Garlic: Difference between revisions
Created page with "{{short description|Species of edible plant}} {{Other uses}} {{Speciesbox | name = Garlic | image = Allium sativum Woodwill 1793.jpg | image_caption = ''Allium sativum'', known as garlic, from William Woodville, ''Medical Botany'', 1793. | taxon = Allium sativum | parent = Allium subg. Allium | authority = L. | synonyms_ref = | synonyms = {{collapsible list|bullets = true |title=<small>Synonymy</small> |''Allium arenarium'' <small>Sadler ex Rchb. 1830 n..." |
|||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
[[File:Garlic for sale in a market in France.jpg|thumb|Garlic for sale in a market in France]] | [[File:Garlic for sale in a market in France.jpg|thumb|Garlic for sale in a market in France]] | ||
Garlic is easy to cultivate and may grow year-round in mild climates. While sexual propagation of garlic is possible, nearly all of the garlic in cultivation is propagated [[asexual reproduction|asexually]] by planting individual cloves in the ground. | Garlic is easy to cultivate and may grow year-round in mild climates. While sexual propagation of garlic is possible, nearly all of the garlic in cultivation is propagated [[asexual reproduction|asexually]] by planting individual cloves in the ground. | ||
In colder climates, cloves are best planted about six weeks before the soil freezes. The goal is to have the bulbs produce only roots and no shoots above the ground. | In colder climates, cloves are best planted about six weeks before the soil freezes. The goal is to have the bulbs produce only roots and no shoots above the ground. | ||
Harvest is in late spring or early summer. | Harvest is in late spring or early summer. | ||
Revision as of 20:38, 8 June 2025
| Garlic | |
|---|---|
| |
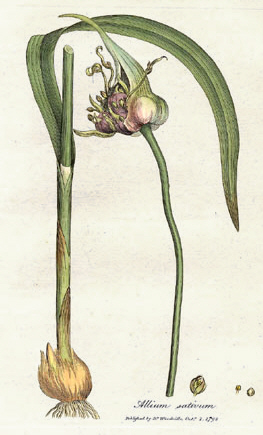
| Allium sativum, known as garlic, from William Woodville, Medical Botany, 1793. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Amaryllidaceae |
| Subfamily: | Allioideae |
| Genus: | Allium |
| Subgenus: | A. subg. Allium |
| Species: | sativum
|
| Binomial name | |
| sativum | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Synonymy
| |
Garlic (Allium sativum) is a species of bulbous flowering plants in the genus Allium. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chives, Welsh onion, and Chinese onion. Garlic is native to central and south Asia, stretching from the Black Sea through the southern Caucasus, northeastern Iran, and the Hindu Kush; it also grows wild in parts of Mediterranean Europe. There are two subspecies and hundreds of varieties of garlic.
Garlic has been used for thousands of years as a seasoning, culinary ingredient, traditional medical remedy; it was known in many ancient civilizations, including the Babylonians, Egyptians, Romans, and Chinese, and remains significant in many cuisines and folk treatments, especially across the Mediterranean and Asia. Garlic propagates in a variety of climates and conditions and is produced globally; China is by far the largest producer, accounting for over two thirds (73%) of the world's supply in 2021.
Description
Garlic is a perennial flowering plant that is native to Central Asia, South Asia and northeastern Iran. It grows from a bulb, with a tall, erect flowering stem that reaches up to 1 m (3 ft). The leaf blade is flat, linear, solid, and approximately 1.25–2.5 cm (0.5–1.0 in) wide, with an acute apex. The plant may produce pink to purple flowers from July to September in the Northern Hemisphere. The bulb has a strong odor and is typically made up of 10 to 20 cloves. The cloves close to the center are symmetrical, and those surrounding the center can be asymmetrical. Each clove is enclosed in an inner sheathing leaf surrounded by layers of outer sheathing leaves. If garlic is planted at the proper time and depth, it can be grown as far north as Alaska. It produces hermaphroditic flowers. It is pollinated by butterflies, moths, and other insects.
Chemistry
Fresh or crushed garlic yields the sulfur-containing compounds allicin, ajoene, diallyl polysulfides, vinyldithiins, and S-allylcysteine, as well as enzymes, saponins, flavonoids, and Maillard reaction products when cooked, which are not sulfur-containing compounds.
The phytochemicals responsible for the sharp flavor of garlic are produced when the plant's cells are damaged. When a cell is broken by chopping, chewing, or crushing, enzymes stored in cell vacuoles trigger the breakdown of several sulfur-containing compounds stored in the cell fluids (cytosol).
Among alliums, garlic has by far the highest concentrations of initial reaction products, making garlic much more potent than onion, shallot, or leeks. Although many humans enjoy the taste of garlic, these compounds are believed to have evolved as a defensive mechanism, deterring animals such as birds, insects, and worms from eating the plant.
A large number of sulfur compounds contribute to the smell and taste of garlic. Allicin has been found to be the compound most responsible for the "hot" sensation of raw garlic. This chemical opens thermo-transient receptor potential channels that are responsible for the burning sense of heat in foods. The process of cooking garlic removes allicin, thus mellowing its spiciness. Allicin, along with its decomposition products diallyl disulfide and diallyl trisulfide, are major contributors to the characteristic odor of garlic, with other allicin-derived compounds, such as vinyldithiins and ajoene.
Taxonomy
Identification of the wild progenitor of common garlic is difficult due to the sterility of its many cultivars, which limits the ability to cross test with wild relatives. Genetically and morphologically, garlic is most similar to the wild species Allium longicuspis, which grows in central and southwestern Asia. However, because A. longicuspis is also mostly sterile, it is doubtful that it is the ancestor of A. sativum. Other candidates that have been suggested include A. tuncelianum, A. macrochaetum, and A. truncatum, all of which are native to the Middle East.
Allium sativum grows in the wild in areas where it has become naturalized. The "wild garlic", "crow garlic", and "field garlic" of Britain are members of the species A. ursinum, A. vineale, and A. oleraceum, respectively. In North America, A. vineale (known as "wild garlic" or "crow garlic") and Allium canadense (known as "meadow garlic", "wild garlic", or "wild onion") are common weeds in fields. So-called elephant garlic is actually a wild leek (A. ampeloprasum) and not a true garlic. Single clove garlic (also called pearl or solo garlic) originated in the Yunnan province of China.
Subspecies and varieties
There are two subspecies of A. sativum, ten major groups of varieties, and hundreds of varieties, or cultivars.
- A. sativum var. ophioscorodon (Link) Döll, called Ophioscorodon or hardneck garlic, includes porcelain garlics, rocambole garlic, and purple stripe garlics. It is sometimes considered to be a separate species, Allium ophioscorodon G.Don.
- A. sativum var. sativum, or softneck garlic, includes artichoke garlic, silverskin garlic, and creole garlic.
There are at least 120 cultivars originating from Central Asia, making it the main center of garlic biodiversity.


Some garlics have protected status in the UK and the EU, including:
| Name | Source |
|---|---|
| Aglio Rosso di Nubia (Red Garlic of Nubia) | Nubia-Paceco, Provincia di Trapani, Sicily, Italy |
| Aglio Bianco Polesano | Rovigo, Veneto, Italy (PDO) |
| Aglio di Voghiera | Ferrara, Emilia-Romagna, Italy (PDO) |
| Ail blanc de Lomagne | Lomagne in the Gascony, France (PGI) |
| Ail de la Drôme | Drôme, France (PGI) |
| Ail rose de Lautrec, a rose/pink garlic | Lautrec, France (PGI) |
| Ail violet de Cadours | Cadours, France (PDO) |
| Ajo Morado de Las Pedroñeras, a rose/pink garlic | Las Pedroñeras, Spain (PGI) |
| 金鄕大蒜 Jīn Xiāng Dà Suàn | China (PGI) |
| Taşköprü Sarımsağı | Turkey (PDO) |
Etymology
The word garlic derives from Old English, garlēac, meaning gar (spear) and leek, as a 'spear-shaped leek'.
Ecology
Garlic plants are usually hardy and not affected by many pests or diseases. Garlic plants are said to repel rabbits and moles. The California Department of Food and Agriculture conducts a certification program to assure freedom from nematode and white rot disease caused by Stromatinia cepivora, two pathogens that can both destroy a crop and remain in the soil indefinitely once introduced. Garlic may also suffer from pink root, a typically non-fatal disease that stunts the roots and turns them pink or red; or leek rust, which usually appears as bright orange spots. The larvae of the leek moth attack garlic by mining into the leaves or bulbs.
Botrytis neck and bulb rot is a disease of onion, garlic, leek and shallot. Botrytis allii and Botrytis aclada cause this disease in onion and Botrytis porri causes it in garlic. According to the University of California,
Initial symptoms usually begin at the neck, where affected tissue softens, becomes water-soaked, and turns brown. In a humid atmosphere, a gray and feltlike growth (where spores are produced) appears on rotting scales, and mycelia may develop between scales. Dark-brown-to-black sclerotia (the resting bodies of the pathogen) may eventually develop in the neck or between scales.
Cultivation

Garlic is easy to cultivate and may grow year-round in mild climates. While sexual propagation of garlic is possible, nearly all of the garlic in cultivation is propagated asexually by planting individual cloves in the ground. In colder climates, cloves are best planted about six weeks before the soil freezes. The goal is to have the bulbs produce only roots and no shoots above the ground. Harvest is in late spring or early summer.
Garlic plants can be grown closely together, leaving enough space for the bulbs to mature, and are easily grown in containers of sufficient depth. Garlic does well in loose, dry, well-drained soils in sunny locations, and is hardy throughout USDA climate zones 4–9. When selecting garlic for planting, it is important to pick large bulbs from which to separate cloves. Large cloves, along with proper spacing in the planting bed, will also increase bulb size. Garlic plants prefer to grow in a soil with a high organic material content, but are capable of growing in a wide range of soil conditions and pH levels.
There are different varieties of garlic, most notably split into the subspecies of hardneck garlic and softneck garlic. The latitude where the garlic is grown affects the choice of type, as garlic can be day-length sensitive. Hardneck garlic is generally grown in cooler climates and produces relatively large cloves, whereas softneck garlic is generally grown closer to the equator and produces small, tightly packed cloves.
Garlic scapes are removed to focus all the garlic's energy into bulb growth. The scapes can be eaten raw or cooked.

Propagation
The method of propagating garlic from planting cloves is called division. Asexual propagation of garlic for production purposes requires cool temperatures that can vary depending on the cultivar. Hardneck varieties require long cold temperature exposure whereas softneck varieties thrive in milder climates. This cold climate is required for the process of vernalization, a form of stratification of the cloves necessary for the development of multiple-clove bulbs. Solo garlic is the result of garlic grown without the process of vernalization.
Production
| Country | Millions of tonnes |
|---|---|
| 20.5 | |
| 3.2 | |
| 0.8 | |
| 0.5 | |
| 0.3 | |
| 0.3 | |
| World | 28.2 |
In 2021, world production of garlic was 28 million tonnes, with China accounting for 73% of the total.
-
Bulbs (top-setting, grown in lieu of flowers)
-
Garlic, from The Book of Health, 1898, by Henry Munson Lyman
Adverse effects and toxicology
The scent of garlic is known to linger upon the human body and cause bad breath (halitosis) and body odor. This is caused by allyl methyl sulfide (AMS). AMS is a volatile liquid which is absorbed into the blood during the metabolism of garlic-derived sulfur compounds; from the blood it travels to the lungs (and from there to the mouth, causing garlic breath) and skin, where it is exuded through skin pores. Since digestion takes several hours, and release of AMS several hours more, the effect of eating garlic may be present for a long time. Washing the skin with soap is only a partial and imperfect solution to the smell. Studies have shown sipping milk at the same time as consuming garlic can significantly neutralize bad breath. Mixing garlic with milk in the mouth before swallowing reduced the odor better than drinking milk afterward. Plain water, mushrooms, and basil may also reduce the odor; the mix of fat and water found in milk, however, was the most effective. Garlic breath is allegedly alleviated by eating fresh parsley.
Abundant sulfur compounds in garlic are also responsible for turning garlic green or blue during pickling and cooking. Under these conditions (i.e., acidity, heat) the sulfur-containing compound alliin reacts with common amino acids to make pyrroles, clusters of carbon-nitrogen rings. These rings can be linked together into polypyrrole molecules. Ring structures absorb particular wavelengths of light and thus appear colored. The two-pyrrole molecule looks red, the three-pyrrole molecule looks blue, and the four-pyrrole molecule looks green (like chlorophyll, a tetrapyrrole). Like chlorophyll, the pyrrole pigments are safe to eat. Upon cutting, similar to a color change in onion caused by reactions of amino acids with sulfur compounds, garlic can turn green.
The green, dry "folds" in the center of the garlic clove are especially pungent. The sulfur compound allicin, produced by crushing or chewing fresh garlic, produces other sulfur compounds: ajoene, allyl polysulfides, and vinyldithiins. Aged garlic lacks allicin, but may have some activity due to the presence of S-allylcysteine.
Some people suffer from allergies to garlic and other species of Allium.[1] Symptoms can include irritable bowel, diarrhea, mouth and throat ulcerations, nausea, breathing difficulties, and, in rare cases, anaphylaxis. Garlic-sensitive people show positive tests to diallyl disulfide, allylpropyldisulfide, allylmercaptan, and allicin, all of which are present in garlic. People who suffer from garlic allergies are often sensitive to many other plants, including onions, chives, leeks, shallots, garden lilies, ginger, and bananas.

Several reports of serious burns resulting from garlic being applied topically for various purposes, including naturopathic uses and acne treatment, indicate care must be taken for these uses, usually testing a small area of skin using a low concentration of garlic. On the basis of numerous reports of such burns, including burns to children, topical use of raw garlic, as well as insertion of raw garlic into body cavities, is discouraged. In particular, topical application of raw garlic to young children is not advisable.
The side effects of long-term garlic supplementation are largely unknown. Possible side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort, sweating, dizziness, allergic reactions, bleeding, and menstrual irregularities.
Some breastfeeding mothers have found, after consuming garlic, that their babies can be slow to feed, and have noted a garlic odor coming from them.

If higher-than-recommended doses of garlic are taken with anticoagulant medications, this can lead to a higher risk of bleeding. Garlic may interact with warfarin, saquinavir, antihypertensives, calcium channel blockers, the quinolone family of antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, and hypoglycemic drugs, as well as other medications.[2] The American Veterinary Medical Association considers garlic to be toxic to pets.
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 623 kJ (149 kcal) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
33.06 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sugars | 1 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dietary fiber | 2.1 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.5 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6.36 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other constituents | Quantity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Water | 59 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Selenium | 14.2 μg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| †Percentages estimated using US recommendations for adults, except for potassium, which is estimated based on expert recommendation from the National Academies. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Uses
Because of sulfur compounds circulating in blood, consumed garlic may act as a mosquito repellent, although there is no scientific evidence of its efficacy.
Nutrition
In the typical serving size of 1–3 cloves (3–9 grams), raw garlic provides no significant nutritional value, with the content of all essential nutrients below 10% of the Daily Value (DV). In a reference amount of 100 g (3.5 oz), raw garlic contains some micronutrients in rich amounts (20% or more of the DV), including vitamins B6 (73% DV) and C (35% DV), and the dietary mineral, manganese (73% DV). Per 100 gram serving, raw garlic is a moderate source (10–19% DV) of the B vitamins, thiamin and pantothenic acid, as well as the dietary minerals, calcium, potassium, phosphorus, and zinc.
The composition of raw garlic is 59% water, 33% carbohydrates, 6% protein, 2% dietary fiber, and less than 1% fat.
Culinary


Garlic is widely used around the world for its pungent flavor as a seasoning or condiment.
The garlic plant's bulb is the most commonly used part of the plant. With the exception of the single clove types, garlic bulbs are normally divided into numerous fleshy sections called cloves. Garlic cloves are used for consumption (raw or cooked) or for medicinal purposes. They have a characteristic pungent, spicy flavor that mellows and sweetens considerably with cooking. The distinctive aroma is mainly due to organosulfur compounds including allicin present in fresh garlic cloves and ajoene which forms when they are crushed or chopped. A further metabolite allyl methyl sulfide is responsible for garlic breath.
Other parts of the garlic plant are also edible. The leaves and flowers (bulbils) on the head (spathe) are sometimes eaten. They are milder in flavor than the bulbs, and are most often consumed while immature and still tender. Immature garlic is sometimes pulled, rather like a scallion, and sold as "green garlic". When green garlic is allowed to grow past the "scallion" stage, but not permitted to fully mature, it may produce a garlic "round", a bulb like a boiling onion, but not separated into cloves like a mature bulb.
Green garlic imparts a garlic flavor and aroma in food, minus the spiciness. Green garlic is often chopped and stir-fried or cooked in soup or hot pot in Southeast Asian (i.e. Vietnamese, Thai, Myanmar, Lao, Cambodian, Singaporean), and Chinese cookery, and is very abundant and low-priced. Additionally, the immature flower stalks (scapes) of the hardneck are sometimes marketed for uses similar to asparagus in stir-fries.

Inedible or rarely eaten parts of the garlic plant include the "skin" covering each clove and root cluster. The papery, protective layers of "skin" over various parts of the plant are generally discarded during preparation for most culinary uses, though in Korea immature whole heads are sometimes prepared with the tender skins intact.[3] The root cluster attached to the basal plate of the bulb is the only part not typically considered palatable in any form.
An alternative is to cut the top off the bulb, coat the cloves by dribbling olive oil (or other oil-based seasoning) over them, and roast them in an oven. Garlic softens and can be extracted from the cloves by squeezing the (root) end of the bulb, or individually by squeezing one end of the clove. In Korea, heads of garlic are heated over the course of several weeks; the resulting product, called black garlic, is sweet and syrupy, and is exported to the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia.
Garlic may be applied to different kinds of bread, usually in a medium of butter or oil, to create a variety of classic dishes, such as garlic bread, garlic toast, bruschetta, crostini, and canapé. The flavor varies in intensity and aroma with the different cooking methods. It is often paired with onion, tomato, or ginger.

Immature scapes are tender and edible. They are also known as "garlic spears", "stems", or "tops". Scapes generally have a milder taste than the cloves. They are often used in stir frying or braised like asparagus. Garlic leaves are a popular vegetable in many parts of Asia. The leaves are cut, cleaned, and then stir-fried with eggs, meat, or vegetables.
Garlic powder is made from dehydrated garlic and can be used as a substitute for fresh garlic, though the taste is not quite the same. Garlic salt combines garlic powder with table salt.
Regions

Garlic is a fundamental component in many or most dishes of various regions, including eastern Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, the Middle East, northern Africa, southern Europe, Eastern Europe and parts of Latin America. Latin American seasonings, particularly, use garlic in sofritos and mofongos.
Oils can be flavored with garlic cloves. These infused oils are used to season all categories of vegetables, meats, breads, and pasta. Garlic, along with fish sauce, chopped fresh chilis, lime juice, sugar, and water, is a basic essential item in dipping fish sauce, a highly used dipping sauce condiment used in Indochina. In East and Southeast Asia, chili oil with garlic is a popular dipping sauce, especially for meat and seafood. Tuong ot toi Viet Nam (Vietnam chili garlic sauce) is a highly popular condiment and dip across North America and Asia.
In some cuisines, the young bulbs are pickled for three to six weeks in a mixture of sugar, salt, and spices. In eastern Europe, the shoots are pickled and eaten as an appetizer. Laba garlic, prepared by soaking garlic in vinegar, is a type of pickled garlic served with dumplings in northern China to celebrate the Chinese New Year.
Garlic is essential in Middle Eastern and Arabic cooking, with its presence in many food items. In the Levant, garlic is traditionally crushed together with olive oil, and occasionally salt, to create a Middle Eastern garlic sauce called Toum (تُوم; meaning "garlic" in Arabic). While not exclusively served with meats, toum is commonly paired with chicken or other meat dishes such as shawarma. Garlic is also a key component in some hummus varieties, an Arabic dip composed of chickpeas, tahini, garlic, lemon juice, and salt.
Lightly smoked garlic is used in British and other European cuisine. It is particularly prized for stuffing poultry and game, and in soups and stews.
Emulsifying garlic with olive oil produces aioli. Garlic, oil, and a chunky base produce skordalia. Crushed garlic, oil, and water produce a strong flavored sauce, mujdei. Blending garlic, almond, oil, and soaked bread produces ajoblanco. Tzatziki, yogurt mixed with garlic and salt, is a common sauce in Eastern Mediterranean cuisines.
Culinary history
Numerous cuneiform records show that garlic has been cultivated in Mesopotamia for at least 4,000 years. The use of garlic in China and Egypt also dates back thousands of years. Well-preserved garlic was found in the tomb of Tutankhamun (c. 1325 BC). It was consumed by ancient Greek and Roman soldiers, sailors, and rural classes (Virgil, Eclogues ii. 11), and, according to Pliny the Elder (Natural History xix. 32), by the African peasantry. Garlic was placed by the ancient Greeks on the piles of stones at crossroads, as a supper for Hecate (Theophrastus, Characters, The Superstitious Man).
Garlic was rare in traditional English cuisine (though it is said to have been grown in England before 1548) but has been a common ingredient in Mediterranean Europe. Translations of the c. 1300 Assize of Weights and Measures, an English statute generally dated to the 13th century, indicate a passage as dealing with standardized units of garlic production, sale, and taxation—the hundred of 15 ropes of 15 heads each but the Latin version of the text may refer to herring rather than garlic.
Storage

Domestically, garlic is stored warm [above 18°C (64°F)] and dry to keep it dormant (to inhibit sprouting). It is traditionally hung; softneck varieties are often braided in strands called plaits or grappes. Peeled cloves may be stored in wine or vinegar in the refrigerator. Commercially, garlic is stored at 0°C (32°F), in a dry, low-humidity environment. Garlic will keep longer if the tops remain attached.
Garlic is often kept in oil to produce flavored oil; however, the practice requires measures to be taken to prevent the garlic from spoiling which may include rancidity and growth of Clostridium botulinum. Acidification with a mild solution of vinegar minimizes bacterial growth. Refrigeration does not assure the safety of garlic kept in oil, requiring use within one month to avoid bacterial spoilage.
Stored garlic can be affected by Penicillium decay known as "blue mold" (or "green mold" in some locales), especially in high humidity. Infection may first appear as soft or water-soaked spots, followed by white patches (of mycelium) which turn blue or green with sporulation. As sporulation and germination are delayed at low temperature, and at −4 °C are inhibited entirely, in refrigerated cloves one may only see the white mycelium during early stages. Penicillium hirsutum and Penicillium allii are two of the predominant species identified in blue mold.
Medical research
Cardiovascular
As of 2016, clinical research found that consuming garlic produces only a small reduction in blood pressure (4 mmHg), and there is no clear long-term effect on hypertension, cardiovascular morbidity or mortality. A 2016 meta-analysis indicated there was no effect of garlic consumption on blood levels of lipoprotein(a), a biomarker of atherosclerosis.
Because garlic might reduce platelet aggregation, people taking anticoagulant medication are cautioned about consuming garlic.
Cancer
Two reviews found no effect of consuming garlic on colorectal cancer. A 2016 meta-analysis of case-control and cohort studies found a moderate inverse association between garlic intake and some cancers of the upper digestive tract.
Common cold
A 2014 review found insufficient evidence to determine the effects of garlic in preventing or treating the common cold. Other reviews concluded a similar absence of high-quality evidence for garlic having a significant effect on the common cold.

Folk medicine
Garlic has been used for traditional medicine in diverse cultures such as in Korea, Egypt, Japan, China, Rome, and Greece. In his Natural History, Pliny gave a list of conditions in which garlic was considered beneficial (N.H. xx. 23). Galen, writing in the second century, eulogized garlic as the "rustic's theriac" (cure-all) (see F. Adams' Paulus Aegineta, p. 99). Alexander Neckam, a writer of the 12th century (see Wright's edition of his works, p. 473, 1863), discussed it as a palliative for the heat of the sun in field labor. In the 17th century, Thomas Sydenham valued it as an application in confluent smallpox, and William Cullen's Materia Medica of 1789 found some dropsies cured by it alone.
Other uses
The sticky juice within the bulb cloves is used as an adhesive in mending glass and porcelain.[4] An environmentally benign garlic-derived polysulfide product is approved for use in the European Union (under Annex 1 of 91/414) and the UK as a nematicide and insecticide, including for use in the control of cabbage root fly and red mite in poultry.
In culture
Garlic is present in the folklore of many cultures. In Europe, many cultures have used garlic for protection or white magic, perhaps owing to its reputation in folk medicine.[5] Central European folk beliefs considered garlic a powerful ward against demons, werewolves, and vampires. To ward off vampires, garlic could be worn, hung in windows, or rubbed on chimneys and keyholes.
In the foundation myth of the ancient Korean kingdom of Gojoseon, eating nothing but 20 cloves of garlic and a bundle of Korean mugwort for 100 days let a bear be transformed into a woman.
In celebration of Nowruz (Persian calendar New Year), garlic is one of the essential items in a haft-sin ('seven things beginning with "S"') table, a traditional New Year's display: the name for garlic in Persian is سیر (seer), which begins with س (sin, fa, seen) the Perso-Arabic letter corresponding to "S".
In Islam, it is recommended not to eat raw garlic prior to going to the mosque. This is based on several hadith.
Some Mahāyāna Buddhists and sects in China and Vietnam avoid eating onions, garlic, scallions, chives and leeks, which are known as Wu hun (Chinese: 五葷; pinyin: Wǔ hūn, 'the five forbidden pungent vegetables').
Because of its strong odor, garlic is sometimes called the "stinking rose".
Gallery
-
Chopped garlic
-
Garlic plant
-
Harvested garlic left to dry
-
A garlic bulb
-
Blended garlic confit
See also
- Garlic Is as Good as Ten Mothers
- Garlic oil
- Garlic sauce
- Herbalism
- International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants
- List of garlic dishes
- List of garlic festivals
- Pyruvate scale
External links
 Data related to Allium sativum at Wikispecies
Data related to Allium sativum at Wikispecies The dictionary definition of garlic at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of garlic at Wiktionary
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Garlic(2 June 2025, at 21:34編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Item:Q19061 |
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedBlock2010 - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedUKMi - ↑ Amanda. "Glossary of Foods and Food Terms in Korea". Food-links.com. Retrieved April 14, 2010.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedAN - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namednih







