Pyridoxal
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
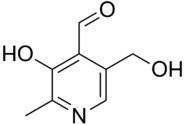 Idealised skeletal formula
| |
 Ball-and-stick model based on the crystal structure. Note that the acidic phenol group has donated a proton to the basic pyridine group to form a zwitterion, and the hydroxymethyl group has reacted with the aldehyde group to form a hemiacetal.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridine-4-carbaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H9NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 167.16 g/mol |
| Melting point | 165 °C (329 °F; 438 K) (decomposes) |
| Related compounds | |
Related arylformaldehydes
|
Damnacanthal |
Pyridoxal is one form of vitamin B6.
Some medically relevant bacteria, such as those in the genera Granulicatella and Abiotrophia, require pyridoxal for growth. This nutritional requirement can lead to the culture phenomenon of satellite growth. In in vitro culture, these pyridoxal-dependent bacteria may only grow in areas surrounding colonies of bacteria from other genera ("satellitism") that are capable of producing pyridoxal.
Pyridoxal is involved in what is believed to be the most ancient reaction of aerobic metabolism on Earth, about 2.9 billion years ago, a forerunner of the Great Oxidation Event.
See also
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Pyridoxal(20 March 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Item:Q21884 |