Translations:Omega-3 fatty acid/9/en
Nomenclature
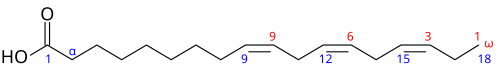
The terms ω−3 ("omega−3") fatty acid and n−3 fatty acid are derived from the nomenclature of organic chemistry. One way in which an unsaturated fatty acid is named is determined by the location, in its carbon chain, of the double bond which is closest to the methyl end of the molecule. In general terminology, n (or ω) represents the locant of the methyl end of the molecule, while the number n−x (or ω−x) refers to the locant of its nearest double bond. Thus, in omega−3 fatty acids in particular, there is a double bond located at the carbon numbered 3, starting from the methyl end of the fatty acid chain. This classification scheme is useful since most chemical changes occur at the carboxyl end of the molecule, while the methyl group and its nearest double bond are unchanged in most chemical or enzymatic reactions.