Cytochrome P450/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "=== 微生物 ===" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "=== 菌類 ===" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 173: | Line 173: | ||
=== 微生物 === | === 微生物 === | ||
微生物のシトクロムP450は多くの場合可溶性酵素であり、多様な代謝過程に関与している。細菌におけるP450の分布は非常に多様で、多くの細菌はP450を持たない(例えば''大腸菌'')。放線菌を中心に、多数のP450を持つ細菌もいる。これまでに同定されているものは、一般的に、異種化合物の生体内変換(例えば、''[[Streptomyces griseolus/ja|Streptomyces griseolus]]''由来の[[Vitamin D3 dihydroxylase/ja|CYP105A1]]は[[sulfonylurea herbicide/ja|スルホニルウレア除草剤]]を毒性の低い誘導体に代謝する)に関与しているか、特殊な代謝産物生合成経路の一部である(例えば、[[CYP170B1/ja|CYP170B1]]は[[Streptomyces albus/ja|Streptomyces albus]]の[[sesquiterpenoid/ja|セスキテルペノイド]]アルバフラベノンの生産を触媒する)。微生物において必須であることが示されているP450はまだないが、[[CYP105 family/ja|CYP105ファミリー]]は高度に保存されており、これまでに配列決定されたすべての[[streptomycete/ja|放線菌]]ゲノムに代表的なものが存在する。バクテリアのP450酵素は溶解性が高いため、主に膜に結合している真核生物のP450よりも扱いやすいと一般に考えられている。このことは、P450が触媒する驚くべき化学反応と相まって、試験管内で[[heterologously expressed protein/ja|異種発現タンパク質]]を用いた多くの研究につながっている。P450が生体内でどのような働きをするのか、天然の基質は何なのか、そしてP450が自然環境におけるバクテリアの生存にどのように貢献しているのかを調べた研究はほとんどない。構造的・機構的研究に大きく貢献した3つの例をここに挙げるが、多くの異なるファミリーが存在する。 | |||
* 多くのシトクロムP450のモデルとして使用されており、X線結晶構造解析によって解かれた最初の[[Cytochrome P450 cam/ja|シトクロムP450立体構造]]である。 この酵素は、[[putidaredoxin/ja|プチダレドキシン]]、2Fe-2Sクラスター含有タンパク質補因子からの2段階の電子伝達からなる樟脳水酸化触媒サイクルの一部である。 | |||
* [[Cytochrome P450 cam]] | * 放線菌''[[Saccharopolyspora erythraea/ja|Saccharopolyspora erythraea]]''に由来する[[Cytochrome P450 eryF/ja|シトクロムP450 eryF]](CYP107A1)は、[[antibiotic/ja|抗生物質]]の生合成を担う。マクロライドである6-デオキシエリスロノライドBのC6-ヒドロキシル化による[[erythromycin/ja|エリスロマイシン]]の生合成を担っている。 | ||
* | * 土壌細菌''[[Bacillus megaterium/ja|Bacillus megaterium]]''由来の[[Cytochrome P450 BM3/ja|シトクロムP450 BM3]] (CYP102A1)は、ω-1位からω-3位までのいくつかの[[ong-chain fatty acid/ja|長鎖脂肪酸]]のNADPH依存的な水酸化を触媒する。ほとんど全ての既知のCYP(CYP505A1、シトクロムP450フォクシーを除く)とは異なり、CYPドメインと電子供与性補酵素との天然の融合タンパク質を構成している。したがって、BM3はバイオテクノロジーの応用において非常に有用である可能性がある。 | ||
* [[thermophillic/ja|好熱菌]]である[[Sulfolobus solfataricus/ja|Sulfolobus solfataricus]]から単離されたシトクロムP450 119([[CYP119A1/ja|CYP119A1]])は、様々なメカニズム研究に利用されている。好熱性酵素は高温で機能するように進化したため、室温では(機能するとしても)ゆっくりと機能する傾向があり、そのため優れた機構モデルとなっている。 | |||
* | |||
=== 菌類 === | |||
=== | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 09:57, 16 March 2024
シトクロムP450(P450sまたはCYPs)は、ヘムを補因子として含む酵素のスーパーファミリーの一つであり、そのほとんどがモノオキシゲナーゼとして機能するが、それだけに限定されるわけではない。哺乳類では、これらのタンパク質はステロイド類、脂肪酸類、異種物質類を酸化し、様々な化合物のクリアランス、ホルモン合成と分解、ステロイドホルモン合成、薬物代謝、防御化合物、脂肪酸、ホルモンの生合成に重要である。CYP450酵素はゼノバイオティクスを親水性の誘導体に変換し、排泄されやすくする。触媒する変換のほとんどすべてにおいて、P450はヒドロキシル化に影響を及ぼす。
P450酵素は、動物、植物、菌類、原生生物、細菌、古細菌、およびウイルスのすべての界で同定されている。例えば、大腸菌では見つかっていない。2018年現在、30万以上の異なるCYPタンパク質が知られている。
P450は一般に電子伝達鎖の末端酸化酵素であり、大別するとP450含有系となる。"P450"という用語は、酵素が酸化還元状態で一酸化炭素と複合体化したときの吸収極大の分光光度波長(450 nm)にあるピークに由来する。ほとんどのP450は、鉄(そして最終的には分子状の酸素)を還元するために1つ以上の電子を供給するタンパク質パートナーを必要とする。
命名法
P450酵素をコードする遺伝子および酵素自体は、スーパーファミリーを表すルート記号CYPの後に、遺伝子ファミリーを表す数字、サブファミリーを表す大文字、個々の遺伝子を表す別の数字が続く。遺伝子に言及する際にはイタリック体で表記するのが慣例である。例えば、CYP2E1 はパラセタモール(アセトアミノフェン)の代謝に関与する酵素の一つであるCYP2E1をコードする遺伝子である。CYP命名法は公式の命名規則であるが、CYP450またはCYP450が同義語として用いられることもある。これらの名称は、命名規則に従って(ファミリー番号450のP450を示すため)決して使用すべきではない。しかし、P450の遺伝子名や酵素名の中には、歴史的な名称(例えば、CYP102A1のP450BM3)や、触媒活性や基質として使用される化合物の名称を示す機能名で呼ばれるものもある。例えば、CYP5A1、トロンボキサンA2合成, TBXAS1(ThromBoXane A2 Synthase 1)、CYP51A1, ラノステロール14-α-デメチラーゼ、基質(Lanosterol)と活性(DeMethylation)により、非公式にLDMと略されることもある。
現在の命名法ガイドラインでは、新しいCYPファミリーのメンバーは少なくとも40%のアミノ酸同一性を共有し、サブファミリーのメンバーは少なくとも55%のアミノ酸同一性を共有することが推奨されている。命名法委員会は、基本遺伝子名(Cytochrome P450 Homepage Archived 2010-06-27 at the Wayback Machine)と対立遺伝子名(CYP Allele Nomenclature Committee)の両方を割り当て、追跡している。
分類
電子伝達タンパク質の性質に基づき、P450はいくつかのグループに分類される:
- ミクロソームP450系:電子がNADPHからシトクロムP450還元酵素(CPR、POR、CYPORなど様々)を介して移動する。シトクロムb5(cyb5)もまた、シトクロムb5レダクターゼ(CYB5R)によって還元された後、この系に還元力を寄与することができる。
- ミトコンドリアP450システム:NADPHからP450に電子を移動させるためにアドレノドキシン還元酵素とアドレノドキシンを用いる。
- バクテリアP450システム:P450に電子を伝達するためにフェレドキシン還元酵素とフェレドキシンを用いる。
- CYB5R/cyb5/P450系:CYPが必要とする両方の電子がシトクロムb5から来る。
- FMN/Fd/P450システム:もともとはロドコッカス属で発見されたもので、FMNドメインを含む還元酵素がCYPに融合している。
- P450系のみ:外部からの還元力を必要としない。代表的なものにトロンボキサン合成酵素(CYP5)、プロスタサイクリン合成酵素(CYP8)、CYP74A(アレンオキシド合成酵素)がある。
シトクロムP450が触媒する最も一般的な反応はモノオキシゲナーゼ反応であり、例えば、有機基質(RH)の脂肪族位に酸素の1原子を挿入し、もう1つの酸素原子は還元されて水になる:
メカニズム
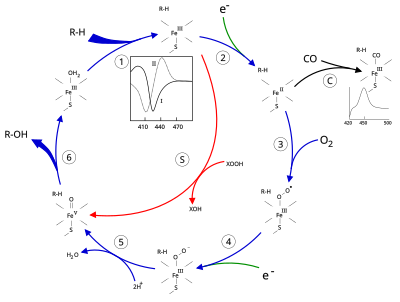
構造
シトクロムP450の活性部位にはヘム鉄中心がある。鉄はシステインチオラートリガンドを介してタンパク質に結合している。このシステインといくつかの隣接残基は、既知のP450において高度に保存されており、正式なPROSITEシグネチャーコンセンサスパターン[FW] - [SGNH] - x - [GD] - {F} - [RKHPT] - {P} - C - [LIVMFAP] - [GAD]を持っている。P450によって触媒される反応は多種多様であるため、多くのP450の活性と特性は多くの点で異なっている。一般的に、P450の触媒サイクルは以下のように進行する:
触媒サイクル
- 基質はヘム基に近接し、チオラート軸とは反対側に結合する。 基質が結合すると、活性部位のコンフォメーションが変化し、多くの場合、水分子がヘム鉄の遠位軸配位位置からはずれ、ヘム鉄の状態が低スピンから高スピンへと変化する。
- 基質が結合すると、NAD(P)HからシトクロムP450還元酵素または関連する別の還元酵素を介して電子移動が起こる。
- 分子状酸素は、結果として生じる第一鉄ヘム中心に遠位軸配位で結合し、最初はオキシミオグロビンに似た酸素付加体を与える。
- 第2の電子は、シトクロムP450還元酵素、フェレドキシン、|シトクロムb5のいずれかから移動し、Fe-O2付加体を還元して短命のペルオキソ状態を与える。
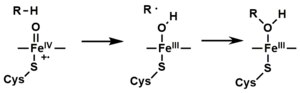
- ステップ4で形成されたペルオキソ基は急速に2回プロトン化され、1分子の水を放出し、P450化合物1(または単に化合物I)と呼ばれる高反応性種を形成する。 この反応性の高い中間体は2010年に単離され、P450化合物1は、ポルフィリンとチオラート配位子上にさらに酸化当量が非局在化した鉄(IV)オキソ(またはフェリル)種である。代替的なフェリル鉄(V)-オキソの証拠は不足している。
- 関与する基質と酵素に応じて、P450酵素は多種多様な反応のいずれかを触媒することができる。 この図に、仮定の水酸化反応を示す。 生成物が活性部位から放出された後、酵素は元の状態に戻り、水分子が鉄核の遠位配位位置を占めるように戻る。
- モノ酸素化の代替経路は、"過酸化物シャント"(図中の経路 "S")である。この経路は、過酸化物や次亜塩素酸塩のような酸素原子供与体による第二鉄-基質複合体の酸化を伴う。 仮想的な過酸化物 "XOOH "を図に示す。
スペクトロスコピー
基質の結合は酵素のスペクトル特性に反映され、390 nmで吸光度が増加し、420 nmで減少する。これは差スペクトルによって測定することができ、"type I"差スペクトルと呼ばれる(図の挿入グラフ参照)。 基質によっては、スペクトル特性に逆の変化、すなわち "逆タイプ I"スペクトルを引き起こすものもあり、その過程はまだ不明である。 ヘム鉄に直接結合する阻害剤とある種の基質は、430 nmに極大、390 nmに極小を持つタイプ II差スペクトルを生じる(図の挿入グラフ参照)。 還元当量がない場合、この複合体は安定なままである可能性があり、吸光度測定から結合の程度を試験管内で決定することができる。 C: 一酸化炭素(CO)が還元型P450に結合すると、触媒サイクルは中断される。この反応により、450 nmに極大を持つ古典的なCO差スペクトルが得られる。しかし、COの触媒阻害作用はCYPによって異なり、CYP3Aファミリーは比較的影響を受けにくい。
ヒトにおけるP450
ヒトのP450は、主にミトコンドリアの内膜か細胞の小胞体に存在する膜関連タンパク質である。P450は何千もの内因性および外因性化学物質を代謝する。P450の中には、CYP19(アロマターゼ)のように1つの基質(またはごく少数の基質)のみを代謝するものもあれば、複数の基質を代謝するものもある。これらの特徴の両方が、医学における中心的な重要性の理由である。シトクロムP450酵素は身体のほとんどの組織に存在し、ホルモンの合成と分解(エストロゲンとテストステロンの合成と代謝を含む)、コレステロールの合成、ビタミンDの代謝において重要な役割を担っている。シトクロムP450酵素はまた、主に肝臓において、薬物やビリルビンのような内因性代謝産物など、潜在的に毒性のある化合物を代謝する働きもする。
ヒトゲノムプロジェクトは、様々なシトクロームP450酵素をコードする57のヒト遺伝子を同定した。
薬物代謝

。
P450は薬物代謝に関与する主要な酵素であり、代謝全体の約75%を占める。ほとんどの薬物は、P450によって直接または体外への排泄促進によって不活性化される。しかし、多くの物質はP450によって生物活性化され、抗血小板薬のような活性化合物を形成する。クロピドグレルやアヘンコデインのようにである。
CYP450酵素スーパーファミリーは57の活性サブセットからなり、7つがほとんどの医薬品の代謝に重要な役割を果たしている。第1相(解毒)におけるCYP450酵素(CYP1A2、CYP2C8、CYP2C9、CYP2C19、CYP2D6、CYP3A4、CYP3A5)の量の変動は、遺伝子発現に個人差があるため、個人によって様々な影響を及ぼす可能性がある。このばらつきは、酵素の遺伝子多型によるもので、酵素の機能と発現にばらつきが生じる。個人の薬物代謝を最適化するためには、遺伝子検査を行い、個人のCYP450多型に対応した機能性食品や特定の植物栄養素を決定する必要がある。このような遺伝的変異を理解することは、薬物療法の有効性を高め、副作用を軽減するための個別化に役立つ。
薬物相互作用
多くの薬物は、アイソザイムの生合成を誘導する(酵素誘導)か、P450の活性を直接阻害する(酵素阻害)かのどちらかによって、様々なP450アイソザイムの活性を増減させる可能性がある。古典的な例としては、CYP1A2、CYP2C9、CYP2C19、CYP3A4を誘導するフェニトインなどの抗てんかん薬が挙げられる。
P450酵素活性の変化は、様々な薬物の代謝やクリアランスに影響を及ぼす可能性があるからである。例えば、ある薬物が別の薬物のP450を介した代謝を阻害した場合、2番目の薬物は体内で毒性レベルまで蓄積する可能性がある。したがって、このような薬物相互作用がある場合には、投与量を調節するか、P450系と相互作用しない薬物を選択する必要がある。このような薬物相互作用は、患者にとって極めて重要な薬物、重大な副作用を伴う薬物、または治療指数の狭い薬物を使用する場合に特に考慮する必要があるが、どのような薬物でも薬物代謝の変化により血漿中濃度が変化する可能性がある。
CYP3A4の基質の多くは、アミオダロンやカルバマゼピンなどの治療指数が狭い薬物である。これらの薬物はCYP3A4によって代謝されるため、これらの薬物の平均血漿中濃度は酵素阻害によって上昇することもあれば、酵素誘導によって低下することもある。
CYP450酵素の栄養調節: 誘導と阻害のバランス アブラナ科の野菜はCYP1A1を誘導し、CYP1B1のアップレギュレーションを助ける。これらの野菜はベリー類とともに、体内でのエストロゲンの処理にも影響を与える。ベリー類はCYP1A1の活性を低下させると考えられているが、アブラナ科の野菜はCYP1B1酵素よりもCYP1A酵素の活性を高める可能性がある。
多くの食品に含まれるレスベラトロール、エラグ酸、ケルセチンは、CYP1A2活性に影響を及ぼす。
他の物質との相互作用
天然に存在する化合物もP450活性を誘導または阻害する可能性がある。例えば、ベルガモッティン、ジヒドロキシベルガモッティン、パラダイシン-Aなど、グレープフルーツジュースや他のいくつかの果汁に含まれる生理活性化合物は、CYP3A4を介した特定の医薬品の代謝を阻害し、バイオアベイラビリティの上昇につながり、その結果、過剰投与の可能性が高いことがわかっている。このようなリスクがあるため、薬物を服用している間はグレープフルーツジュースや生のグレープフルーツを完全に避けることが通常勧められる。
他の例もある:
- セイヨウオトギリソウはCYP3A4を誘導する一般的なハーブ療法である。また、CYP1A1, CYP1B1を阻害する。
- タバコ喫煙はCYP1A2を誘導する(CYP1A2基質の例はクロザピン、オランザピン、フルボキサミン)。
- 比較的高濃度では、スターフルーツジュースもCYP2A6や他のP450を阻害することが示されている。クレソンはシトクロームP450CYP2E1の阻害剤としても知られており、特定の医薬品(例えばクロルゾキサゾン)を服用している人の薬物代謝を変化させる可能性がある。
- トリブチルスズはシトクロームP450の機能を阻害し、軟体動物の男性化をもたらすことが判明している。
- 2つの注目すべきアルカロイドベルベリンとヒドラスチンを含む金ニンジンは、P450マーカー酵素活性(CYP2C9、CYP2D6、CYP3A4が関与)を変化させることが示されている。
その他のP450特有の機能
ステロイドホルモン
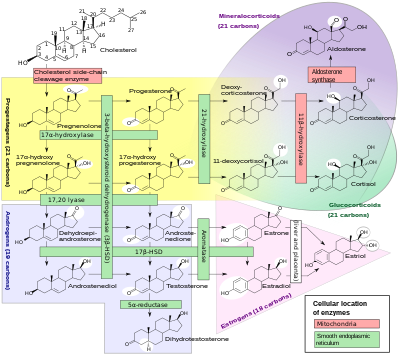
シトクロムP450酵素のサブセットは、副腎、生殖腺、および末梢組織によるステロイドホルモンの合成(ステロイド生成)において重要な役割を果たしている:
- 副腎ミトコンドリアのCYP11A1(P450sccまたはP450c11a1としても知られる)は、「以前は20,22-デスモラーゼとして知られていた活性」(ステロイド20α-ヒドロキシラーゼ、ステロイド22-ヒドロキシラーゼ、コレステロール側鎖切断)に影響を及ぼす。
- 副腎皮質のミトコンドリア内膜に存在するCYP11B1(P450c11βタンパク質をコードする)は、ステロイド11β-ヒドロキシラーゼ、ステロイド18-ヒドロキシラーゼ、ステロイド18-メチルオキシダーゼ活性を持つ。
- 副腎糸球体座のミトコンドリアのみに存在するCYP11B2(P450c11ASタンパク質をコードする)は、ステロイド11β-ヒドロキシラーゼ活性、ステロイド18-ヒドロキシラーゼ活性、ステロイド18-メチルオキシダーゼ活性を持つ。
- 副腎皮質の小胞体にあるCYP17A1は、ステロイド17α-ヒドロキシラーゼ活性と17,20-リアーゼ活性を持つ。
- 副腎皮質のCYP21A2(P450c21)は21-ヒドロキシラーゼ活性を持つ。
- 生殖腺、脳、脂肪組織などの小胞体に存在するCYP19A(P450arom、アロマターゼ)は、アンドロゲンからエストロゲンへの芳香族化を触媒する。
多価不飽和脂肪酸とエイコサノイド
ある種のチトクロームP450酵素は、多価不飽和脂肪酸(PUFA)を生物学的に活性な細胞間細胞シグナル伝達分子(エイコサノイド)に代謝すること、および/またはPUFAの生物学的に活性な代謝産物を活性の低いまたは不活性な産物に代謝することに重要である。 これらのCYPはシトクロムP450オメガヒドロキシラーゼおよび/またはエポキシゲナーゼ酵素活性を有する。
- CYP1A1、CYP1A2、CYP2E1は内因性PUFAをシグナル伝達分子に代謝する:これらはアラキドン酸(すなわちAA)を19-ヒドロキシエイコサテトラエン酸(すなわち19-HETE)に代謝する。19-HETE;20-ヒドロキシエイコサテトラエン酸を参照);エイコサペンタエン酸(すなわち。EPA)からエポキシエイコサテトラエン酸(すなわちEEQ)へ、そしてドコサヘキサエン酸(すなわちDHA)からエポキシドコサペンタエン酸(すなわちEDP)へと変化する。
- CYP2C8、CYP2C9、CYP2C18、CYP2C19、およびCYP2J2は、内因性PUFAをシグナル伝達分子に代謝する:これらの分子は、AAをポキシエイコサテトラエン酸(すなわちEETs)に、EPAをEEQsに、DHAをEDPsに代謝する。
- CYP2S1はPUFAをシグナル伝達分子に代謝する:AAをEETに、EPAをEEQに代謝する。
- CYP3A4はAAをEETシグナル伝達分子に代謝する。
- CYP4A11は、内因性PUFAをシグナル伝達分子に代謝する:AAを20-HETEとEETsに代謝し、DHAを22-ヒドロキシ-DHA(すなわち12-HDHA)にヒドロキシル化する。
- CYP4F2、CYP4F3A、CYP4F3B(後の2つのCYPについてはCYP4F3を参照)は、PUFAをシグナル伝達分子に代謝する。また、EPAを19-ヒドロキシエイコサペンタエン酸(19-HEPE)と20-ヒドロキシエイコサペンタエン酸(20-HEPE)に代謝し、DHAを22-HDAに代謝する。 また、シグナル伝達分子の活性を不活性化または低下させる: ロイコトリエンB4(LTB4)を20-ヒドロキシLTB4に、5-ヒドロキシエイコサテトラエン酸(5-HETE)を5,20-ジHETEに、5-オキソエイコサテトラエン酸(5-オキソ-ETE)を5-オキソに代謝する、 20-ヒドロキシ-ETE、12-ヒドロキシエイコサテトラエン酸(12-HETE)→12,20-ジHETE、EETs→20-ヒドロキシ-EETs、リポキシン類→20-ヒドロキシ生成物である。
- CYP4F8とCYP4F12はPUFAをシグナル伝達分子に代謝する:EPAをEEQに、DHAをEDPに代謝する。これらはまた、AAを18-ヒドロキシエイコサテトラエン酸(18-HETE)と19-HETEに代謝する。
- LTB4は20-ヒドロキシ-LTB4に、(5-HETE)は5,20-ジHETEに、(5-オキソ-ETE)は5-オキソ,20-ヒドロキシ-ETEに、(12-HETE)は12,20-ジHETEに、EETsは20-ヒドロキシ-EETsに、リポキシン類は20-ヒドロキシ生成物に代謝される。
- CYP4F22は、非常に長い「超長鎖脂肪酸」、すなわち炭素数28以上の脂肪酸をω-水酸化する。これらの特殊な脂肪酸のω-ヒドロキシル化は、皮膚の水分バリア機能を作り、維持するために重要である。CYP4F22の常染色体劣性不活性化突然変異は、ヒトの先天性魚鱗癬様紅斑のラメラ魚鱗癬亜型と関連している。
ヒトのCYPファミリー
ヒトには57の遺伝子と59以上の偽遺伝子があり、18のシトクロームP450遺伝子ファミリーと43のサブファミリーに分かれている。これは遺伝子とそれらがコードするタンパク質の要約である。詳しい情報はシトクロームP450命名法委員会のホームページを参照のこと。
| ファミリー | 機能 | メンバー | 遺伝子 | 偽遺伝子 |
| CYP1 | 薬物およびステロイド(特にエストロゲン)の代謝、ベンゾ[a]ピレンの毒化((+)-ベンゾ[a]ピレン-7,8-ジヒドロジオール-9,10-エポキシドを形成する) | 3サブファミリー、3遺伝子、1偽遺伝子 | CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP1B1 | CYP1D1P |
| CYP2 | 薬物およびステロイドの代謝 | 13サブファミリー, 16遺伝子, 16 偽遺伝子 | CYP2A6, CYP2A7, CYP2A13, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C18, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP2F1, CYP2J2, CYP2R1, CYP2S1, CYP2U1, CYP2W1 | 枚挙にいとまがない |
| CYP3 | 薬物とステロイド (テストステロンを含む) の代謝 | 1サブファミリー, 4遺伝子, 4偽遺伝子 | CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP3A7, CYP3A43 | CYP3A51P, CYP3A52P, CYP3A54P, CYP3A137P |
| CYP4 | アラキドン酸あるいは脂肪酸代謝 | 6サブファミリー, 12遺伝子, 10偽遺伝子 | CYP4A11, CYP4A22, CYP4B1, CYP4F2, CYP4F3, CYP4F8, CYP4F11, CYP4F12, CYP4F22, CYP4V2, CYP4X1, CYP4Z1 | 枚挙にいとまがない |
| CYP5 | トロンボキサン A2 合成 | 1サブファミリー, 1遺伝子 | CYP5A1 | |
| CYP7 | [胆汁酸生合成 ステロイド核の7α水酸化酵素 | 2サブファミリー, 2遺伝子 | CYP7A1, CYP7B1 | |
| CYP8 | さまざま | 2サブファミリー, 2遺伝子 | CYP8A1 (プロスタサイクリン合成酵素), CYP8B1 (胆汁酸生合成) | |
| CYP11 | steroid/ja生合成 | 2サブファミリー, 3遺伝子 | CYP11A1, CYP11B1, CYP11B2 | |
| CYP17 | steroid biosynthesis, 17-alpha hydroxylase | 1 subfamily, 1 gene | CYP17A1 | |
| CYP19 | ステロイド生合成、17α水酸化酵素: アロマターゼはエストロゲンを合成する。 | 1サブファミリー, 1遺伝子 | CYP19A1 | |
| CYP20 | 機能不明 | 1サブファミリー, 1遺伝子 | CYP20A1 | |
| CYP21 | steroid/ja生合成 | 1サブファミリー, 1遺伝子, 1偽遺伝子 | CYP21A2 | CYP21A1P |
| CYP24 | vitamin D/ja劣化 | 1サブファミリー, 1遺伝子 | CYP24A1 | |
| CYP26 | レチノイン酸水酸化酵素 | 3サブファミリー, 3遺伝子 | CYP26A1, CYP26B1, CYP26C1 | |
| CYP27 | さまざま | 3サブファミリー, 3遺伝子 | CYP27A1 (胆汁酸生合成), CYP27B1 (ビタミンD3 1-α水酸化酵素、ビタミンD3を活性化する), CYP27C1 (ビタミンA1からA2へ) | |
| CYP39 | 24-ヒドロキシコレステロールの7α水酸化反応 | 1サブファミリー, 1遺伝子 | CYP39A1 | |
| CYP46 | コレステロール24-水酸化酵素 | 1サブファミリー, 1遺伝子, 1偽遺伝子 | CYP46A1 | CYP46A4P |
| CYP51 | コレステロール生合成 | 1サブファミリー, 1遺伝子, 3偽遺伝子 | CYP51A1 ([[lanosterol/ja|ラノステロール] 14α脱メチル化酵素) | CYP51P1, CYP51P2, CYP51P3 |
他の種のP450
動物
他の動物はヒトよりも多くのP450遺伝子を持つことが多い。報告されている数は、海綿動物Amphimedon queenslandicaの35遺伝子から、頭索動物Branchiostoma floridaeの235遺伝子に及ぶ。マウスは101のP450の遺伝子を持っており、ウニはさらに多い(おそらく120もの遺伝子を持っている)。 ほとんどのCYP酵素はモノオキシゲナーゼ活性を持つと推定されており、これまで研究されてきたほとんどの哺乳類のCYPがそうである(例えば、CYP19やCYP5を除く)。遺伝子やゲノムの配列決定は、酵素機能の生化学的特徴付けをはるかに凌駕しているが、機能が知られているCYPに近い相同性を持つ多くの遺伝子が見つかっており、機能性を知る手がかりとなっている。
ヒト以外の動物で最もよく研究されるP450のクラスは、発達に関与するもの(例えば、レチノイン酸やホルモン代謝)、または毒性化合物(複素環アミンや多芳香族炭化水素など)の代謝に関与するものである。多くの場合、近縁動物におけるP450の遺伝子制御や酵素機能に違いがあり、毒性化合物に対する感受性の違いを説明することができる(例:イヌはカフェインなどのキサンチンを代謝できない)。薬物の中には、異なる酵素を介して両方の種で代謝を受け、異なる代謝物を生じるものもあれば、ある種では代謝されるが別の種ではそのまま排泄されるものもある。このため、ある物質に対するある種の反応は、ヒトにおけるその物質の効果を示す信頼できる指標とはならない。サボテン腐敗の解毒にCYP28A1遺伝子の発現上昇を利用するソノラ砂漠のショウジョウバエの一種にDrosophila mettleriがある。この種のハエは、宿主植物中の高レベルのアルカロイドにさらされることにより、この遺伝子のアップレギュレーションに適応した。
P450はマウス、ラット、イヌで広く調べられてきたが、ゼブラフィッシュではあまり調べられてこなかった。最近では、鳥類、特に七面鳥でもP450が発見されており、ヒトのがん研究の有用なモデルになるかもしれない。七面鳥のCYP1A5とCYP3A37は、それぞれヒトのCYP1A2とCYP3A4に速度論的特性やアフラトキシンB1の代謝において非常に類似していることが判明した。
CYPは昆虫でも盛んに研究されており、その多くは殺虫剤耐性を理解するためである。 例えば、CYP6G1はDDT耐性のショウジョウバエの殺虫剤耐性と関連しており、マラリア媒介蚊アノフェレス・ガンビエのCYP6M2はピレスロイドを直接代謝することができる。
微生物
微生物のシトクロムP450は多くの場合可溶性酵素であり、多様な代謝過程に関与している。細菌におけるP450の分布は非常に多様で、多くの細菌はP450を持たない(例えば大腸菌)。放線菌を中心に、多数のP450を持つ細菌もいる。これまでに同定されているものは、一般的に、異種化合物の生体内変換(例えば、Streptomyces griseolus由来のCYP105A1はスルホニルウレア除草剤を毒性の低い誘導体に代謝する)に関与しているか、特殊な代謝産物生合成経路の一部である(例えば、CYP170B1はStreptomyces albusのセスキテルペノイドアルバフラベノンの生産を触媒する)。微生物において必須であることが示されているP450はまだないが、CYP105ファミリーは高度に保存されており、これまでに配列決定されたすべての放線菌ゲノムに代表的なものが存在する。バクテリアのP450酵素は溶解性が高いため、主に膜に結合している真核生物のP450よりも扱いやすいと一般に考えられている。このことは、P450が触媒する驚くべき化学反応と相まって、試験管内で異種発現タンパク質を用いた多くの研究につながっている。P450が生体内でどのような働きをするのか、天然の基質は何なのか、そしてP450が自然環境におけるバクテリアの生存にどのように貢献しているのかを調べた研究はほとんどない。構造的・機構的研究に大きく貢献した3つの例をここに挙げるが、多くの異なるファミリーが存在する。
- 多くのシトクロムP450のモデルとして使用されており、X線結晶構造解析によって解かれた最初のシトクロムP450立体構造である。 この酵素は、プチダレドキシン、2Fe-2Sクラスター含有タンパク質補因子からの2段階の電子伝達からなる樟脳水酸化触媒サイクルの一部である。
- 放線菌Saccharopolyspora erythraeaに由来するシトクロムP450 eryF(CYP107A1)は、抗生物質の生合成を担う。マクロライドである6-デオキシエリスロノライドBのC6-ヒドロキシル化によるエリスロマイシンの生合成を担っている。
- 土壌細菌Bacillus megaterium由来のシトクロムP450 BM3 (CYP102A1)は、ω-1位からω-3位までのいくつかの長鎖脂肪酸のNADPH依存的な水酸化を触媒する。ほとんど全ての既知のCYP(CYP505A1、シトクロムP450フォクシーを除く)とは異なり、CYPドメインと電子供与性補酵素との天然の融合タンパク質を構成している。したがって、BM3はバイオテクノロジーの応用において非常に有用である可能性がある。
- 好熱菌であるSulfolobus solfataricusから単離されたシトクロムP450 119(CYP119A1)は、様々なメカニズム研究に利用されている。好熱性酵素は高温で機能するように進化したため、室温では(機能するとしても)ゆっくりと機能する傾向があり、そのため優れた機構モデルとなっている。
菌類
The commonly used azole class antifungal drugs work by inhibition of the fungal cytochrome P450 14α-demethylase. This interrupts the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol, a component of the fungal cell membrane. (This is useful only because humans' P450 have a different sensitivity; this is how this class of antifungals work.)
Significant research is ongoing into fungal P450s, as a number of fungi are pathogenic to humans (such as Candida yeast and Aspergillus) and to plants.
Cunninghamella elegans is a candidate for use as a model for mammalian drug metabolism.
Plants
Cytochromes P450 are involved in a variety of processes of plant growth, development, and defense. It is estimated that P450 genes make up approximately 1% of the plant genome. These enzymes lead to various fatty acid conjugates, plant hormones, secondary metabolites, lignins, and a variety of defensive compounds.
Cytochromes P450 play an important role in plant defense– involvement in phytoalexin biosynthesis, hormone metabolism, and biosynthesis of diverse secondary metabolites. The expression of cytochrome p450 genes is regulated in response to environmental stresses indicative of a critical role in plant defense mechanisms.
Phytoalexins have shown to be important in plant defense mechanisms as they are antimicrobial compounds produced by plants in response to plant pathogens. Phytoalexins are not pathogen-specific, but rather plant-specific; each plant has its own unique set of phytoalexins. However, they can still attack a wide range of different pathogens. Arabidopsis is a plant closely related to cabbage and mustard and produces the phytoalexin camalexin. Camalexin originates from tryptophan and its biosynthesis involves five cytochrome P450 enzymes. The five cytochrome P450 enzymes include CYP79B2, CYP79B3, CYP71A12, CYP71A13, and CYP71B15. The first step of camalexin biosynthesis produces indole-3-acetaldoxime (IAOx) from tryptophan and is catalyzed by either CYP79B2 or CYP79B3. IAOx is then immediately converted to indole-3-acetonitrile (IAN) and is controlled by either CYP71A13 or its homolog CYP71A12. The last two steps of the biosynthesis pathway of camalexin are catalyzed by CYP71B15. In these steps, indole-3-carboxylic acid (DHCA) is formed from cysteine-indole-3-acetonitrile (Cys(IAN)) followed by the biosynthesis of camalexin. There are some intermediate steps within the pathway that remain unclear, but it is well understood that cytochrome P450 is pivotal in camalexin biosynthesis and that this phytoalexin plays a major role in plant defense mechanisms.
Cytochromes P450 are largely responsible for the synthesis of the jasmonic acid (JA), a common hormonal defenses against abiotic and biotic stresses for plant cells. For example, a P450, CYP74A is involved in the dehydration reaction to produce an insatiable allene oxide from hydroperoxide. JA chemical reactions are critical in the presence of biotic stresses that can be caused by plant wounding, specifically shown in the plant, Arabidopsis. As a prohormone, jasmonic acid must be converted to the JA-isoleucine (JA-Ile) conjugate by JAR1 catalysation in order to be considered activated. Then, JA-Ile synthesis leads to the assembly of the co-receptor complex compo`sed of COI1 and several JAZ proteins. Under low JA-Ile conditions, the JAZ protein components act as transcriptional repressors to suppress downstream JA genes. However, under adequate JA-Ile conditions, the JAZ proteins are ubiquitinated and undergo degradation through the 26S proteasome, resulting in functional downstream effects. Furthermore, several CYP94s (CYP94C1 and CYP94B3) are related to JA-Ile turnover and show that JA-Ile oxidation status impacts plant signaling in a catabolic manner. Cytochrome P450 hormonal regulation in response to extracellular and intracellular stresses is critical for proper plant defense response. This has been proven through thorough analysis of various CYP P450s in jasmonic acid and phytoalexin pathways.
Cytochrome P450 aromatic O-demethylase, which is made of two distinct promiscuous parts: a cytochrome P450 protein (GcoA) and three domain reductase, is significant for its ability to convert Lignin, the aromatic biopolymer common in plant cell walls, into renewable carbon chains in a catabolic set of reactions. In short, it is a facilitator of a critical step in Lignin conversion.
InterPro subfamilies
InterPro subfamilies:
- Cytochrome P450, B-class InterPro: IPR002397
- Cytochrome P450, mitochondrial InterPro: IPR002399
- Cytochrome P450, E-class, group I InterPro: IPR002401
- Cytochrome P450, E-class, group II InterPro: IPR002402
- Cytochrome P450, E-class, group IV InterPro: IPR002403
- Aromatase
Clozapine, imipramine, paracetamol, phenacetin Heterocyclic aryl amines Inducible and CYP1A2 5-10% deficient oxidize uroporphyrinogen to uroporphyrin (CYP1A2) in heme metabolism, but they may have additional undiscovered endogenous substrates. are inducible by some polycyclic hydrocarbons, some of which are found in cigarette smoke and charred food.
These enzymes are of interest, because in assays, they can activate compounds to carcinogens. High levels of CYP1A2 have been linked to an increased risk of colon cancer. Since the 1A2 enzyme can be induced by cigarette smoking, this links smoking with colon cancer.
歴史
1963年、エスタブルック、クーパー、ローゼンタールは、ステロイドホルモン合成と薬物代謝における触媒としてのCYPの役割を説明した。植物では、これらのタンパク質は防御化合物、脂肪酸、ホルモンの生合成に重要である。
こちらも参照
- Steroidogenic enzyme/ja
- Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency/ja
- CYP11 family/ja
- Cytochrome P450 engineering/ja
さらに読む
- Gelboin HV, Krausz K (March 2006). "Monoclonal antibodies and multifunctional cytochrome P450: drug metabolism as paradigm". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 46 (3): 353–372. doi:10.1177/0091270005285200. PMID 16490812. S2CID 33325397.
- Gelboin HV, Krausz KW, Gonzalez FJ, Yang TJ (November 1999). "Inhibitory monoclonal antibodies to human cytochrome P450 enzymes: a new avenue for drug discovery". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 20 (11): 432–438. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(99)01382-6. PMID 10542439.
- "Cytochrome P450 Mediated Drug and Carcinogen Metabolism using Monoclonal Antibodies". home.ccr.cancer.gov. Retrieved 2018-04-02.
- Krausz KW, Goldfarb I, Buters JT, Yang TJ, Gonzalez FJ, Gelboin HV (November 2001). "Monoclonal antibodies specific and inhibitory to human cytochromes P450 2C8, 2C9, and 2C19". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 29 (11): 1410–1423. PMID 11602516.
- Gonzalez FJ, Gelboin HV (1994). "Role of human cytochromes P450 in the metabolic activation of chemical carcinogens and toxins". Drug Metabolism Reviews. 26 (1–2): 165–183. doi:10.3109/03602539409029789. PMID 8082563.
- Estabrook RW (December 2003). "A passion for P450s (Remembrances of the early history of research on cytochrome P450)". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 31 (12): 1461–1473. doi:10.1124/dmd.31.12.1461. PMID 14625342. S2CID 43655270.
外部リンク
- Degtyarenko K (2009-01-09). "Directory of P450-containing Systems". International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology. Archived from the original on 2016-07-16. Retrieved 2009-02-10.
- Flockhart DA (2008-09-04). "Human Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Allele Nomenclature Committee". Karolinska Institutet. Retrieved 2009-02-10.
- Preissner S (2010). "Cytochrome P450 database". Nucleic Acids Research. Archived from the original on 2011-11-03. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- Sigaroudi A, Vollbrecht H (2019). "pharmacokinetic interaction table". Sigaroudi & Vollbrecht.
- Sim SC (2007). "Cytochrome P450 drug interaction table". Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis. Retrieved 2009-02-10.