオキシダーゼは細胞外の銅依存性酵素であり、コラーゲン合成経路の最終段階を作り出す。この酵素はリジンとヒドロキシリジンに作用してアルデヒド基を生成し、最終的にトロポコラーゲン分子間で共有結合を起こす。このトロポコラーゲンのポリマーはコラーゲン線維として知られている。

アミノ酸
コラーゲンは珍しいアミノ酸組成と配列を持っている:
- グリシンはほぼ3番目の残基ごとに存在する。
- プロリンはコラーゲンの約17%を占める。
- コラーゲンは翻訳の際に直接挿入されない2つの珍しい誘導体アミノ酸を含んでいる。これらのアミノ酸はグリシンに対して特定の位置に存在し、異なる酵素によって翻訳後に修飾されるが、どちらも補因子としてビタミンCを必要とする。
コルチゾールは、(皮膚の)コラーゲンのアミノ酸への分解を刺激する。
コラーゲンI型の形成
ほとんどのコラーゲンは似たような方法で形成されるが、I型は次のような過程を経るのが典型的である:
- 細胞内
- α-1とα-2の2種類のα鎖は、粗面小胞体(RER)に沿ってリボソーム上で翻訳される間に形成される。プレプロコラーゲンとして知られるこれらのペプチド鎖は、両端に登録ペプチドとシグナルペプチドを持つ。
- ポリペプチド鎖は小胞体の内腔に放出される。
- シグナルペプチドはRER内で切断され、鎖はプロα鎖として知られるようになる。
- 内腔でリジンとプロリンアミノ酸の水酸化が起こる。このプロセスはアスコルビン酸(ビタミンC)に依存し、補因子として消費される。
- 特定のヒドロキシリジン残基のグリコシル化が起こる。
- 2本のα1鎖と1本のα2鎖から小胞体内で3重のαらせん構造が形成される。
- プロコラーゲンはゴルジ装置に輸送され、そこでパッケージ化され、エキソサイトーシスによって細胞外に分泌される。
- 細胞外
合成病原体
ビタミンCの欠乏は壊血病を引き起こす。この病気は、コラーゲンの欠陥が強い結合組織の形成を妨げる、重篤で痛みを伴う病気である。歯肉が悪化して出血し、歯を失う;皮膚が変色し、傷が治らない。18世紀以前には、この症状は長期間の軍事遠征、特に海軍遠征で悪名高く、参加者はビタミンCを含む食品を奪われた。
エリテマトーデスや関節リウマチなどの自己免疫疾患は、健康なコラーゲン線維を攻撃することがある。
多くの細菌やウイルスは、コラーゲンを破壊したり、その産生を阻害したりする酵素コラゲナーゼなどの病原性因子を分泌する。
分子構造
1個のコラーゲン分子であるトロポコラーゲンは、線維のような大きなコラーゲン凝集体を構成するために使用される。長さは約300 nm、直径は1.5 nmで、3本のポリペプチド鎖(アルファペプチドと呼ばれる。ステップ2参照)これら3つの左巻きらせんは、ねじれながら右巻きの3重らせん、または「スーパーらせん」となり、多くの水素結合によって安定化された協力的な4次構造を形成する。全てのコラーゲンではないにせよ、I型コラーゲンやおそらく全ての線維性コラーゲンでは、各三重らせんはコラーゲン・ミクロフィブリルと呼ばれる右巻きの超スーパーコイルに結合する。各ミクロフィブリルは隣接するミクロフィブリルと聯絡しており、コラーゲン線維内では結晶と言えるほど整然と並んでいるが、個々が不安定であることを示唆する程度である。

コラーゲンの特徴は、コラーゲンサブユニットの3本の鎖のそれぞれにアミノ酸が規則正しく並んでいることである。その配列はしばしばGly-Pro-XまたはGly-X-Hypのパターンに従う。プロリンまたはヒドロキシプロリンは全塩基配列の約1/6を占める。コラーゲン配列の1/3がグリシンであることから、コラーゲン配列の約半分はグリシン、プロリン、ヒドロキシプロリンではないことになる。コラーゲンの高いグリシン含量は、コラーゲンらせんの安定化に関して重要である。これは、分子内のコラーゲン線維の非常に密接な結合を可能にし、水素結合と分子間架橋の形成を促進するからである。このような規則的な繰り返しと高いグリシン含量は、絹フィブロインのような数少ない繊維状タンパク質にしか見られない。
コラーゲンは単なる構造タンパク質ではない。細胞表現型の決定、細胞接着、組織調節、およびインフラストラクチャーにおいて重要な役割を担っているため、その非プロリンリッチ領域の多くの部分が、細胞またはマトリックスとの会合/調節の役割を担っている。幾何学的に拘束されたカルボキシル基と(二次的な)アミノ基を持つプロリン環とヒドロキシプロリン環が比較的多く、グリシンが豊富であることが、個々のポリペプチド鎖が鎖内水素結合なしに自発的に左巻きらせんを形成する傾向を説明する。
グリシンは側鎖を持たない最小のアミノ酸であるため、繊維状構造タンパク質においてユニークな役割を果たしている。コラーゲンでは、三重らせんの組み立てにより、この残基がらせんの内側(軸)に置かれるため、グリシンの水素原子1個よりも大きな側基を置くスペースがないため、3番目ごとにグリシンが必要とされる。同じ理由で、ProとHypの環は外側を向いていなければならない。魚のように体温がほとんどの温血動物よりも低い動物では、より低濃度のアミノ酸が必要とされる。より低いプロリンとヒドロキシプロリン含量は冷水性魚類に特徴的であるが、温水性魚類には特徴的ではない。冷水魚やその他の恒温動物のプロリンやヒドロキシプロリン含量が低いということは、そのコラーゲンが哺乳類のコラーゲンよりも熱安定性が低いということにつながる。この低い熱安定性は、魚類コラーゲン由来のゼラチンが多くの食品や工業用途に適していないことを意味する。
トロポコラーゲンサブユニットは自発的に自己組織化し、規則正しくずらされた末端を持ち、組織の細胞外空間でさらに大きな配列になる。線維の追加的な組み立ては線維芽細胞によって誘導され、線維芽細胞は線維形成因子から完全に形成された線維を沈着させる。線維性コラーゲンでは、分子は隣接する分子に対して約67 nmずらされている(単位は「D」と呼ばれ、凝集体の水和状態によって変化する)。ミクロフィブリルの各D周期の繰り返しには、断面で5つの分子を含む「オーバーラップ」と呼ばれる部分と、4つの分子のみを含む「ギャップ」と呼ばれる部分がある。これらのオーバーラップ領域とギャップ領域は、ミクロフィブリルがフィブリルに集合する際に保持されるため、電子顕微鏡で観察することができる。ミクロフィブリル中の三重らせん状のトロポコラーゲンは、準六角形のパッキングパターンで配列している。

三重らせん内にはいくつかの共有架橋があり、トロポコラーゲンらせん間には様々な量の共有結合架橋があり、よく組織化された凝集体(フィブリルなど)を形成している。より大きな線維束は、いくつかの異なるクラスのタンパク質(異なるコラーゲンタイプを含む)、糖タンパク質、プロテオグリカンの助けを借りて形成され、同じキープレーヤーの交互の組み合わせから異なるタイプの成熟組織を形成する。コラーゲンの不溶性は、まだ完全に架橋していないため、若い動物からトロポコラーゲンを抽出できることが発見されるまで、単量体コラーゲンの研究の障壁であった。しかし、顕微鏡技術(電子顕微鏡(EM)や原子間力顕微鏡(AFM)など)やX線回折の進歩により、研究者はコラーゲン構造の詳細な画像をその場で得ることができるようになった。コラーゲンの構造が、細胞間や細胞-マトリックス間のコミュニケーションにどのような影響を与えるのか、また、組織がどのように成長・修復され、発生や疾患においてどのように変化するのかをより深く理解するためには、これらの進歩は特に重要である。例えば、AFMベースのナノインデンテーションを用いて、1本のコラーゲン線維がその軸方向に沿って不均質な材料であり、そのギャップ領域とオーバーラップ領域で機械的特性が著しく異なることが示され、この2つの領域における分子組織の違いと相関している。
コラーゲン線維/凝集体は、様々な組織において様々な組み合わせと濃度で配列され、様々な組織特性をもたらしている。骨では、コラーゲンの三重らせん全体が平行に、千鳥配列で並んでいる。トロポコラーゲンサブユニットの末端間の40 nmの隙間(隙間領域とほぼ等しい)は、おそらくヒドロキシルアパタイト(約)Ca10(OH)2(PO4)6であるミネラル成分の長く硬い微細な結晶の沈着の核形成部位として機能する。I型コラーゲンは骨に引っ張り強度を与える。
関連疾患
コラーゲン関連疾患は、最も一般的には、正常なコラーゲン産生に関与する生合成、アセンブリー、翻訳後修飾、分泌、その他の過程に影響を及ぼす遺伝的欠陥や栄養欠乏から生じる。
上記の疾患に加えて、強皮症ではコラーゲンの過剰沈着が起こる。
病気
20種類以上のコラーゲンのうち12種類で1000もの変異が同定されている。これらの変異は組織レベルで様々な病気を引き起こす可能性がある。
骨形成不全症 - 1型コラーゲンの突然変異によって引き起こされ、優性常染色体疾患であり、骨が弱く、結合組織が不規則である。軽症例では1型コラーゲンのレベルが低下しているが、重症例ではコラーゲンの構造的欠陥がある。
軟骨異形成症 - 2型コラーゲンの突然変異によって引き起こされると考えられている骨格障害であるが、これを確認するためにさらなる研究が行われている。
エーラス・ダンロス症候群 - 結合組織の変形を引き起こすこの疾患は、13の異なるタイプが知られている。まれなタイプでは、動脈が破裂する致死的なものもある。それぞれの症候群は異なる突然変異によって引き起こされる。例えば、この疾患の血管型(vEDS)は3型コラーゲンの突然変異によって起こる。
アルポート症候群 - 遺伝的に受け継がれる可能性があり、通常はX連鎖優性遺伝であるが、常染色体優性遺伝や常染色体劣性遺伝もある。
ノブロッホ症候群 - コラーゲンXVIIIの産生をコードするCOL18A1遺伝子の変異によって引き起こされる。脳組織の突出と網膜の変性がみられる。家族にこの疾患の患者がいる場合、遺伝的な関連性があるため、自分自身が発症するリスクが高くなる。
特徴
コラーゲンは長い繊維構造タンパク質の一つであり、その機能は酵素などの球状タンパク質とは全く異なる。コラーゲン線維と呼ばれる丈夫なコラーゲンの束は、ほとんどの組織を支え、細胞に外側から構造を与える細胞外マトリックスの主要な構成要素であるが、コラーゲンはある種の細胞内部にも存在する。コラーゲンは大きな引っ張り強度を持ち、筋膜、軟骨、靭帯、腱、骨、皮膚の主成分である。エラスチンや柔らかいケラチンとともに皮膚の強度と弾力性を担っており、その劣化は老化に伴うしわの原因となる。血管を強化し、組織の発達に関与する。眼の角膜や水晶体には結晶線状で存在する。中生代や古生代の骨でも頻繁に化石化することから、化石記録では最も豊富なタンパク質の1つかもしれない。
用途

コラーゲンの用途は食品から医薬品まで多岐にわたる。医療業界では、美容外科や火傷手術に使用されている。食品分野では、ソーセージ用ケーシングが使用例のひとつである。
コラーゲンが加熱などの十分な変性を受けると、3本のトロポコラーゲン鎖は部分的または完全に分離して球状ドメインとなり、ランダムコイルの通常のコラーゲン・ポリプロリンII(PPII)とは異なる二次構造を含む。このプロセスはゼラチンの形成を説明するものであり、味付けされたゼラチンデザートを含む多くの食品に使用されている。食品以外にも、ゼラチンは製薬、化粧品、写真産業で使用されている。ゼラチンは栄養補助食品としても使用され、老化防止薬としても宣伝されている。
ギリシア語で糊を意味するkollaから、コラーゲンという言葉は「糊生産者」を意味し、糊を得るために馬や他の動物の皮膚や筋を煮沸する初期のプロセスを指す。コラーゲン接着剤は約4,000年前にエジプト人によって使用され、ネイティブ・アメリカンは約1,500年前に弓に使用していた。世界最古の接着剤は炭素年代で8,000年以上前のもので、コラーゲンであることが判明した-縄籠や刺繍されたファブリックの保護裏地として、食器をつなぎ合わせるために、また人間の頭蓋骨の十字の装飾に使われていた。コラーゲンは通常ゼラチンに変化するが、乾燥状態のために生き残った。動物の接着剤は熱可塑性であり、再加熱すると再び軟化するため、現在でも高級バイオリンやギターなどの楽器の製作に使われている。永久的で強靭な合成プラスチック接着剤とは相容れない用途である。革を含む動物のすじや皮は、何千年もの間、有用な物品を作るために使われてきた。
ゼラチン-レゾルシノール-ホルムアルデヒド接着剤(およびホルムアルデヒドを毒性の低いペンタンジアルとエタンジアルに置き換えたもの)は、ウサギの肺の実験的切開の修復に用いられてきた。
=== 化粧品 ウシコラーゲンは、シワや皮膚の老化のエステティック矯正のための皮膚充填剤に広く使用されている。コラーゲンの繊維は大きすぎるため皮膚に浸透しないが、コラーゲンクリームも広く販売されている。コラーゲンサプリメントに関する研究のほとんどは、肯定的な研究結果から利益を得ることができる産業によって資金提供されている。
歴史
コラーゲンの分子構造や充填構造については、何十年にもわたる研究の間、科学者たちの頭を悩ませてきた。コラーゲンが分子レベルで規則正しい構造を持っているという最初の証拠は、1930年代半ばに発表された。その後、研究はコラーゲンモノマーのコンフォメーションに集中し、個々のペプチド鎖のコンフォメーションを正しく扱いながらも、いくつかの競合するモデルが生み出された。1955年にG. N. Ramachandranによって提唱された三重らせん状の「マドラス」モデルは、コラーゲンの四次構造の正確なモデルを提供した。このモデルは、20世紀後半により高い解像度の研究によって支持された。
コラーゲンの充填構造は、六角形であることは古くから知られているが、線維性コラーゲンタイプ以外では同程度には定義されていない。コラーゲンの単量体構造と同様に、コラーゲン分子のパッキング配列は「シート状」であるか、あるいはミクロフィブリル状であるという、いくつかの相反するモデルが提唱されている。腱、角膜、軟骨のコラーゲン線維のミクロフィブリル構造は、20世紀後半から21世紀初頭にかけて電子顕微鏡で直接撮影された。ラット尾腱のミクロフィブリル構造は、観察された構造に最も近いものとしてモデル化されたが、隣接するコラーゲン分子のトポロジカルな進行を単純化しすぎたため、ミクロフィブリルと呼ばれる不連続なD-周期的5量体配列の正しいコンフォメーションは予測できなかった。
こちらも参照
- コラーゲンハイブリダイジングペプチド, 変性コラーゲンに結合できるペプチド
- Hypermobility spectrum disorder/ja
- Metalloprotease inhibitor/ja
- オステオイド, 骨のコラーゲン含有成分
- Collagen loss/ja