Protein (nutrient)/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "さらに、減量のためにカロリー制限食を使用しているアスリートは、除脂肪体重の減少を避けるために、タンパク質の消費量をさらに増やすべきであり、おそらく1.8~2.0g/kgまで増やすべきであるという意見もある。" |
Created page with "===有酸素運動におけるタンパク質の必要性=== 持久系アスリートが筋力系アスリートと異なる点は、持久系アスリートは筋力系アスリートほどトレーニングで筋肉量を増やさないという点である。持久系アスリートは、筋力系アスリートほどトレーニングで筋肉量を増やさないという点で、持久系アスリートとは異なる。持久系アスリートは、持久系トレ..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
さらに、減量のために[[Calorie restriction/ja|カロリー制限食]]を使用しているアスリートは、除脂肪体重の減少を避けるために、タンパク質の消費量をさらに増やすべきであり、おそらく1.8~2.0g/kgまで増やすべきであるという意見もある。 | さらに、減量のために[[Calorie restriction/ja|カロリー制限食]]を使用しているアスリートは、除脂肪体重の減少を避けるために、タンパク質の消費量をさらに増やすべきであり、おそらく1.8~2.0g/kgまで増やすべきであるという意見もある。 | ||
===有酸素運動におけるタンパク質の必要性=== | |||
持久系アスリートが筋力系アスリートと異なる点は、持久系アスリートは筋力系アスリートほどトレーニングで筋肉量を増やさないという点である。持久系アスリートは、筋力系アスリートほどトレーニングで筋肉量を増やさないという点で、持久系アスリートとは異なる。持久系アスリートは、持久系トレーニングで分解された筋肉を修復するために、座っている人よりも多くのタンパク質を摂取する必要があるという研究結果がある。アスリートに必要なタンパク質についてはまだ議論の余地があるが(例えば、Lamont, Nutrition Research Reviews, pages 142 - 149, 2012を参照)、持久系アスリートが参加する運動の種類によってタンパク質代謝経路が変化するため、持久系アスリートはタンパク質の摂取量を増やすことで恩恵を受けられるという研究結果がある。持久力トレーニングのアスリートではアミノ酸が酸化されるため、全体的なタンパク質必要量が増加する。長時間(1回のトレーニングで2~5時間)運動する持久系アスリートは、消費する総エネルギーの5~10%をタンパク質でまかなう。したがって、持久系アスリートにとって、エネルギー消費で失われたタンパク質と筋肉の修復で失われたタンパク質を補うことで、タンパク質の摂取量を少し増やすことは有益かもしれない。あるレビューでは、持久系アスリートは1日のタンパク質摂取量を体重1kgあたり最大1.2~1.4gまで増やしてもよいと結論づけている。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 18:11, 25 February 2024
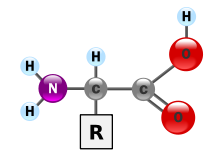
タンパク質は、人体にとって不可欠な栄養素である。体組織の構成要素の一つであり、燃料源としても機能する。燃料として、タンパク質は炭水化物と同じくらいのエネルギー密度を提供する: 1グラムあたり4kcal(17kJ)であるのに対し、脂質は1グラムあたり9kcal(37kJ)である。 栄養学的見地から見たタンパク質の最も重要な側面と特徴は、そのアミノ酸組成である。
タンパク質はアミノ酸がペプチド結合で結合したポリマー鎖である。ヒトの消化の際、タンパク質は胃の中で塩酸とプロテアーゼの作用によってより小さなポリペプチド鎖に分解される。これは、体内で生合成できない必須アミノ酸を吸収するために極めて重要である。
タンパク質-エネルギー栄養失調とその結果としての死を防ぐために、人間が食事から摂取しなければならない9つの必須アミノ酸がある。それらはフェニルアラニン、バリン、スレオニン、トリプトファン、メチオニン、ロイシン、イソロイシン、リジン、ヒスチジンである。必須アミノ酸が8種類か9種類かについては議論がある。ヒスチジンは成人では合成されないため、コンセンサスは9に傾いているようだ。人間が体内で合成できるアミノ酸は5つある。アラニン、アスパラギン酸、アスパラギン、グルタミン酸、セリンである。乳幼児の未熟児や重度の異化不全にある人など、特殊な病態生理学的条件下で合成が制限される6種類の条件付き必須アミノ酸がある。これらの6つはアルギニン、システイン、グリシン、グルタミン、プロリン、チロシンである。タンパク質の食事源としては、穀物、豆類、種子類が挙げられる、
人体におけるタンパク質の働き
タンパク質は人体の成長と維持に必要な栄養素である。水を除けば、タンパク質は体内で最も豊富な種類の分子である。タンパク質は全身の細胞に存在し、特に筋肉の主要な構造成分である。これには身体の臓器、毛髪、皮膚も含まれる。タンパク質は糖タンパク質などの膜にも使われる。アミノ酸に分解されると、核酸、補酵素、ホルモン、免疫反応、細胞修復、その他生命維持に不可欠な分子の前駆体として使われる。さらに、タンパク質は血液細胞を形成するためにも必要である。
摂取源
| カテゴリ | 畜産物の貢献 [%] |
|---|---|
| カロリー | 18
|
| タンパク質 | 37
|
| 土地利用 | 83
|
| 温室効果ガス | 58
|
| 水汚染 | 57
|
| 空気汚染 | 56
|
| 淡水取水量 | 33
|
タンパク質は様々な食品に含まれている。世界的に見ると、植物性タンパク質食品は一人当たりのタンパク質供給量の60%以上を占めている。北米では、動物由来の食品がタンパク質源の約70%を占めている。昆虫は世界の多くの地域でタンパク源となっている。アフリカの一部では、食事性タンパク質の最大50%が昆虫由来である。毎日20億人以上の人が昆虫を食べていると推定されている。
肉、乳製品、卵、大豆、魚、全粒穀物、穀類がタンパク質源である。主食であり、7%以上の濃度を持つ穀類のタンパク源としては、ソバ、オート麦、ライ麦、キビ、トウモロコシ、米、小麦、ソルガムきび、アマランサス、キヌアなどがある(順不同)。タンパク質源としてジビエ肉に注目する研究もある。
植物性タンパク源には、豆類、ナッツ類、種子類、穀類、一部の野菜や果物が含まれる。タンパク質濃度が7%を超える植物性食品には、大豆、レンズ豆、インゲン豆、白インゲン豆、緑豆、ひよこ豆、ササゲ、ライマメ、キマメ、ルピナス、手裏豆、アーモンド、ブラジルナッツ、カシューナッツ、ピーカン、クルミ、綿の実、カボチャの種、麻の実、ゴマ、ヒマワリの種などがある(ただし、これらに限定されない)。
太陽光発電を利用した微生物によるタンパク質生産は、ソーラーパネルからの電力と空気中の二酸化炭素を利用して微生物用の燃料を作り、バイオリアクター槽で増殖させ、乾燥したタンパク質粉末に加工する。このプロセスは、土地、水、肥料を非常に効率的に利用する。
バランスの取れた食事をしている人には、タンパク質サプリメントは必要ない。
下の表は、タンパク質源としての食品群を示している。
| Food source | Lysine/ja | Threonine/ja | Tryptophan/ja | 含硫 アミノ酸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legumes/ja | 64 | 38 | 12 | 25 |
| Cereals/jaとwhole grain/ja | 31 | 32 | 12 | 37 |
| ナッツとseed/ja | 45 | 36 | 17 | 46 |
| Fruit/ja | 45 | 29 | 11 | 27 |
| Animal/ja | 85 | 44 | 12 | 38 |
Colour key:
- 各アミノ酸の密度が最も高いタンパク質源
- 各アミノ酸の密度が最も低いタンパク質源

カゼイン、ホエイ、卵、米、大豆、コオロギ粉などのプロテインパウダーは、加工・製造されたタンパク源である。
食品中の検査
食品中のタンパク質濃度の古典的な測定法は、ケルダール法とデュマ法である。これらの検査は試料中の全窒素を測定する。ほとんどの食品で窒素を含む唯一の主要成分はタンパク質である(脂肪、炭水化物、食物繊維は窒素を含まない)。窒素の量に、食品に含まれるタンパク質の種類に応じた係数をかけると、総タンパク質が求められる。この値は「粗タンパク質」含有量として知られている。正しい換算係数の使用については、特に植物由来のタンパク質製品の導入に伴い、激しい議論が交わされている。しかし、食品表示上のタンパク質は、窒素に6.25を掛けた値で計算される。ケルダール法は、AOACインターナショナルが採用している方法であるため、世界中の多くの食品標準機関で使用されているが、デュマ法もいくつかの標準機関では承認されている。
プロテインミールに非タンパク質窒素源を混入し、粗タンパク質含量の測定値を膨張させる事故や意図的な混入は、何十年も前から食品業界で発生していることが知られている。食品の品質を保証するために、プロテインミールの購入者は、尿素や硝酸アンモニウムなどの最も一般的な非タンパク質窒素汚染物質を検出するように設計された品質管理テストを日常的に実施している。
食品業界の少なくとも一分野である乳製品業界では、一部の国(少なくとも米国、オーストラリア、フランス、ハンガリー)が、粗タンパク質測定とは対照的に、「真のタンパク質」測定を支払いや検査の基準として採用している: 「真のタンパク質は生乳中のタンパク質のみを測定するのに対し、粗タンパク質はすべての窒素源を測定するもので、尿素のような人間にとって食品価値のない非タンパク質窒素も含まれる。... 現在の生乳検査装置はペプチド結合を測定する。穀物中のペプチド結合の測定は、カナダ、イギリス、オーストラリア、ロシア、アルゼンチンを含むいくつかの国でも実用化されており、そこでは赤外分光法の一種である近赤外反射率(NIR)技術が使われている。国際連合食糧農業機関(FAO)は、特に、乳児用粉ミルクのような唯一の栄養源として使用される食品のタンパク質を決定するためにアミノ酸分析のみを使用することを推奨しているが、また、提供している: 「アミノ酸分析のデータが入手できない場合は、ケルダール法(AOAC、2000年)または類似の方法による総窒素含有量に基づくタンパク質の測定が...許容されると考えられる。
肉牛の飼料中のタンパク質の検査法は、戦後数年の間に科学として発展してきた。米国における標準的なテキストであるNutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle(肉牛の栄養要求量)は、少なくとも70年以上にわたって8版を重ねてきた。1996年の第6版では、第5版の粗タンパク質を代謝可能タンパク質という概念に置き換え、2000年頃には「微生物タンパク質と未分解の摂取タンパク質から供給される、腸で吸収される真のタンパク質」と定義された。
ケルダール法の限界は、2007年の中国産タンパク質輸出汚染や、工業化学物質メラミンが牛乳やグルテンに添加され、測定された「タンパク質」を増加させた2008年中国産牛乳スキャンダルの核心であった。
タンパク質の質
栄養学的な観点からのタンパク質の最も重要な側面と定義特性は、そのアミノ酸組成である。アミノ酸の相対的な割合と、いくつかのシステムではタンパク質源の消化率に基づいて、生物に対する有用性によってタンパク質を評価する複数のシステムがある。これには生物学的価値、正味タンパク質利用率、PDCAAS(タンパク質消化率補正アミノ酸スコア)などがある。PDCAAS評価は、1993年にタンパク質効率比(PER)法を修正するものとして米国食品医薬品局(FDA)および国連食糧農業機関/世界保健機関(FAO/WHO)によって、タンパク質の品質を決定するための「望ましい『最良』の」方法として採用された。これらの機関は、タンパク質の品質を評価する他の方法は劣っていると示唆している。2013年、FAOは難消化性必須アミノ酸スコアへの変更を提案した。
消化
ほとんどのタンパク質は消化管で消化され、単一アミノ酸に分解される。
消化は通常、胃でペプシノーゲンが塩酸の作用によってペプシンに変換されるところから始まり、小腸でトリプシンとキモトリプシンによって続けられる。 ほとんどのタンパク質は小腸で吸収される前に、すでに1個のアミノ酸か数個のアミノ酸からなるペプチドに還元されている。4アミノ酸より長いペプチドのほとんどは吸収されない。腸管吸収細胞への吸収は終わりではない。そこでほとんどのペプチドは単一アミノ酸に分解される。
食物タンパク質が分解されたアミノ酸とその誘導体の吸収は消化管で行われる。例えば、ヒトにおける多くのアミノ酸の消化率、大豆と乳タンパク質の違い、個々の乳タンパク質であるβ-ラクトグロブリンとカゼインの違いなどである。乳タンパク質の場合、摂取されたタンパク質の約50%が胃から空腸の間で吸収され、消化された食物が回腸に到達するまでに90%が吸収される。生物学的価値(BV)とは、食品から吸収されたタンパク質のうち、生物の体内のタンパク質に組み込まれる割合を示す指標である。
新生児
哺乳類の新生児は、小腸で無傷のタンパク質を吸収できるという点で、タンパク質の消化と同化において例外的である。これによって、受動免疫、すなわち母乳を介して母親から新生児への免疫グロブリンの移行が可能になる。
食事の必要条件


タンパク質の必要摂取量をめぐる問題については、かなりの議論がなされてきた。 人の食事に必要なタンパク質の量は、全体的なエネルギー摂取量、窒素と必須アミノ酸に対する体の必要量、体重と体組成、個人の成長速度、身体活動レベル、個人のエネルギーと炭水化物の摂取量、病気や怪我の有無によって大きく左右される。 身体活動や労作、筋肉量の増加により、タンパク質の必要量は増加する。 また、成長発育のための小児期、妊娠中、赤ちゃんに栄養を与えるための授乳中、栄養不良や外傷から回復する必要があるとき、手術後などにも必要量が増える。
食事に関する推奨事項
米国とカナダの食事摂取基準ガイドラインによると、19~70歳の女性は1日あたり46 gのタンパク質を摂取する必要があり、19~70歳の男性は1日あたり56 gのタンパク質を摂取する必要がある。これらの推奨食事摂取量(RDA)は、体重1kgあたり0.8gのタンパク質と、それぞれ57 kg(126ポンド)と70 kg(154ポンド)の平均体重に基づいて算出された。しかし、この推奨量は構造上の必要量に基づいているが、エネルギー代謝のためのタンパク質の利用は無視している。この必要量は、普通に座っている人の場合である。米国では、タンパク質の平均消費量はRDAより多い。国民健康栄養調査(NHANES 2013-2014)の結果によると、20歳以上の女性の平均タンパク質消費量は69.8g/日、男性は98.3g/日であった。
活動的な人
いくつかの研究では、活動的な人々やアスリートは、筋肉量の増加や発汗量の減少、身体の修復やエネルギー源の必要性から、(0.8g/kgよりも)高いタンパク質摂取量を必要とする可能性があると結論付けている。推奨される摂取量は、持久的運動をする人の場合は1.2~1.4g/kg、筋力運動をする人の場合は1.6~1.8g/kg、高齢者の場合は2.0g/kg/日までと様々で、1日の「最大」タンパク質摂取量は、エネルギー必要量の約25%、すなわち約2~2.5g/kgと提案されている。しかし、まだ多くの疑問が残っている。
さらに、減量のためにカロリー制限食を使用しているアスリートは、除脂肪体重の減少を避けるために、タンパク質の消費量をさらに増やすべきであり、おそらく1.8~2.0g/kgまで増やすべきであるという意見もある。
有酸素運動におけるタンパク質の必要性
持久系アスリートが筋力系アスリートと異なる点は、持久系アスリートは筋力系アスリートほどトレーニングで筋肉量を増やさないという点である。持久系アスリートは、筋力系アスリートほどトレーニングで筋肉量を増やさないという点で、持久系アスリートとは異なる。持久系アスリートは、持久系トレーニングで分解された筋肉を修復するために、座っている人よりも多くのタンパク質を摂取する必要があるという研究結果がある。アスリートに必要なタンパク質についてはまだ議論の余地があるが(例えば、Lamont, Nutrition Research Reviews, pages 142 - 149, 2012を参照)、持久系アスリートが参加する運動の種類によってタンパク質代謝経路が変化するため、持久系アスリートはタンパク質の摂取量を増やすことで恩恵を受けられるという研究結果がある。持久力トレーニングのアスリートではアミノ酸が酸化されるため、全体的なタンパク質必要量が増加する。長時間(1回のトレーニングで2~5時間)運動する持久系アスリートは、消費する総エネルギーの5~10%をタンパク質でまかなう。したがって、持久系アスリートにとって、エネルギー消費で失われたタンパク質と筋肉の修復で失われたタンパク質を補うことで、タンパク質の摂取量を少し増やすことは有益かもしれない。あるレビューでは、持久系アスリートは1日のタンパク質摂取量を体重1kgあたり最大1.2~1.4gまで増やしてもよいと結論づけている。
Anaerobic exercise protein needs
Research also indicates that individuals performing strength training activity require more protein than sedentary individuals. Strength-training athletes may increase their daily protein intake to a maximum of 1.4–1.8 g per kg body weight to enhance muscle protein synthesis, or to make up for the loss of amino acid oxidation during exercise. Many athletes maintain a high-protein diet as part of their training. In fact, some athletes who specialize in anaerobic sports (e.g., weightlifting) believe a very high level of protein intake is necessary, and so consume high protein meals and also protein supplements.
特別な集団
たんぱく質アレルギー
食物アレルギーは、食品中のタンパク質に対する異常な免疫反応である。その兆候や症状は軽度から重度までさまざまです。かゆみ、舌の腫れ、嘔吐、下痢、じんましん、呼吸困難、または低血圧が含まれることがあります。これらの症状は通常、曝露後数分から1時間以内に発生します。症状が重度な場合、それはアナフィラキシーとして知られている。以下の8つの食品がアレルギー反応の約90%を引き起こす原因となっている: 牛乳、卵、小麦、貝、魚、ピーナッツ、木の実、および大豆
慢性腎臓病
高タンパク食が慢性腎臓病の原因になるという決定的な証拠はないが、この病気の患者はタンパク質の消費を減らすべきだというコンセンサスはある。2009年のあるレビューによると、タンパク質の摂取を減らした慢性腎臓病患者は、末期腎臓病に進行する可能性が低い。さらに、低タンパク食(0.6g/kg/d~0.8g/kg/d)を使用しているこの疾患の患者は、腎機能を維持する代謝代償を発症する可能性があるが、一部の患者では栄養失調が起こる可能性がある。
フェニルケトン尿症
フェニルケトン尿症(PKU)の人は、知的障害や他の代謝性合併症を防ぐために、必須アミノ酸 – であるフェニルアラニン – の摂取量を極端に低く抑えなければならない。フェニルアラニンは人工甘味料アスパルテームの成分であるため、PKU患者はこの成分を含む低カロリー飲料や食品を避ける必要がある。
過剰消費
米国とカナダにおけるタンパク質の食事摂取基準に関する検討では、耐容上限摂取量、すなわちタンパク質を安全に摂取できる量の上限を設定するには十分な証拠がないと結論づけられた。
アミノ酸が必要量を超えると、肝臓はアミノ酸を取り込み、脱アミノ化する。この過程でアミノ酸の窒素はアンモニアに変換され、さらに肝臓で尿素サイクルを介して尿素に処理される。尿素の排泄は腎臓を介して行われる。アミノ酸分子の他の部分はグルコースに変換され、燃料として利用される。食物のタンパク質摂取量が周期的に多かったり少なかったりする場合、身体は「不安定なタンパク質予備軍」を使ってタンパク質摂取量の日々の変動を補うことで、タンパク質レベルを平衡に保とうとする。しかし、将来必要となるカロリーの予備としての体脂肪とは異なり、将来必要となるタンパク質の貯蔵はない。
タンパク質の過剰摂取は、硫黄アミノ酸の酸化によるpHの不均衡を補うために起こり、尿中のカルシウム排泄を増加させる可能性がある。このため、腎循環系内のカルシウムから腎結石が形成されるリスクが高くなる可能性がある。あるメタアナリシスでは、高タンパク質摂取による骨密度への悪影響はないと報告している。別のメタアナリシスでは、動物性タンパク質と植物性タンパク質の間に差はないが、タンパク質の多い食事によって収縮期血圧と拡張期血圧がわずかに低下することが報告されている。
高タンパク質食は、メタアナリシスにおいて、ベースラインのタンパク質食と比較して、3ヶ月間でさらに1.21 kgの体重減少につながることが示されている。BMIの低下やHDLコレステロールの減少という利益は、高タンパク質摂取量が総エネルギー摂取量の45%と分類された研究よりも、むしろタンパク質摂取量がわずかに増加した研究において、より強く観察された。心血管系の活動に対する有害な影響は、6ヵ月以下の短期間の食事では観察されなかった。長期的な高タンパク質食が健康な個人に及ぼす潜在的な有害影響については、ほとんどコンセンサスが得られていないため、高タンパク質摂取を減量の一形態として使用することについては注意が必要である。
2015-2020年版アメリカ人のための食事摂取基準(DGA)は、男性および10代の少年に対し、果物、野菜、その他摂取量の少ない食品の摂取量を増やすよう推奨しており、そのための手段として、タンパク質食品の摂取量を全体的に減らすことを挙げている。2015〜2020年のDGA報告書では、赤身肉と加工肉の推奨摂取量は設定されていない。報告書は、赤肉や加工肉の摂取量の減少が成人の心血管系疾患のリスク低下と相関していることを示す研究を認める一方で、これらの肉から得られる栄養素の価値にも言及している。推奨されているのは、肉やタンパク質の摂取を制限することではなく、特定の肉やタンパク質の摂取によって増加する可能性のあるナトリウム(2300 mg未満)、飽和脂肪(1日あたりの総カロリーの10%未満)、加糖(1日あたりの総カロリーの10%未満)を監視し、1日の制限値内に抑えることである。2015年のDGA報告書では、赤身肉や加工肉の摂取量を減らすよう勧告しているが、2015-2020年のDGA主要勧告では、ベジタリアンおよび非ベジタリアンの両方のタンパク源を含む、様々なタンパク質食品を摂取するよう勧告している。
タンパク質欠乏症

タンパク質欠乏・栄養不良(PEM)は、知的障害やクワシオルコルを含む様々な病気を引き起こす可能性がある。クワシオルコルの症状には、無気力、下痢、不活発、成長不全、皮膚のかさつき、脂肪肝、腹と脚の浮腫などがある。この浮腫は、リポキシゲナーゼがアラキドン酸に作用してロイコトリエンを形成することと、体液バランスおよびリポ蛋白輸送における蛋白質の正常な機能によって説明される。
PEMは小児、成人ともに世界的にかなり多くみられ、年間600万人が死亡している。先進工業国では、PEMは主に病院でみられ、疾患と関連しているか、高齢者に多くみられる。











