Turmeric: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Marked this version for translation |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | <languages /> | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
<!--T:1--> | |||
{{short description|Plant used as spice }} | {{short description|Plant used as spice }} | ||
{{About|the plant and rhizome used as a spice||}} | {{About|the plant and rhizome used as a spice||}} | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--T:2--> | |||
'''Turmeric''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|t|ɜːr|m|ər|ɪ|k|,_|ˈ|tj|uː|-}}), or '''''Curcuma longa''''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|k|ɜːr|k|j|ʊ|m|ə|_|ˈ|l|ɒ|ŋ|ɡ|ə}}), is a [[flowering plant]] in the [[ginger]] family [[Zingiberaceae]]. It is a [[perennial]], [[rhizomatous]], [[herbaceous plant]] native to the [[Indian subcontinent]] and [[Southeast Asia]] that requires temperatures between {{cvt|20|and|30|C}} and high [[Annual rainfall in india|annual rainfall]] to thrive. Plants are gathered each year for their [[rhizome]]s, some for propagation in the following season and some for consumption or [[dye]]ing. | '''Turmeric''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|t|ɜːr|m|ər|ɪ|k|,_|ˈ|tj|uː|-}}), or '''''Curcuma longa''''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|k|ɜːr|k|j|ʊ|m|ə|_|ˈ|l|ɒ|ŋ|ɡ|ə}}), is a [[flowering plant]] in the [[ginger]] family [[Zingiberaceae]]. It is a [[perennial]], [[rhizomatous]], [[herbaceous plant]] native to the [[Indian subcontinent]] and [[Southeast Asia]] that requires temperatures between {{cvt|20|and|30|C}} and high [[Annual rainfall in india|annual rainfall]] to thrive. Plants are gathered each year for their [[rhizome]]s, some for propagation in the following season and some for consumption or [[dye]]ing. | ||
<!--T:3--> | |||
The rhizomes can be used fresh, but they are often boiled in water and dried, after which they are ground into a deep orange-yellow shelf-stable spice powder commonly used as a [[food coloring#Natural food dyes|coloring]] and flavoring agent in many [[Asian cuisine]]s, especially for [[Curry|curries]] ([[curry powder]]). Turmeric powder has a warm, bitter, [[black pepper]]-like flavor and earthy, [[mustard plant|mustard]]-like [[aroma]]. | The rhizomes can be used fresh, but they are often boiled in water and dried, after which they are ground into a deep orange-yellow shelf-stable spice powder commonly used as a [[food coloring#Natural food dyes|coloring]] and flavoring agent in many [[Asian cuisine]]s, especially for [[Curry|curries]] ([[curry powder]]). Turmeric powder has a warm, bitter, [[black pepper]]-like flavor and earthy, [[mustard plant|mustard]]-like [[aroma]]. | ||
<!--T:4--> | |||
Although long used in [[Ayurvedic medicine]], there is no [[evidence-based medicine|high-quality clinical evidence]] that consuming turmeric or the principal turmeric constituent, [[curcumin]], is effective for treating any disease. Curcumin, a bright yellow chemical produced by the turmeric plant, is approved as a [[food additive]] by the [[World Health Organization]], [[European Parliament]], and United States [[Food and Drug Administration]]. Turmeric [[Dietary supplement|supplements]] have been an increasing cause of [[herb-induced liver injury]], leading to government regulation. | Although long used in [[Ayurvedic medicine]], there is no [[evidence-based medicine|high-quality clinical evidence]] that consuming turmeric or the principal turmeric constituent, [[curcumin]], is effective for treating any disease. Curcumin, a bright yellow chemical produced by the turmeric plant, is approved as a [[food additive]] by the [[World Health Organization]], [[European Parliament]], and United States [[Food and Drug Administration]]. Turmeric [[Dietary supplement|supplements]] have been an increasing cause of [[herb-induced liver injury]], leading to government regulation. | ||
<!--T:5--> | |||
[[File:Curcuma longa - Köhler–s Medizinal-Pflanzen-199.jpg|thumb|Botanical view of ''Curcuma longa'']] | [[File:Curcuma longa - Köhler–s Medizinal-Pflanzen-199.jpg|thumb|Botanical view of ''Curcuma longa'']] | ||
<!--T:6--> | |||
==Origin and distribution== | ==Origin and distribution== | ||
The greatest diversity of ''[[Curcuma]]'' species by number alone is in [[India]], at around 40 to 45 species. [[Thailand]] has a comparable 30 to 40 species. Other countries in tropical Asia also have numerous wild species of ''Curcuma''. Recent studies have also shown that the taxonomy of ''C. longa'' is problematic, with only the specimens from South India being identifiable as ''C. longa''. The phylogeny, relationships, intraspecific and interspecific variation, and even identity of other species and cultivars in other parts of the world still need to be established and validated. Various species currently utilized and sold as "turmeric" in other parts of Asia have been shown to belong to several physically similar taxa, with overlapping local names. | The greatest diversity of ''[[Curcuma]]'' species by number alone is in [[India]], at around 40 to 45 species. [[Thailand]] has a comparable 30 to 40 species. Other countries in tropical Asia also have numerous wild species of ''Curcuma''. Recent studies have also shown that the taxonomy of ''C. longa'' is problematic, with only the specimens from South India being identifiable as ''C. longa''. The phylogeny, relationships, intraspecific and interspecific variation, and even identity of other species and cultivars in other parts of the world still need to be established and validated. Various species currently utilized and sold as "turmeric" in other parts of Asia have been shown to belong to several physically similar taxa, with overlapping local names. | ||
<!--T:7--> | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
Turmeric has been used in Asia for centuries and is a major part of [[Ayurveda]], [[Siddha medicine]], [[traditional Chinese medicine]], [[Unani]], and the animistic rituals of [[Austronesian peoples]]. It was first used as a [[dye]], and then later for its supposed properties in [[traditional medicine|folk medicine]]. | Turmeric has been used in Asia for centuries and is a major part of [[Ayurveda]], [[Siddha medicine]], [[traditional Chinese medicine]], [[Unani]], and the animistic rituals of [[Austronesian peoples]]. It was first used as a [[dye]], and then later for its supposed properties in [[traditional medicine|folk medicine]]. | ||
<!--T:8--> | |||
In India, it spread with Hinduism and Buddhism, as the yellow dye is used to color the robes of monks and priests. | In India, it spread with Hinduism and Buddhism, as the yellow dye is used to color the robes of monks and priests. | ||
<!--T:9--> | |||
In [[Island Southeast Asia]], there is linguistic and circumstantial evidence of the ancient use of turmeric among the [[Austronesian peoples]] soon after dispersal from [[Taiwan]] (starting {{circa|3000 BCE}}), before contact with India. In [[Indonesia]] and the [[Philippines]], turmeric was used for food, dyeing textiles, medicine, as well as body painting. It was commonly an important ingredient in various animistic rituals. Kikusawa and Reid (2007) have concluded that *kunij, the oldest reconstructed [[Proto-Malayo-Polynesian]] form for "turmeric" in the Austronesian languages, is primarily associated with the importance of its use as a dye. Other members of the genus ''Curcuma'' native to Southeast Asia (like ''[[Curcuma zedoaria]]'') were also used for food and spice, but not as dyes. | In [[Island Southeast Asia]], there is linguistic and circumstantial evidence of the ancient use of turmeric among the [[Austronesian peoples]] soon after dispersal from [[Taiwan]] (starting {{circa|3000 BCE}}), before contact with India. In [[Indonesia]] and the [[Philippines]], turmeric was used for food, dyeing textiles, medicine, as well as body painting. It was commonly an important ingredient in various animistic rituals. Kikusawa and Reid (2007) have concluded that *kunij, the oldest reconstructed [[Proto-Malayo-Polynesian]] form for "turmeric" in the Austronesian languages, is primarily associated with the importance of its use as a dye. Other members of the genus ''Curcuma'' native to Southeast Asia (like ''[[Curcuma zedoaria]]'') were also used for food and spice, but not as dyes. | ||
<!--T:10--> | |||
Turmeric (along with ''[[Curcuma zedoaria]]'') was also spread with the [[Lapita people]] of the [[Austronesian expansion]] into [[Oceania]]. Turmeric can only be propagated with rhizomes, thus its pre-contact distribution into the [[Pacific Islands]] can only be via human introduction. The populations in [[Micronesia]], [[Island Melanesia]], and [[Polynesia]] (including as far as [[Hawaii]] and [[Easter Island]]) use turmeric widely for both food and dye before European contact. In [[Micronesia]], it was an important trade item in the ''[[sawei]]'' maritime exchange between [[Yap]] and further [[atoll]]s in the [[Caroline Islands|Carolines]], where it couldn't grow. In some smaller islands, the dye was extracted from the leaves, since the rhizomes remained too small in sandy soils. It was also carried by the Austronesian migrations to [[Madagascar]]. | Turmeric (along with ''[[Curcuma zedoaria]]'') was also spread with the [[Lapita people]] of the [[Austronesian expansion]] into [[Oceania]]. Turmeric can only be propagated with rhizomes, thus its pre-contact distribution into the [[Pacific Islands]] can only be via human introduction. The populations in [[Micronesia]], [[Island Melanesia]], and [[Polynesia]] (including as far as [[Hawaii]] and [[Easter Island]]) use turmeric widely for both food and dye before European contact. In [[Micronesia]], it was an important trade item in the ''[[sawei]]'' maritime exchange between [[Yap]] and further [[atoll]]s in the [[Caroline Islands|Carolines]], where it couldn't grow. In some smaller islands, the dye was extracted from the leaves, since the rhizomes remained too small in sandy soils. It was also carried by the Austronesian migrations to [[Madagascar]]. | ||
<!--T:11--> | |||
Turmeric was found in [[Farmana]], dating to between 2600 and 2200 BCE, and in a merchant's tomb in [[Megiddo, Israel]], dating from the second millennium BCE. It was noted as a dye plant in the [[Assyria]]ns' Cuneiform medical texts from [[Ashurbanipal]]’s library at Nineveh from 7th century BCE. In [[Medieval Europe]], turmeric was called "Indian [[saffron]]." | Turmeric was found in [[Farmana]], dating to between 2600 and 2200 BCE, and in a merchant's tomb in [[Megiddo, Israel]], dating from the second millennium BCE. It was noted as a dye plant in the [[Assyria]]ns' Cuneiform medical texts from [[Ashurbanipal]]’s library at Nineveh from 7th century BCE. In [[Medieval Europe]], turmeric was called "Indian [[saffron]]." | ||
<!--T:12--> | |||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
The name possibly derives from [[Middle English]] or Early Modern English as ''{{lang|enm|turmeryte}}'' or ''{{lang|enm|tarmaret}}''. It may be of [[Latin]] origin, ''{{lang|la|terra merita}}'' ("deserved earth"). The Latin specific epithet ''longa'' means long. | The name possibly derives from [[Middle English]] or Early Modern English as ''{{lang|enm|turmeryte}}'' or ''{{lang|enm|tarmaret}}''. It may be of [[Latin]] origin, ''{{lang|la|terra merita}}'' ("deserved earth"). The Latin specific epithet ''longa'' means long. | ||
<!--T:13--> | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
Turmeric is a [[Perennial plant|perennial]] [[herbaceous plant]] that reaches up to {{convert|1|m|ftin|abbr=on}} tall. It has highly branched, yellow to orange, cylindrical, aromatic rhizomes. | Turmeric is a [[Perennial plant|perennial]] [[herbaceous plant]] that reaches up to {{convert|1|m|ftin|abbr=on}} tall. It has highly branched, yellow to orange, cylindrical, aromatic rhizomes. | ||
<!--T:14--> | |||
The leaves are [[Phyllotaxis#Leaf arrangement|alternate]] and arranged in two rows. They are divided into leaf sheath, [[Petiole (botany)|petiole]], and leaf blade. From the leaf sheaths, a false stem is formed. The petiole is {{convert|50|to(-)|115|cm|in|abbr=on}} long. The simple leaf blades are usually {{convert|76 |to(-)|115|cm|in|abbr=on}} long and rarely up to {{convert|230|cm|ftin|abbr=on}}. They have a width of {{convert|38|to|45|cm|in|frac=2|abbr=on}} and are oblong to elliptical, narrowing at the tip. | The leaves are [[Phyllotaxis#Leaf arrangement|alternate]] and arranged in two rows. They are divided into leaf sheath, [[Petiole (botany)|petiole]], and leaf blade. From the leaf sheaths, a false stem is formed. The petiole is {{convert|50|to(-)|115|cm|in|abbr=on}} long. The simple leaf blades are usually {{convert|76 |to(-)|115|cm|in|abbr=on}} long and rarely up to {{convert|230|cm|ftin|abbr=on}}. They have a width of {{convert|38|to|45|cm|in|frac=2|abbr=on}} and are oblong to elliptical, narrowing at the tip. | ||
<!--T:15--> | |||
===Inflorescence, flower, and fruit=== | ===Inflorescence, flower, and fruit=== | ||
At the top of the inflorescence, stem bracts are present on which no flowers occur; these are white to green and sometimes tinged reddish-purple, and the upper ends are tapered. | At the top of the inflorescence, stem bracts are present on which no flowers occur; these are white to green and sometimes tinged reddish-purple, and the upper ends are tapered. | ||
<!--T:16--> | |||
The [[Hermaphrodite (botany)|hermaphrodite]] flowers are [[zygomorphic]] and threefold. The three [[sepal]]s are {{convert|0.8|to|1.2|cm|in|frac=8|abbr=on}} long, fused, and white, and have fluffy hairs; the three [[Sepal|calyx]] teeth are unequal. The three bright-yellow [[petal]]s are fused into a [[Corolla (flower)|corolla]] tube up to {{convert|3|cm|in|frac=4|abbr=on}} long. The three corolla lobes have a length of {{convert|1.0|to(-)|1.5|cm|in|frac=8|abbr=on|sigfig=2}} and are triangular with soft-spiny upper ends. While the average corolla lobe is larger than the two lateral, only the median [[stamen]] of the inner circle is fertile. The dust bag is spurred at its base. All other stamens are converted to [[staminode]]s. The outer staminodes are shorter than the [[Labellum (botany)|labellum]]. The labellum is yellowish, with a yellow ribbon in its center and it is [[obovate]], with a length from {{convert|1.2|to|2.0|cm|in|frac=8|abbr=on|sigfig=2}}. Three [[carpels]] are under a constant, trilobed ovary adherent, which is sparsely hairy. The fruit capsule opens with three compartments. | The [[Hermaphrodite (botany)|hermaphrodite]] flowers are [[zygomorphic]] and threefold. The three [[sepal]]s are {{convert|0.8|to|1.2|cm|in|frac=8|abbr=on}} long, fused, and white, and have fluffy hairs; the three [[Sepal|calyx]] teeth are unequal. The three bright-yellow [[petal]]s are fused into a [[Corolla (flower)|corolla]] tube up to {{convert|3|cm|in|frac=4|abbr=on}} long. The three corolla lobes have a length of {{convert|1.0|to(-)|1.5|cm|in|frac=8|abbr=on|sigfig=2}} and are triangular with soft-spiny upper ends. While the average corolla lobe is larger than the two lateral, only the median [[stamen]] of the inner circle is fertile. The dust bag is spurred at its base. All other stamens are converted to [[staminode]]s. The outer staminodes are shorter than the [[Labellum (botany)|labellum]]. The labellum is yellowish, with a yellow ribbon in its center and it is [[obovate]], with a length from {{convert|1.2|to|2.0|cm|in|frac=8|abbr=on|sigfig=2}}. Three [[carpels]] are under a constant, trilobed ovary adherent, which is sparsely hairy. The fruit capsule opens with three compartments. | ||
<!--T:17--> | |||
In [[East Asia]], the flowering time is usually in August. Terminally on the false stem is an [[inflorescence]] stem, {{convert|12|to|20|cm|in|frac=2|abbr=on}} long, containing many flowers. The [[bract]]s are light green and ovate to oblong with a blunt upper end with a length of {{convert|3|to|5|cm|in|frac=2|abbr=on}}. | In [[East Asia]], the flowering time is usually in August. Terminally on the false stem is an [[inflorescence]] stem, {{convert|12|to|20|cm|in|frac=2|abbr=on}} long, containing many flowers. The [[bract]]s are light green and ovate to oblong with a blunt upper end with a length of {{convert|3|to|5|cm|in|frac=2|abbr=on}}. | ||
<!--T:18--> | |||
{{Gallery| align=center | {{Gallery| align=center | ||
| File:Naturalis Biodiversity Center - L.0939330 - Bernecker, A. - Curcuma domestica Valeton - Artwork.jpeg | | File:Naturalis Biodiversity Center - L.0939330 - Bernecker, A. - Curcuma domestica Valeton - Artwork.jpeg | ||
| Line 61: | Line 79: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--T:19--> | |||
==Phytochemistry== | ==Phytochemistry== | ||
[[File:curcuminKeto.svg|right|frame|Curcumin [[Ketone|keto]] form]] | [[File:curcuminKeto.svg|right|frame|Curcumin [[Ketone|keto]] form]] | ||
| Line 66: | Line 85: | ||
Turmeric powder is about 60–70% [[carbohydrates]], 6–13% water, 6–8% [[protein]], 5–10% [[fat]], 3–7% [[dietary minerals]], 3–7% [[essential oil]]s, 2–7% [[dietary fiber]], and 1–6% [[curcuminoid]]s. The golden yellow color of turmeric is due to curcumin. | Turmeric powder is about 60–70% [[carbohydrates]], 6–13% water, 6–8% [[protein]], 5–10% [[fat]], 3–7% [[dietary minerals]], 3–7% [[essential oil]]s, 2–7% [[dietary fiber]], and 1–6% [[curcuminoid]]s. The golden yellow color of turmeric is due to curcumin. | ||
<!--T:20--> | |||
[[Phytochemistry|Phytochemical]] components of turmeric include [[diarylheptanoid]]s, a class including numerous curcuminoids, such as [[curcumin]], [[demethoxycurcumin]], and [[bisdemethoxycurcumin]]. Curcumin constitutes up to 3.14% of assayed commercial samples of turmeric powder (the average was 1.51%); curry powder contains much less (an average of 0.29%). Some 34 essential oils are present in turmeric, among which [[turmerone]], [[germacrone]], atlantone, and [[zingiberene]] are major constituents. | [[Phytochemistry|Phytochemical]] components of turmeric include [[diarylheptanoid]]s, a class including numerous curcuminoids, such as [[curcumin]], [[demethoxycurcumin]], and [[bisdemethoxycurcumin]]. Curcumin constitutes up to 3.14% of assayed commercial samples of turmeric powder (the average was 1.51%); curry powder contains much less (an average of 0.29%). Some 34 essential oils are present in turmeric, among which [[turmerone]], [[germacrone]], atlantone, and [[zingiberene]] are major constituents. | ||
==Uses== | ==Uses== <!--T:21--> | ||
<!--T:22--> | |||
===Culinary=== | ===Culinary=== | ||
Turmeric is one of the key ingredients in many Asian dishes, imparting a mustard-like, earthy aroma and pungent, slightly bitter flavor to foods. It is used mostly in savory dishes, but also is used in some sweet dishes, such as the Lebanese cake ''[[sfouf]]''. In India, turmeric leaf is used to prepare special sweet dishes, ''[[patoleo]]'', by layering rice flour and [[coconut]]-[[jaggery]] mixture on the leaf, then closing and steaming it in a special utensil (''chondrõ''). Most turmeric is used in the form of [[rhizome]] powder to impart a golden yellow color. It is used in many products such as canned beverages, baked products, dairy products, ice cream, yogurt, yellow cakes, orange juice, biscuits, popcorn, cereals and sauces. It is a principal ingredient in curry powders. Although typically used in its dried, powdered form, turmeric also is used fresh, like ginger. | Turmeric is one of the key ingredients in many Asian dishes, imparting a mustard-like, earthy aroma and pungent, slightly bitter flavor to foods. It is used mostly in savory dishes, but also is used in some sweet dishes, such as the Lebanese cake ''[[sfouf]]''. In India, turmeric leaf is used to prepare special sweet dishes, ''[[patoleo]]'', by layering rice flour and [[coconut]]-[[jaggery]] mixture on the leaf, then closing and steaming it in a special utensil (''chondrõ''). Most turmeric is used in the form of [[rhizome]] powder to impart a golden yellow color. It is used in many products such as canned beverages, baked products, dairy products, ice cream, yogurt, yellow cakes, orange juice, biscuits, popcorn, cereals and sauces. It is a principal ingredient in curry powders. Although typically used in its dried, powdered form, turmeric also is used fresh, like ginger. | ||
<!--T:23--> | |||
Turmeric is used widely as a spice in South Asian and Middle Eastern cooking. Various [[Iranian cuisine|Iranian]] ''[[khoresh]]'' recipes begin with onions [[Caramelization|caramelized]] in oil and turmeric. The [[Moroccan cuisine|Moroccan]] spice mix [[ras el hanout]] typically includes turmeric. In South Africa, turmeric is used to give boiled white rice a golden color, known as ''geelrys'' (yellow rice) traditionally served with [[bobotie]]. In [[Vietnamese cuisine]], turmeric powder is used to color and enhance the flavors of certain dishes, such as ''[[bánh xèo]]'', ''bánh khọt'', and ''[[mì Quảng]]''. The staple [[Cambodian cuisine|Cambodian]] curry paste, ''[[kroeung]]'', used in many dishes, including [[fish amok]], typically contains fresh turmeric. In [[Indonesia]], turmeric leaves are used for [[Minangkabau people|Minang]] or [[Padang cuisine|Padang]] curry base of [[Sumatra]], such as ''[[rendang]]'', ''[[sate padang]]'', and many other varieties. In the [[Philippines]], turmeric is used in the preparation and cooking of ''[[kuning]]'', [[Satay|''satti'']], and some variants of [[Philippine adobo|''adobo'']]. In [[Thailand]], fresh turmeric rhizomes are used widely in many dishes, in particular in the southern [[Thai cuisine]], such as yellow curry and turmeric soup. Turmeric is used in a hot drink called "turmeric [[latte]]" or "golden milk" that is made with milk, frequently [[coconut milk]]. The turmeric milk drink known as ''haldī dūdh'' (''haldī'' [{{lang|hi|हलदी}}] means turmeric in [[Hindi]]) is a traditional Indian recipe. Sold in the US and UK, the drink known as "golden milk" uses nondairy milk and sweetener, and sometimes black pepper after the traditional recipe (which may also use ghee). | Turmeric is used widely as a spice in South Asian and Middle Eastern cooking. Various [[Iranian cuisine|Iranian]] ''[[khoresh]]'' recipes begin with onions [[Caramelization|caramelized]] in oil and turmeric. The [[Moroccan cuisine|Moroccan]] spice mix [[ras el hanout]] typically includes turmeric. In South Africa, turmeric is used to give boiled white rice a golden color, known as ''geelrys'' (yellow rice) traditionally served with [[bobotie]]. In [[Vietnamese cuisine]], turmeric powder is used to color and enhance the flavors of certain dishes, such as ''[[bánh xèo]]'', ''bánh khọt'', and ''[[mì Quảng]]''. The staple [[Cambodian cuisine|Cambodian]] curry paste, ''[[kroeung]]'', used in many dishes, including [[fish amok]], typically contains fresh turmeric. In [[Indonesia]], turmeric leaves are used for [[Minangkabau people|Minang]] or [[Padang cuisine|Padang]] curry base of [[Sumatra]], such as ''[[rendang]]'', ''[[sate padang]]'', and many other varieties. In the [[Philippines]], turmeric is used in the preparation and cooking of ''[[kuning]]'', [[Satay|''satti'']], and some variants of [[Philippine adobo|''adobo'']]. In [[Thailand]], fresh turmeric rhizomes are used widely in many dishes, in particular in the southern [[Thai cuisine]], such as yellow curry and turmeric soup. Turmeric is used in a hot drink called "turmeric [[latte]]" or "golden milk" that is made with milk, frequently [[coconut milk]]. The turmeric milk drink known as ''haldī dūdh'' (''haldī'' [{{lang|hi|हलदी}}] means turmeric in [[Hindi]]) is a traditional Indian recipe. Sold in the US and UK, the drink known as "golden milk" uses nondairy milk and sweetener, and sometimes black pepper after the traditional recipe (which may also use ghee). | ||
<!--T:24--> | |||
Turmeric is approved for use as a [[food color]], assigned the code [[E number|E100]]. The [[oleoresin]] is used for oil-containing products. | Turmeric is approved for use as a [[food color]], assigned the code [[E number|E100]]. The [[oleoresin]] is used for oil-containing products. | ||
<!--T:25--> | |||
In combination with [[annatto]] (E160b), turmeric has been used to color numerous food products. Turmeric is used to give a yellow color to some prepared [[Mustard (condiment)|mustards]], canned chicken [[broth]]s, and other foods{{mdash}}often as a much cheaper replacement for [[saffron]]. | In combination with [[annatto]] (E160b), turmeric has been used to color numerous food products. Turmeric is used to give a yellow color to some prepared [[Mustard (condiment)|mustards]], canned chicken [[broth]]s, and other foods{{mdash}}often as a much cheaper replacement for [[saffron]]. | ||
<!--T:26--> | |||
{{Gallery| align= center | {{Gallery| align= center | ||
| File:TurmericMyanmar2.jpg | | File:TurmericMyanmar2.jpg | ||
| Line 94: | Line 119: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--T:27--> | |||
===Traditional uses=== | ===Traditional uses=== | ||
[[File:Khandoba temple Pune.jpg|thumb|[[Khandoba]]'s newer temple in [[Jejuri]], where devotees shower turmeric powder (''bhandara'') on each other]] | [[File:Khandoba temple Pune.jpg|thumb|[[Khandoba]]'s newer temple in [[Jejuri]], where devotees shower turmeric powder (''bhandara'') on each other]] | ||
In 2019, the [[European Medicines Agency]] concluded that turmeric herbal teas, or other forms taken by mouth, on the basis of their long-standing traditional use, could be used to relieve mild digestive problems, such as feelings of fullness and [[flatulence]]. | In 2019, the [[European Medicines Agency]] concluded that turmeric herbal teas, or other forms taken by mouth, on the basis of their long-standing traditional use, could be used to relieve mild digestive problems, such as feelings of fullness and [[flatulence]]. | ||
<!--T:28--> | |||
Turmeric grows wild in the forests of South and Southeast Asia, where it is collected for use in classical Indian medicine (Siddha or Ayurveda). In Eastern India, the plant is used as one of the nine components of {{Transliteration|sa|nabapatrika}} along with young [[plantain (cooking)|plantain]] or banana plant, [[taro]] leaves, [[barley]] ({{Transliteration|sa|jayanti}}), [[Aegle marmelos|wood apple]] ({{Transliteration|sa|bilva}}), [[pomegranate]] ({{Transliteration|sa|darimba}}), ''[[Saraca indica]]'', {{Transliteration|sa|manaka}} (''[[Arum]]''), or {{Transliteration|sa|manakochu}}, and rice paddy. The Haldi ceremony called {{Transliteration|bn|[[gaye holud]]}} in Bengal (literally "yellow on the body") is a ceremony observed during wedding celebrations of people of Indian culture all throughout the Indian subcontinent. | Turmeric grows wild in the forests of South and Southeast Asia, where it is collected for use in classical Indian medicine (Siddha or Ayurveda). In Eastern India, the plant is used as one of the nine components of {{Transliteration|sa|nabapatrika}} along with young [[plantain (cooking)|plantain]] or banana plant, [[taro]] leaves, [[barley]] ({{Transliteration|sa|jayanti}}), [[Aegle marmelos|wood apple]] ({{Transliteration|sa|bilva}}), [[pomegranate]] ({{Transliteration|sa|darimba}}), ''[[Saraca indica]]'', {{Transliteration|sa|manaka}} (''[[Arum]]''), or {{Transliteration|sa|manakochu}}, and rice paddy. The Haldi ceremony called {{Transliteration|bn|[[gaye holud]]}} in Bengal (literally "yellow on the body") is a ceremony observed during wedding celebrations of people of Indian culture all throughout the Indian subcontinent. | ||
<!--T:29--> | |||
In [[Tamil Nadu]] and [[Andhra Pradesh]], as a part of the Tamil–Telugu marriage ritual, a dried turmeric tuber tied with a string is used to create a [[Thali necklace]]. In western and coastal India, during weddings of the [[Marathi people|Marathi]] and [[Konkani people]], [[Kannada people|Kannada]] [[Brahmins]], turmeric tubers are tied with strings by the couple to their wrists during a ceremony, ''Kankana Bandhana''. In many Hindu communities, turmeric paste is applied to the bride and groom as part of pre-wedding festivities known as the haldi ceremony. | In [[Tamil Nadu]] and [[Andhra Pradesh]], as a part of the Tamil–Telugu marriage ritual, a dried turmeric tuber tied with a string is used to create a [[Thali necklace]]. In western and coastal India, during weddings of the [[Marathi people|Marathi]] and [[Konkani people]], [[Kannada people|Kannada]] [[Brahmins]], turmeric tubers are tied with strings by the couple to their wrists during a ceremony, ''Kankana Bandhana''. In many Hindu communities, turmeric paste is applied to the bride and groom as part of pre-wedding festivities known as the haldi ceremony. | ||
<!--T:30--> | |||
Turmeric makes a poor fabric [[dye]], as it is not [[Colour fastness|light fast]], but is commonly used in Indian clothing, such as [[sari]]s and [[Kasaya (clothing)|Buddhist monks' robes]]. During the late [[Edo period]] (1603–1867), turmeric was used to dilute or substitute more expensive [[safflower]] dyestuff in the production of {{Transliteration|ja|[[shibori#Beni itajime|beni itajime shibori]]}}. [[Friedrich Ratzel]] reported in ''The History of Mankind'' during 1896, that in Micronesia, turmeric powder was applied for embellishment of body, clothing, utensils, and ceremonial uses. [[Native Hawaiians]] who introduced it to [[Hawaii]] ({{langx|haw|{{okina}}ōlena}}) make a bright yellow dye out of it. | Turmeric makes a poor fabric [[dye]], as it is not [[Colour fastness|light fast]], but is commonly used in Indian clothing, such as [[sari]]s and [[Kasaya (clothing)|Buddhist monks' robes]]. During the late [[Edo period]] (1603–1867), turmeric was used to dilute or substitute more expensive [[safflower]] dyestuff in the production of {{Transliteration|ja|[[shibori#Beni itajime|beni itajime shibori]]}}. [[Friedrich Ratzel]] reported in ''The History of Mankind'' during 1896, that in Micronesia, turmeric powder was applied for embellishment of body, clothing, utensils, and ceremonial uses. [[Native Hawaiians]] who introduced it to [[Hawaii]] ({{langx|haw|{{okina}}ōlena}}) make a bright yellow dye out of it. | ||
<!--T:31--> | |||
===Indicator=== | ===Indicator=== | ||
[[File:TurmericAcidBase.jpg|thumb|Turmeric dispersed in water is yellow under acid and red under alkaline conditions]] | [[File:TurmericAcidBase.jpg|thumb|Turmeric dispersed in water is yellow under acid and red under alkaline conditions]] | ||
Turmeric paper, also called curcuma paper or in German literature, ''Curcumapapier'', is paper steeped in a [[tincture]] of turmeric and allowed to dry. It is used in [[chemical analysis]] as an [[pH indicator|indicator]] for [[acidity]] and [[alkalinity]]. The paper is yellow in acidic and [[neutral solution]]s and turns brown to reddish-brown in alkaline solutions, with transition between pH of 7.4 and 9.2. | Turmeric paper, also called curcuma paper or in German literature, ''Curcumapapier'', is paper steeped in a [[tincture]] of turmeric and allowed to dry. It is used in [[chemical analysis]] as an [[pH indicator|indicator]] for [[acidity]] and [[alkalinity]]. The paper is yellow in acidic and [[neutral solution]]s and turns brown to reddish-brown in alkaline solutions, with transition between pH of 7.4 and 9.2. | ||
<!--T:32--> | |||
==Adulteration== | ==Adulteration== | ||
As turmeric and other spices are commonly sold by weight, the potential exists for powders of toxic, cheaper agents with a similar color to be added, such as [[lead(II,IV) oxide]] ("red lead"). These additives give turmeric an orange-red color instead of its native gold-yellow, and such conditions led the US [[Food and Drug Administration]] (FDA) to issue import alerts from 2013 to 2019 on turmeric originating in [[India]] and [[Bangladesh]]. Imported into the United States in 2014 were approximately {{convert|12|e6lb|e6kg|abbr=off|order=flip}} of turmeric, some of which was used for [[food coloring]], [[traditional medicine]], or [[dietary supplement]]. Lead detection in turmeric products led to [[product recall|recalls]] across the United States, Canada, Japan, Korea, and the United Kingdom through 2016. | As turmeric and other spices are commonly sold by weight, the potential exists for powders of toxic, cheaper agents with a similar color to be added, such as [[lead(II,IV) oxide]] ("red lead"). These additives give turmeric an orange-red color instead of its native gold-yellow, and such conditions led the US [[Food and Drug Administration]] (FDA) to issue import alerts from 2013 to 2019 on turmeric originating in [[India]] and [[Bangladesh]]. Imported into the United States in 2014 were approximately {{convert|12|e6lb|e6kg|abbr=off|order=flip}} of turmeric, some of which was used for [[food coloring]], [[traditional medicine]], or [[dietary supplement]]. Lead detection in turmeric products led to [[product recall|recalls]] across the United States, Canada, Japan, Korea, and the United Kingdom through 2016. | ||
<!--T:33--> | |||
[[Lead chromate]], a bright yellow chemical compound, was found as an adulterant of turmeric in Bangladesh, where turmeric is used commonly in foods and the contamination levels were up to 500 times higher than the national limit. Researchers identified a chain of sources adulterating the turmeric with lead chromate: from farmers to merchants selling low-grade turmeric roots to "polishers" who added lead chromate for yellow color enhancement, to [[wholesale]]rs for market distribution, all unaware of the potential consequences of lead toxicity. | [[Lead chromate]], a bright yellow chemical compound, was found as an adulterant of turmeric in Bangladesh, where turmeric is used commonly in foods and the contamination levels were up to 500 times higher than the national limit. Researchers identified a chain of sources adulterating the turmeric with lead chromate: from farmers to merchants selling low-grade turmeric roots to "polishers" who added lead chromate for yellow color enhancement, to [[wholesale]]rs for market distribution, all unaware of the potential consequences of lead toxicity. | ||
<!--T:34--> | |||
Another common adulterant in turmeric, [[metanil yellow]] (also known as acid yellow 36), is considered by the [[Great Britain|British]] [[Food Standards Agency]] as an illegal [[dye]] for use in foods. | Another common adulterant in turmeric, [[metanil yellow]] (also known as acid yellow 36), is considered by the [[Great Britain|British]] [[Food Standards Agency]] as an illegal [[dye]] for use in foods. | ||
<!--T:35--> | |||
==Medical research== | ==Medical research== | ||
{{see also|Curcumin|label 1=Curcumin}} | {{see also|Curcumin|label 1=Curcumin}} | ||
<!--T:36--> | |||
Turmeric and curcumin have been studied in numerous [[clinical trial]]s for various human diseases and conditions, with no high-quality evidence of any anti-disease effect or health benefit. There is no scientific evidence that curcumin reduces [[inflammation]], {{as of | 2020| lc=yes}}. There is weak evidence that turmeric extracts may be beneficial for relieving symptoms of knee [[osteoarthritis]], as well as for reducing pain and muscle damage following physical exercise. There is good evidence that turmeric is an allergen. | Turmeric and curcumin have been studied in numerous [[clinical trial]]s for various human diseases and conditions, with no high-quality evidence of any anti-disease effect or health benefit. There is no scientific evidence that curcumin reduces [[inflammation]], {{as of | 2020| lc=yes}}. There is weak evidence that turmeric extracts may be beneficial for relieving symptoms of knee [[osteoarthritis]], as well as for reducing pain and muscle damage following physical exercise. There is good evidence that turmeric is an allergen. | ||
<!--T:37--> | |||
Although turmeric is of low [[bioavailability]], some supplements boost potency via a variety of preparation techniques. Turmeric supplements are hepatotoxic and have caused a recorded rise in incidence of [[herb-induced liver injury]]. In Italy, the government has banned any claims of turmeric health benefits and mandated warning for turmeric-based supplements. | Although turmeric is of low [[bioavailability]], some supplements boost potency via a variety of preparation techniques. Turmeric supplements are hepatotoxic and have caused a recorded rise in incidence of [[herb-induced liver injury]]. In Italy, the government has banned any claims of turmeric health benefits and mandated warning for turmeric-based supplements. | ||
<!--T:38--> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
{{div col|colwidth=20em|small=yes}} | {{div col|colwidth=20em|small=yes}} | ||
| Line 132: | Line 169: | ||
{{div col end}} | {{div col end}} | ||
<!--T:39--> | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
* {{wiktionary-inline}} | * {{wiktionary-inline}} | ||
* {{Cookbook-inline}} | * {{Cookbook-inline}} | ||
<!--T:40--> | |||
{{Herbs & spices}} | {{Herbs & spices}} | ||
{{Transient receptor potential channel modulators}} | {{Transient receptor potential channel modulators}} | ||
<!--T:41--> | |||
[[Category:Curcuma|longa]] | [[Category:Curcuma|longa]] | ||
[[Category:Flora of tropical Asia]] | [[Category:Flora of tropical Asia]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:09, 9 June 2025
| Turmeric | |
|---|---|

| |
| Inflorescence of Curcuma longa | |

| |
| Turmeric rhizome and powder | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Zingiberales |
| Family: | Zingiberaceae |
| Genus: | Curcuma |
| Species: | longa
|
| Binomial name | |
| longa | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Curcuma domestica Valeton | |
Turmeric (/ˈtɜːrmərɪk, ˈtjuː-/), or Curcuma longa (/ˈkɜːrkjʊmə ˈlɒŋɡə/), is a flowering plant in the ginger family Zingiberaceae. It is a perennial, rhizomatous, herbaceous plant native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia that requires temperatures between 20 and 30 °C (68 and 86 °F) and high annual rainfall to thrive. Plants are gathered each year for their rhizomes, some for propagation in the following season and some for consumption or dyeing.
The rhizomes can be used fresh, but they are often boiled in water and dried, after which they are ground into a deep orange-yellow shelf-stable spice powder commonly used as a coloring and flavoring agent in many Asian cuisines, especially for curries (curry powder). Turmeric powder has a warm, bitter, black pepper-like flavor and earthy, mustard-like aroma.
Although long used in Ayurvedic medicine, there is no high-quality clinical evidence that consuming turmeric or the principal turmeric constituent, curcumin, is effective for treating any disease. Curcumin, a bright yellow chemical produced by the turmeric plant, is approved as a food additive by the World Health Organization, European Parliament, and United States Food and Drug Administration. Turmeric supplements have been an increasing cause of herb-induced liver injury, leading to government regulation.
Origin and distribution
The greatest diversity of Curcuma species by number alone is in India, at around 40 to 45 species. Thailand has a comparable 30 to 40 species. Other countries in tropical Asia also have numerous wild species of Curcuma. Recent studies have also shown that the taxonomy of C. longa is problematic, with only the specimens from South India being identifiable as C. longa. The phylogeny, relationships, intraspecific and interspecific variation, and even identity of other species and cultivars in other parts of the world still need to be established and validated. Various species currently utilized and sold as "turmeric" in other parts of Asia have been shown to belong to several physically similar taxa, with overlapping local names.
History
Turmeric has been used in Asia for centuries and is a major part of Ayurveda, Siddha medicine, traditional Chinese medicine, Unani, and the animistic rituals of Austronesian peoples. It was first used as a dye, and then later for its supposed properties in folk medicine.
In India, it spread with Hinduism and Buddhism, as the yellow dye is used to color the robes of monks and priests.
In Island Southeast Asia, there is linguistic and circumstantial evidence of the ancient use of turmeric among the Austronesian peoples soon after dispersal from Taiwan (starting c. 3000 BCE), before contact with India. In Indonesia and the Philippines, turmeric was used for food, dyeing textiles, medicine, as well as body painting. It was commonly an important ingredient in various animistic rituals. Kikusawa and Reid (2007) have concluded that *kunij, the oldest reconstructed Proto-Malayo-Polynesian form for "turmeric" in the Austronesian languages, is primarily associated with the importance of its use as a dye. Other members of the genus Curcuma native to Southeast Asia (like Curcuma zedoaria) were also used for food and spice, but not as dyes.
Turmeric (along with Curcuma zedoaria) was also spread with the Lapita people of the Austronesian expansion into Oceania. Turmeric can only be propagated with rhizomes, thus its pre-contact distribution into the Pacific Islands can only be via human introduction. The populations in Micronesia, Island Melanesia, and Polynesia (including as far as Hawaii and Easter Island) use turmeric widely for both food and dye before European contact. In Micronesia, it was an important trade item in the sawei maritime exchange between Yap and further atolls in the Carolines, where it couldn't grow. In some smaller islands, the dye was extracted from the leaves, since the rhizomes remained too small in sandy soils. It was also carried by the Austronesian migrations to Madagascar.
Turmeric was found in Farmana, dating to between 2600 and 2200 BCE, and in a merchant's tomb in Megiddo, Israel, dating from the second millennium BCE. It was noted as a dye plant in the Assyrians' Cuneiform medical texts from Ashurbanipal’s library at Nineveh from 7th century BCE. In Medieval Europe, turmeric was called "Indian saffron."
Etymology
The name possibly derives from Middle English or Early Modern English as turmeryte or tarmaret. It may be of Latin origin, terra merita ("deserved earth"). The Latin specific epithet longa means long.
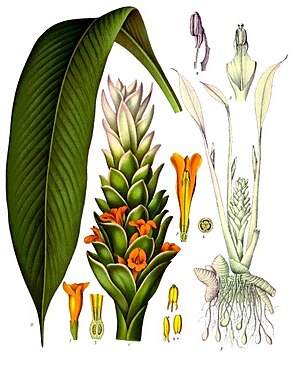
Description
Turmeric is a perennial herbaceous plant that reaches up to 1 m (3 ft 3 in) tall. It has highly branched, yellow to orange, cylindrical, aromatic rhizomes.
The leaves are alternate and arranged in two rows. They are divided into leaf sheath, petiole, and leaf blade. From the leaf sheaths, a false stem is formed. The petiole is 50 to 115 cm (20–45 in) long. The simple leaf blades are usually 76 to 115 cm (30–45 in) long and rarely up to 230 cm (7 ft 7 in). They have a width of 38 to 45 cm (15 to 17 1⁄2 in) and are oblong to elliptical, narrowing at the tip.
Inflorescence, flower, and fruit
At the top of the inflorescence, stem bracts are present on which no flowers occur; these are white to green and sometimes tinged reddish-purple, and the upper ends are tapered.
The hermaphrodite flowers are zygomorphic and threefold. The three sepals are 0.8 to 1.2 cm (3⁄8 to 1⁄2 in) long, fused, and white, and have fluffy hairs; the three calyx teeth are unequal. The three bright-yellow petals are fused into a corolla tube up to 3 cm (1 1⁄4 in) long. The three corolla lobes have a length of 1.0 to 1.5 cm (3⁄8–5⁄8 in) and are triangular with soft-spiny upper ends. While the average corolla lobe is larger than the two lateral, only the median stamen of the inner circle is fertile. The dust bag is spurred at its base. All other stamens are converted to staminodes. The outer staminodes are shorter than the labellum. The labellum is yellowish, with a yellow ribbon in its center and it is obovate, with a length from 1.2 to 2.0 cm (1⁄2 to 3⁄4 in). Three carpels are under a constant, trilobed ovary adherent, which is sparsely hairy. The fruit capsule opens with three compartments.
In East Asia, the flowering time is usually in August. Terminally on the false stem is an inflorescence stem, 12 to 20 cm (4 1⁄2 to 8 in) long, containing many flowers. The bracts are light green and ovate to oblong with a blunt upper end with a length of 3 to 5 cm (1 to 2 in).
-
Curcuma domestica Valeton, a drawing by A. Bernecker around 1860
-
Turmeric farm on Deccan Plateau
-
Turmeric flower
Phytochemistry


Turmeric powder is about 60–70% carbohydrates, 6–13% water, 6–8% protein, 5–10% fat, 3–7% dietary minerals, 3–7% essential oils, 2–7% dietary fiber, and 1–6% curcuminoids. The golden yellow color of turmeric is due to curcumin.
Phytochemical components of turmeric include diarylheptanoids, a class including numerous curcuminoids, such as curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin. Curcumin constitutes up to 3.14% of assayed commercial samples of turmeric powder (the average was 1.51%); curry powder contains much less (an average of 0.29%). Some 34 essential oils are present in turmeric, among which turmerone, germacrone, atlantone, and zingiberene are major constituents.
Uses
Culinary
Turmeric is one of the key ingredients in many Asian dishes, imparting a mustard-like, earthy aroma and pungent, slightly bitter flavor to foods. It is used mostly in savory dishes, but also is used in some sweet dishes, such as the Lebanese cake sfouf. In India, turmeric leaf is used to prepare special sweet dishes, patoleo, by layering rice flour and coconut-jaggery mixture on the leaf, then closing and steaming it in a special utensil (chondrõ). Most turmeric is used in the form of rhizome powder to impart a golden yellow color. It is used in many products such as canned beverages, baked products, dairy products, ice cream, yogurt, yellow cakes, orange juice, biscuits, popcorn, cereals and sauces. It is a principal ingredient in curry powders. Although typically used in its dried, powdered form, turmeric also is used fresh, like ginger.
Turmeric is used widely as a spice in South Asian and Middle Eastern cooking. Various Iranian khoresh recipes begin with onions caramelized in oil and turmeric. The Moroccan spice mix ras el hanout typically includes turmeric. In South Africa, turmeric is used to give boiled white rice a golden color, known as geelrys (yellow rice) traditionally served with bobotie. In Vietnamese cuisine, turmeric powder is used to color and enhance the flavors of certain dishes, such as bánh xèo, bánh khọt, and mì Quảng. The staple Cambodian curry paste, kroeung, used in many dishes, including fish amok, typically contains fresh turmeric. In Indonesia, turmeric leaves are used for Minang or Padang curry base of Sumatra, such as rendang, sate padang, and many other varieties. In the Philippines, turmeric is used in the preparation and cooking of kuning, satti, and some variants of adobo. In Thailand, fresh turmeric rhizomes are used widely in many dishes, in particular in the southern Thai cuisine, such as yellow curry and turmeric soup. Turmeric is used in a hot drink called "turmeric latte" or "golden milk" that is made with milk, frequently coconut milk. The turmeric milk drink known as haldī dūdh (haldī [हलदी] means turmeric in Hindi) is a traditional Indian recipe. Sold in the US and UK, the drink known as "golden milk" uses nondairy milk and sweetener, and sometimes black pepper after the traditional recipe (which may also use ghee).
Turmeric is approved for use as a food color, assigned the code E100. The oleoresin is used for oil-containing products.
In combination with annatto (E160b), turmeric has been used to color numerous food products. Turmeric is used to give a yellow color to some prepared mustards, canned chicken broths, and other foods—often as a much cheaper replacement for saffron.
-
Cleaning turmeric rhizomes with boiling water
-
Drying turmeric rhizomes
-
Turmeric powder
-
Cooked vegetables with turmeric as one of its key ingredients, referred to as Sabzi, a dish from India
-
Ganghwang-bap (turmeric rice)
-
Patoleo – sweet rice cakes steamed in turmeric leaves consisting of a filling of coconut and coconut palm sugar prepared in Goan Catholic style
Traditional uses

In 2019, the European Medicines Agency concluded that turmeric herbal teas, or other forms taken by mouth, on the basis of their long-standing traditional use, could be used to relieve mild digestive problems, such as feelings of fullness and flatulence.
Turmeric grows wild in the forests of South and Southeast Asia, where it is collected for use in classical Indian medicine (Siddha or Ayurveda). In Eastern India, the plant is used as one of the nine components of nabapatrika along with young plantain or banana plant, taro leaves, barley (jayanti), wood apple (bilva), pomegranate (darimba), Saraca indica, manaka (Arum), or manakochu, and rice paddy. The Haldi ceremony called gaye holud in Bengal (literally "yellow on the body") is a ceremony observed during wedding celebrations of people of Indian culture all throughout the Indian subcontinent.
In Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh, as a part of the Tamil–Telugu marriage ritual, a dried turmeric tuber tied with a string is used to create a Thali necklace. In western and coastal India, during weddings of the Marathi and Konkani people, Kannada Brahmins, turmeric tubers are tied with strings by the couple to their wrists during a ceremony, Kankana Bandhana. In many Hindu communities, turmeric paste is applied to the bride and groom as part of pre-wedding festivities known as the haldi ceremony.
Turmeric makes a poor fabric dye, as it is not light fast, but is commonly used in Indian clothing, such as saris and Buddhist monks' robes. During the late Edo period (1603–1867), turmeric was used to dilute or substitute more expensive safflower dyestuff in the production of beni itajime shibori. Friedrich Ratzel reported in The History of Mankind during 1896, that in Micronesia, turmeric powder was applied for embellishment of body, clothing, utensils, and ceremonial uses. Native Hawaiians who introduced it to Hawaii (Hawaiian: ʻōlena) make a bright yellow dye out of it.
Indicator

Turmeric paper, also called curcuma paper or in German literature, Curcumapapier, is paper steeped in a tincture of turmeric and allowed to dry. It is used in chemical analysis as an indicator for acidity and alkalinity. The paper is yellow in acidic and neutral solutions and turns brown to reddish-brown in alkaline solutions, with transition between pH of 7.4 and 9.2.
Adulteration
As turmeric and other spices are commonly sold by weight, the potential exists for powders of toxic, cheaper agents with a similar color to be added, such as lead(II,IV) oxide ("red lead"). These additives give turmeric an orange-red color instead of its native gold-yellow, and such conditions led the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to issue import alerts from 2013 to 2019 on turmeric originating in India and Bangladesh. Imported into the United States in 2014 were approximately 5.4 million kilograms (12 million pounds) of turmeric, some of which was used for food coloring, traditional medicine, or dietary supplement. Lead detection in turmeric products led to recalls across the United States, Canada, Japan, Korea, and the United Kingdom through 2016.
Lead chromate, a bright yellow chemical compound, was found as an adulterant of turmeric in Bangladesh, where turmeric is used commonly in foods and the contamination levels were up to 500 times higher than the national limit. Researchers identified a chain of sources adulterating the turmeric with lead chromate: from farmers to merchants selling low-grade turmeric roots to "polishers" who added lead chromate for yellow color enhancement, to wholesalers for market distribution, all unaware of the potential consequences of lead toxicity.
Another common adulterant in turmeric, metanil yellow (also known as acid yellow 36), is considered by the British Food Standards Agency as an illegal dye for use in foods.
Medical research
Turmeric and curcumin have been studied in numerous clinical trials for various human diseases and conditions, with no high-quality evidence of any anti-disease effect or health benefit. There is no scientific evidence that curcumin reduces inflammation, 2020年現在[update]. There is weak evidence that turmeric extracts may be beneficial for relieving symptoms of knee osteoarthritis, as well as for reducing pain and muscle damage following physical exercise. There is good evidence that turmeric is an allergen.
Although turmeric is of low bioavailability, some supplements boost potency via a variety of preparation techniques. Turmeric supplements are hepatotoxic and have caused a recorded rise in incidence of herb-induced liver injury. In Italy, the government has banned any claims of turmeric health benefits and mandated warning for turmeric-based supplements.
See also
External links
 The dictionary definition of turmeric at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of turmeric at Wiktionary [[wikibooks:Cookbook:Turmeric |]] at the Wikibooks Cookbook subproject
[[wikibooks:Cookbook:Turmeric |]] at the Wikibooks Cookbook subproject
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Turmeric(24 May 2025, at 14:58編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Item:Q22304 |








