乳酸カルシウム
Calcium lactate/ja
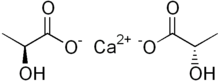
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Calcium bis(2-hydroxypropanoate) | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10CaO6 | |
| Molar mass | 218.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | white or off-white powder, slightly efflorescent |
| Density | 1.494 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 240 °C (464 °F; 513 K) (anhydrous) 120 °C (pentahydrate) |
| L-lactate, anhydrous, g/100 mL: 4.8 (10 °C), 5.8 (20 °C), 6.7 (25 °C), 8.5 (30 °C); 7.9 g/100 mL (30 °C) | |
| Solubility | very soluble in methanol, insoluble in ethanol |
| Acidity (pKa) | 6.0-8.5 |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.470 |
| Pharmacology | |
| A12AA05 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H319 | |
| P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Not applicable |
| No data | |
乳酸カルシウムは、式C
6H
10CaO
6で表される白色の結晶塩で、各カルシウム陽イオンCa2+
に対して2つの乳酸陰イオン H
3C(CHOH)CO−
2からなる。いくつかの水和物を形成するが、最も一般的なものは5水和物C
6H
10CaO
6·5H
2Oである。
乳酸カルシウムは主にカルシウム欠乏症の治療薬として、またE数がE327の食品添加物として用いられる。 乳酸カルシウムからなるチーズの結晶もある。
特性
乳酸イオンはキラルであり、D(-,R)とL(+,S)の2つのエナンチオマーを持つ。 通常、生物によって合成・代謝されるのはL異性体であるが、一部の細菌はD異性体を生成したり、L異性体をD異性体に変換したりする。
合成プロセスによっては、両者が等量混合したDL塩(ラセミ体)が得られる。 L型もDL型も、熟成したチェダーチーズの表面に結晶として現れる。
L-乳酸カルシウムの水への溶解度は、d-グルコン酸イオンの存在下で著しく増加し、25 °Cで6.7[[::en:gram|g]]/dl)から9.74g/dl以上になる。 逆説的だが、L-乳酸カルシウムの溶解度は10 °C(4.8g/dl)から30 °C(8.5g/dl)まで温度とともに上昇するが、遊離Ca2+
イオンの濃度はほぼ半分に減少する。これは、乳酸イオンとカルシウムイオンが水和しにくくなり、複合体C
3H
5O
3Ca+
を形成するためと説明される。
塩のDL型(ラセミ型)は、純粋なLまたはD異性体よりも水に溶けにくいため、D型を25%でも含む溶液では、L-乳酸塩の代わりにラセミ型のDL-乳酸塩結晶が析出する。
五水和物は35~135℃の乾燥した雰囲気で水分を失い、無水形態に還元されて結晶性を失う。 この過程は25 °C、75%相対湿度で逆転する。
調製法
乳酸カルシウムは、炭酸カルシウムまたは水酸化カルシウムと乳酸の反応によって調製することができる。
Since the 19th century, the salt has been obtained industrially by fermentation of carbohydrates in the presence of calcium mineral sources such as calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide. Fermentation may produce either D or L lactate, or a racemic mixture of both, depending on the type of organism used.
Calcium lactate is used in medicine as an antacid.
It is also used to treat hypocalcaemia (calcium deficiencies). It can be absorbed at various pHs, thus it does not need to be taken with food. However, in this use it has been found to be less convenient than calcium citrate. Calcium lactate contains 13% elemental calcium.
In the early 20th century, oral administration of calcium lactate dissolved in water (but not in milk or tablets) was found to be effective in prevention of tetany in humans and dogs with parathyroid insufficiency or who underwent parathyroidectomy.
The compound is also found in some mouth washes and toothpaste as an anti-tartar agent.
Calcium lactate (or other calcium salts) is an antidote for soluble fluoride ingestion and hydrofluoric acid.
Food industry
The compound is a food additive classified by the United States FDA as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), for uses as a firming agent, a flavor enhancer or flavoring agent, a leavening agent, a nutritional supplement, and a stabilizer and thickener.
Calcium lactate is also known as cheese lactate because it coagulates milk, making the chhena used in the production of paneer cheese. Chhena is also used to make various sweets and other milk proteins.
Calcium lactate is an ingredient in some baking powders containing sodium acid pyrophosphate. It provides calcium in order to delay leavening.
Calcium lactate is added to sugar-free foods to prevent tooth decay. When added to chewing gum containing xylitol, it increases the remineralization of tooth enamel.
The compound is also added to fresh-cut fruits, such as cantaloupes, to keep them firm and extend their shelf life, without the bitter taste caused by calcium chloride, which can also be used for this purpose.
Calcium lactate is used in molecular gastronomy as a flavorless fat-soluble agent for plain and reverse spherification. It reacts with sodium alginate to form a skin around the food item.
Animal feeds
Calcium lactate may be added to animal rations as a source of calcium.
Chemistry
The compound was formerly an intermediate in the preparation of lactic acid for food and medical uses. The impure acid from various sources was converted to calcium lactate, purified by crystallization, and then converted back to acid by treatment with sulfuric acid, which precipitated the calcium as calcium sulfate. This method yielded a purer product than would be obtained by distillation of the original acid. Recently ammonium lactate has been used as an alternative to calcium in this process.
Water treatment
Calcium lactate has been considered as a coagulant for removing suspended solids from water, as a renewable, non-toxic, and biodegradable alternative to aluminum chloride AlCl
3.
バイオコンクリート
乳酸カルシウムの添加は、Enterococcus faecalis、Bacillus cohnii、Bacillus pseudofirmus、Sporosarcina pasteuriiなどの細菌がより多くの方解石を生成することを可能にすることによって、バイオコンクリートの圧縮強度を大幅に増加させ、透水性を低下させる。
こちらも参照
