Zinc/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "===亜鉛(I)化合物=== 亜鉛(I)化合物は非常に稀である。[Zn<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>イオンは、溶融ZnCl<sub>2</sub>に金属亜鉛を溶かすと黄色い反磁性ガラスが形成されることから示唆されている。[Zn<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>コアは、水銀(I)化合物に存在する[Hg<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>カチオンと類似している。このイオンの反磁的な性質..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "===亜鉛(II)化合物=== thumb|left|[[Zinc acetate/ja|酢酸亜鉛, {{chem|Zn|(|C|H|3|C|O|2|)|2}}|alt=ゆっくりとした蒸発によって形成される酢酸亜鉛のシート]] thumb|塩化亜鉛|alt=ガラス板上の白い塊状の粉 亜鉛の二元化合物は、ほとんどのメタロイドと希ガスを除くすべてのNonmetal (chemistry)/ja|..." |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
亜鉛(I)化合物は非常に稀である。[Zn<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>イオンは、溶融ZnCl<sub>2</sub>に金属亜鉛を溶かすと黄色い反磁性ガラスが形成されることから示唆されている。[Zn<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>コアは、[[mercury (element)/ja|水銀]](I)化合物に存在する[Hg<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>カチオンと類似している。このイオンの[[diamagnetism/ja|反磁的]]な性質は、その二量体構造を裏付けている。Zn-Zn結合を含む最初の亜鉛(I)化合物[[Decamethyldizincocene/ja|(η<sup>5</sup>-C<sub>5</sub>Me<sub>5</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Zn<sub>2</sub>]]である。 | 亜鉛(I)化合物は非常に稀である。[Zn<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>イオンは、溶融ZnCl<sub>2</sub>に金属亜鉛を溶かすと黄色い反磁性ガラスが形成されることから示唆されている。[Zn<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>コアは、[[mercury (element)/ja|水銀]](I)化合物に存在する[Hg<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>カチオンと類似している。このイオンの[[diamagnetism/ja|反磁的]]な性質は、その二量体構造を裏付けている。Zn-Zn結合を含む最初の亜鉛(I)化合物[[Decamethyldizincocene/ja|(η<sup>5</sup>-C<sub>5</sub>Me<sub>5</sub>)<sub>2</sub>Zn<sub>2</sub>]]である。 | ||
<div | <div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> | ||
=== | ===亜鉛(II)化合物=== | ||
[[File:Zinc acetate.JPG|thumb|left|[[Zinc acetate]], {{chem|Zn|(|C|H|3|C|O|2|)|2}}|alt= | [[File:Zinc acetate.JPG|thumb|left|[[Zinc acetate/ja|酢酸亜鉛]], {{chem|Zn|(|C|H|3|C|O|2|)|2}}|alt=ゆっくりとした蒸発によって形成される酢酸亜鉛のシート]] | ||
[[File:Zinc chloride.jpg|thumb| | [[File:Zinc chloride.jpg|thumb|塩化亜鉛|alt=ガラス板上の白い塊状の粉]] | ||
[[Binary compound]] | 亜鉛の[[Binary compound/ja|二元化合物]]は、ほとんどの[[metalloid/ja|メタロイド]]と[[noble gas/ja|希ガス]]を除くすべての[[Nonmetal (chemistry)/ja|非金属]]で知られている。酸化物[[zinc oxide/ja|ZnO]]は白色の粉末で、中性の水溶液にはほとんど溶けないが、[[amphoteric/ja|両性]]であり、強い塩基性溶液にも酸性溶液にも溶ける。他の[[chalcogen/ja|カルコゲン]]化物([[zinc sulfide/ja|ZnS]]、[[zinc selenide/ja|ZnSe]]、[[zinc telluride/ja|ZnTe]])は電子工学や光学で様々な用途がある。また、[[Zinc nitride/ja|{{chem|Zn|3|N|2}}]、[[zinc phosphide/ja|{{chem|Zn|3|P|2}}]、[[zinc arsenide/ja|{chem|Zn|3|As|2}}]などの[[Pnictogenide/ja|ニクトゲン化物]]材料もある、また、[[zinc antimonide/ja|{chem|Zn|3|Sb|2}}]、過酸化物([[zinc peroxide/ja|{{Chem|ZnO|2}}])、水素化物([[zinc hydride/ja|{Chem|ZnH|2}}])、炭化物({{Chem|ZnC|2}})も知られている。4つの[[halide/ja|ハロゲン化物]]のうち、[[zinc fluoride/ja|{{化学式|ZnF|2}}]は最もイオン的な性質を持ち、他のもの([[zinc chloride/ja|{{化学式|ZnCl|2}}]、[[zinc bromide/ja|{{化学式|ZnBr|2}}]、[[zinc iodide/ja|{{化学式|ZnI|2}}])は比較的融点が低く、共有結合的な性質が強いと考えられている。 | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 19:08, 20 April 2024
Page Template:Infobox element/styles.css has no content.
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zinc | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | silver-gray | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(Zn) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zinc in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 692.68 K (419.53 °C, 787.15 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 1180 K (907 °C, 1665 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 7.14 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 6.57 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 7.32 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 115 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.470 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −2, 0, +1, +2 (an amphoteric oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 134 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 122±4 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 139 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | hexagonal close-packed (hcp) (hP2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice constants | a = 266.46 pm c = 494.55 pm (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 30.2 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 116 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 59.0 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −11.4×10−6 cm3/mol (298 K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 108 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 43 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 70 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 3850 m/s (at r.t.) (rolled) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 2.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 327–412 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-66-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Indian metallurgists (before 1000 BCE) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Andreas Sigismund Marggraf (1746) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognized as a unique metal by | Rasaratna Samuccaya (1300) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of zinc | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
亜鉛は化学元素の一つであり、シンボルはZn、原子番号は30である。室温ではやや脆い金属であり、酸化を取り除くと光沢のある灰色がかった外観を持つ。周期表の12族 (IIB)の最初の元素である。いくつかの点で、マグネシウムと化学的に似ている:両元素とも通常の酸化状態は1つだけ(+2)であり、Zn2+とMg2+のイオンの大きさは似ている。亜鉛は24番目に豊富な地殻中の元素であり、5つの安定な同位体を持っている。最も一般的な亜鉛鉱石は閃亜鉛鉱(zinc blende)で、硫化亜鉛鉱物である。加工可能な最大の鉱脈はオーストラリア、アジア、アメリカにある。亜鉛は鉱石の泡沫浮遊、焙焼、そして最終的に電気(電解)を用いた抽出によって精製される。
亜鉛はヒト、動物、植物、微生物にとって必須の微量元素であり、出生前と出生後の発育に必要である。人間にとって鉄に次いで2番目に多い微量金属であり、すべての酵素クラスに登場する唯一の金属である。また、多くの酵素の重要な補因子であるため、サンゴの成長に不可欠な栄養元素でもある。
亜鉛欠乏症は発展途上国の約20億人に影響を及ぼし、多くの病気と関連している。子どもの場合、欠乏は成長遅延、性成熟遅延、感染症感受性、下痢を引き起こす。亜鉛原子を反応中心に持つ酵素は、ヒトのアルコールデヒドロゲナーゼなど、生化学に広く存在する。過剰な亜鉛の摂取は運動失調、嗜眠、銅欠乏を引き起こすことがある。海洋生物群、特に極域では、亜鉛が不足すると一次藻類群集の活力が損なわれ、複雑な海洋栄養構造を不安定にし、結果として生物多様性に影響を与える可能性がある。
真鍮は銅と亜鉛を様々な割合で混ぜた合金であり、紀元前3千年紀には早くもエーゲ海地域と現在のイラク、アラブ首長国連邦、カルムイキア、トルクメニスタン、ジョージアを含む地域で使用されていた。紀元前2千年紀には、現在西インド、ウズベキスタン、イラン、シリア、イラク、イスラエルを含む地域で使用されていた。ラジャスタンの鉱山は、紀元前6世紀まで遡る亜鉛生産の明確な証拠を与えている。現在までに、純粋な亜鉛の最古の証拠は、純粋な亜鉛を作るために蒸留プロセスが採用された紀元後9世紀には、ラジャスタン州のザワールから来ている。錬金術師たちは空気中で亜鉛を燃やし、「哲学者の羊毛」または「白い雪」と呼ばれるものを形成した。
この元素はおそらく錬金術師パラケルススによってドイツ語のZinke(突起、歯)にちなんで命名された。ドイツの化学者アンドレアス・シギスムント・マルグラーフは1746年に純粋な金属亜鉛を発見したとされている。1800年までにルイジ・ガルヴァーニとアレッサンドロ・ボルタによって亜鉛の電気化学的特性が明らかにされた。鉄の腐食に対する亜鉛めっき(溶融亜鉛メッキ)は、亜鉛の主要な用途である。その他の用途としては、電気電池、小さな非構造鋳造品、そして真鍮などの合金があります。亜鉛化合物はさまざまな用途で一般的に使用されており、亜鉛炭酸塩や亜鉛グルコン酸塩(栄養補助剤として)、塩化亜鉛(制汗剤に)、ピリチオン亜鉛(抗フケシャンプーに)、亜鉛硫化物(蛍光ペイントに)、そしてジメチル亜鉛やジエチル亜鉛(有機実験室で)が含まれる。
特徴
物理的性質
亜鉛は青みがかった白色で光沢のある反磁性金属であるが、一般的な市販グレードの多くはくすんだ仕上げが施されている。密度は鉄よりもやや低く、六角形の結晶構造を持ち、歪んだ形の六角クローズパッキングを持つ。この金属はほとんどの温度で硬く脆いが、100~150 °Cの間では可鍛性になる。210 °Cを超えると再び脆くなり、叩いて粉砕することができる。亜鉛はかなりの電気伝導体である。金属としては融点(419.5 °C)と沸点(907 °C)が比較的低い。融点は水銀とカドミウムを除けばd-ブロック金属の中で最も低く、このため亜鉛、カドミウム、水銀は他のd-ブロック金属と同様に遷移金属とは見なされないことが多い。
真鍮を含む多くの合金が亜鉛を含む。亜鉛と二元合金を形成することが古くから知られている他の金属は、アルミニウム、アンチモン、ビスマス、金、鉄、鉛、水銀、銀、錫、マグネシウム、コバルト、ニッケル、テルル、ナトリウムである。亜鉛もジルコニウムも強磁性ではないが、それらの合金であるZrZn
2は35 K以下で強磁性を示す。
出現率
亜鉛は地殻の約75 ppm(0.0075%)を占め、24番目に豊富な元素である。亜鉛の典型的なバックグラウンド濃度は、大気中では1 μg/m3、土壌中では300 mg/kg、植生中では100 mg/kg、淡水中では20 μg/L、海水中では5 μg/Lを超えない。この元素は通常、銅や鉛などの他の卑金属と結びついて鉱石に含まれている。亜鉛は好塩基性であり、鉱物中では酸素のような軽いカルコゲンやハロゲンのような非カルコゲンの電気陰性元素よりもむしろ、硫黄や他の重いカルコゲンと共に発見されやすい。硫化物は、初期の地球大気の還元条件下で地殻が固化する際に形成された。硫化亜鉛の一種である閃亜鉛鉱は、その精鉱が亜鉛を60~62%含むため、亜鉛を含む鉱石の中で最も多く採掘されている。
他の亜鉛源鉱物には、スミソナイト(亜鉛炭酸塩)、ヘミモルファイト(亜鉛ケイ酸塩)、ウルツァイト(別の硫化亜鉛)、時にはハイドロ亜鉛鉱(塩基性炭酸亜鉛)がある。ウルツァイトを除いて、これら他の鉱物はすべて原初の硫化亜鉛の風化によって形成されたものである。
確認されている世界の亜鉛資源は合計約19億~28億トンである。大規模な鉱床はオーストラリア、カナダ、アメリカにあり、最大の埋蔵量はイランにある。一方、亜鉛の埋蔵量とは、地質学的に確認された鉱体のうち、回収の適否が決定時の経済性(位置、品位、質、量)に基づいているものを指す。探鉱と鉱山開発は現在進行中のプロセスであるため、亜鉛埋蔵量は固定された数字ではなく、現在の亜鉛鉱山の鉱山寿命を単純に外挿することで亜鉛鉱石供給の持続可能性を判断することはできない。この考え方は、米国地質調査所(USGS)のデータによって裏付けられている。USGSによると、1990年から2010年の間に亜鉛精錬生産量は80%増加したが、亜鉛の埋蔵量は変わっていない。2002年までの歴史を通じて約3億4600万トンが採掘され、学者たちは約1億900万トンから3億500万トンが使用されていると推定している。

同位体
自然界には亜鉛の5つの安定な同位体が存在し、64Znが最も豊富な同位体である(49.17%自然存在量)。自然界に存在する他の同位体は66
Znである。(27.73%), 67
Zn である。(4.04%), 68
Zn である。(18.45%)、70
Znである。(0.61%).
数十種類の放射性同位体が特徴づけられている。半減期が243.66 日の65
Znは最も活性の低い放射性同位体であり、半減期が46.5 時間の72
Znがそれに続く。亜鉛には10個の核異性体があり、そのうち69mZnの半減期は13.76時間と最も長い。上付き文字mは準安定同位体を示す。準安定同位体の原子核は励起状態にあり、ガンマ線の形で光子を放出することで基底状態に戻る。61
Znには3つの励起準安定状態があり、73
Znには2つの励起準安定状態がある。同位体65
Zn、71
Zn、77
Zn、78
Znはそれぞれ1つの励起準安定状態しか持たない。
質量数が66より小さい亜鉛の放射性同位体の最も一般的な崩壊様式は陽電子放出(β+)であり、銅の同位体が生じる。
質量数66以上の亜鉛の放射性同位体の最も一般的な崩壊様式はβ崩壊(β-)であり、ガリウムの同位体を生成する。
化合物と化学
反応性
亜鉛は電子配置が[Ar]3d104s2であり、周期表の12族の一員である。中程度の反応性を持つ金属であり、強い還元剤である。純金属の表面は変色が早く、最終的には大気中の二酸化炭素との反応によって塩基性の炭酸亜鉛、Zn
5(OH)
6(CO3)
2の保護不動態化層を形成する。
亜鉛は空気中で明るい青緑色の炎で燃え、酸化亜鉛の煙霧を出す。亜鉛は酸やアルカリ、その他の非金属と容易に反応する。極めて純粋な亜鉛は室温では酸とゆっくりとしか反応しない。塩酸や硫酸のような強い酸は不動態化層を除去することができ、その後の酸との反応によって水素ガスが放出される。
亜鉛の化学的性質は+2酸化状態が支配的である。この酸化状態の化合物が形成されると、外側のシェルのs電子が失われ、電子配置[Ar]3d10の裸の亜鉛イオンが生じる。水溶液中では八面体錯体[Zn(H
2O)6]2+
が優勢な種である。285 °C以上の温度で塩化亜鉛と組み合わせた亜鉛の揮発は、酸化状態が+1の亜鉛化合物Zn
2Cl
2の形成を示す。1または+2以外の正の酸化状態の亜鉛化合物は知られていない。計算では、+4の酸化状態の亜鉛化合物は存在しそうにない。Zn(III)は電気陰性度の強いトリアニオンの存在下で存在すると予測されているが、この可能性には疑問がある。しかし2021年、ZnBeB11(CN)12という式で表される、酸化状態が+3である別の化合物が、より多くの証拠とともに報告された。
亜鉛の化学的性質は後期第一遷移金属であるニッケルと銅の化学的性質に似ているが、充填d殻を持ち、化合物は反磁性でほとんどが無色である。亜鉛とマグネシウムのイオン半径は偶然にもほぼ同じである。このため、等価塩の中には同じ結晶構造を持つものもあり、イオン半径が決定要因となる他の状況では、亜鉛の化学はマグネシウムの化学と共通点が多い。他の点では、後期第一遷移金属との類似性はほとんどない。亜鉛は、NおよびSドナーと、より高度な共有結合性を持ち、はるかに安定な錯体を形成する傾向がある。亜鉛の錯体は5配位錯体も知られているが、ほとんどが4配位または6配位の配位錯体である。
亜鉛(I)化合物
亜鉛(I)化合物は非常に稀である。[Zn2]2+イオンは、溶融ZnCl2に金属亜鉛を溶かすと黄色い反磁性ガラスが形成されることから示唆されている。[Zn2]2+コアは、水銀(I)化合物に存在する[Hg2]2+カチオンと類似している。このイオンの反磁的な性質は、その二量体構造を裏付けている。Zn-Zn結合を含む最初の亜鉛(I)化合物(η5-C5Me5)2Zn2である。
亜鉛(II)化合物

3CO
2)
2

亜鉛の二元化合物は、ほとんどのメタロイドと希ガスを除くすべての非金属で知られている。酸化物ZnOは白色の粉末で、中性の水溶液にはほとんど溶けないが、両性であり、強い塩基性溶液にも酸性溶液にも溶ける。他のカルコゲン化物(ZnS、ZnSe、ZnTe)は電子工学や光学で様々な用途がある。また、[[Zinc nitride/ja|Zn
3N
2]、[[zinc phosphide/ja|Zn
3P
2]、[[zinc arsenide/ja|{chem|Zn|3|As|2}}]などのニクトゲン化物材料もある、また、[[zinc antimonide/ja|{chem|Zn|3|Sb|2}}]、過酸化物([[zinc peroxide/ja|ZnO
2])、水素化物([[zinc hydride/ja|{Chem|ZnH|2}}])、炭化物(ZnC
2)も知られている。4つのハロゲン化物のうち、[[zinc fluoride/ja|Template:化学式]は最もイオン的な性質を持ち、他のもの([[zinc chloride/ja|Template:化学式]、[[zinc bromide/ja|Template:化学式]、[[zinc iodide/ja|Template:化学式])は比較的融点が低く、共有結合的な性質が強いと考えられている。
In weak basic solutions containing Zn2+
ions, the hydroxide Zn(OH)
2 forms as a white precipitate. In stronger alkaline solutions, this hydroxide is dissolved to form zincates ([Zn(OH)4]2−
). The nitrate Zn(NO3)
2, chlorate Zn(ClO3)
2, sulfate ZnSO
4, phosphate Zn
3(PO4)
2, molybdate ZnMoO
4, cyanide Zn(CN)
2, arsenite Zn(AsO2)
2, arsenate Zn(AsO4)
2·8H
2O and the chromate ZnCrO
4 (one of the few colored zinc compounds) are a few examples of other common inorganic compounds of zinc.
Organozinc compounds are those that contain zinc–carbon covalent bonds. Diethylzinc ((C
2H5)
2Zn) is a reagent in synthetic chemistry. It was first reported in 1848 from the reaction of zinc and ethyl iodide, and was the first compound known to contain a metal–carbon sigma bond.
Test for zinc
Cobalticyanide paper (Rinnmann's test for Zn) can be used as a chemical indicator for zinc. 4 g of K3Co(CN)6 and 1 g of KClO3 is dissolved on 100 ml of water. Paper is dipped in the solution and dried at 100 °C. One drop of the sample is dropped onto the dry paper and heated. A green disc indicates the presence of zinc.
History
Ancient use
Various isolated examples of the use of impure zinc in ancient times have been discovered. Zinc ores were used to make the zinc–copper alloy brass thousands of years prior to the discovery of zinc as a separate element. Judean brass from the 14th to 10th centuries BC contains 23% zinc.
Knowledge of how to produce brass spread to Ancient Greece by the 7th century BC, but few varieties were made. Ornaments made of alloys containing 80–90% zinc, with lead, iron, antimony, and other metals making up the remainder, have been found that are 2,500 years old.
Strabo writing in the 1st century BC (but quoting a now lost work of the 4th century BC historian Theopompus) mentions "drops of false silver" which when mixed with copper make brass. This may refer to small quantities of zinc that is a by-product of smelting sulfide ores.
The manufacture of brass was known to the Romans by about 30 BC. They made brass by heating powdered calamine (zinc silicate or carbonate), charcoal and copper together in a crucible. The resulting calamine brass was then either cast or hammered into shape for use in weaponry. Some coins struck by Romans in the Christian era are made of what is probably calamine brass.

The oldest known pills were made of the zinc carbonates hydrozincite and smithsonite. The pills were used for sore eyes and were found aboard the Roman ship Relitto del Pozzino, wrecked in 140 BC.
The Berne zinc tablet is a votive plaque dating to Roman Gaul made of an alloy that is mostly zinc.
The Charaka Samhita, thought to have been written between 300 and 500 AD, mentions a metal which, when oxidized, produces pushpanjan, thought to be zinc oxide. Zinc mines at Zawar, near Udaipur in India, have been active since the Mauryan period (c. 322 and 187 BC). The smelting of metallic zinc here, however, appears to have begun around the 12th century AD. One estimate is that this location produced an estimated million tonnes of metallic zinc and zinc oxide from the 12th to 16th centuries. Another estimate gives a total production of 60,000 tonnes of metallic zinc over this period. The Rasaratna Samuccaya, written in approximately the 13th century AD, mentions two types of zinc-containing ores: one used for metal extraction and another used for medicinal purposes.
Early studies and naming
Zinc was distinctly recognized as a metal under the designation of Yasada or Jasada in the medical Lexicon ascribed to the Hindu king Madanapala (of Taka dynasty) and written about the year 1374. Smelting and extraction of impure zinc by reducing calamine with wool and other organic substances was accomplished in the 13th century in India. The Chinese did not learn of the technique until the 17th century.

Alchemists burned zinc metal in air and collected the resulting zinc oxide on a condenser. Some alchemists called this zinc oxide lana philosophica, Latin for "philosopher's wool", because it collected in wooly tufts, whereas others thought it looked like white snow and named it nix album.
The name of the metal was probably first documented by Paracelsus, a Swiss-born German alchemist, who referred to the metal as "zincum" or "zinken" in his book Liber Mineralium II, in the 16th century. The word is probably derived from the German zinke, and supposedly meant "tooth-like, pointed or jagged" (metallic zinc crystals have a needle-like appearance). Zink could also imply "tin-like" because of its relation to German zinn meaning tin. Yet another possibility is that the word is derived from the Persian word سنگ seng meaning stone. The metal was also called Indian tin, tutanego, calamine, and spinter.
German metallurgist Andreas Libavius received a quantity of what he called "calay" (from the Malay or Hindi word for tin) originating from Malabar off a cargo ship captured from the Portuguese in the year 1596. Libavius described the properties of the sample, which may have been zinc. Zinc was regularly imported to Europe from the Orient in the 17th and early 18th centuries, but was at times very expensive.
Isolation

Metallic zinc was isolated in India by 1300 AD. Before it was isolated in Europe, it was imported from India in about 1600 AD. Postlewayt's Universal Dictionary, a contemporary source giving technological information in Europe, did not mention zinc before 1751 but the element was studied before then.
Flemish metallurgist and alchemist P. M. de Respour reported that he had extracted metallic zinc from zinc oxide in 1668. By the start of the 18th century, Étienne François Geoffroy described how zinc oxide condenses as yellow crystals on bars of iron placed above zinc ore that is being smelted. In Britain, John Lane is said to have carried out experiments to smelt zinc, probably at Landore, prior to his bankruptcy in 1726.
In 1738 in Great Britain, William Champion patented a process to extract zinc from calamine in a vertical retort-style smelter. His technique resembled that used at Zawar zinc mines in Rajasthan, but no evidence suggests he visited the Orient. Champion's process was used through 1851.
German chemist Andreas Marggraf normally gets credit for isolating pure metallic zinc in the West, even though Swedish chemist Anton von Swab had distilled zinc from calamine four years previously. In his 1746 experiment, Marggraf heated a mixture of calamine and charcoal in a closed vessel without copper to obtain a metal.
Later work

William Champion's brother, John, patented a process in 1758 for calcining zinc sulfide into an oxide usable in the retort process. Prior to this, only calamine could be used to produce zinc. In 1798, Johann Christian Ruberg improved on the smelting process by building the first horizontal retort smelter. Jean-Jacques Daniel Dony built a different kind of horizontal zinc smelter in Belgium that processed even more zinc.
Italian doctor Luigi Galvani discovered in 1780 that connecting the spinal cord of a freshly dissected frog to an iron rail attached by a brass hook caused the frog's leg to twitch. He incorrectly thought he had discovered an ability of nerves and muscles to create electricity and called the effect "animal electricity". The galvanic cell and the process of galvanization were both named for Luigi Galvani, and his discoveries paved the way for electrical batteries, galvanization, and cathodic protection.
Galvani's friend, Alessandro Volta, continued researching the effect and invented the Voltaic pile in 1800. Volta's pile consisted of a stack of simplified galvanic cells, each being one plate of copper and one of zinc connected by an electrolyte. By stacking these units in series, the Voltaic pile (or "battery") as a whole had a higher voltage, which could be used more easily than single cells. Electricity is produced because the Volta potential between the two metal plates makes electrons flow from the zinc to the copper and corrode the zinc.
The non-magnetic character of zinc and its lack of color in solution delayed discovery of its importance to biochemistry and nutrition. This changed in 1940 when carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme that scrubs carbon dioxide from blood, was shown to have zinc in its active site.
Production
Mining and processing
| Rank | Country | Tonnes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 4,210,000 |
| 2 | Peru | 1,400,000 |
| 3 | Australia | 1,330,000 |
| 4 | United States | 753,000 |
| 5 | India | 720,000 |
| 6 | Mexico | 677,000 |




27°57′17″S 016°46′00″E / 27.95472°S 16.76667°E

27°49′09″S 016°36′28″E / 27.81917°S 16.60778°E
Zinc is the fourth most common metal in use, trailing only iron, aluminium, and copper with an annual production of about 13 million tonnes. The world's largest zinc producer is Nyrstar, a merger of the Australian OZ Minerals and the Belgian Umicore. About 70% of the world's zinc originates from mining, while the remaining 30% comes from recycling secondary zinc.
Commercially pure zinc is known as Special High Grade, often abbreviated SHG, and is 99.995% pure.
Worldwide, 95% of new zinc is mined from sulfidic ore deposits, in which sphalerite (ZnS) is nearly always mixed with the sulfides of copper, lead and iron. Zinc mines are scattered throughout the world, with the main areas being China, Australia, and Peru. China produced 38% of the global zinc output in 2014.
Zinc metal is produced using extractive metallurgy. The ore is finely ground, then put through froth flotation to separate minerals from gangue (on the property of hydrophobicity), to get a zinc sulfide ore concentrate consisting of about 50% zinc, 32% sulfur, 13% iron, and 5% SiO
2.
Roasting converts the zinc sulfide concentrate to zinc oxide:
The sulfur dioxide is used for the production of sulfuric acid, which is necessary for the leaching process. If deposits of zinc carbonate, zinc silicate, or zinc-spinel (like the Skorpion Deposit in Namibia) are used for zinc production, the roasting can be omitted.
For further processing two basic methods are used: pyrometallurgy or electrowinning. Pyrometallurgy reduces zinc oxide with carbon or carbon monoxide at 950 °C (1,740 °F) into the metal, which is distilled as zinc vapor to separate it from other metals, which are not volatile at those temperatures. The zinc vapor is collected in a condenser. The equations below describe this process:
In electrowinning, zinc is leached from the ore concentrate by sulfuric acid and impurities are precipitated:
Finally, the zinc is reduced by electrolysis.
The sulfuric acid is regenerated and recycled to the leaching step.
When galvanised feedstock is fed to an electric arc furnace, the zinc is recovered from the dust by a number of processes, predominantly the Waelz process (90% as of 2014).
Environmental impact
Refinement of sulfidic zinc ores produces large volumes of sulfur dioxide and cadmium vapor. Smelter slag and other residues contain significant quantities of metals. About 1.1 million tonnes of metallic zinc and 130 thousand tonnes of lead were mined and smelted in the Belgian towns of La Calamine and Plombières between 1806 and 1882. The dumps of the past mining operations leach zinc and cadmium, and the sediments of the Geul River contain non-trivial amounts of metals. About two thousand years ago, emissions of zinc from mining and smelting totaled 10 thousand tonnes a year. After increasing 10-fold from 1850, zinc emissions peaked at 3.4 million tonnes per year in the 1980s and declined to 2.7 million tonnes in the 1990s, although a 2005 study of the Arctic troposphere found that the concentrations there did not reflect the decline. Man-made and natural emissions occur at a ratio of 20 to 1.
Zinc in rivers flowing through industrial and mining areas can be as high as 20 ppm. Effective sewage treatment greatly reduces this; treatment along the Rhine, for example, has decreased zinc levels to 50 ppb. Concentrations of zinc as low as 2 ppm adversely affects the amount of oxygen that fish can carry in their blood.
Soils contaminated with zinc from mining, refining, or fertilizing with zinc-bearing sludge can contain several grams of zinc per kilogram of dry soil. Levels of zinc in excess of 500 ppm in soil interfere with the ability of plants to absorb other essential metals, such as iron and manganese. Zinc levels of 2000 ppm to 180,000 ppm (18%) have been recorded in some soil samples. The European Soil Observatory has published the first high resolution spatial assessment of topsoil Zinc (Zn) concentrations in Europe. The mean concentration of Zn in topsoils is 47 mg/kg while 1% of the measured 22,000 samples had concentrations higher than 167 mg/kg.
Applications
Major applications of zinc include, with percentages given for the US
- Galvanizing (55%)
- Brass and bronze (16%)
- Other alloys (21%)
- Miscellaneous (8%)
Anti-corrosion and batteries


Zinc is most commonly used as an anti-corrosion agent, and galvanization (coating of iron or steel) is the most familiar form. In 2009 in the United States, 55% or 893,000 tons of the zinc metal was used for galvanization.
Zinc is more reactive than iron or steel and thus will attract almost all local oxidation until it completely corrodes away. A protective surface layer of oxide and carbonate (Zn
5(OH)
6(CO
3)
2) forms as the zinc corrodes. This protection lasts even after the zinc layer is scratched but degrades through time as the zinc corrodes away. The zinc is applied electrochemically or as molten zinc by hot-dip galvanizing or spraying. Galvanization is used on chain-link fencing, guard rails, suspension bridges, lightposts, metal roofs, heat exchangers, and car bodies.
The relative reactivity of zinc and its ability to attract oxidation to itself makes it an efficient sacrificial anode in cathodic protection (CP). For example, cathodic protection of a buried pipeline can be achieved by connecting anodes made from zinc to the pipe. Zinc acts as the anode (negative terminus) by slowly corroding away as it passes electric current to the steel pipeline. Zinc is also used to cathodically protect metals that are exposed to sea water. A zinc disc attached to a ship's iron rudder will slowly corrode while the rudder stays intact. Similarly, a zinc plug attached to a propeller or the metal protective guard for the keel of the ship provides temporary protection.
With a standard electrode potential (SEP) of −0.76 volts, zinc is used as an anode material for batteries. (More reactive lithium (SEP −3.04 V) is used for anodes in lithium batteries ). Powdered zinc is used in this way in alkaline batteries and the case (which also serves as the anode) of zinc–carbon batteries is formed from sheet zinc. Zinc is used as the anode or fuel of the zinc–air battery/fuel cell. The zinc-cerium redox flow battery also relies on a zinc-based negative half-cell.
Alloys
A widely used zinc alloy is brass, in which copper is alloyed with anywhere from 3% to 45% zinc, depending upon the type of brass. Brass is generally more ductile and stronger than copper, and has superior corrosion resistance. These properties make it useful in communication equipment, hardware, musical instruments, and water valves.

Other widely used zinc alloys include nickel silver, typewriter metal, soft and aluminium solder, and commercial bronze. Zinc is also used in contemporary pipe organs as a substitute for the traditional lead/tin alloy in pipes. Alloys of 85–88% zinc, 4–10% copper, and 2–8% aluminium find limited use in certain types of machine bearings. Zinc has been the primary metal in American one cent coins (pennies) since 1982. The zinc core is coated with a thin layer of copper to give the appearance of a copper coin. In 1994, 33,200 tonnes (36,600 short tons) of zinc were used to produce 13.6 billion pennies in the United States.
Alloys of zinc with small amounts of copper, aluminium, and magnesium are useful in die casting as well as spin casting, especially in the automotive, electrical, and hardware industries. These alloys are marketed under the name Zamak. An example of this is zinc aluminium. The low melting point together with the low viscosity of the alloy makes possible the production of small and intricate shapes. The low working temperature leads to rapid cooling of the cast products and fast production for assembly. Another alloy, marketed under the brand name Prestal, contains 78% zinc and 22% aluminium, and is reported to be nearly as strong as steel but as malleable as plastic. This superplasticity of the alloy allows it to be molded using die casts made of ceramics and cement.
Similar alloys with the addition of a small amount of lead can be cold-rolled into sheets. An alloy of 96% zinc and 4% aluminium is used to make stamping dies for low production run applications for which ferrous metal dies would be too expensive. For building facades, roofing, and other applications for sheet metal formed by deep drawing, roll forming, or bending, zinc alloys with titanium and copper are used. Unalloyed zinc is too brittle for these manufacturing processes.
As a dense, inexpensive, easily worked material, zinc is used as a lead replacement. In the wake of lead concerns, zinc appears in weights for various applications ranging from fishing to tire balances and flywheels.
Cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) is a semiconductive alloy that can be divided into an array of small sensing devices. These devices are similar to an integrated circuit and can detect the energy of incoming gamma ray photons. When behind an absorbing mask, the CZT sensor array can determine the direction of the rays.
Other industrial uses

Roughly one quarter of all zinc output in the United States in 2009 was consumed in zinc compounds; a variety of which are used industrially. Zinc oxide is widely used as a white pigment in paints and as a catalyst in the manufacture of rubber to disperse heat. Zinc oxide is used to protect rubber polymers and plastics from ultraviolet radiation (UV). The semiconductor properties of zinc oxide make it useful in varistors and photocopying products. The zinc zinc-oxide cycle is a two step thermochemical process based on zinc and zinc oxide for hydrogen production.
Zinc chloride is often added to lumber as a fire retardant It is used in the manufacture of other chemicals. Zinc methyl (Zn(CH3)
2) is used in a number of organic syntheses. Zinc sulfide (ZnS) is used in luminescent pigments such as on the hands of clocks, X-ray and television screens, and luminous paints. Crystals of ZnS are used in lasers that operate in the mid-infrared part of the spectrum. Zinc sulfate is a chemical in dyes and pigments. Zinc pyrithione is used in antifouling paints.
Zinc powder is sometimes used as a propellant in model rockets. When a compressed mixture of 70% zinc and 30% sulfur powder is ignited there is a violent chemical reaction. This produces zinc sulfide, together with large amounts of hot gas, heat, and light.
Zinc sheet metal is used as a durable covering for roofs, walls, and countertops, the last often seen in bistros and oyster bars, and is known for the rustic look imparted by its surface oxidation in use to a blue-gray patina and susceptibility to scratching.
64
Zn, the most abundant isotope of zinc, is very susceptible to neutron activation, being transmuted into the highly radioactive 65
Zn, which has a half-life of 244 days and produces intense gamma radiation. Because of this, zinc oxide used in nuclear reactors as an anti-corrosion agent is depleted of 64
Zn before use, this is called depleted zinc oxide. For the same reason, zinc has been proposed as a salting material for nuclear weapons (cobalt is another, better-known salting material). A jacket of isotopically enriched 64
Zn would be irradiated by the intense high-energy neutron flux from an exploding thermonuclear weapon, forming a large amount of 65
Zn significantly increasing the radioactivity of the weapon's fallout.
65
Zn is used as a tracer to study how alloys that contain zinc wear out, or the path and the role of zinc in organisms.
Zinc dithiocarbamate complexes are used as agricultural fungicides; these include Zineb, Metiram, Propineb and Ziram. Zinc in the form of ZDDP, is used as an anti-wear additive for metal parts in engine oil.
Organic chemistry

Organozinc chemistry is the science of compounds that contain carbon-zinc bonds, describing the physical properties, synthesis, and chemical reactions. Many organozinc compounds are commercially important. Among important applications are:
- The Frankland-Duppa Reaction in which an oxalate ester (ROCOCOOR) reacts with an alkyl halide R'X, zinc and hydrochloric acid to form α-hydroxycarboxylic esters RR'COHCOOR
- Organozincs have similar reactivity to Grignard reagents but are much less nucleophilic, and they are expensive and difficult to handle. Organozincs typically perform nucleophilic addition on electrophiles such as aldehydes, which are then reduced to alcohols. Commercially available diorganozinc compounds include dimethylzinc, diethylzinc and diphenylzinc. Like Grignard reagents, organozincs are commonly produced from organobromine precursors.
Zinc has found many uses in catalysis in organic synthesis including enantioselective synthesis, being a cheap and readily available alternative to precious metal complexes. Quantitative results (yield and enantiomeric excess) obtained with chiral zinc catalysts can be comparable to those achieved with palladium, ruthenium, iridium and others.
Dietary supplement

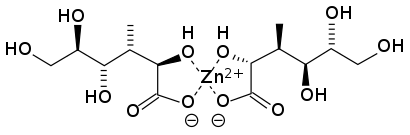
Zinc, a vital trace mineral, is not stored in the body in large quantities, necessitating regular dietary intake for optimal health. Regular intake is particularly crucial given zinc's extensive involvement in human health, including its roles in cellular metabolism (zinc is integral to the function of over 300 enzymes in the human body), immune function, protein synthesis, DNA synthesis, and cell division.
In most single-tablet, over-the-counter, daily vitamin and mineral supplements, zinc is included in such forms as zinc oxide, zinc acetate, zinc gluconate, or zinc amino acid chelate.
Generally, zinc supplement is recommended where there is high risk of zinc deficiency (such as low and middle income countries) as a preventive measure. Although zinc sulfate is a commonly used zinc form, zinc citrate, gluconate and picolinate may be valid options as well. These forms are better absorbed than zinc oxide.
Gastroenteritis
Zinc is an inexpensive and effective part of treatment of diarrhea among children in the developing world. Zinc becomes depleted in the body during diarrhea and replenishing zinc with a 10- to 14-day course of treatment can reduce the duration and severity of diarrheal episodes and may also prevent future episodes for as long as three months. Gastroenteritis is strongly attenuated by ingestion of zinc, possibly by direct antimicrobial action of the ions in the gastrointestinal tract, or by the absorption of the zinc and re-release from immune cells (all granulocytes secrete zinc), or both.
Common cold
<translate>
Zinc supplements (frequently zinc acetate or zinc gluconate lozenges) are a group of dietary supplements that are commonly used for the treatment of the common cold. The use of zinc supplements at doses in excess of 75 mg/day within 24 hours of the onset of symptoms has been shown to reduce the duration of cold symptoms by about 1 day in adults. Adverse effects with zinc supplements by mouth include bad taste and nausea. The intranasal use of zinc-containing nasal sprays has been associated with the loss of the sense of smell; consequently, in June 2009, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) warned consumers to stop using intranasal zinc.
The human rhinovirus – the most common viral pathogen in humans – is the predominant cause of the common cold. The hypothesized mechanism of action by which zinc reduces the severity and/or duration of cold symptoms is the suppression of nasal inflammation and the direct inhibition of rhinoviral receptor binding and rhinoviral replication in the nasal mucosa.Weight gain
Zinc deficiency may lead to loss of appetite. The use of zinc in the treatment of anorexia has been advocated since 1979. At least 15 clinical trials have shown that zinc improved weight gain in anorexia. A 1994 trial showed that zinc doubled the rate of body mass increase in the treatment of anorexia nervosa. Deficiency of other nutrients such as tyrosine, tryptophan and thiamine could contribute to this phenomenon of "malnutrition-induced malnutrition". A meta-analysis of 33 prospective intervention trials regarding zinc supplementation and its effects on the growth of children in many countries showed that zinc supplementation alone had a statistically significant effect on linear growth and body weight gain, indicating that other deficiencies that may have been present were not responsible for growth retardation.
Other
A 2023 Cochrane review stated that people taking zinc supplements may be less likely to progress to age-related macular degeneration. Zinc supplement is an effective treatment for acrodermatitis enteropathica, a genetic disorder affecting zinc absorption that was previously fatal to affected infants. Zinc deficiency has been associated with major depressive disorder (MDD), and zinc supplements may be an effective treatment. Zinc may help individuals sleep more.
Topical use
Topical preparations of zinc include those used on the skin, often in the form of zinc oxide. Zinc oxide is generally recognised by the FDA as safe and effective and is considered a very photo-stable. Zinc oxide is one of the most common active ingredients formulated into a sunscreen to mitigate sunburn. Applied thinly to a baby's diaper area (perineum) with each diaper change, it can protect against diaper rash.
Chelated zinc is used in toothpastes and mouthwashes to prevent bad breath; zinc citrate helps reduce the build-up of calculus (tartar).
Zinc pyrithione is widely included in shampoos to prevent dandruff.
Topical zinc has also been shown to effectively treat, as well as prolong remission in genital herpes.
Biological role
Zinc is an essential trace element for humans and other animals, for plants and for microorganisms. Zinc is required for the function of over 300 enzymes and 1000 transcription factors, and is stored and transferred in metallothioneins. It is the second most abundant trace metal in humans after iron and it is the only metal which appears in all enzyme classes.
In proteins, zinc ions are often coordinated to the amino acid side chains of aspartic acid, glutamic acid, cysteine and histidine. The theoretical and computational description of this zinc binding in proteins (as well as that of other transition metals) is difficult.
Roughly 2–4 grams of zinc are distributed throughout the human body. Most zinc is in the brain, muscle, bones, kidney, and liver, with the highest concentrations in the prostate and parts of the eye. Semen is particularly rich in zinc, a key factor in prostate gland function and reproductive organ growth.
Zinc homeostasis of the body is mainly controlled by the intestine. Here, ZIP4 and especially TRPM7 were linked to intestinal zinc uptake essential for postnatal survival.
In humans, the biological roles of zinc are ubiquitous. It interacts with "a wide range of organic ligands", and has roles in the metabolism of RNA and DNA, signal transduction, and gene expression. It also regulates apoptosis. A review from 2015 indicated that about 10% of human proteins (~3000) bind zinc, in addition to hundreds more that transport and traffic zinc; a similar in silico study in the plant Arabidopsis thaliana found 2367 zinc-related proteins.
In the brain, zinc is stored in specific synaptic vesicles by glutamatergic neurons and can modulate neuronal excitability. It plays a key role in synaptic plasticity and so in learning. Zinc homeostasis also plays a critical role in the functional regulation of the central nervous system. Dysregulation of zinc homeostasis in the central nervous system that results in excessive synaptic zinc concentrations is believed to induce neurotoxicity through mitochondrial oxidative stress (e.g., by disrupting certain enzymes involved in the electron transport chain, including complex I, complex III, and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase), the dysregulation of calcium homeostasis, glutamatergic neuronal excitotoxicity, and interference with intraneuronal signal transduction. L- and D-histidine facilitate brain zinc uptake. SLC30A3 is the primary zinc transporter involved in cerebral zinc homeostasis.
Enzymes


Zinc is an efficient Lewis acid, making it a useful catalytic agent in hydroxylation and other enzymatic reactions. The metal also has a flexible coordination geometry, which allows proteins using it to rapidly shift conformations to perform biological reactions. Two examples of zinc-containing enzymes are carbonic anhydrase and carboxypeptidase, which are vital to the processes of carbon dioxide (CO
2) regulation and digestion of proteins, respectively.
In vertebrate blood, carbonic anhydrase converts CO
2 into bicarbonate and the same enzyme transforms the bicarbonate back into CO
2 for exhalation through the lungs. Without this enzyme, this conversion would occur about one million times slower at the normal blood pH of 7 or would require a pH of 10 or more. The non-related β-carbonic anhydrase is required in plants for leaf formation, the synthesis of indole acetic acid (auxin) and alcoholic fermentation.
Carboxypeptidase cleaves peptide linkages during digestion of proteins. A coordinate covalent bond is formed between the terminal peptide and a C=O group attached to zinc, which gives the carbon a positive charge. This helps to create a hydrophobic pocket on the enzyme near the zinc, which attracts the non-polar part of the protein being digested.
Signalling
Zinc has been recognized as a messenger, able to activate signalling pathways. Many of these pathways provide the driving force in aberrant cancer growth. They can be targeted through ZIP transporters.
Other proteins
Zinc serves a purely structural role in zinc fingers, twists and clusters. Zinc fingers form parts of some transcription factors, which are proteins that recognize DNA base sequences during the replication and transcription of DNA. Each of the nine or ten Zn2+
ions in a zinc finger helps maintain the finger's structure by coordinately binding to four amino acids in the transcription factor.
In blood plasma, zinc is bound to and transported by albumin (60%, low-affinity) and transferrin (10%). Because transferrin also transports iron, excessive iron reduces zinc absorption, and vice versa. A similar antagonism exists with copper. The concentration of zinc in blood plasma stays relatively constant regardless of zinc intake. Cells in the salivary gland, prostate, immune system, and intestine use zinc signaling to communicate with other cells.
Zinc may be held in metallothionein reserves within microorganisms or in the intestines or liver of animals. However, inadequate or excessive zinc intake can be harmful; excess zinc particularly impairs copper absorption because metallothionein absorbs both metals.
The human dopamine transporter contains a high affinity extracellular zinc binding site which, upon zinc binding, inhibits dopamine reuptake and amplifies amphetamine-induced dopamine efflux in vitro. The human serotonin transporter and norepinephrine transporter do not contain zinc binding sites. Some EF-hand calcium binding proteins such as S100 or NCS-1 are also able to bind zinc ions.
Nutrition
Dietary recommendations
The U.S. Institute of Medicine (IOM) updated Estimated Average Requirements (EARs) and Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for zinc in 2001. The current EARs for zinc for women and men ages 14 and up is 6.8 and 9.4 mg/day, respectively. The RDAs are 8 and 11 mg/day. RDAs are higher than EARs so as to identify amounts that will cover people with higher than average requirements. RDA for pregnancy is 11 mg/day. RDA for lactation is 12 mg/day. For infants up to 12 months the RDA is 3 mg/day. For children ages 1–13 years the RDA increases with age from 3 to 8 mg/day. As for safety, the IOM sets Tolerable upper intake levels (ULs) for vitamins and minerals when evidence is sufficient. In the case of zinc the adult UL is 40 mg/day including both food and supplements combined (lower for children). Collectively the EARs, RDAs, AIs and ULs are referred to as Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs).
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) refers to the collective set of information as Dietary Reference Values, with Population Reference Intake (PRI) instead of RDA, and Average Requirement instead of EAR. AI and UL are defined the same as in the United States. For people ages 18 and older the PRI calculations are complex, as the EFSA has set higher and higher values as the phytate content of the diet increases. For women, PRIs increase from 7.5 to 12.7 mg/day as phytate intake increases from 300 to 1200 mg/day; for men the range is 9.4 to 16.3 mg/day. These PRIs are higher than the U.S. RDAs. The EFSA reviewed the same safety question and set its UL at 25 mg/day, which is much lower than the U.S. value.
For U.S. food and dietary supplement labeling purposes the amount in a serving is expressed as a percent of Daily Value (%DV). For zinc labeling purposes 100% of the Daily Value was 15 mg, but on May 27, 2016, it was revised to 11 mg. A table of the old and new adult daily values is provided at Reference Daily Intake.
Dietary intake

Animal products such as meat, fish, shellfish, fowl, eggs, and dairy contain zinc. The concentration of zinc in plants varies with the level in the soil. With adequate zinc in the soil, the food plants that contain the most zinc are wheat (germ and bran) and various seeds, including sesame, poppy, alfalfa, celery, and mustard. Zinc is also found in beans, nuts, almonds, whole grains, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, and blackcurrant.
Other sources include fortified food and dietary supplements in various forms. A 1998 review concluded that zinc oxide, one of the most common supplements in the United States, and zinc carbonate are nearly insoluble and poorly absorbed in the body. This review cited studies that found lower plasma zinc concentrations in the subjects who consumed zinc oxide and zinc carbonate than in those who took zinc acetate and sulfate salts. For fortification, however, a 2003 review recommended cereals (containing zinc oxide) as a cheap, stable source that is as easily absorbed as the more expensive forms. A 2005 study found that various compounds of zinc, including oxide and sulfate, did not show statistically significant differences in absorption when added as fortificants to maize tortillas.
Deficiency
Nearly two billion people in the developing world are deficient in zinc. Groups at risk include children in developing countries and elderly with chronic illnesses. In children, it causes an increase in infection and diarrhea and contributes to the death of about 800,000 children worldwide per year. The World Health Organization advocates zinc supplementation for severe malnutrition and diarrhea. Zinc supplements help prevent disease and reduce mortality, especially among children with low birth weight or stunted growth. However, zinc supplements should not be administered alone, because many in the developing world have several deficiencies, and zinc interacts with other micronutrients. While zinc deficiency is usually due to insufficient dietary intake, it can be associated with malabsorption, acrodermatitis enteropathica, chronic liver disease, chronic renal disease, sickle cell disease, diabetes, malignancy, and other chronic illnesses.
In the United States, a federal survey of food consumption determined that for women and men over the age of 19, average consumption was 9.7 and 14.2 mg/day, respectively. For women, 17% consumed less than the EAR, for men 11%. The percentages below EAR increased with age. The most recent published update of the survey (NHANES 2013–2014) reported lower averages – 9.3 and 13.2 mg/day – again with intake decreasing with age.
Symptoms of mild zinc deficiency are diverse. Clinical outcomes include depressed growth, diarrhea, impotence and delayed sexual maturation, alopecia, eye and skin lesions, impaired appetite, altered cognition, impaired immune functions, defects in carbohydrate use, and reproductive teratogenesis. but excessive zinc does also.
Despite some concerns, western vegetarians and vegans do not suffer any more from overt zinc deficiency than meat-eaters. Major plant sources of zinc include cooked dried beans, sea vegetables, fortified cereals, soy foods, nuts, peas, and seeds. However, phytates in many whole-grains and fibers may interfere with zinc absorption and marginal zinc intake has poorly understood effects. The zinc chelator phytate, found in seeds and cereal bran, can contribute to zinc malabsorption. Some evidence suggests that more than the US RDA (8 mg/day for adult women; 11 mg/day for adult men) may be needed in those whose diet is high in phytates, such as some vegetarians. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) guidelines attempt to compensate for this by recommending higher zinc intake when dietary phytate intake is greater. These considerations must be balanced against the paucity of adequate zinc biomarkers, and the most widely used indicator, plasma zinc, has poor sensitivity and specificity.
Soil remediation
Species of Calluna, Erica and Vaccinium can grow in zinc-metalliferous soils, because translocation of toxic ions is prevented by the action of ericoid mycorrhizal fungi.
Agriculture
Zinc deficiency appears to be the most common micronutrient deficiency in crop plants; it is particularly common in high-pH soils. Zinc-deficient soil is cultivated in the cropland of about half of Turkey and India, a third of China, and most of Western Australia. Substantial responses to zinc fertilization have been reported in these areas. Plants that grow in soils that are zinc-deficient are more susceptible to disease. Zinc is added to the soil primarily through the weathering of rocks, but humans have added zinc through fossil fuel combustion, mine waste, phosphate fertilizers, pesticide (zinc phosphide), limestone, manure, sewage sludge, and particles from galvanized surfaces. Excess zinc is toxic to plants, although zinc toxicity is far less widespread.
Precautions
Toxicity
Although zinc is an essential requirement for good health, excess zinc can be harmful. Excessive absorption of zinc suppresses copper and iron absorption. The free zinc ion in solution is highly toxic to plants, invertebrates, and even vertebrate fish. The Free Ion Activity Model is well-established in the literature, and shows that just micromolar amounts of the free ion kills some organisms. A recent example showed 6 micromolar killing 93% of all Daphnia in water.
The free zinc ion is a powerful Lewis acid up to the point of being corrosive. Stomach acid contains hydrochloric acid, in which metallic zinc dissolves readily to give corrosive zinc chloride. Swallowing a post-1982 American one cent piece (97.5% zinc) can cause damage to the stomach lining through the high solubility of the zinc ion in the acidic stomach.
Evidence shows that people taking 100–300 mg of zinc daily may suffer induced copper deficiency. A 2007 trial observed that elderly men taking 80 mg daily were hospitalized for urinary complications more often than those taking a placebo. Levels of 100–300 mg may interfere with the use of copper and iron or adversely affect cholesterol. Zinc in excess of 500 ppm in soil interferes with the plant absorption of other essential metals, such as iron and manganese. A condition called the zinc shakes or "zinc chills" can be induced by inhalation of zinc fumes while brazing or welding galvanized materials. Zinc is a common ingredient of denture cream which may contain between 17 and 38 mg of zinc per gram. Disability and even deaths from excessive use of these products have been claimed.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) states that zinc damages nerve receptors in the nose, causing anosmia. Reports of anosmia were also observed in the 1930s when zinc preparations were used in a failed attempt to prevent polio infections. On June 16, 2009, the FDA ordered removal of zinc-based intranasal cold products from store shelves. The FDA said the loss of smell can be life-threatening because people with impaired smell cannot detect leaking gas or smoke, and cannot tell if food has spoiled before they eat it.
Recent research suggests that the topical antimicrobial zinc pyrithione is a potent heat shock response inducer that may impair genomic integrity with induction of PARP-dependent energy crisis in cultured human keratinocytes and melanocytes.
Poisoning
In 1982, the US Mint began minting pennies coated in copper but containing primarily zinc. Zinc pennies pose a risk of zinc toxicosis, which can be fatal. One reported case of chronic ingestion of 425 pennies (over 1 kg of zinc) resulted in death due to gastrointestinal bacterial and fungal sepsis. Another patient who ingested 12 grams of zinc showed only lethargy and ataxia (gross lack of coordination of muscle movements). Several other cases have been reported of humans suffering zinc intoxication by the ingestion of zinc coins.
Pennies and other small coins are sometimes ingested by dogs, requiring veterinary removal of the foreign objects. The zinc content of some coins can cause zinc toxicity, commonly fatal in dogs through severe hemolytic anemia and liver or kidney damage; vomiting and diarrhea are possible symptoms. Zinc is highly toxic in parrots and poisoning can often be fatal. The consumption of fruit juices stored in galvanized cans has resulted in mass parrot poisonings with zinc.
See also
Bibliography
- Chambers, William and Robert (1901). Chambers's Encyclopaedia: A Dictionary of Universal Knowledge (Revised ed.). London and Edinburgh: J. B. Lippincott Company. Archived from the original on March 17, 2024. Retrieved September 27, 2020.
- Cotton, F. Albert; Wilkinson, Geoffrey; Murillo, Carlos A.; Bochmann, Manfred (1999). Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (6th ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 978-0-471-19957-1.
- David R. Lide, ed. (2006). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group. ISBN 978-0-8493-0487-3. Archived from the original on March 17, 2024. Retrieved September 27, 2020.
- Emsley, John (2001). "Zinc". Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements. Oxford, England, UK: Oxford University Press. pp. 499–505. ISBN 978-0-19-850340-8.
- Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-3365-9.
- Heiserman, David L. (1992). "Element 30: Zinc". Exploring Chemical Elements and their Compounds. New York: TAB Books. ISBN 978-0-8306-3018-9.
- Lehto, R. S. (1968). "Zinc". In Clifford A. Hampel (ed.). The Encyclopedia of the Chemical Elements. New York: Reinhold Book Corporation. pp. 822–830. ISBN 978-0-442-15598-8. LCCN 68-29938.
- Stwertka, Albert (1998). "Zinc". Guide to the Elements (Revised ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-508083-4.
- Weeks, Mary Elvira (1933). "III. Some Eighteenth-Century Metals". The Discovery of the Elements. Easton, PA: Journal of Chemical Education. ISBN 978-0-7661-3872-8.
External links
- Zinc: Fact Sheet for Health Professionals from the U.S. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements
- Zinc Statistics and Information from the U.S. Geological Survey's National Minerals Information Center
- Zinc.org - official website of the International Zinc Association, a zinc industry association
- Zinc video from the Periodic Videos series (University of Nottingham)
- ZincBind.net – a database identifying biological zinc binding sites from within the Protein Data Bank
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Zinc/ja(8 April 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Lua error in Module:Itemnumber at line 91: attempt to concatenate local 'qid' (a nil value). |