Endocrine disease: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | <languages /> | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
<!--T:1--> | |||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) | {{Infobox medical condition (new) | ||
| name = Endocrine diseases | | name = Endocrine diseases | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
| caption = Major [[endocrine gland]]s. ([[Male]] left, [[female]] on the right.) '''1.''' [[Pineal gland]] '''2.''' [[Pituitary gland]] '''3.''' [[Thyroid gland]] '''4.''' [[Thymus]] '''5.''' [[Adrenal gland]] '''6.''' [[Pancreas]] '''7.''' [[Ovary]] '''8.''' [[Testes]] | | caption = Major [[endocrine gland]]s. ([[Male]] left, [[female]] on the right.) '''1.''' [[Pineal gland]] '''2.''' [[Pituitary gland]] '''3.''' [[Thyroid gland]] '''4.''' [[Thymus]] '''5.''' [[Adrenal gland]] '''6.''' [[Pancreas]] '''7.''' [[Ovary]] '''8.''' [[Testes]] | ||
| field = [[Endocrinology]] | | field = [[Endocrinology]] | ||
| | | QID = Q16861 | ||
| pronounce = | | pronounce = | ||
| synonyms = Endocrinopathy | | synonyms = Endocrinopathy | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--T:2--> | |||
'''Endocrine diseases''' are disorders of the [[endocrine system]]. The branch of [[medicine]] associated with endocrine disorders is known as [[endocrinology]]. | '''Endocrine diseases''' are disorders of the [[endocrine system]]. The branch of [[medicine]] associated with endocrine disorders is known as [[endocrinology]]. | ||
==Types of disease== | ==Types of disease== <!--T:3--> | ||
Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups: | Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups: | ||
# Endocrine gland hypofunction/hypo[[secretion]] (leading to hormone deficiency) | # Endocrine gland hypofunction/hypo[[secretion]] (leading to hormone deficiency) | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
# Tumours (benign or malignant) of endocrine glands | # Tumours (benign or malignant) of endocrine glands | ||
<!--T:4--> | |||
Endocrine disorders are often quite complex, involving a mixed picture of hyposecretion and hypersecretion because of the feedback mechanisms involved in the endocrine system. For example, most forms of [[hyperthyroidism]] are associated with an excess of [[thyroid hormone]] and a low level of [[thyroid stimulating hormone]]. | Endocrine disorders are often quite complex, involving a mixed picture of hyposecretion and hypersecretion because of the feedback mechanisms involved in the endocrine system. For example, most forms of [[hyperthyroidism]] are associated with an excess of [[thyroid hormone]] and a low level of [[thyroid stimulating hormone]]. | ||
==List of diseases== | ==List of diseases== <!--T:5--> | ||
=== Glucose homeostasis disorders === | === Glucose homeostasis disorders === <!--T:6--> | ||
* [[Diabetes]] | * [[Diabetes]] | ||
** [[Diabetes mellitus type 1|Type 1 Diabetes]] | ** [[Diabetes mellitus type 1|Type 1 Diabetes]] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 53: | ||
* [[Glucagonoma]] | * [[Glucagonoma]] | ||
=== Thyroid disorders === | === Thyroid disorders === <!--T:7--> | ||
* [[Goitre]] | * [[Goitre]] | ||
* [[Hyperthyroidism]] | * [[Hyperthyroidism]] | ||
| Line 67: | Line 70: | ||
* [[Thyroid hormone resistance]] | * [[Thyroid hormone resistance]] | ||
=== Calcium homeostasis disorders and Metabolic bone disease === | === Calcium homeostasis disorders and Metabolic bone disease === <!--T:8--> | ||
* [[Parathyroid gland]] disorders | * [[Parathyroid gland]] disorders | ||
** [[Hyperparathyroidism]] | ** [[Hyperparathyroidism]] | ||
| Line 82: | Line 85: | ||
* [[Osteomalacia]] | * [[Osteomalacia]] | ||
===Pituitary gland disorders=== | ===Pituitary gland disorders=== <!--T:9--> | ||
====Posterior pituitary==== | ====Posterior pituitary==== <!--T:10--> | ||
* [[Diabetes insipidus]] | * [[Diabetes insipidus]] | ||
* Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH) | * Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH) | ||
====Anterior pituitary==== | ====Anterior pituitary==== <!--T:11--> | ||
* [[Hypopituitarism]] (or [[hypopituitarism|Panhypopituitarism]]) | * [[Hypopituitarism]] (or [[hypopituitarism|Panhypopituitarism]]) | ||
* [[Pituitary tumor]]s | * [[Pituitary tumor]]s | ||
| Line 96: | Line 99: | ||
** [[Cushing's disease]] | ** [[Cushing's disease]] | ||
=== Adrenal gland disorders === | === Adrenal gland disorders === <!--T:12--> | ||
* [[Addison's disease]] | * [[Addison's disease]] | ||
* [[Adrenal crisis]] | * [[Adrenal crisis]] | ||
| Line 107: | Line 110: | ||
* [[Hyperaldosteronism]] | * [[Hyperaldosteronism]] | ||
=== Sex hormone disorders === | === Sex hormone disorders === <!--T:13--> | ||
* [[Disorders of sex development]] or intersex disorders | * [[Disorders of sex development]] or intersex disorders | ||
** [[Hermaphroditism]] | ** [[Hermaphroditism]] | ||
| Line 128: | Line 131: | ||
** [[Polycystic ovary syndrome|Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)]] | ** [[Polycystic ovary syndrome|Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)]] | ||
=== Tumours of the endocrine glands not mentioned elsewhere === | === Tumours of the endocrine glands not mentioned elsewhere === <!--T:14--> | ||
[[File:Multiple endocrine neoplasia.png|thumb|[[Multiple endocrine neoplasia]] types.]] | [[File:Multiple endocrine neoplasia.png|thumb|[[Multiple endocrine neoplasia]] types.]] | ||
* [[Multiple endocrine neoplasia]] | * [[Multiple endocrine neoplasia]] | ||
| Line 136: | Line 139: | ||
* [[Carcinoid syndrome]] | * [[Carcinoid syndrome]] | ||
=== See also separate organs === | === See also separate organs === <!--T:15--> | ||
* [[Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome]]s | * [[Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome]]s | ||
* [[Incidentaloma]] - an unexpected finding on diagnostic imaging, often of endocrine glands | * [[Incidentaloma]] - an unexpected finding on diagnostic imaging, often of endocrine glands | ||
==Endocrine emergencies== | ==Endocrine emergencies== <!--T:16--> | ||
In endocrinology, medical emergencies include [[diabetic ketoacidosis]], [[hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state]], [[hypoglycemia|hypoglycemic coma]], [[adrenal insufficiency|acute adrenocortical insufficiency]], [[phaeochromocytoma]] crisis, [[hypercalcemic crisis]], [[thyroid storm]], [[myxoedema coma]] and [[pituitary apoplexy]]. | In endocrinology, medical emergencies include [[diabetic ketoacidosis]], [[hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state]], [[hypoglycemia|hypoglycemic coma]], [[adrenal insufficiency|acute adrenocortical insufficiency]], [[phaeochromocytoma]] crisis, [[hypercalcemic crisis]], [[thyroid storm]], [[myxoedema coma]] and [[pituitary apoplexy]]. | ||
<!--T:17--> | |||
Emergencies arising from decompensated [[pheochromocytoma]]s or [[parathyroid]] adenomas are sometimes referred for emergency resection when aggressive medical therapies fail to control the patient's state, however the surgical risks are significant, especially blood pressure lability and the possibility of cardiovascular collapse after resection (due to a brutal drop in respectively catecholamines and calcium, which must be compensated with gradual normalization). It remains debated when emergency surgery is appropriate as opposed to urgent or elective surgery after continued attempts to stabilize the patient, notably in view of newer and more efficient medications and protocols. | Emergencies arising from decompensated [[pheochromocytoma]]s or [[parathyroid]] adenomas are sometimes referred for emergency resection when aggressive medical therapies fail to control the patient's state, however the surgical risks are significant, especially blood pressure lability and the possibility of cardiovascular collapse after resection (due to a brutal drop in respectively catecholamines and calcium, which must be compensated with gradual normalization). It remains debated when emergency surgery is appropriate as opposed to urgent or elective surgery after continued attempts to stabilize the patient, notably in view of newer and more efficient medications and protocols. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== <!--T:18--> | ||
* [[List of MeSH codes (C19)]] | * [[List of MeSH codes (C19)]] | ||
* [[List of ICD-9 codes 240-279: Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases, and immunity disorders]] | * [[List of ICD-9 codes 240-279: Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases, and immunity disorders]] | ||
==References== | ==References== <!--T:19--> | ||
{{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
== External links == | == External links == <!--T:20--> | ||
{{Medical resources | {{Medical resources | ||
| DiseasesDB = | | DiseasesDB = | ||
| Line 178: | Line 182: | ||
{{Disease groups}} | {{Disease groups}} | ||
<!--T:21--> | |||
{{二次利用|date=17 October 2023}} | {{二次利用|date=17 October 2023}} | ||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Endocrine Disease}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Endocrine Disease}} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:22, 17 February 2024
| Endocrine diseases | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Endocrinopathy |
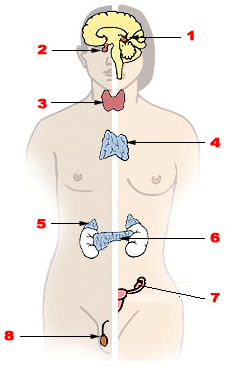 | |
| Major endocrine glands. (Male left, female on the right.) 1. Pineal gland 2. Pituitary gland 3. Thyroid gland 4. Thymus 5. Adrenal gland 6. Pancreas 7. Ovary 8. Testes | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.
Types of disease
Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups:
- Endocrine gland hypofunction/hyposecretion (leading to hormone deficiency)
- Endocrine gland hyperfunction/hypersecretion (leading to hormone excess)
- Tumours (benign or malignant) of endocrine glands
Endocrine disorders are often quite complex, involving a mixed picture of hyposecretion and hypersecretion because of the feedback mechanisms involved in the endocrine system. For example, most forms of hyperthyroidism are associated with an excess of thyroid hormone and a low level of thyroid stimulating hormone.
List of diseases
Glucose homeostasis disorders
- Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Gestational Diabetes
- Mature Onset Diabetes of the Young
- Diabetic myopathy
- Hypoglycemia
- Glucagonoma
Thyroid disorders
- Goitre
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroid myopathies
- Thyroiditis
- Thyroid cancer
- Thyroid hormone resistance
Calcium homeostasis disorders and Metabolic bone disease
- Parathyroid gland disorders
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
- Hyperparathyroid myopathy
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism
- Hypoparathyroid myopathy
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Osteoporosis
- Osteitis deformans (Paget's disease of bone)
- Rickets
- Osteomalacia
Pituitary gland disorders
Posterior pituitary
- Diabetes insipidus
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)
Anterior pituitary
Adrenal gland disorders
- Addison's disease
- Adrenal crisis
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Adrenal tumour
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Hypercortisolism (Cushing's disease)
- Hypoaldosteronism
- Hyperaldosteronism
Sex hormone disorders
- Disorders of sex development or intersex disorders
- Hypogonadism (Gonadotropin deficiency)
- Inherited (genetic and chromosomal) disorders
- Acquired disorders
- Ovarian failure (also known as Premature Menopause)
- Testicular failure
- Disorders of Puberty
- Menstrual function or fertility disorders
Tumours of the endocrine glands not mentioned elsewhere
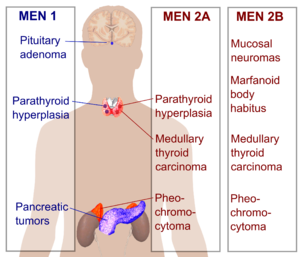
See also separate organs
- Autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes
- Incidentaloma - an unexpected finding on diagnostic imaging, often of endocrine glands
Endocrine emergencies
In endocrinology, medical emergencies include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, hypoglycemic coma, acute adrenocortical insufficiency, phaeochromocytoma crisis, hypercalcemic crisis, thyroid storm, myxoedema coma and pituitary apoplexy.
Emergencies arising from decompensated pheochromocytomas or parathyroid adenomas are sometimes referred for emergency resection when aggressive medical therapies fail to control the patient's state, however the surgical risks are significant, especially blood pressure lability and the possibility of cardiovascular collapse after resection (due to a brutal drop in respectively catecholamines and calcium, which must be compensated with gradual normalization). It remains debated when emergency surgery is appropriate as opposed to urgent or elective surgery after continued attempts to stabilize the patient, notably in view of newer and more efficient medications and protocols.
See also
- List of MeSH codes (C19)
- List of ICD-9 codes 240-279: Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases, and immunity disorders
References
External links
- Endocrine+system+diseases at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- MedlinePlus Overview endocrinediseases
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Endocrine disease(17 October 2023編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Item:Q16861 |