Amino acid: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==General structure== | ==General structure== | ||
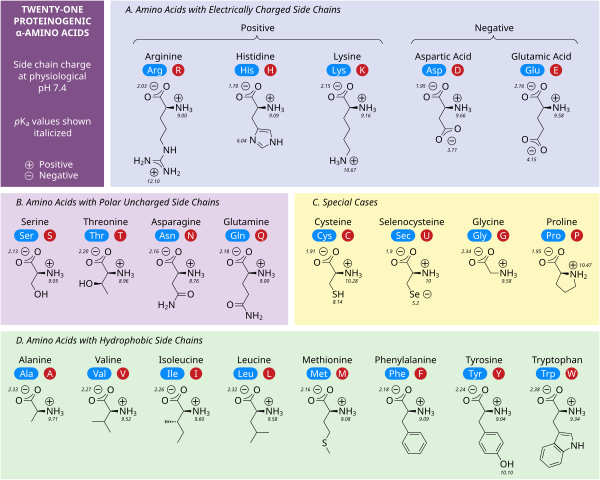
[[File:ProteinogenicAminoAcids.svg|thumb|600x600px|The 21 [[Proteinogenic amino acid|proteinogenic α-amino acids]] found in [[Eukaryote|eukaryotes]], grouped according to their side chains' [[PKa|p''K''<sub>a</sub>]] values and charges carried at [[PH#Living systems|physiological pH (7.4)]].]] | [[File:ProteinogenicAminoAcids.svg|thumb|600x600px|The 21 [[Proteinogenic amino acid|proteinogenic α-amino acids]] found in [[Eukaryote|eukaryotes]], grouped according to their side chains' [[PKa|p''K''<sub>a</sub>]] values and charges carried at [[PH#Living systems|physiological pH (7.4)]].]] | ||
'''2-''', '''alpha-''', or '''α-amino acids''' have the generic [[Chemical formula|formula]] {{chem2|H2NCHRCOOH}} in most cases, | '''2-''', '''alpha-''', or '''α-amino acids''' have the generic [[Chemical formula|formula]] {{chem2|H2NCHRCOOH}} in most cases, where R is an [[organic chemistry|organic]] [[substituent]] known as a "[[Substituent|side chain]]". | ||
Of the many hundreds of described amino acids, 22 are [[Proteinogenic amino acid|proteinogenic]] ("protein-building"). It is these 22 compounds that combine to give a vast array of peptides and proteins assembled by [[Ribosome|ribosomes]]. Non-proteinogenic or modified amino acids may arise from [[post-translational modification]] or during [[nonribosomal peptide]] synthesis. | Of the many hundreds of described amino acids, 22 are [[Proteinogenic amino acid|proteinogenic]] ("protein-building"). It is these 22 compounds that combine to give a vast array of peptides and proteins assembled by [[Ribosome|ribosomes]]. Non-proteinogenic or modified amino acids may arise from [[post-translational modification]] or during [[nonribosomal peptide]] synthesis. | ||
Revision as of 10:23, 29 March 2024

Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life.
Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups (alpha- (α-), beta- (β-), gamma- (γ-) amino acids, etc.), other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid residues form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence.
Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC-IUBMB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature in terms of the fictitious "neutral" structure shown in the illustration. For example, the systematic name of alanine is 2-aminopropanoic acid, based on the formula CH
3−CH(NH
2)−COOH. The Commission justified this approach as follows:
The systematic names and formulas given refer to hypothetical forms in which amino groups are unprotonated and carboxyl groups are undissociated. This convention is useful to avoid various nomenclatural problems but should not be taken to imply that these structures represent an appreciable fraction of the amino-acid molecules.
History
The first few amino acids were discovered in the early 1800s. In 1806, French chemists Louis-Nicolas Vauquelin and Pierre Jean Robiquet isolated a compound from asparagus that was subsequently named asparagine, the first amino acid to be discovered. Cystine was discovered in 1810, although its monomer, cysteine, remained undiscovered until 1884. Glycine and leucine were discovered in 1820. The last of the 20 common amino acids to be discovered was threonine in 1935 by William Cumming Rose, who also determined the essential amino acids and established the minimum daily requirements of all amino acids for optimal growth.
The unity of the chemical category was recognized by Wurtz in 1865, but he gave no particular name to it. The first use of the term "amino acid" in the English language dates from 1898, while the German term, Aminosäure, was used earlier. Proteins were found to yield amino acids after enzymatic digestion or acid hydrolysis. In 1902, Emil Fischer and Franz Hofmeister independently proposed that proteins are formed from many amino acids, whereby bonds are formed between the amino group of one amino acid with the carboxyl group of another, resulting in a linear structure that Fischer termed "peptide".
General structure
2-, alpha-, or α-amino acids have the generic formula H
2NCHRCOOH in most cases, where R is an organic substituent known as a "side chain".
Of the many hundreds of described amino acids, 22 are proteinogenic ("protein-building"). It is these 22 compounds that combine to give a vast array of peptides and proteins assembled by ribosomes. Non-proteinogenic or modified amino acids may arise from post-translational modification or during nonribosomal peptide synthesis.
Chirality
The carbon atom next to the carboxyl group is called the α–carbon. In proteinogenic amino acids, it bears the amine and the R group or side chain specific to each amino acid. With four distinct substituents, the α–carbon is stereogenic in all α-amino acids except glycine. All chiral proteogenic amino acids have the L configuration. They are "left-handed" enantiomers, which refers to the stereoisomers of the alpha carbon.
A few D-amino acids ("right-handed") have been found in nature, e.g., in bacterial envelopes, as a neuromodulator (D-serine), and in some antibiotics. Rarely, D-amino acid residues are found in proteins, and are converted from the L-amino acid as a post-translational modification.[lower-alpha 1]
Side chains
Polar charged side chains
Five amino acids possess a charge at neutral pH. Often these side chains appear at the surfaces on proteins to enable their solubility in water, and side chains with opposite charges form important electrostatic contacts called salt bridges that maintain structures within a single protein or between interfacing proteins. Many proteins bind metal into their structures specifically, and these interactions are commonly mediated by charged side chains such as aspartate, glutamate and histidine. Under certain conditions, each ion-forming group can be charged, forming double salts.
The two negatively charged amino acids at neutral pH are aspartate (Asp, D) and glutamate (Glu, E). The anionic carboxylate groups behave as Brønsted bases in most circumstances. Enzymes in very low pH environments, like the aspartic protease pepsin in mammalian stomachs, may have catalytic aspartate or glutamate residues that act as Brønsted acids.

There are three amino acids with side chains that are cations at neutral pH: arginine (Arg, R), lysine (Lys, K) and histidine (His, H). Arginine has a charged guanidino group and lysine a charged alkyl amino group, and are fully protonated at pH 7. Histidine's imidazole group has a pKa of 6.0, and is only around 10 % protonated at neutral pH. Because histidine is easily found in its basic and conjugate acid forms it often participates in catalytic proton transfers in enzyme reactions.
Polar uncharged side chains
The polar, uncharged amino acids serine (Ser, S), threonine (Thr, T), asparagine (Asn, N) and glutamine (Gln, Q) readily form hydrogen bonds with water and other amino acids. They do not ionize in normal conditions, a prominent exception being the catalytic serine in serine proteases. This is an example of severe perturbation, and is not characteristic of serine residues in general. Threonine has two chiral centers, not only the L (2S) chiral center at the α-carbon shared by all amino acids apart from achiral glycine, but also (3R) at the β-carbon. The full stereochemical specification is (2S,3R)-L-threonine.
Hydrophobic side chains
Nonpolar amino acid interactions are the primary driving force behind the processes that fold proteins into their functional three dimensional structures. None of these amino acids' side chains ionize easily, and therefore do not have pKas, with the exception of tyrosine (Tyr, Y). The hydroxyl of tyrosine can deprotonate at high pH forming the negatively charged phenolate. Because of this one could place tyrosine into the polar, uncharged amino acid category, but its very low solubility in water matches the characteristics of hydrophobic amino acids well.
Special case side chains
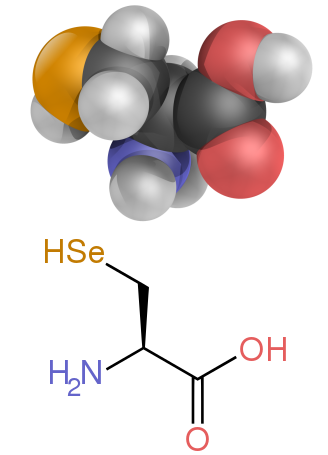
Several side chains are not described well by the charged, polar and hydrophobic categories. Glycine (Gly, G) could be considered a polar amino acid since its small size means that its solubility is largely determined by the amino and carboxylate groups. However, the lack of any side chain provides glycine with a unique flexibility among amino acids with large ramifications to protein folding. Cysteine (Cys, C) can also form hydrogen bonds readily, which would place it in the polar amino acid category, though it can often be found in protein structures forming covalent bonds, called disulphide bonds, with other cysteines. These bonds influence the folding and stability of proteins, and are essential in the formation of antibodies. Proline (Pro, P) has an alkyl side chain and could be considered hydrophobic, but because the side chain joins back onto the alpha amino group it becomes particularly inflexible when incorporated into proteins. Similar to glycine this influences protein structure in a way unique among amino acids. Selenocysteine (Sec, U) is a rare amino acid not directly encoded by DNA, but is incorporated into proteins via the ribosome. Selenocysteine has a lower redox potential compared to the similar cysteine, and participates in several unique enzymatic reactions. Pyrrolysine (Pyl, O) is another amino acid not encoded in DNA, but synthesized into protein by ribosomes. It is found in archaeal species where it participates in the catalytic activity of several methyltransferases.
β- and γ-amino acids
Amino acids with the structure NH+
3−CXY−CXY−CO−
2, such as β-alanine, a component of carnosine and a few other peptides, are β-amino acids. Ones with the structure NH+
3−CXY−CXY−CXY−CO−
2 are γ-amino acids, and so on, where X and Y are two substituents (one of which is normally H).
Zwitterions

The common natural forms of amino acids have a zwitterionic structure, with −NH+
3 (−NH+
2− in the case of proline) and −CO−
2 functional groups attached to the same C atom, and are thus α-amino acids, and are the only ones found in proteins during translation in the ribosome.
In aqueous solution at pH close to neutrality, amino acids exist as zwitterions, i.e. as dipolar ions with both NH+
3 and CO−
2 in charged states, so the overall structure is NH+
3−CHR−CO−
2. At physiological pH the so-called "neutral forms" −NH
2−CHR−CO
2H are not present to any measurable degree. Although the two charges in the zwitterion structure add up to zero it is misleading to call a species with a net charge of zero "uncharged".
In strongly acidic conditions (pH below 3), the carboxylate group becomes protonated and the structure becomes an ammonio carboxylic acid, NH+
3−CHR−CO
2H. This is relevant for enzymes like pepsin that are active in acidic environments such as the mammalian stomach and lysosomes, but does not significantly apply to intracellular enzymes. In highly basic conditions (pH greater than 10, not normally seen in physiological conditions), the ammonio group is deprotonated to give NH
2−CHR−CO−
2.
Although various definitions of acids and bases are used in chemistry, the only one that is useful for chemistry in aqueous solution is that of Brønsted: an acid is a species that can donate a proton to another species, and a base is one that can accept a proton. This criterion is used to label the groups in the above illustration. The carboxylate side chains of aspartate and glutamate residues are the principal Brønsted bases in proteins. Likewise, lysine, tyrosine and cysteine will typically act as a Brønsted acid. Histidine under these conditions can act both as a Brønsted acid and a base.
Isoelectric point

For amino acids with uncharged side-chains the zwitterion predominates at pH values between the two pKa values, but coexists in equilibrium with small amounts of net negative and net positive ions. At the midpoint between the two pKa values, the trace amount of net negative and trace of net positive ions balance, so that average net charge of all forms present is zero. This pH is known as the isoelectric point pI, so pI = 1/2(pKa1 + pKa2).
For amino acids with charged side chains, the pKa of the side chain is involved. Thus for aspartate or glutamate with negative side chains, the terminal amino group is essentially entirely in the charged form −NH+
3, but this positive charge needs to be balanced by the state with just one C-terminal carboxylate group is negatively charged. This occurs halfway between the two carboxylate pKa values: pI = 1/2(pKa1 + pKa(R)), where pKa(R) is the side chain pKa.
Similar considerations apply to other amino acids with ionizable side-chains, including not only glutamate (similar to aspartate), but also cysteine, histidine, lysine, tyrosine and arginine with positive side chains.
Amino acids have zero mobility in electrophoresis at their isoelectric point, although this behaviour is more usually exploited for peptides and proteins than single amino acids. Zwitterions have minimum solubility at their isoelectric point, and some amino acids (in particular, with nonpolar side chains) can be isolated by precipitation from water by adjusting the pH to the required isoelectric point.
Physicochemical properties
The 20 canonical amino acids can be classified according to their properties. Important factors are charge, hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity, size, and functional groups. These properties influence protein structure and protein–protein interactions. The water-soluble proteins tend to have their hydrophobic residues (Leu, Ile, Val, Phe, and Trp) buried in the middle of the protein, whereas hydrophilic side chains are exposed to the aqueous solvent. (In biochemistry, a residue refers to a specific monomer within the polymeric chain of a polysaccharide, protein or nucleic acid.) The integral membrane proteins tend to have outer rings of exposed hydrophobic amino acids that anchor them in the lipid bilayer. Some peripheral membrane proteins have a patch of hydrophobic amino acids on their surface that sticks to the membrane. In a similar fashion, proteins that have to bind to positively charged molecules have surfaces rich in negatively charged amino acids such as glutamate and aspartate, while proteins binding to negatively charged molecules have surfaces rich in positively charged amino acids like lysine and arginine. For example, lysine and arginine are present in large amounts in the low-complexity regions of nucleic-acid binding proteins. There are various hydrophobicity scales of amino acid residues.
Some amino acids have special properties. Cysteine can form covalent disulfide bonds to other cysteine residues. Proline forms a cycle to the polypeptide backbone, and glycine is more flexible than other amino acids.
Glycine and proline are strongly present within low complexity regions of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins, whereas the opposite is the case with cysteine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, methionine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, which are highly reactive, or complex, or hydrophobic.
Many proteins undergo a range of posttranslational modifications, whereby additional chemical groups are attached to the amino acid residue side chains sometimes producing lipoproteins (that are hydrophobic), or glycoproteins (that are hydrophilic) allowing the protein to attach temporarily to a membrane. For example, a signaling protein can attach and then detach from a cell membrane, because it contains cysteine residues that can have the fatty acid palmitic acid added to them and subsequently removed.
Table of standard amino acid abbreviations and properties
Although one-letter symbols are included in the table, IUPAC–IUBMB recommend that "Use of the one-letter symbols should be restricted to the comparison of long sequences".
The one-letter notation was chosen by IUPAC-IUB based on the following rules:
- Initial letters are used where there is no ambuiguity: C cysteine, H histidine, I isoleucine, M methionine, S serine, V valine,
- Where arbitrary assignment is needed, the structurally simpler amino acids are given precedence: A Alanine, G glycine, L leucine, P proline, T threonine,
- F PHenylalanine and R aRginine are assigned by being phonetically suggestive,
- W tryptophane is assigned based on the double ring being visually suggestive to the bulky letter W,
- K lysine and Y tyrosine are assigned as alphabetically nearest to their initials L and T (note that U was avoided for its similarity with V, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids); for tyrosine the mnemonic tYrosine was also proposed,
- D aspartate was assigned arbitrarily, with the proposed mnemonic asparDic acid; E glutamate was assigned in alphabetical sequence being larger by merely one methylene –CH2– group,
- N asparagine was assigned arbitrarily, with the proposed mnemonic asparagiNe; Q glutamine was assigned in alphabetical sequence of those still available (note again that O was avoided due to similarity with D), with the proposed mnemonic Qlutamine.
| Amino acid | 3- and 1-letter symbols | Side chain | Hydropathy index |
Molar absorptivity | Molecular mass | Abundance in proteins (%) |
Standard genetic coding, IUPAC notation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 1 | Class | Chemical polarity | Net charge at pH 7.4 |
Wavelength, λmax (nm) |
Coefficient ε (mM−1·cm−1) | |||||
| Alanine | Ala | A | Aliphatic | Nonpolar | Neutral | 1.8 | 89.094 | 8.76 | GCN | ||
| Arginine | Arg | R | Fixed cation | Basic polar | Positive | −4.5 | 174.203 | 5.78 | MGR, CGY | ||
| Asparagine | Asn | N | Amide | Polar | Neutral | −3.5 | 132.119 | 3.93 | AAY | ||
| Aspartate | Asp | D | Anion | Brønsted base | Negative | −3.5 | 133.104 | 5.49 | GAY | ||
| Cysteine | Cys | C | Thiol | Brønsted acid | Neutral | 2.5 | 250 | 0.3 | 121.154 | 1.38 | UGY |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q | Amide | Polar | Neutral | −3.5 | 146.146 | 3.9 | CAR | ||
| Glutamate | Glu | E | Anion | Brønsted base | Negative | −3.5 | 147.131 | 6.32 | GAR | ||
| Glycine | Gly | G | Aliphatic | Nonpolar | Neutral | −0.4 | 75.067 | 7.03 | GGN | ||
| Histidine | His | H | Cationic | Brønsted acid and base | Positive, 10% Neutral, 90% |
−3.2 | 211 | 5.9 | 155.156 | 2.26 | CAY |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I | Aliphatic | Nonpolar | Neutral | 4.5 | 131.175 | 5.49 | AUH | ||
| Leucine | Leu | L | Aliphatic | Nonpolar | Neutral | 3.8 | 131.175 | 9.68 | YUR, CUY | ||
| Lysine | Lys | K | Cation | Brønsted acid | Positive | −3.9 | 146.189 | 5.19 | AAR | ||
| Methionine | Met | M | Thioether | Nonpolar | Neutral | 1.9 | 149.208 | 2.32 | AUG | ||
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F | Aromatic | Nonpolar | Neutral | 2.8 | 257, 206, 188 | 0.2, 9.3, 60.0 | 165.192 | 3.87 | UUY |
| Proline | Pro | P | Cyclic | Nonpolar | Neutral | −1.6 | 115.132 | 5.02 | CCN | ||
| Serine | Ser | S | Hydroxylic | Polar | Neutral | −0.8 | 105.093 | 7.14 | UCN, AGY | ||
| Threonine | Thr | T | Hydroxylic | Polar | Neutral | −0.7 | 119.119 | 5.53 | ACN | ||
| Tryptophan | Trp | W | Aromatic | Nonpolar | Neutral | −0.9 | 280, 219 | 5.6, 47.0 | 204.228 | 1.25 | UGG |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y | Aromatic | Brønsted acid | Neutral | −1.3 | 274, 222, 193 | 1.4, 8.0, 48.0 | 181.191 | 2.91 | UAY |
| Valine | Val | V | Aliphatic | Nonpolar | Neutral | 4.2 | 117.148 | 6.73 | GUN | ||
Two additional amino acids are in some species coded for by codons that are usually interpreted as stop codons:
| 21st and 22nd amino acids | 3-letter | 1-letter | Molecular mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selenocysteine | Sec | U | 168.064 |
| Pyrrolysine | Pyl | O | 255.313 |
In addition to the specific amino acid codes, placeholders are used in cases where chemical or crystallographic analysis of a peptide or protein cannot conclusively determine the identity of a residue. They are also used to summarize conserved protein sequence motifs. The use of single letters to indicate sets of similar residues is similar to the use of abbreviation codes for degenerate bases.
| Ambiguous amino acids | 3-letter | 1-letter | Amino acids included | Codons included |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any / unknown | Xaa | X | All | NNN |
| Asparagine or aspartate | Asx | B | D, N | RAY |
| Glutamine or glutamate | Glx | Z | E, Q | SAR |
| Leucine or isoleucine | Xle | J | I, L | YTR, ATH, CTY |
| Hydrophobic | Φ | V, I, L, F, W, Y, M | NTN, TAY, TGG | |
| Aromatic | Ω | F, W, Y, H | YWY, TTY, TGG | |
| Aliphatic (non-aromatic) | Ψ | V, I, L, M | VTN, TTR | |
| Small | π | P, G, A, S | BCN, RGY, GGR | |
| Hydrophilic | ζ | S, T, H, N, Q, E, D, K, R | VAN, WCN, CGN, AGY | |
| Positively-charged | + | K, R, H | ARR, CRY, CGR | |
| Negatively-charged | − | D, E | GAN |
Unk is sometimes used instead of Xaa, but is less standard.
Ter or * (from termination) is used in notation for mutations in proteins when a stop codon occurs. It corresponds to no amino acid at all.
In addition, many nonstandard amino acids have a specific code. For example, several peptide drugs, such as Bortezomib and MG132, are artificially synthesized and retain their protecting groups, which have specific codes. Bortezomib is Pyz–Phe–boroLeu, and MG132 is Z–Leu–Leu–Leu–al. To aid in the analysis of protein structure, photo-reactive amino acid analogs are available. These include photoleucine (pLeu) and photomethionine (pMet).
Occurrence and functions in biochemistry
Proteinogenic amino acids
Amino acids are the precursors to proteins. They join by condensation reactions to form short polymer chains called peptides or longer chains called either polypeptides or proteins. These chains are linear and unbranched, with each amino acid residue within the chain attached to two neighboring amino acids. In nature, the process of making proteins encoded by DNA/RNA genetic material is called translation and involves the step-by-step addition of amino acids to a growing protein chain by a ribozyme that is called a ribosome The order in which the amino acids are added is read through the genetic code from an mRNA template, which is an RNA copy of one of the organism's genes.
Twenty-two amino acids are naturally incorporated into polypeptides and are called proteinogenic or natural amino acids. Of these, 20 are encoded by the universal genetic code. The remaining 2, selenocysteine and pyrrolysine, are incorporated into proteins by unique synthetic mechanisms. Selenocysteine is incorporated when the mRNA being translated includes a SECIS element, which causes the UGA codon to encode selenocysteine instead of a stop codon. Pyrrolysine is used by some methanogenic archaea in enzymes that they use to produce methane. It is coded for with the codon UAG, which is normally a stop codon in other organisms. This UAG codon is followed by a PYLIS downstream sequence.
Several independent evolutionary studies have suggested that Gly, Ala, Asp, Val, Ser, Pro, Glu, Leu, Thr may belong to a group of amino acids that constituted the early genetic code, whereas Cys, Met, Tyr, Trp, His, Phe may belong to a group of amino acids that constituted later additions of the genetic code.
Standard vs nonstandard amino acids
The 20 amino acids that are encoded directly by the codons of the universal genetic code are called standard or canonical amino acids. A modified form of methionine (N-formylmethionine) is often incorporated in place of methionine as the initial amino acid of proteins in bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts. Other amino acids are called nonstandard or non-canonical. Most of the nonstandard amino acids are also non-proteinogenic (i.e. they cannot be incorporated into proteins during translation), but two of them are proteinogenic, as they can be incorporated translationally into proteins by exploiting information not encoded in the universal genetic code.
The two nonstandard proteinogenic amino acids are selenocysteine (present in many non-eukaryotes as well as most eukaryotes, but not coded directly by DNA) and pyrrolysine (found only in some archaea and at least one bacterium). The incorporation of these nonstandard amino acids is rare. For example, 25 human proteins include selenocysteine in their primary structure, and the structurally characterized enzymes (selenoenzymes) employ selenocysteine as the catalytic moiety in their active sites. Pyrrolysine and selenocysteine are encoded via variant codons. For example, selenocysteine is encoded by stop codon and SECIS element.
N-formylmethionine (which is often the initial amino acid of proteins in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts) is generally considered as a form of methionine rather than as a separate proteinogenic amino acid. Codon–tRNA combinations not found in nature can also be used to "expand" the genetic code and form novel proteins known as alloproteins incorporating non-proteinogenic amino acids.
Non-proteinogenic amino acids
Aside from the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, many non-proteinogenic amino acids are known. Those either are not found in proteins (for example carnitine, GABA, levothyroxine) or are not produced directly and in isolation by standard cellular machinery. For example, hydroxyproline , is synthesised from proline. Another example is selenomethionine).
Non-proteinogenic amino acids that are found in proteins are formed by post-translational modification. Such modifications can also determine the localization of the protein, e.g., the addition of long hydrophobic groups can cause a protein to bind to a phospholipid membrane. Examples:
- the carboxylation of glutamate allows for better binding of calcium cations,
- Hydroxyproline, generated by hydroxylation of proline, is a major component of the connective tissue collagen.
- Hypusine in the translation initiation factor EIF5A, contains a modification of lysine.
Some non-proteinogenic amino acids are not found in proteins. Examples include 2-aminoisobutyric acid and the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid. Non-proteinogenic amino acids often occur as intermediates in the metabolic pathways for standard amino acids – for example, ornithine and citrulline occur in the urea cycle, part of amino acid catabolism (see below). A rare exception to the dominance of α-amino acids in biology is the β-amino acid beta alanine (3-aminopropanoic acid), which is used in plants and microorganisms in the synthesis of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), a component of coenzyme A.
In mammalian nutrition
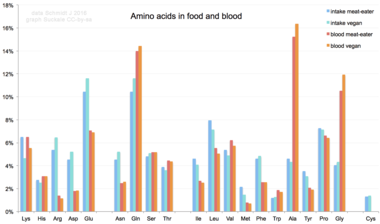
Amino acids are not typical component of food: animals eat proteins. The protein is broken down into amino acids in the process of digestion. They are then used to synthesize new proteins, other biomolecules, or are oxidized to urea and carbon dioxide as a source of energy. The oxidation pathway starts with the removal of the amino group by a transaminase; the amino group is then fed into the urea cycle. The other product of transamidation is a keto acid that enters the citric acid cycle. Glucogenic amino acids can also be converted into glucose, through gluconeogenesis.
Of the 20 standard amino acids, nine (His, Ile, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Thr, Trp and Val) are called essential amino acids because the human body cannot synthesize them from other compounds at the level needed for normal growth, so they must be obtained from food.
Semi-essential and conditionally essential amino acids, and juvenile requirements
In addition, cysteine, tyrosine, and arginine are considered semiessential amino acids, and taurine a semi-essential aminosulfonic acid in children. Some amino acids are conditionally essential for certain ages or medical conditions. Essential amino acids may also vary from species to species. The metabolic pathways that synthesize these monomers are not fully developed.
Non-protein functions
Many proteinogenic and non-proteinogenic amino acids have biological functions beyond being precursors to proteins and peptides.In humans, amino acids also have important roles in diverse biosynthetic pathways. Defenses against herbivores in plants sometimes employ amino acids. Examples:
Standard amino acids
- Tryptophan is a precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin.
- Tyrosine (and its precursor phenylalanine) are precursors of the catecholamine neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine and various trace amines.
- Phenylalanine is a precursor of phenethylamine and tyrosine in humans. In plants, it is a precursor of various phenylpropanoids, which are important in plant metabolism.
- Glycine is a precursor of porphyrins such as heme.
- Arginine is a precursor of nitric oxide.
- Ornithine and S-adenosylmethionine are precursors of polyamines.
- Aspartate, glycine, and glutamine are precursors of nucleotides. However, not all of the functions of other abundant nonstandard amino acids are known.
Roles for nonstandard amino acids
- Carnitine is used in lipid transport.
- gamma-aminobutyric acid is a neurotransmitter.
- 5-HTP (5-hydroxytryptophan) is used for experimental treatment of depression.
- L-DOPA (L-dihydroxyphenylalanine) for Parkinson's treatment,
- Eflornithine inhibits ornithine decarboxylase and used in the treatment of sleeping sickness.
- Canavanine, an analogue of arginine found in many legumes is an antifeedant, protecting the plant from predators.
- Mimosine found in some legumes, is another possible antifeedant. This compound is an analogue of tyrosine and can poison animals that graze on these plants.
Uses in industry
Animal feed
Amino acids are sometimes added to animal feed because some of the components of these feeds, such as soybeans, have low levels of some of the essential amino acids, especially of lysine, methionine, threonine, and tryptophan. Likewise amino acids are used to chelate metal cations in order to improve the absorption of minerals from feed supplements.
Food
The food industry is a major consumer of amino acids, especially glutamic acid, which is used as a flavor enhancer, and aspartame (aspartylphenylalanine 1-methyl ester), which is used as an artificial sweetener. Amino acids are sometimes added to food by manufacturers to alleviate symptoms of mineral deficiencies, such as anemia, by improving mineral absorption and reducing negative side effects from inorganic mineral supplementation.
Chemical building blocks
Amino acids are low-cost feedstocks used in chiral pool synthesis as enantiomerically pure building blocks.
Amino acids are used in the synthesis of some cosmetics.
Aspirational uses
Fertilizer
The chelating ability of amino acids is sometimes used in fertilizers to facilitate the delivery of minerals to plants in order to correct mineral deficiencies, such as iron chlorosis. These fertilizers are also used to prevent deficiencies from occurring and to improve the overall health of the plants.
Biodegradable plastics
Amino acids have been considered as components of biodegradable polymers, which have applications as environmentally friendly packaging and in medicine in drug delivery and the construction of prosthetic implants. An interesting example of such materials is polyaspartate, a water-soluble biodegradable polymer that may have applications in disposable diapers and agriculture. Due to its solubility and ability to chelate metal ions, polyaspartate is also being used as a biodegradable antiscaling agent and a corrosion inhibitor.
Synthesis

Chemical synthesis
The commercial production of amino acids usually relies on mutant bacteria that overproduce individual amino acids using glucose as a carbon source. Some amino acids are produced by enzymatic conversions of synthetic intermediates. 2-Aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid is an intermediate in one industrial synthesis of L-cysteine for example. Aspartic acid is produced by the addition of ammonia to fumarate using a lyase.
Biosynthesis
In plants, nitrogen is first assimilated into organic compounds in the form of glutamate, formed from alpha-ketoglutarate and ammonia in the mitochondrion. For other amino acids, plants use transaminases to move the amino group from glutamate to another alpha-keto acid. For example, aspartate aminotransferase converts glutamate and oxaloacetate to alpha-ketoglutarate and aspartate. Other organisms use transaminases for amino acid synthesis, too.
Nonstandard amino acids are usually formed through modifications to standard amino acids. For example, homocysteine is formed through the transsulfuration pathway or by the demethylation of methionine via the intermediate metabolite S-adenosylmethionine, while hydroxyproline is made by a post translational modification of proline.
Microorganisms and plants synthesize many uncommon amino acids. For example, some microbes make 2-aminoisobutyric acid and lanthionine, which is a sulfide-bridged derivative of alanine. Both of these amino acids are found in peptidic lantibiotics such as alamethicin. However, in plants, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid is a small disubstituted cyclic amino acid that is an intermediate in the production of the plant hormone ethylene.
Primordial synthesis
The formation of amino acids and peptides are assumed to precede and perhaps induce the emergence of life on earth. Amino acids can form from simple precursors under various conditions. Surface-based chemical metabolism of amino acids and very small compounds may have led to the build-up of amino acids, coenzymes and phosphate-based small carbon molecules. Amino acids and similar building blocks could have been elaborated into proto-peptides, with peptides being considered key players in the origin of life.
In the famous Urey-Miller experiment, the passage of an electric arc through a mixture of methane, hydrogen, and ammonia produces a large number of amino acids. Since then, scientists have discovered a range of ways and components by which the potentially prebiotic formation and chemical evolution of peptides may have occurred, such as condensing agents, the design of self-replicating peptides and a number of non-enzymatic mechanisms by which amino acids could have emerged and elaborated into peptides. Several hypotheses invoke the Strecker synthesis whereby hydrogen cyanide, simple aldehydes, ammonia, and water produce amino acids.
According to a review, amino acids, and even peptides, "turn up fairly regularly in the various experimental broths that have been allowed to be cooked from simple chemicals. This is because nucleotides are far more difficult to synthesize chemically than amino acids." For a chronological order, it suggests that there must have been a 'protein world' or at least a 'polypeptide world', possibly later followed by the 'RNA world' and the 'DNA world'. Codon–amino acids mappings may be the biological information system at the primordial origin of life on Earth. While amino acids and consequently simple peptides must have formed under different experimentally probed geochemical scenarios, the transition from an abiotic world to the first life forms is to a large extent still unresolved.
Reactions
Amino acids undergo the reactions expected of the constituent functional groups.
Peptide bond formation
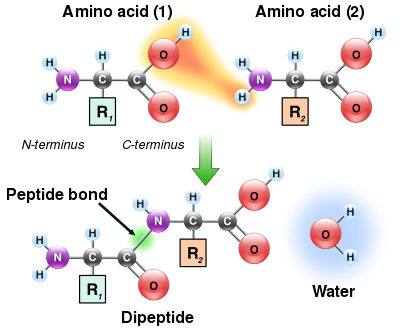
As both the amine and carboxylic acid groups of amino acids can react to form amide bonds, one amino acid molecule can react with another and become joined through an amide linkage. This polymerization of amino acids is what creates proteins. This condensation reaction yields the newly formed peptide bond and a molecule of water. In cells, this reaction does not occur directly; instead, the amino acid is first activated by attachment to a transfer RNA molecule through an ester bond. This aminoacyl-tRNA is produced in an ATP-dependent reaction carried out by an aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. This aminoacyl-tRNA is then a substrate for the ribosome, which catalyzes the attack of the amino group of the elongating protein chain on the ester bond. As a result of this mechanism, all proteins made by ribosomes are synthesized starting at their N-terminus and moving toward their C-terminus.
However, not all peptide bonds are formed in this way. In a few cases, peptides are synthesized by specific enzymes. For example, the tripeptide glutathione is an essential part of the defenses of cells against oxidative stress. This peptide is synthesized in two steps from free amino acids. In the first step, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase condenses cysteine and glutamate through a peptide bond formed between the side chain carboxyl of the glutamate (the gamma carbon of this side chain) and the amino group of the cysteine. This dipeptide is then condensed with glycine by glutathione synthetase to form glutathione.
In chemistry, peptides are synthesized by a variety of reactions. One of the most-used in solid-phase peptide synthesis uses the aromatic oxime derivatives of amino acids as activated units. These are added in sequence onto the growing peptide chain, which is attached to a solid resin support. Libraries of peptides are used in drug discovery through high-throughput screening.
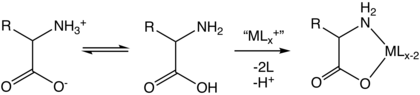
The combination of functional groups allow amino acids to be effective polydentate ligands for metal–amino acid chelates. The multiple side chains of amino acids can also undergo chemical reactions.
Catabolism
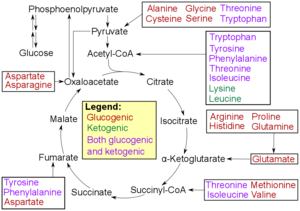
* Glucogenic, with the products having the ability to form glucose by gluconeogenesis
* Ketogenic, with the products not having the ability to form glucose. These products may still be used for ketogenesis or lipid synthesis.
* Amino acids catabolized into both glucogenic and ketogenic products.
Degradation of an amino acid often involves deamination by moving its amino group to α-ketoglutarate, forming glutamate. This process involves transaminases, often the same as those used in amination during synthesis. In many vertebrates, the amino group is then removed through the urea cycle and is excreted in the form of urea. However, amino acid degradation can produce uric acid or ammonia instead. For example, serine dehydratase converts serine to pyruvate and ammonia. After removal of one or more amino groups, the remainder of the molecule can sometimes be used to synthesize new amino acids, or it can be used for energy by entering glycolysis or the citric acid cycle, as detailed in image at right.
Complexation
Amino acids are bidentate ligands, forming transition metal amino acid complexes.
Chemical analysis
The total nitrogen content of organic matter is mainly formed by the amino groups in proteins. The Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) is a measure of nitrogen widely used in the analysis of (waste) water, soil, food, feed and organic matter in general. As the name suggests, the Kjeldahl method is applied. More sensitive methods are available.
See also
Notes
- ↑ The L and D convention for amino acid configuration refers not to the optical activity of the amino acid itself but rather to the optical activity of the isomer of glyceraldehyde from which that amino acid can, in theory, be synthesized (D-glyceraldehyde is dextrorotatory; L-glyceraldehyde is levorotatory). An alternative convention is to use the (S) and (R) designators to specify the absolute configuration. Almost all of the amino acids in proteins are (S) at the α carbon, with cysteine being (R) and glycine non-chiral. Cysteine has its side chain in the same geometric location as the other amino acids, but the R/S terminology is reversed because sulfur has higher atomic number compared to the carboxyl oxygen which gives the side chain a higher priority by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog sequence rules.
Further reading
- Tymoczko JL (2012). "Protein Composition and Structure". Biochemistry. New York: W. H. Freeman and company. pp. 28–31. ISBN 9781429229364.
- Doolittle RF (1989). "Redundancies in protein sequences". In Fasman GD (ed.). Predictions of Protein Structure and the Principles of Protein Conformation. New York: Plenum Press. pp. 599–623. ISBN 978-0-306-43131-9. LCCN 89008555.
- Nelson DL, Cox MM (2000). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (3rd ed.). Worth Publishers. ISBN 978-1-57259-153-0. LCCN 99049137.
- Meierhenrich U (2008). Amino acids and the asymmetry of life (PDF). Berlin: Springer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-540-76885-2. LCCN 2008930865. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 January 2012.
External links
 Media related to Amino acids at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Amino acids at Wikimedia Commons
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Amino acid(24 March 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Item:Q4323 |