Potassium citrate: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Marked this version for translation |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | <languages /> | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
<!--T:1--> | |||
{{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| ImageFile = Kaliumcitrat V2.svg | | ImageFile = Kaliumcitrat V2.svg | ||
| Line 53: | Line 54: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--T:2--> | |||
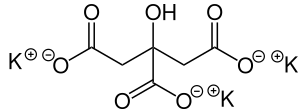
'''Potassium citrate''' (also known as '''tripotassium citrate''') is a [[potassium]] [[salt (chemistry)|salt]] of [[citric acid]] with the molecular formula K<sub>3</sub>C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>O<sub>7</sub>. It is a white, [[hygroscopic]] crystalline powder. It is odorless with a [[salt|saline]] taste. It contains 38.28% potassium by mass. In the monohydrate form, it is highly [[hygroscopic]] and [[deliquescent]]. | '''Potassium citrate''' (also known as '''tripotassium citrate''') is a [[potassium]] [[salt (chemistry)|salt]] of [[citric acid]] with the molecular formula K<sub>3</sub>C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>O<sub>7</sub>. It is a white, [[hygroscopic]] crystalline powder. It is odorless with a [[salt|saline]] taste. It contains 38.28% potassium by mass. In the monohydrate form, it is highly [[hygroscopic]] and [[deliquescent]]. | ||
<!--T:3--> | |||
As a [[food additive]], potassium citrate is used to regulate acidity, and is known as [[E number]] E332. Medicinally, it may be used to control [[kidney stone]]s derived from [[uric acid]] or [[cystine]]. | As a [[food additive]], potassium citrate is used to regulate acidity, and is known as [[E number]] E332. Medicinally, it may be used to control [[kidney stone]]s derived from [[uric acid]] or [[cystine]]. | ||
<!--T:4--> | |||
In 2020, it was the 297th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1{{nbsp}}million prescriptions. | In 2020, it was the 297th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1{{nbsp}}million prescriptions. | ||
<!--T:5--> | |||
==Synthesis== | ==Synthesis== | ||
Potassium citrate can be synthesized by the neutralization of [[citric acid]] which is achieved by the addition of [[potassium bicarbonate]], [[potassium carbonate]] or [[potassium hydroxide]] to it. The solution can then be filtered and the solvent can be evaporated till granulation. | Potassium citrate can be synthesized by the neutralization of [[citric acid]] which is achieved by the addition of [[potassium bicarbonate]], [[potassium carbonate]] or [[potassium hydroxide]] to it. The solution can then be filtered and the solvent can be evaporated till granulation. | ||
<!--T:6--> | |||
==Uses== | ==Uses== | ||
Potassium citrate is rapidly absorbed when given by mouth, and is excreted in the urine. Since it is an alkaline salt, it is effective in reducing the pain and frequency of [[urination]] when these are caused by highly acidic urine. It is used for this purpose in dogs and cats, but is chiefly employed as a non-irritating [[diuretic]]. | Potassium citrate is rapidly absorbed when given by mouth, and is excreted in the urine. Since it is an alkaline salt, it is effective in reducing the pain and frequency of [[urination]] when these are caused by highly acidic urine. It is used for this purpose in dogs and cats, but is chiefly employed as a non-irritating [[diuretic]]. | ||
<!--T:7--> | |||
Potassium citrate is an effective way to treat/manage [[Heart arrhythmia|arrhythmia]], if the patient is [[hypokalemia|hypokalemic]]. | Potassium citrate is an effective way to treat/manage [[Heart arrhythmia|arrhythmia]], if the patient is [[hypokalemia|hypokalemic]]. | ||
<!--T:8--> | |||
It is widely used to treat urinary calculi ([[kidney stones]]), and is often used by patients with [[cystinuria]]. A systematic review showed a significant reduction in the incidence of stone formation [[Relative risk|RR]] 0.26, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.68. | It is widely used to treat urinary calculi ([[kidney stones]]), and is often used by patients with [[cystinuria]]. A systematic review showed a significant reduction in the incidence of stone formation [[Relative risk|RR]] 0.26, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.68. | ||
<!--T:9--> | |||
It is also used as an [[alkalizing agent]] in the treatment of mild urinary tract infections, such as [[cystitis]]. | It is also used as an [[alkalizing agent]] in the treatment of mild urinary tract infections, such as [[cystitis]]. | ||
<!--T:10--> | |||
It is also used in many [[soft drinks]] as a [[buffering agent]]. | It is also used in many [[soft drinks]] as a [[buffering agent]]. | ||
<!--T:11--> | |||
Frequently used in an aqueous solution with other potassium salts, it is a [[Fire extinguisher#Wet_chemical_types|wet chemical fire suppressant]] that is particularly useful against kitchen fires. Its alkaline pH encourages [[saponification]] to insulate the fuel from oxidizing air, and the [[endothermic]] [[dehydration reaction]] absorbs heat energy to reduce temperatures. | Frequently used in an aqueous solution with other potassium salts, it is a [[Fire extinguisher#Wet_chemical_types|wet chemical fire suppressant]] that is particularly useful against kitchen fires. Its alkaline pH encourages [[saponification]] to insulate the fuel from oxidizing air, and the [[endothermic]] [[dehydration reaction]] absorbs heat energy to reduce temperatures. | ||
<!--T:12--> | |||
==Administration== | ==Administration== | ||
Potassium citrate liquid is usually administered by mouth in a diluted aqueous solution, because of its somewhat caustic effect on the stomach lining, and the potential for other mild health hazards. Pill tablets also exist in normal, and extended-release formulations. | Potassium citrate liquid is usually administered by mouth in a diluted aqueous solution, because of its somewhat caustic effect on the stomach lining, and the potential for other mild health hazards. Pill tablets also exist in normal, and extended-release formulations. | ||
<!--T:13--> | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
*Tanner, G.A. [http://jasn.asnjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/9/7/1242 "Potassium citrate improves renal function in rats with polycystic kidney disease"]. ''Journal of the American Society of Nephrology''. Retrieved December 17, 2016. | *Tanner, G.A. [http://jasn.asnjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/9/7/1242 "Potassium citrate improves renal function in rats with polycystic kidney disease"]. ''Journal of the American Society of Nephrology''. Retrieved December 17, 2016. | ||
<!--T:14--> | |||
{{Mineral supplements}} | {{Mineral supplements}} | ||
<!--T:15--> | |||
{{二次利用|date=19 April 2024}} | {{二次利用|date=19 April 2024}} | ||
[[Category:Food acidity regulators]] | [[Category:Food acidity regulators]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:30, 21 April 2024
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Tripotassium 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| K3C6H5O7 | |
| Molar mass | 306.395 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder hygroscopic |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.98 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) |
| Boiling point | 230 °C (446 °F; 503 K) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in glycerin insoluble in ethanol (95%) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 8.5 |
| Pharmacology | |
| A12BA02 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
170 mg/kg (IV, dog) 5400mg/kg (oral, rat) |
Potassium citrate (also known as tripotassium citrate) is a potassium salt of citric acid with the molecular formula K3C6H5O7. It is a white, hygroscopic crystalline powder. It is odorless with a saline taste. It contains 38.28% potassium by mass. In the monohydrate form, it is highly hygroscopic and deliquescent.
As a food additive, potassium citrate is used to regulate acidity, and is known as E number E332. Medicinally, it may be used to control kidney stones derived from uric acid or cystine.
In 2020, it was the 297th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions.
Synthesis
Potassium citrate can be synthesized by the neutralization of citric acid which is achieved by the addition of potassium bicarbonate, potassium carbonate or potassium hydroxide to it. The solution can then be filtered and the solvent can be evaporated till granulation.
Uses
Potassium citrate is rapidly absorbed when given by mouth, and is excreted in the urine. Since it is an alkaline salt, it is effective in reducing the pain and frequency of urination when these are caused by highly acidic urine. It is used for this purpose in dogs and cats, but is chiefly employed as a non-irritating diuretic.
Potassium citrate is an effective way to treat/manage arrhythmia, if the patient is hypokalemic.
It is widely used to treat urinary calculi (kidney stones), and is often used by patients with cystinuria. A systematic review showed a significant reduction in the incidence of stone formation RR 0.26, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.68.
It is also used as an alkalizing agent in the treatment of mild urinary tract infections, such as cystitis.
It is also used in many soft drinks as a buffering agent.
Frequently used in an aqueous solution with other potassium salts, it is a wet chemical fire suppressant that is particularly useful against kitchen fires. Its alkaline pH encourages saponification to insulate the fuel from oxidizing air, and the endothermic dehydration reaction absorbs heat energy to reduce temperatures.
Administration
Potassium citrate liquid is usually administered by mouth in a diluted aqueous solution, because of its somewhat caustic effect on the stomach lining, and the potential for other mild health hazards. Pill tablets also exist in normal, and extended-release formulations.
External links
- Tanner, G.A. "Potassium citrate improves renal function in rats with polycystic kidney disease". Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Potassium citrate(19 April 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Item:Q22113 |