Pantothenic acid/en: Difference between revisions
Updating to match new version of source page |
Updating to match new version of source page Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
# PPC is [[Decarboxylation|decarboxylated]] to [[4'-phosphopantetheine|4′-phosphopantetheine]] by [[phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase]] | # PPC is [[Decarboxylation|decarboxylated]] to [[4'-phosphopantetheine|4′-phosphopantetheine]] by [[phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase]] | ||
# 4′-Phosphopantetheine is adenylated (or more properly, [[Adenylation|AMPylated]]) to form dephospho-CoA by the enzyme [[Pantetheine-phosphate adenylyltransferase|phosphopantetheine adenylyl transferase]] | # 4′-Phosphopantetheine is adenylated (or more properly, [[Adenylation|AMPylated]]) to form dephospho-CoA by the enzyme [[Pantetheine-phosphate adenylyltransferase|phosphopantetheine adenylyl transferase]] | ||
# Finally, dephospho-CoA is phosphorylated to coenzyme A by the enzyme [[dephospho-CoA kinase|dephosphocoenzyme A kinase]]. This final step also requires ATP. | # Finally, dephospho-CoA is phosphorylated to coenzyme A by the enzyme [[dephospho-CoA kinase|dephosphocoenzyme A kinase]]. This final step also requires ATP. | ||
This pathway is suppressed by [[end-product inhibition]], meaning that CoA is a competitive inhibitor of pantothenate kinase, the enzyme responsible for the first step. | This pathway is suppressed by [[end-product inhibition]], meaning that CoA is a competitive inhibitor of pantothenate kinase, the enzyme responsible for the first step. | ||
Latest revision as of 17:36, 20 February 2024
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
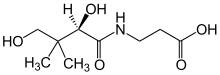
3-[(2R)-2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido]propanoic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-[(2R)-(2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl)amino]propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1727062, 1727064 (R) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Pantothenic+Acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H17NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 219.237 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow oil Colorless crystals (Ca2+ salt) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.266 g/cm3 1.32 g/cm3 (Ca2+ salt) |
| Melting point | 183.833 °C (362.899 °F; 456.983 K) 196–200 °C (385–392 °F; 469–473 K) decomposes (Ca2+ salt) |
| Very soluble | |
| Solubility | Very soluble in C6H6, ether |
| log P | −1.416 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.41 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 9.698 |
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
+37.5° +24.3° (Ca2+ salt) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
> 10 mg/g (Ca2+ salt) |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids
|
Arginine Hopantenic acid 4-(γ-Glutamylamino)butanoic acid |
Related compounds
|
Panthenol |
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is a B vitamin and an essential nutrient. All animals need pantothenic acid in order to synthesize coenzyme A (CoA)—essential for metabolizing fatty acid—and to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
Pantothenic acid is the combination of pantoic acid and β-alanine. Its name comes from the Greek πάντοθεν pantothen, meaning "from everywhere", because pantothenic acid, at least in small amounts, is in almost all foods. Deficiency of pantothenic acid is very rare in humans. In dietary supplements and animal feed, the form commonly used is calcium pantothenate, because chemically it is more stable, and hence makes for longer product shelf-life, than sodium pantothenate and free pantothenic acid.
Definition

Pantothenic acid is a water-soluble vitamin, one of the B vitamins. It is synthesized from the amino acid β-alanine and pantoic acid (see biosynthesis and structure of coenzyme A figures). Unlike vitamin E or vitamin K, which occurs in several chemically related forms known as vitamers, pantothenic acid is only one chemical compound. It is a starting compound in the synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA), a cofactor for many enzyme processes.
Use in biosynthesis of coenzyme A

Pantothenic acid is a precursor to CoA via a five-step process. The biosynthesis requires pantothenic acid, cysteine, and four equivalents of ATP (see figure).
- Pantothenic acid is phosphorylated to 4′-phosphopantothenate by the enzyme pantothenate kinase. This is the committed step in CoA biosynthesis and requires ATP.
- A cysteine is added to 4′-phosphopantothenate by the enzyme phosphopantothenoylcysteine synthetase to form 4'-phospho-N-pantothenoylcysteine (PPC). This step is coupled with ATP hydrolysis.
- PPC is decarboxylated to 4′-phosphopantetheine by phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase
- 4′-Phosphopantetheine is adenylated (or more properly, AMPylated) to form dephospho-CoA by the enzyme phosphopantetheine adenylyl transferase
- Finally, dephospho-CoA is phosphorylated to coenzyme A by the enzyme dephosphocoenzyme A kinase. This final step also requires ATP.
This pathway is suppressed by end-product inhibition, meaning that CoA is a competitive inhibitor of pantothenate kinase, the enzyme responsible for the first step.
Coenzyme A is necessary in the reaction mechanism of the citric acid cycle. This process is the body's primary catabolic pathway and is essential in breaking down the building blocks of the cell such as carbohydrates, amino acids and lipids, for fuel. CoA is important in energy metabolism for pyruvate to enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) as acetyl-CoA, and for α-ketoglutarate to be transformed to succinyl-CoA in the cycle. CoA is also required for acylation and acetylation, which, for example, are involved in signal transduction, and various enzyme functions. In addition to functioning as CoA, this compound can act as an acyl group carrier to form acetyl-CoA and other related compounds; this is a way to transport carbon atoms within the cell. CoA is also required in the formation of acyl carrier protein (ACP), which is required for fatty acid synthesis. Its synthesis also connects with other vitamins such as thiamin and folic acid.
Dietary recommendations
The US Institute of Medicine (IOM) updated Estimated Average Requirements (EARs) and Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for B vitamins in 1998. At that time there was not sufficient information to establish EARs and RDAs for pantothenic acid. In instances such as this, the Board sets Adequate Intakes (AIs), with the understanding that at some later date, AIs may be replaced by more exact information.
The current AI for teens and adults ages 14 and up is 5 mg/day. This was based in part on the observation that for a typical diet, urinary excretion was approximately 2.6 mg/day, and that bioavailability of food-bound pantothenic acid was roughly 50%. AI for pregnancy is 6 mg/day. AI for lactation is 7 mg/day. For infants up to 12 months the AI is 1.8 mg/day. For children ages 1–13 years the AI increases with age from 2 to 4 mg/day. Collectively the EARs, RDAs, AIs and ULs are referred to as Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs).
| Age group | Age | Adequate intake |
|---|---|---|
| Infants | 0–6 months | 1.7 mg |
| Infants | 7–12 months | 1.8 mg |
| Children | 1–3 years | 2 mg |
| Children | 4–8 years | 3 mg |
| Children | 9–13 years | 4 mg |
| Adult men and women | 14+ years | 5 mg |
| Pregnant women | (vs. 5) | 6 mg |
| Breastfeeding women | (vs. 5) | 7 mg |
While for many nutrients, the US Department of Agriculture uses food composition data combined with food consumption survey results to estimate average consumption, the surveys and reports do not include pantothenic acid in the analyses. Less formal estimates of adult daily intakes report about 4 to 7 mg/day.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) refers to the collective set of information as Dietary Reference Values, with Population Reference Intake (PRI) instead of RDA, and Average Requirement instead of EAR. AI and UL are defined the same as in the US. For women and men over age 11 the Adequate Intake (AI) is set at 5 mg/day. AI for pregnancy is 5 mg/day, for lactation 7 mg/day. For children ages 1–10 years the AI is 4 mg/day. These AIs are similar to the US AIs.
Safety
As for safety, the IOM sets Tolerable upper intake levels (ULs) for vitamins and minerals when evidence is sufficient. In the case of pantothenic acid there is no UL, as there is no human data for adverse effects from high doses. The EFSA also reviewed the safety question and reached the same conclusion as in United States – that there was not sufficient evidence to set a UL for pantothenic acid.
Labeling requirements
For US food and dietary supplement labeling purposes the amount in a serving is expressed as a percent of Daily Value (%DV). For pantothenic acid labeling purposes 100% of the Daily Value was 10 mg, but as of 27 May 2016 it was revised to 5 mg to bring it into agreement with the AI. Compliance with the updated labeling regulations was required by 1 January 2020 for manufacturers with US$10 million or more in annual food sales, and by 1 January 2021 for manufacturers with lower volume food sales. A table of the old and new adult daily values is provided at Reference Daily Intake.
Sources
Dietary
Food sources of pantothenic acid include animal-sourced foods, including dairy foods and eggs. Potatoes, tomato products, oat-cereals, sunflower seeds, avocado are good plant sources. Mushrooms are good sources, too. Whole grains are another source of the vitamin, but milling to make white rice or white flour removes much of the pantothenic acid, as it is found in the outer layers of whole grains. In animal feeds, the most important sources are alfalfa, cereal, fish meal, peanut meal, molasses, rice bran, wheat bran, and yeasts.
Supplements
Dietary supplements of pantothenic acid commonly use pantothenol (or panthenol), a shelf-stable analog, which is converted to pantothenic acid once consumed. Calcium pantothenate – a salt – may be used in manufacturing because it is more resistant than pantothenic acid to factors that deteriorate stability, such as acid, alkali or heat. The amount of pantothenic acid in dietary supplement products may contain up to 1,000 mg (200 times the Adequate Intake level for adults), without evidence that such large amounts provide any benefit. According to WebMD, pantothenic acid supplements have a long list of claimed uses, but there is insufficient scientific evidence to support any of them.
As a dietary supplement, pantothenic acid is not the same as pantethine, which is composed of two pantothenic acid molecules linked by a disulfide bridge. Sold as a high-dose supplement (600 mg), pantethine may be effective for lowering blood levels of LDL cholesterol – a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases – but its long-term effects are unknown, requiring that its use be supervised by a physician. Dietary supplementation with pantothenic acid does not have the same effect on LDL.
Fortification
According to the Global Fortification Data Exchange, pantothenic acid deficiency is so rare that no countries require that foods be fortified.
Absorption, metabolism and excretion
When found in foods, most pantothenic acid is in the form of CoA or bound to acyl carrier protein (ACP). For the intestinal cells to absorb this vitamin, it must be converted into free pantothenic acid. Within the lumen of the intestine, CoA and ACP are hydrolyzed into 4'-phosphopantetheine. The 4'-phosphopantetheine is then dephosphorylated into pantetheine. Pantetheinase, an intestinal enzyme, then hydrolyzes pantetheine into free pantothenic acid. Free pantothenic acid is absorbed into intestinal cells via a saturable, sodium-dependent active transport system. At high levels of intake, when this mechanism is saturated, some pantothenic acid may also be additionally absorbed via passive diffusion. As a whole, when intake increases 10-fold, absorption rate decreases to 10%.
Pantothenic acid is excreted in urine. This occurs after its release from CoA. Urinary amounts are on the order of 2.6 mg/day, but decreased to negligible amounts when subjects in multi-week experimental situations were fed diets devoid of the vitamin.
Deficiency
Pantothenic acid deficiency in humans is very rare and has not been thoroughly studied. In the few cases where deficiency has been seen (prisoners of war during World War II, victims of starvation, or limited volunteer trials), nearly all symptoms were reversed with orally administered pantothenic acid. Symptoms of deficiency are similar to other vitamin B deficiencies. There is impaired energy production, due to low CoA levels, which could cause symptoms of irritability, fatigue, and apathy. Acetylcholine synthesis is also impaired; therefore, neurological symptoms can also appear in deficiency; they include sensation of numbness in hands and feet, paresthesia and muscle cramps. Additional symptoms could include restlessness, malaise, sleep disturbances, nausea, vomiting and abdominal cramps.
In animals, symptoms include disorders of the nervous, gastrointestinal, and immune systems, reduced growth rate, decreased food intake, skin lesions and changes in hair coat, and alterations in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. In rodents, there can be loss of hair color, which led to marketing of pantothenic acid as a dietary supplement which could prevent or treat graying of hair in humans (despite the lack of any human trial evidence).
Pantothenic acid status can be assessed by measuring either whole blood concentration or 24-hour urinary excretion. In humans, whole blood values less than 1 μmol/L are considered low, as is urinary excretion of less than 4.56 mmol/day.
Animal nutrition
Calcium pantothenate and dexpanthenol (D-panthenol) are European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) approved additives to animal feed. Supplementation is on the order of 8–20 mg/kg for pigs, 10–15 mg/kg for poultry, 30–50 mg/kg for fish and 8–14 mg/kg feed for pets. These are recommended concentrations, designed to be higher than what are thought to be requirements. There is some evidence that feed supplementation increases pantothenic acid concentration in tissues, i.e., meat, consumed by humans, and also for eggs, but this raises no concerns for consumer safety.
No dietary requirement for pantothenic acid has been established in ruminant species. Synthesis of pantothenic acid by ruminal microorganisms appears to be 20 to 30 times more than dietary amounts. Net microbial synthesis of pantothenic acid in the rumen of steer calves has been estimated to be 2.2 mg/kg of digestible organic matter consumed per day. Supplementation of pantothenic acid at 5 to 10 times theoretical requirements did not improve growth performance of feedlot cattle.
Synthesis
Biosynthesis
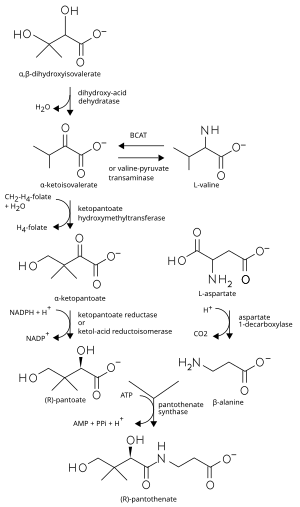
Bacteria synthesize pantothenic acid from the amino acids aspartate and a precursor to the amino acid valine. Aspartate is converted to β-alanine. The amino group of valine is replaced by a keto-moiety to yield α-ketoisovalerate, which, in turn, forms α-ketopantoate following transfer of a methyl group, then D-pantoate (also known as pantoic acid) following reduction. β-alanine and pantoic acid are then condensed to form pantothenic acid (see figure).
Industrial synthesis
The industrial synthesis of pantothenic acid starts with the aldol condensation of isobutyraldehyde and formaldehyde. The resulting hydroxypivaldehyde is converted to its cyanohydrin derivative. which is cyclised to give racemic pantolactone. This sequence of reactions was first published in 1904.
Synthesis of the vitamin is completed by resolution of the lactone using quinine, for example, followed by treatment with the calcium or sodium salt of β-alanine.
History
The term vitamin is derived from the word vitamine, which was coined in 1912 by Polish biochemist Casimir Funk, who isolated a complex of water-soluble micronutrients essential to life, all of which he presumed to be amines. When this presumption was later determined not to be true, the "e" was dropped from the name, hence "vitamin". Vitamin nomenclature was alphabetical, with Elmer McCollum calling these fat-soluble A and water-soluble B. Over time, eight chemically distinct, water-soluble B vitamins were isolated and numbered, with pantothenic acid as vitamin B5.
The essential nature of pantothenic acid was discovered by Roger J. Williams in 1933 by showing it was required for the growth of yeast. Three years later Elvehjem and Jukes demonstrated that it was a growth and anti-dermatitis factor in chickens. Williams dubbed the compound "pantothenic acid", deriving the name from the Greek word pantothen, which translates as "from everywhere". His reason was that he found it to be present in almost every food he tested. Williams went on to determine the chemical structure in 1940. In 1953, Fritz Lipmann shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for his discovery of co-enzyme A and its importance for intermediary metabolism", work he had published in 1946.
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Pantothenic acid/en(27 January 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Lua error in Module:Itemnumber at line 91: attempt to concatenate local 'qid' (a nil value). |

