Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "グルカゴンは血糖値を上昇させ、DPP-4阻害薬はグルカゴンと血糖値を低下させる。DPP-4阻害薬の機序は、インクレチンレベル(GLP-1とGIP)を増加させ、グルカゴン放出を阻害し、その結果、インスリン分泌を増加させ、胃排出を減少させ、blood glucose/ja|血..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Glucagon/ja|グルカゴン]]は[[blood glucose/ja|血糖値]]を上昇させ、DPP-4阻害薬はグルカゴンと血糖値を低下させる。DPP-4阻害薬の機序は、[[incretin/ja|インクレチン]]レベル([[GLP-1/ja|GLP-1]]と[[gastric inhibitory polypeptide/ja|GIP]])を増加させ、[[glucagon/ja|グルカゴン]]放出を阻害し、その結果、[[insulin/ja|インスリン]]分泌を増加させ、胃排出を減少させ、[[blood glucose/ja|血糖値]]を低下させる。 | [[Glucagon/ja|グルカゴン]]は[[blood glucose/ja|血糖値]]を上昇させ、DPP-4阻害薬はグルカゴンと血糖値を低下させる。DPP-4阻害薬の機序は、[[incretin/ja|インクレチン]]レベル([[GLP-1/ja|GLP-1]]と[[gastric inhibitory polypeptide/ja|GIP]])を増加させ、[[glucagon/ja|グルカゴン]]放出を阻害し、その結果、[[insulin/ja|インスリン]]分泌を増加させ、胃排出を減少させ、[[blood glucose/ja|血糖値]]を低下させる。 | ||
2018年の[[meta-analysis/ja|メタアナリシス]]では、2型糖尿病患者の全死亡、心血管死亡、[[myocardial infarction/ja|心筋梗塞]]、[[stroke/ja|脳卒中]]に対するDPP-4阻害薬の好ましい効果は認められなかった。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 19:29, 12 March 2024
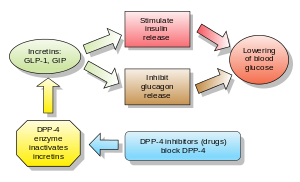
ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ4阻害薬(DPP-4 inhibitorまたはgliptins)は、経口血糖降下薬の一種であり、ブロック薬である。酵素ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4(DPP-4)を阻害する。これらは2型糖尿病の治療に使用できる。
このクラスの最初の薬物であるシタグリプチンは、2006年にFDAによって承認された。
グルカゴンは血糖値を上昇させ、DPP-4阻害薬はグルカゴンと血糖値を低下させる。DPP-4阻害薬の機序は、インクレチンレベル(GLP-1とGIP)を増加させ、グルカゴン放出を阻害し、その結果、インスリン分泌を増加させ、胃排出を減少させ、血糖値を低下させる。
2018年のメタアナリシスでは、2型糖尿病患者の全死亡、心血管死亡、心筋梗塞、脳卒中に対するDPP-4阻害薬の好ましい効果は認められなかった。
Examples
Drugs belonging to this class are:
- Sitagliptin (FDA approved 2006, marketed by Merck & Co. as Januvia)
- Vildagliptin (EU approved 2007, marketed in the EU by Novartis as Galvus)
- Saxagliptin (FDA approved in 2009, marketed as Onglyza)
- Linagliptin (FDA approved in 2011, marketed as Tradjenta by Eli Lilly and Company and Boehringer Ingelheim)
- Gemigliptin (approved in Korea in 2012, marketed by LG Life Sciences) Marketed as Zemiglo
- Anagliptin (approved in Japan as Suiny in 2012, marketed by Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd. and Kowa Company, Ltd.)
- Teneligliptin (approved in Japan as Tenelia in 2012)
- Alogliptin (FDA approved 2013 as Nesina/ Vipidia, marketed by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company)
- Trelagliptin (approved for use in Japan as Zafatek/ Wedica in 2015)
- Omarigliptin (MK-3102) (approved as Marizev in Japan in 2015, developed by Merck & Co.; research showed that omarigliptin can be used as once-weekly treatment and generally well tolerated throughout the base and extension studies)
- Evogliptin (approved as Suganon/ Evodine for use in South Korea)
- Gosogliptin (approved as Saterex for use in Russia)
- Dutogliptin (PHX- 1149 free base, being developed by Phenomix Corporation), Phase III
- Retagliptin (SP-2086), approved in China.
- Denagliptin
- Cofrogliptin (HSK- 7653, compound 2)
- Fotagliptin
- Prusogliptin
Other chemicals which may inhibit DPP-4 include:
Adverse effects
In those already taking sulphonylureas, there is an increased risk of low blood sugar when taking a medicine in the DPP-4 drug class.
Adverse effects include nasopharyngitis, headache, nausea, heart failure, hypersensitivity and skin reactions.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is warning that the type 2 diabetes medicines like sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin, and alogliptin may cause joint pain that can be severe and disabling. FDA has added a new Warning and Precaution about this risk to the labels of all medicines in this drug class, called dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. However, studies assessing risk of rheumatoid arthritis among DPP-4 inhibitor users have been inconclusive.
A 2014 review found increased risk of heart failure with saxagliptin and alogliptin, prompting the FDA in 2016 to add warnings to the relevant drug labels.
A 2018 meta analysis showed that use of DPP-4 inhibitors was associated with a 58% increased risk of developing acute pancreatitis compared with placebo or no treatment.
A 2018 observational study suggested an elevated risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease (specifically, ulcerative colitis), reaching a peak after three to four years of use and decreasing after more than four years of use.
A 2020 Cochrane systematic review did not find enough evidence of reduction of all-cause mortality, serious adverse events, cardiovascular mortality, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke or end-stage renal disease when comparing metformin monotherapy to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Cancer
In response to a report of precancerous changes in the pancreases of rats and organ donors treated with the DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin, the United States FDA and the European Medicines Agency each undertook independent reviews of all clinical and preclinical data related to the possible association of DPP-4 inhibitors with pancreatic cancer. In a joint letter to the New England Journal of Medicine, the agencies stated that they had not yet reached a final conclusion regarding a possible causative relationship.
A 2014 meta-analysis found no evidence for increased pancreatic cancer risk in people treated with DPP-4 inhibitors, but owing to the modest amount of data available, was not able to completely exclude possible risk.
Combination drugs
Some DPP-4 inhibitor drugs have received approval from the FDA to be used with metformin concomitantly with additive effect to increase the level of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) which also decreases hepatic glucose production.
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor/ja(1 February 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Lua error in Module:Itemnumber at line 91: attempt to concatenate local 'qid' (a nil value). |