Omega-3 fatty acid/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "==命名法{{Anchor|Nomenclature}}== {{main/ja|Fatty acid/ja#Nomenclature}} 500px|right|thumb|α-リノレン酸(ALA)の化学構造。炭素数9、12、15の3つの[[double bond/ja|二重結合を持つ炭素数18の鎖を持つ脂肪酸である。鎖のオメガ(ω)末端は炭素18にあり、オメガ炭素に最も近い二重結合は炭素15=18-3から始まる。したがって、ALAは''ω''=18の''ω-''3脂肪酸である。..." |
Created page with "===例=== 例えば、α-リノレン酸(ALA;図)は、3つの二重結合を持つ18個の炭素鎖であり、最初の二重結合は脂肪酸鎖のメチル末端から3番目の炭素に位置している。したがって、オメガ3脂肪酸である。鎖のもう一方の端、つまりカルボキシル端から数えると、3つの二重結合は炭素9、12、15に位置する。これらの3つの位置は通常、Δ9c、Δ12c..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
用語''ω-3脂肪酸''と''n-3脂肪酸''は有機化学の[[Chemical nomenclature/ja|命名法]]に由来する。[[unsaturated fatty acid/ja|不飽和脂肪酸]]が命名される1つの方法は、その[[carbon/ja|炭素]]鎖において、分子の[[methyl group/ja|メチル]]末端に最も近い[[double bond/ja|二重結合]]の位置によって決定される。一般的な用語では、''n''(またはω)は分子のメチル末端の[[locant/ja|位置]]を表し、数''n-x''(またはω-''x'')は最も近い[[double bond/ja|二重結合]]の位置を指す。したがって、特にω''-''3脂肪酸では、脂肪酸鎖のメチル末端から始まる炭素番号3の位置に二重結合がある。ほとんどの化学変化は分子の[[carboxyl group/ja|カルボキシル]]末端で起こるが、メチル基とそれに最も近い二重結合はほとんどの化学反応や酵素反応において変化しないので、この分類法は有用である。 | 用語''ω-3脂肪酸''と''n-3脂肪酸''は有機化学の[[Chemical nomenclature/ja|命名法]]に由来する。[[unsaturated fatty acid/ja|不飽和脂肪酸]]が命名される1つの方法は、その[[carbon/ja|炭素]]鎖において、分子の[[methyl group/ja|メチル]]末端に最も近い[[double bond/ja|二重結合]]の位置によって決定される。一般的な用語では、''n''(またはω)は分子のメチル末端の[[locant/ja|位置]]を表し、数''n-x''(またはω-''x'')は最も近い[[double bond/ja|二重結合]]の位置を指す。したがって、特にω''-''3脂肪酸では、脂肪酸鎖のメチル末端から始まる炭素番号3の位置に二重結合がある。ほとんどの化学変化は分子の[[carboxyl group/ja|カルボキシル]]末端で起こるが、メチル基とそれに最も近い二重結合はほとんどの化学反応や酵素反応において変化しないので、この分類法は有用である。 | ||
''n-x''またはω-''x''という表現では、記号はハイフン(またはダッシュ)ではなくマイナス記号であるが、そのように読まれることはない。また、記号''n''(またはω)は、脂肪酸の炭素鎖の[[carboxyl group/ja|カルボキシル]]末端から数えて、メチル末端の位置を表す。例えば、メチル末端がカルボキシル末端から18番目の位置にある18個の炭素原子を持つオメガ3脂肪酸(図を参照)では、''n''(またはω)は18という数を表し、n-3(またはω-3)という表記は18-3=15という減算を表し、ここで15は鎖のカルボキシル末端から数えてメチル末端に最も近い二重結合の位置である。 | |||
''n''とω(オメガ)は同義語であるが、[[:en:International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry|IUPAC]]は脂肪酸の最高炭素数を特定するために''n''を使用することを推奨している。とはいえ、より一般的な名称であるオメガ3脂肪酸は、一般メディアでも科学文献でも使用されている。 | |||
===例=== | |||
=== | 例えば、α-リノレン酸(ALA;図)は、3つの二重結合を持つ18個の炭素鎖であり、最初の二重結合は脂肪酸鎖のメチル末端から3番目の炭素に位置している。したがって、オメガ3脂肪酸である。鎖のもう一方の端、つまり[[carboxyl group/ja|カルボキシル]]端から数えると、3つの二重結合は炭素9、12、15に位置する。これらの3つの位置は通常、Δ9c、Δ12c、Δ15c、またはシスΔ<sup>9</sup>、シスΔ<sup>12</sup>、シスΔ<sup>15</sup>と示される、 またはcis-cis-cis-Δ<sup>9,12,15</sup>であり、''c''または''cis''は二重結合が[[Cis–trans isomerism/ja|''シス''配置]]であることを意味する。 | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 09:40, 14 April 2024
| 食品に含まれる脂肪の種類 |
|---|
| コンポーネント |
| 製造脂肪 |
ω-3脂肪酸(Omega-3 fatty acids)は、オメガ3油、オメガ3脂肪酸またはn-3脂肪酸とも呼ばれ、その化学構造において末端のメチル基から3原子離れたところに二重結合が存在することを特徴とする多価不飽和脂肪酸(PUFA)である。オメガ3脂肪酸は自然界に広く分布し、動物の脂質代謝の重要な構成成分である。ヒトの生理学に関与するオメガ3脂肪酸は、α-リノレン酸(ALA)、エイコサペンタエン酸(EPA)、ドコサヘキサエン酸(DHA)の3種類である。ALAは植物に含まれ、DHAとEPAは藻類や魚類に含まれる。海藻や物プランクトンはオメガ3脂肪酸の主な供給源である。DHAとEPAは、これらの藻類を食べる魚に蓄積される。ALAを含む植物油の一般的な供給源としては、クルミ、食用種子、フラックスシード、および麻実油があり、EPAとDHAの供給源としては、魚および魚油、および藻類油がある。
哺乳類は必須オメガ3脂肪酸であるALAを合成することができず、食事を通じてのみ摂取することができる。しかし、ALAが入手可能な場合は、その炭素鎖に沿って二重結合をさらに作り(脱飽和)、それを伸ばす(伸長)ことによって、EPAとDHAを形成するためにALAを使用することができる。すなわち、ALA(炭素数18、二重結合3個)を使ってEPA(炭素数20、二重結合5個)を作り、それを使ってDHA(炭素数22、二重結合6個)を作る。加齢により、ALAから長鎖オメガ3脂肪酸を作る能力が低下する可能性がある。空気に触れる食品では、不飽和脂肪酸は酸化や腐敗を起こしやすい。
オメガ3脂肪酸の栄養補助食品摂取ががんや心血管系疾患のリスクを低減するという質の高い証拠はない。魚油サプリメントの研究では、心筋梗塞や脳卒中、あるいは血管疾患の転帰を予防するという主張を支持することはできなかった。
歴史
1929年、ジョージ・バーとミルドレッド・バーは、脂肪酸が健康に不可欠であることを発見した。食事から脂肪酸が欠乏すると、生命を脅かす欠乏症が起こる。バー夫妻は「必須脂肪酸」という言葉を生み出した。それ以来、生物の細胞膜の骨格を形成する不飽和必須脂肪酸への関心が研究者の間で高まっている。その後、1980年代以降、必須脂肪酸の健康効果に対する認識が飛躍的に高まった。
2004年9月8日、米国食品医薬品局は、EPAとDHAのオメガ3脂肪酸に「適格健康強調表示」のステータスを与え、「決定的な研究ではないが、EPAとDHA(オメガ3)脂肪酸の摂取が冠動脈性心臓病のリスクを減らす可能性があることを示している」と述べた。これは、2001年の健康リスクアドバイスレター(下記参照)を更新し、変更した。
カナダ食品検査庁は、DHAオメガ3の重要性を認識し、DHAについて次のような表示を許可している。"オメガ3脂肪酸であるDHAは、主に2歳未満の子供の脳、目、神経の正常な身体発達をサポートする"。
歴史的には、ホールフードの食事には十分な量のオメガ3が含まれていたが、オメガ3は酸化されやすいため、保存のきく加工食品への傾向が、製造された食品におけるオメガ3の欠乏につながっている。
命名法
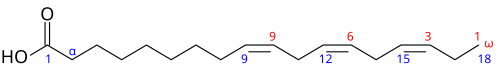
用語ω-3脂肪酸とn-3脂肪酸は有機化学の命名法に由来する。不飽和脂肪酸が命名される1つの方法は、その炭素鎖において、分子のメチル末端に最も近い二重結合の位置によって決定される。一般的な用語では、n(またはω)は分子のメチル末端の位置を表し、数n-x(またはω-x)は最も近い二重結合の位置を指す。したがって、特にω-3脂肪酸では、脂肪酸鎖のメチル末端から始まる炭素番号3の位置に二重結合がある。ほとんどの化学変化は分子のカルボキシル末端で起こるが、メチル基とそれに最も近い二重結合はほとんどの化学反応や酵素反応において変化しないので、この分類法は有用である。
n-xまたはω-xという表現では、記号はハイフン(またはダッシュ)ではなくマイナス記号であるが、そのように読まれることはない。また、記号n(またはω)は、脂肪酸の炭素鎖のカルボキシル末端から数えて、メチル末端の位置を表す。例えば、メチル末端がカルボキシル末端から18番目の位置にある18個の炭素原子を持つオメガ3脂肪酸(図を参照)では、n(またはω)は18という数を表し、n-3(またはω-3)という表記は18-3=15という減算を表し、ここで15は鎖のカルボキシル末端から数えてメチル末端に最も近い二重結合の位置である。
nとω(オメガ)は同義語であるが、IUPACは脂肪酸の最高炭素数を特定するためにnを使用することを推奨している。とはいえ、より一般的な名称であるオメガ3脂肪酸は、一般メディアでも科学文献でも使用されている。
例
例えば、α-リノレン酸(ALA;図)は、3つの二重結合を持つ18個の炭素鎖であり、最初の二重結合は脂肪酸鎖のメチル末端から3番目の炭素に位置している。したがって、オメガ3脂肪酸である。鎖のもう一方の端、つまりカルボキシル端から数えると、3つの二重結合は炭素9、12、15に位置する。これらの3つの位置は通常、Δ9c、Δ12c、Δ15c、またはシスΔ9、シスΔ12、シスΔ15と示される、 またはcis-cis-cis-Δ9,12,15であり、cまたはcisは二重結合がシス配置であることを意味する。
α-Linolenic acid is polyunsaturated (containing more than one double bond) and is also described by a lipid number, 18:3, meaning that there are 18 carbon atoms and 3 double bonds.
Chemistry


An omega−3 fatty acid is a fatty acid with multiple double bonds, where the first double bond is between the third and fourth carbon atoms from the end of the carbon atom chain. "Short-chain" omega−3 fatty acids have a chain of 18 carbon atoms or less, while "long-chain" omega−3 fatty acids have a chain of 20 or more.
Three omega−3 fatty acids are important in human physiology, α-linolenic acid (18:3, n-3; ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5, n-3; EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (22:6, n-3; DHA). These three polyunsaturates have either 3, 5, or 6 double bonds in a carbon chain of 18, 20, or 22 carbon atoms, respectively. As with most naturally-produced fatty acids, all double bonds are in the cis-configuration, in other words, the two hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the double bond; and the double bonds are interrupted by methylene bridges (-CH
2-), so that there are two single bonds between each pair of adjacent double bonds.
The atoms at bis-allylic (between double bonds) sites are prone to oxidation by free radicals. Replacement of hydrogen atoms with deuterium atoms in this location protects the omega-3 fatty acid from lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis.
List of omega−3 fatty acids
This table lists several different names for the most common omega−3 fatty acids found in nature.
| Common name | Lipid number | Chemical name |
|---|---|---|
| Hexadecatrienoic acid (HTA) | 16:3 (n−3) | all-cis-7,10,13-hexadecatrienoic acid |
| α-Linolenic acid (ALA) | 18:3 (n−3) | all-cis-9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid |
| Stearidonic acid (SDA) | 18:4 (n−3) | all-cis-6,9,12,15-octadecatetraenoic acid |
| Eicosatrienoic acid (ETE) | 20:3 (n−3) | all-cis-11,14,17-eicosatrienoic acid |
| Eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA) | 20:4 (n−3) | all-cis-8,11,14,17-eicosatetraenoic acid |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) | 20:5 (n−3) | all-cis-5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoic acid |
| Heneicosapentaenoic acid (HPA) | 21:5 (n−3) | all-cis-6,9,12,15,18-heneicosapentaenoic acid |
| Docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), Clupanodonic acid |
22:5 (n−3) | all-cis-7,10,13,16,19-docosapentaenoic acid |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | 22:6 (n−3) | all-cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid |
| Tetracosapentaenoic acid | 24:5 (n−3) | all-cis-9,12,15,18,21-tetracosapentaenoic acid |
| Tetracosahexaenoic acid (Nisinic acid) | 24:6 (n−3) | all-cis-6,9,12,15,18,21-tetracosahexaenoic acid |
Forms
Omega−3 fatty acids occur naturally in two forms, triglycerides and phospholipids. In the triglycerides, they, together with other fatty acids, are bonded to glycerol; three fatty acids are attached to glycerol. Phospholipid omega−3 is composed of two fatty acids attached to a phosphate group via glycerol.
The triglycerides can be converted to the free fatty acid or to methyl or ethyl esters, and the individual esters of omega−3 fatty acids are available.
Mechanism of action
The 'essential' fatty acids were given their name when researchers found that they are essential to normal growth in young children and animals. The omega−3 fatty acid DHA, also known as docosahexaenoic acid, is found in high abundance in the human brain. It is produced by a desaturation process, but humans lack the desaturase enzyme, which acts to insert double bonds at the ω6 and ω3 position. Therefore, the ω6 and ω3 polyunsaturated fatty acids cannot be synthesized, are appropriately called essential fatty acids, and must be obtained from the diet.
In 1964, it was discovered that enzymes found in sheep tissues convert omega−6 arachidonic acid into the inflammatory agent, prostaglandin E2, which is involved in the immune response of traumatized and infected tissues. By 1979, eicosanoids were further identified, including thromboxanes, prostacyclins, and leukotrienes. The eicosanoids typically have a short period of activity in the body, starting with synthesis from fatty acids and ending with metabolism by enzymes. If the rate of synthesis exceeds the rate of metabolism, the excess eicosanoids may have deleterious effects. but at a slower rate. If both omega−3 and omega−6 fatty acids are present, they will "compete" to be transformed, so the ratio of long-chain omega−3:omega−6 fatty acids directly affects the type of eicosanoids that are produced.
Interconversion
Conversion efficiency of ALA to EPA and DHA
Humans can convert short-chain omega−3 fatty acids to long-chain forms (EPA, DHA) with an efficiency below 5%. The omega−3 conversion efficiency is greater in women than in men, but less studied. Higher ALA and DHA values found in plasma phospholipids of women may be due to the higher activity of desaturases, especially that of delta-6-desaturase.
These conversions occur competitively with omega−6 fatty acids, which are essential closely related chemical analogues that are derived from linoleic acid. They both utilize the same desaturase and elongase proteins in order to synthesize inflammatory regulatory proteins. The products of both pathways are vital for growth making a balanced diet of omega−3 and omega−6 important to an individual's health. A balanced intake ratio of 1:1 was believed to be ideal in order for proteins to be able to synthesize both pathways sufficiently, but this has been controversial as of recent research.
The conversion of ALA to EPA and further to DHA in humans has been reported to be limited, but varies with individuals. Women have higher ALA-to-DHA conversion efficiency than men, which is presumed to be due to the lower rate of use of dietary ALA for beta-oxidation. One preliminary study showed that EPA can be increased by lowering the amount of dietary linoleic acid, and DHA can be increased by elevating intake of dietary ALA.
Omega−6 to omega−3 ratio
Human diet has changed rapidly in recent centuries resulting in a reported increased diet of omega−6 in comparison to omega−3. The rapid evolution of human diet away from a 1:1 omega−3 and omega−6 ratio, such as during the Neolithic Agricultural Revolution, has presumably been too fast for humans to have adapted to biological profiles adept at balancing omega−3 and omega−6 ratios of 1:1. This is commonly believed to be the reason why modern diets are correlated with many inflammatory disorders. While omega−3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may be beneficial in preventing heart disease in humans, the level of omega−6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (and, therefore, the ratio) does not matter.
Both omega−6 and omega−3 fatty acids are essential: humans must consume them in their diet. Omega−6 and omega−3 eighteen-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids compete for the same metabolic enzymes, thus the omega−6:omega−3 ratio of ingested fatty acids has significant influence on the ratio and rate of production of eicosanoids, a group of hormones intimately involved in the body's inflammatory and homeostatic processes, which include the prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes, among others. Altering this ratio can change the body's metabolic and inflammatory state.
Metabolites of omega−6 are more inflammatory (esp. arachidonic acid) than those of omega−3. However, in terms of heart health omega-6 fatty acids are less harmful than they are presumed to be. A meta-analysis of six randomized trials found that replacing saturated fat with omega-6 fats reduced the risk of coronary events by 24%.
A healthy ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 is needed; healthy ratios, according to some authors, range from 1:1 to 1:4. Other authors believe that a ratio of 4:1 (4 times as much omega−6 as omega−3) is already healthy.
Typical Western diets provide ratios of between 10:1 and 30:1 (i.e., dramatically higher levels of omega−6 than omega−3). The ratios of omega−6 to omega−3 fatty acids in some common vegetable oils are: canola 2:1, hemp 2–3:1, soybean 7:1, olive 3–13:1, sunflower (no omega−3), flax 1:3, cottonseed (almost no omega−3), peanut (no omega−3), grapeseed oil (almost no omega−3) and corn oil 46:1.
Biochemistry
Transporters
DHA in the form of lysophosphatidylcholine is transported into the brain by a membrane transport protein, MFSD2A, which is exclusively expressed in the endothelium of the blood–brain barrier.
Dietary sources
| Common name | grams omega−3 |
|---|---|
| Herring, sardines | 1.3–2 |
| Mackerel: Spanish/Atlantic/Pacific | 1.1–1.7 |
| Salmon | 1.1–1.9 |
| Halibut | 0.60–1.12 |
| Tuna | 0.21–1.1 |
| Swordfish | 0.97 |
| Greenshell/lipped mussels | 0.95 |
| Tilefish | 0.9 |
| Tuna (canned, light) | 0.17–0.24 |
| Pollock | 0.45 |
| Cod | 0.15–0.24 |
| Catfish | 0.22–0.3 |
| Flounder | 0.48 |
| Grouper | 0.23 |
| Mahi mahi | 0.13 |
| Red snapper | 0.29 |
| Shark | 0.83 |
| King mackerel | 0.36 |
| Hoki (blue grenadier) | 0.41 |
| Gemfish | 0.40 |
| Blue eye cod | 0.31 |
| Sydney rock oysters | 0.30 |
| Tuna, canned | 0.23 |
| Snapper | 0.22 |
| Eggs, large regular | 0.109 |
| Strawberry or Kiwifruit | 0.10–0.20 |
| Broccoli | 0.10–0.20 |
| Barramundi, saltwater | 0.100 |
| Giant tiger prawn | 0.100 |
| Lean red meat | 0.031 |
| Turkey | 0.030 |
| Milk, regular | 0.00 |
Dietary recommendations
In the United States, the Institute of Medicine publishes a system of Dietary Reference Intakes, which includes Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for individual nutrients, and Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDRs) for certain groups of nutrients, such as fats. When there is insufficient evidence to determine an RDA, the institute may publish an Adequate Intake (AI) instead, which has a similar meaning but is less certain. The AI for α-linolenic acid is 1.6 grams/day for men and 1.1 grams/day for women, while the AMDR is 0.6% to 1.2% of total energy. Because the physiological potency of EPA and DHA is much greater than that of ALA, it is not possible to estimate one AMDR for all omega−3 fatty acids. Approximately 10 percent of the AMDR can be consumed as EPA and/or DHA. The Institute of Medicine has not established a RDA or AI for EPA, DHA or the combination, so there is no Daily Value (DVs are derived from RDAs), no labeling of foods or supplements as providing a DV percentage of these fatty acids per serving, and no labeling a food or supplement as an excellent source, or "High in..." As for safety, there was insufficient evidence as of 2005 to set an upper tolerable limit for omega−3 fatty acids, although the FDA has advised that adults can safely consume up to a total of 3 grams per day of combined DHA and EPA, with no more than 2 g from dietary supplements.
The European Commission sponsored a working group to develop recommendations on dietary fat intake in pregnancy and lactation. In 2008, the working group published consensus recommendations, including the following:
- "pregnant and lactating women should aim to achieve an average dietary intake of at least 200 mg DHA/day"
- "women of childbearing age should aim to consume one to two portions of sea fish per week, including oily fish"
- "intake of the DHA precursor, α-linolenic acid, is far less effective with regard to DHA deposition in fetal brain than preformed DHA"
However, the seafood supply to meet these recommendations is currently too low in most European countries and if met would be unsustainable.
In the EU, the EFSA publishes the Dietary Reference Values (DRVs), recommending Adequate Intake values for EPA+DHA and DHA:
| Age group (years) | EPA+DHA (mg/day)1 | DHA (mg/day)1 |
|---|---|---|
| 7–11 months2 | 100 | |
| 1 | 100 | |
| 2-3 | 250 | |
| 4-6 | 250 | |
| 7-10 | 250 | |
| 11-14 | 250 | |
| 15-17 | 250 | |
| ≥18 | 250 | |
| Pregnancy | 250 | + 100—2003 |
| Lactation | 250 | + 100—2003 |
The American Heart Association (AHA) has made recommendations for EPA and DHA due to their cardiovascular benefits: individuals with no history of coronary heart disease or myocardial infarction should consume oily fish two times per week; and "Treatment is reasonable" for those having been diagnosed with coronary heart disease. For the latter the AHA does not recommend a specific amount of EPA + DHA, although it notes that most trials were at or close to 1000 mg/day. The benefit appears to be on the order of a 9% decrease in relative risk. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) approved a claim "EPA and DHA contributes to the normal function of the heart" for products that contain at least 250 mg EPA + DHA. The report did not address the issue of people with pre-existing heart disease. The World Health Organization recommends regular fish consumption (1-2 servings per week, equivalent to 200 to 500 mg/day EPA + DHA) as protective against coronary heart disease and ischaemic stroke.
Contamination
Heavy metal poisoning from consuming fish oil supplements is highly unlikely, because heavy metals (mercury, lead, nickel, arsenic, and cadmium) selectively bind with protein in the fish flesh rather than accumulate in the oil.
However, other contaminants (PCBs, furans, dioxins, and PBDEs) might be found, especially in less-refined fish oil supplements.
Throughout their history, the Council for Responsible Nutrition and the World Health Organization have published acceptability standards regarding contaminants in fish oil. The most stringent current standard is the International Fish Oils Standard. Fish oils that are molecularly distilled under vacuum typically make this highest-grade; levels of contaminants are stated in parts per billion per trillion.
Rancidity
A 2022 study found that a number of products on the market used oxidised oils, with the rancidity often masked by flavourings. Another study in 2015 found that an average of 20% of products had excess oxidation. Whether rancid fish oil is harmful remains unclear. Some studies show that highly oxidised fish oil can have a negative impact on cholesterol levels. Animal testing showed that high doses have toxic effects. Furthermore, rancid oil is likely to be less effective than fresh fish oil.
Fish
The most widely available dietary source of EPA and DHA is oily fish, such as salmon, herring, mackerel, anchovies, and sardines. Oils from these fishes have around seven times as much omega−3 as omega−6. Other oily fish, such as tuna, also contain n-3 in somewhat lesser amounts. Although fish are a dietary source of omega−3 fatty acids, fish do not synthesize omega−3 fatty acids, but rather obtain them via their food supply, including algae or plankton.
In order for farmed marine fish to have amounts of EPA and DHA comparable to those of wild-caught fish, their feed must be supplemented with EPA and DHA, most commonly in the form of fish oil. For this reason, 81% of the global fish oil supply in 2009 was consumed by aquaculture. By 2019, two alternative sources of EPA and DHA for fish have been partially commercialized: genetically-modified canola oil and Schizochytrium algal oil.
Fish oil

Marine and freshwater fish oil vary in content of arachidonic acid, EPA and DHA. They also differ in their effects on organ lipids.
Not all forms of fish oil may be equally digestible. Of four studies that compare bioavailability of the glyceryl ester form of fish oil vs. the ethyl ester form, two have concluded the natural glyceryl ester form is better, and the other two studies did not find a significant difference. No studies have shown the ethyl ester form to be superior, although it is cheaper to manufacture.
Krill
Krill oil is a source of omega−3 fatty acids. The effect of krill oil, at a lower dose of EPA + DHA (62.8%), was demonstrated to be similar to that of fish oil on blood lipid levels and markers of inflammation in healthy humans. While not an endangered species, krill are a mainstay of the diets of many ocean-based species including whales, causing environmental and scientific concerns about their sustainability. Preliminary studies appear to indicate that the DHA and EPA omega−3 fatty acids found in krill oil may be more bio-available than in fish oil. Additionally, krill oil contains astaxanthin, a marine-source keto-carotenoid antioxidant that may act synergistically with EPA and DHA.
Plant sources



| Common name | Alternative name | Linnaean name | % ALA |
|---|---|---|---|
| kiwifruit (fruit) | Chinese gooseberry | Actinidia deliciosa | 63 |
| perilla | shiso | Perilla frutescens | 61 |
| chia | chia sage | Salvia hispanica | 58 |
| linseed | flax | Linum usitatissimum | 53 – 59 |
| lingonberry | cowberry | Vaccinium vitis-idaea | 49 |
| fig | common fig | Ficus carica | 47.7 |
| camelina | gold-of-pleasure | Camelina sativa | 36 |
| purslane | portulaca | Portulaca oleracea | 35 |
| black raspberry | Rubus occidentalis | 33 | |
| hempseed | Cannabis sativa | 19 | |
| canola | rapeseed | mostly Brassica napus | 9 – 11 |
| Common name | Linnaean name | % ALA |
|---|---|---|
| linseed | Linum usitatissimum | 18.1 |
| hempseed | Cannabis sativa | 8.7 |
| butternut | Juglans cinerea | 8.7 |
| Persian walnut | Juglans regia | 6.3 |
| pecan | Carya illinoinensis | 0.6 |
| hazelnut | Corylus avellana | 0.1 |
Linseed (or flaxseed) (Linum usitatissimum) and its oil are perhaps the most widely available botanical source of the omega−3 fatty acid ALA. Flaxseed oil consists of approximately 55% ALA, which makes it six times richer than most fish oils in omega−3 fatty acids. A portion of this is converted by the body to EPA and DHA, though the actual converted percentage may differ between men and women.
The longer-chain EPA and DHA are only naturally made by marine algae and phytoplankton. The microalgae Crypthecodinium cohnii and Schizochytrium are rich sources of DHA, but not EPA, and can be produced commercially in bioreactors for use as food additives. Oil from brown algae (kelp) is a source of EPA. The alga Nannochloropsis also has high levels of EPA.
Some transgenic initiatives have transferred the ability to make EPA and DHA into existing high-yielding crop species of land plants:
- Camelina sativa: In 2013, Rothamsted Research reported two genetically modified forms of this plant. Oil from the seeds of this plant contained on average 15% ALA, 11% EPA, and 8% DHA in one development and 11% ALA and 24% EPA in another.
- Canola: In 2011, CSIRO, GRDC, and Nufarm developed a version of canola that produces DHA in seeds; the oil contains 10% DHA and almost no EPA. In 2018, it was approved as an animal feed additive in Australia. In 2021, the US FDA acknowledged it as a New Dietary Ingredient for humans. Separately, Cargill has commercialized a different strain of canola that produces EPA and DHA for fish feed. The oil contains 8.1% EPA and 0.8% DHA.
Eggs
Eggs produced by hens fed a diet of greens and insects contain higher levels of omega−3 fatty acids than those produced by chickens fed corn or soybeans. In addition to feeding chickens insects and greens, fish oils may be added to their diets to increase the omega−3 fatty acid concentrations in eggs.
The addition of flax and canola seeds, both good sources of alpha-linolenic acid, to the diets of laying chickens, increases the omega−3 content of the eggs, predominantly DHA. However, this enrichment could lead to an increment of lipid oxidation in the eggs if the seeds are used in higher doses, without using an appropriate antioxidant.
The addition of green algae or seaweed to the diets boosts the content of DHA and EPA, which are the forms of omega−3 approved by the FDA for medical claims. A common consumer complaint is "Omega−3 eggs can sometimes have a fishy taste if the hens are fed marine oils".
Meat
Omega−3 fatty acids are formed in the chloroplasts of green leaves and algae. While seaweeds and algae are the sources of omega−3 fatty acids present in fish, grass is the source of omega−3 fatty acids present in grass-fed animals. When cattle are taken off omega−3 fatty acid-rich grass and shipped to a feedlot to be fattened on omega−3 fatty acid deficient grain, they begin losing their store of this beneficial fat. Each day that an animal spends in the feedlot, the amount of omega−3 fatty acids in its meat is diminished.
The omega−6:omega−3 ratio of grass-fed beef is about 2:1, making it a more useful source of omega−3 than grain-fed beef, which usually has a ratio of 4:1.
In a 2009 joint study by the USDA and researchers at Clemson University in South Carolina, grass-fed beef was compared with grain-finished beef. The researchers found that grass-finished beef is higher in moisture content, 42.5% lower total lipid content, 54% lower in total fatty acids, 54% higher in beta-carotene, 288% higher in vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol), higher in the B-vitamins thiamin and riboflavin, higher in the minerals calcium, magnesium, and potassium, 193% higher in total omega−3s, 117% higher in CLA (cis-9, trans-11 octadecenoic acid, a conjugated linoleic acid, which is a potential cancer fighter), 90% higher in vaccenic acid (which can be transformed into CLA), lower in the saturated fats, and has a healthier ratio of omega−6 to omega−3 fatty acids (1.65 vs 4.84). Protein and cholesterol content were equal.
The omega−3 content of chicken meat may be enhanced by increasing the animals' dietary intake of grains high in omega−3, such as flax, chia, and canola.
Kangaroo meat is also a source of omega−3, with fillet and steak containing 74 mg per 100 g of raw meat.
Seal oil
Seal oil is a source of EPA, DPA, and DHA, and is commonly used in Arctic regions. According to Health Canada, it helps to support the development of the brain, eyes, and nerves in children up to 12 years of age. Like all seal products, it is not allowed to be imported into the European Union.
A Canadian company, FeelGood Natural Health, pleaded guilty in 2023 to illegally selling seal oil capsules to American consumers. The company sold over 900 bottles of the capsules, worth over $10,000. Seal oil is made from the blubber of dead seals, and is illegal to sell in the United States under the Marine Mammal Protection Act. The global population of harp seals stands at around 7 million, and they have been hunted in Canada for thousands of years. FeelGood was sentenced to pay a fine of $20,000 and three years of probation.
Other sources
A trend in the early 21st century was to fortify food with omega−3 fatty acids.
Health effects of omega-3 supplementation
The association between supplementation and a lower risk of all-cause mortality is inconclusive.
Cancer
There is insufficient evidence that supplementation with omega−3 fatty acids has an effect on different cancers. Omega-3 supplements do not improve body weight, muscle maintenance or quality of life in cancer patients.
Cardiovascular disease
Moderate and high quality evidence from a 2020 review showed that EPA and DHA, such as that found in omega−3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplements, does not appear to improve mortality or cardiovascular health. There is weak evidence indicating that α-linolenic acid may be associated with a small reduction in the risk of a cardiovascular event or the risk of arrhythmia.
A 2018 meta-analysis found no support that daily intake of one gram of omega−3 fatty acid in individuals with a history of coronary heart disease prevents fatal coronary heart disease, nonfatal myocardial infarction or any other vascular event. However, omega−3 fatty acid supplementation greater than one gram daily for at least a year may be protective against cardiac death, sudden death, and myocardial infarction in people who have a history of cardiovascular disease. No protective effect against the development of stroke or all-cause mortality was seen in this population. A 2021 meta-analysis found that supplementation was associated with a reduced risk of myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease.
Fish oil supplementation has not been shown to benefit revascularization or abnormal heart rhythms and has no effect on heart failure hospital admission rates. Furthermore, fish oil supplement studies have failed to support claims of preventing heart attacks or strokes. In the EU, a review by the European Medicines Agency of omega−3 fatty acid medicines containing a combination of an ethyl ester of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid at a dose of 1 g per day concluded that these medicines are not effective in secondary prevention of heart problems in people who have had a myocardial infarction.
Evidence suggests that omega−3 fatty acids modestly lower blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) in people with hypertension and in people with normal blood pressure. Omega−3 fatty acids can also reduce heart rate, an emerging risk factor. Some evidence suggests that people with certain circulatory problems, such as varicose veins, may benefit from the consumption of EPA and DHA, which may stimulate blood circulation and increase the breakdown of fibrin, a protein involved in blood clotting and scar formation. Omega−3 fatty acids reduce blood triglyceride levels, but do not significantly change the level of LDL cholesterol or HDL cholesterol. The American Heart Association position (2011) is that borderline elevated triglycerides, defined as 150–199 mg/dL, can be lowered by 0.5–1.0 grams of EPA and DHA per day; high triglycerides 200–499 mg/dL benefit from 1–2 g/day; and >500 mg/dL be treated under a physician's supervision with 2–4 g/day using a prescription product. In this population, omega−3 fatty acid supplementation decreases the risk of heart disease by about 25%.
A 2019 review found that omega-3 fatty acid supplements make little or no difference to cardiovascular mortality and that people with myocardial infarction have no benefit in taking the supplements. A 2021 review found that omega-3 supplementation did not affect cardiovascular disease outcomes.
A 2021 review concluded that use of omega-3 supplements was associated with an increased risk of atrial fibrillation in people having high blood triglycerides. A meta-analysis showed that use of marine omega-3 supplementation was associated with an increased risk of atrial fibrillation, with the risk appearing to increase for doses greater than one gram per day.
Chronic kidney disease
In people with chronic kidney disease (CKD) who require hemodialysis, there is a risk that vascular blockage due to clotting, may prevent dialysis therapy from being possible. Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to the production of eicosanoid molecules that reduce clotting. However, a Cochrane review in 2018 did not find clear evidence that omega-3 supplementation has any impact on the prevention of vascular blockage in people with CKD. There was also moderate certainty that supplementation did not prevent hospitalisation or death within a 12-month period.
Stroke
A 2022 Cochrane review of controlled trials did not find clear evidence that marine-derived omega-3 supplementation improves cognitive and physical recovery or social, and emotional wellbeing following stroke diagnosis, nor prevents stroke recurrence and mortality. In this review, mood appeared to worsen slightly among those receiving 3g fish oil supplementation for 12 weeks; psychometric scores changed by 1.41 (0.07 to 2.75) points less than those receiving palm and soy oil. However, this represented only a single small study and was not observed in a study lasting more than 3 months. Overall, the review was limited by the low number of high-quality evidence available.
Inflammation
A 2013 systematic review found tentative evidence of benefit for lowering inflammation levels in healthy adults and in people with one or more biomarkers of metabolic syndrome. Consumption of omega−3 fatty acids from marine sources lowers blood markers of inflammation such as C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and TNF alpha.
For rheumatoid arthritis, one systematic review found consistent but modest evidence for the effect of marine n−3 PUFAs on symptoms such as "joint swelling and pain, duration of morning stiffness, global assessments of pain and disease activity" as well as the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The American College of Rheumatology has stated that there may be modest benefit from the use of fish oils, but that it may take months for effects to be seen, and cautions for possible gastrointestinal side effects and the possibility of the supplements containing mercury or vitamin A at toxic levels. The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health has concluded that "supplements containing omega−3 fatty acids ... may help relieve rheumatoid arthritis symptoms" but warns that such supplements "may interact with drugs that affect blood clotting".
Developmental disabilities
One meta-analysis concluded that omega−3 fatty acid supplementation demonstrated a modest effect for improving ADHD symptoms. A Cochrane review of PUFA (not necessarily omega−3) supplementation found "there is little evidence that PUFA supplementation provides any benefit for the symptoms of ADHD in children and adolescents", while a different review found "insufficient evidence to draw any conclusion about the use of PUFAs for children with specific learning disorders". Another review concluded that the evidence is inconclusive for the use of omega−3 fatty acids in behavior and non-neurodegenerative neuropsychiatric disorders such as ADHD and depression.
A 2015 meta-analysis of the effect of omega−3 supplementation during pregnancy did not demonstrate a decrease in the rate of preterm birth or improve outcomes in women with singleton pregnancies with no prior preterm births. A 2018 Cochrane systematic review with moderate to high quality of evidence suggested that omega−3 fatty acids may reduce risk of perinatal death, risk of low body weight babies; and possibly mildly increased LGA babies.
A 2021 umbrella review with moderate to high quality of evidence suggested that "omega-3 supplementation during pregnancy can exert favorable effects against pre-eclampsia, low-birth weight, pre-term delivery, and post-partum depression, and can improve anthropometric measures, immune system, and visual activity in infants and cardiometabolic risk factors in pregnant mothers."
Mental health
Omega-3 supplementation has not been shown to significantly affect symptoms of anxiety, major depressive disorder or schizophrenia. A 2021 Cochrane review concluded that there is not "sufficient high‐certainty evidence to determine the effects of n‐3PUFAs as a treatment for MDD". Omega−3 fatty acids have also been investigated as an add-on for the treatment of depression associated with bipolar disorder although there is limited data available. Two reviews have suggested that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation significantly improves depressive symptoms in perinatal women.
A 2015 study concluded that there are multiple factors responsible for depression and deficiency of omega 3 fatty acids can be one of them. It further stated that only those patients who have depression due to insufficient omega-3 fatty acids can respond well to the omega 3 supplements while others are unlikely to get any positive effects. Meta-analysis suggest that supplements with higher concentration of EPA than DHA are more likely to act as anti-depressants.
In contrast to dietary supplementation studies, there is significant difficulty in interpreting the literature regarding dietary intake of omega−3 fatty acids (e.g. from fish) due to participant recall and systematic differences in diets. There is also controversy as to the efficacy of omega−3, with many meta-analysis papers finding heterogeneity among results which can be explained mostly by publication bias. A significant correlation between shorter treatment trials was associated with increased omega−3 efficacy for treating depressed symptoms further implicating bias in publication.
Cognitive aging
A 2016 Cochrane review found no convincing evidence for the use of omega‐3 PUFA supplements in treatment of Alzheimer's disease or dementia. There is preliminary evidence of effect on mild cognitive problems, but none supporting an effect in healthy people or those with dementia. A 2020 review suggested that omega 3 supplementation has no effect on global cognitive function but has a mild benefit in improving memory in non-demented adults.
A 2022 review found promising evidence for prevention of cognitive decline in people who regularly eat long-chain omega 3 rich foods. Conversely, clinical trials with participants already diagnosed with Alzheimer's show no effect. A 2020 review concluded that long-chain omega-3 supplements do not deter cognitive decline in older adults.
Brain and visual functions
Brain function and vision rely on dietary intake of DHA to support a broad range of cell membrane properties, particularly in grey matter, which is rich in membranes. A major structural component of the mammalian brain, DHA is the most abundant omega−3 fatty acid in the brain. Omega 3 PUFA supplementation has no effect on macular degeneration or development of visual loss.
Atopic diseases
Results of studies investigating the role of LCPUFA supplementation and LCPUFA status in the prevention and therapy of atopic diseases (allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, atopic dermatitis, and allergic asthma) are controversial; therefore, 2013年現在[update] it could not be stated either that the nutritional intake of n−3 fatty acids has a clear preventive or therapeutic role, or that the intake of n-6 fatty acids has a promoting role in the context of atopic diseases.
Phenylketonuria
People with PKU often have low intake of omega−3 fatty acids, because nutrients rich in omega−3 fatty acids are excluded from their diet due to high protein content.
Asthma
As of 2015, there was no evidence that taking omega−3 supplements can prevent asthma attacks in children.
糖尿病
2019年のレビューでは、オメガ3サプリメントは2型糖尿病の予防と治療に効果がないことがわかった。2021年のメタアナリシスでは、オメガ3のサプリメントは糖尿病のバイオマーカー、例えば空腹時血糖値やインスリン抵抗性にプラスの効果があることがわかった。
こちらも参照
注釈
さらに読む
- Allport S (September 2006). The Queen of Fats: Why Omega−3s Were Removed from the Western Diet and What We Can Do to Replace Them. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-24282-1. OCLC 801139991.
- Chow CK (2001). Fatty Acids in Foods and Their Health Implications. New York: Routledge Publishing. OCLC 25508943.
- Clover C (2004). The End of the Line: How overfishing is changing the world and what we eat. London: Ebury Press. ISBN 0-09-189780-7. OCLC 67383509.
- Greenberg P (2018). The Omega Principle: Seafood and the Quest for a Long Life and a Healthier Planet. New York: Penguin Press. ISBN 9781594206344. OCLC 1007552654. Archived from the original on 2023-09-18. Retrieved 2018-07-13.
- Stoll AL (2001). The Omega−3 Connection: how you can restore your body's natural balance and treat depression. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-684-87138-6. OCLC 670441405.
外部リンク
 Media related to Omega-3 fatty acids at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Omega-3 fatty acids at Wikimedia Commons