Pantothenic acid/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "==摂取源== {{Anchor|Sources}}" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "===安全性=== 安全性に関しては、IOMは十分なエビデンスがある場合、ビタミンとミネラルの耐容上限摂取量レベル(UL)を設定している。パントテン酸の場合、高用量摂取による副作用に関するヒトでのデータがないため、ULは設定されていない。EFSAも安全性の問題を検討し、パントテン酸のULを設定するには十分な証拠がない..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 169: | Line 169: | ||
{{Anchor|Sources}} | {{Anchor|Sources}} | ||
===食事=== | |||
=== | パントテン酸を含む食品としては、乳製品や卵などの動物性食品がある。植物性食品では、ジャガイモ、トマト製品、オート麦、ひまわりの種、アボカドなどがよい。キノコ類もよい摂取源となる。全粒穀物もビタミンの供給源だが、白米や白玉粉を作るために製粉すると、全粒穀物の外層に含まれるパントテン酸の多くが除去されてしまう。動物用飼料では、アルファルファ、穀類、フィッシュミール、ピーナッツミール、糖蜜、米ぬか、小麦ふすま、酵母が最も重要な供給源である。 | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 20:24, 20 February 2024
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-[(2R)-2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanamido]propanoic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-[(2R)-(2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl)amino]propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1727062, 1727064 (R) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Pantothenic+Acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H17NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 219.237 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow oil Colorless crystals (Ca2+ salt) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.266 g/cm3 1.32 g/cm3 (Ca2+ salt) |
| Melting point | 183.833 °C (362.899 °F; 456.983 K) 196–200 °C (385–392 °F; 469–473 K) decomposes (Ca2+ salt) |
| Very soluble | |
| Solubility | Very soluble in C6H6, ether |
| log P | −1.416 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.41 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 9.698 |
Chiral rotation ([α]D)
|
+37.5° +24.3° (Ca2+ salt) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
> 10 mg/g (Ca2+ salt) |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids
|
Arginine/ja Hopantenic acid/ja 4-(γ-Glutamylamino)butanoic acid/ja |
Related compounds
|
パンテノール |
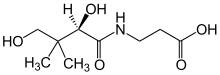
パントテン酸(vitamin B5)はビタミンB群の一種で、必須栄養素である。すべての動物は、脂肪酸の代謝に不可欠な補酵素A(CoA)を合成し、タンパク質、炭水化物、脂肪を合成・代謝するためにパントテン酸を必要とする。
パントテン酸はパント酸とβ-アラニンの組み合わせである。その名前はギリシア語に由来する。πάντοθενに由来する。パントテン酸は、少なくとも少量であれば、ほとんどすべての食品に含まれているためである。パントテン酸の欠乏は、ヒトでは非常にまれである。パントテン酸ナトリウムや遊離パントテン酸よりも化学的に安定しているため、製品の保存期間が長くなる。
定義

パントテン酸は水溶性のビタミンで、ビタミンB群の一つである。アミノ酸のβ-アラニンとパント酸から合成される(生合成および補酵素Aの構造図を参照)。ビタミンEやビタミンKがビタマーとして知られるいくつかの化学的に関連した形で存在するのとは異なり、パントテン酸は1つの化合物である。多くの酵素プロセスの補酵素である補酵素A(CoA)の合成における出発化合物である。
コエンザイムAの生合成に使用

パントテン酸は、5段階の過程を経てCoAの前駆体となる。 生合成にはパントテン酸、システイン、4当量のATPが必要である(図参照)。
- パントテン酸は酵素パントテン酸キナーゼによって4′-ホスホパントテン酸にリン酸化される。これはCoAの生合成におけるコミットメントステップであり、ATPを必要とする。
- ホスホパントテノイルシステイン合成酵素によって4′-ホスホパントテネートにシステインが付加され、4'-ホスホ-N-パントテノイルシステイン(PPC)が形成される。このステップはATP加水分解と結合している。
- PPCはホスホパントテノイルシステイン脱炭酸酵素によって4′-ホスホパンテテインに脱炭酸される。
- 4′-ホスホパンテテインは酵素ホスホパンテインアデニルトランスフェラーゼによってアデニル化(正しくはAMP化)され、脱ホスホ-CoAを形成する。
- 最後に、脱ホスホ-CoAは酵素脱ホスホコエンザイムAキナーゼによってコエンザイムAにリン酸化される。この最終段階にもATPが必要である。
この経路は最終産物阻害によって抑制されるが、これはCoAが第一段階を担う酵素であるパントテン酸キナーゼの競合的阻害剤であることを意味する。
コエンザイムAはクエン酸サイクルの反応機構に必要である。この過程は体内の主要な異化経路であり、燃料として炭水化物、アミノ酸、脂質などの細胞の構成要素を分解するのに不可欠である。CoAはエネルギー代謝において、ピルビン酸がアセチル-CoAとしてトリカルボン酸サイクル(TCAサイクル)に入るため、またα-ケトグルタル酸がサイクルでスクシニル-CoAに変換されるために重要である。CoAはアシル化やアセチル化にも必要であり、それらは例えばシグナル伝達や様々な酵素機能に関与している。CoAとしての機能に加えて、この化合物はアセチル-CoAおよび他の関連化合物を形成するためのアシル基キャリアとして働くことができる;これは細胞内で炭素原子を輸送する方法である。CoAはまた、脂肪酸合成に必要なアシルキャリアタンパク質(ACP)の形成にも必要である。その合成は、チアミンや葉酸などの他のビタミンとも結びついている。
食事の推奨量
米国医学研究所(IOM)は、1998年にビタミンB群の推定平均所要量(EAR)と推奨食事許容量(RDA)を更新した。その時点では、パントテン酸のEARとRDAを設定するのに十分な情報がなかった。このような場合、理事会は、後日、AIがより正確な情報に取って代わられる可能性があることを理解した上で、適正摂取量(AAI)を設定している。
14歳以上の10代と成人に対する現在のAIは、5 mg/日である。これは、典型的な食事の場合、尿中排泄量は約2.6 mg/日であり、食物結合パントテン酸の生物学的利用能はおよそ50%であるという観察に基づいている。妊娠中のAIは6 mg/日である。授乳期のAIは7 mg/日である。12ヵ月までの乳児のAIは1.8 mg/日である。1~13歳の子どもについては、AIは2~4 mg/日と年齢とともに増加する。 EAR、RDA、AI、ULを総称して食事摂取基準(DRI)と呼ぶ。
| 年齢層 | 年齢 | 十分な摂取量 |
|---|---|---|
| 乳幼児 | 0–6 ヶ月 | 1.7 mg |
| 乳幼児 | 7–12 ヶ月 | 1.8 mg |
| 子供 | 1–3 歳 | 2 mg |
| 子供 | 4–8 歳 | 3 mg |
| 子供 | 9–13 歳 | 4 mg |
| 成人男女 | 14+ 歳 | 5 mg |
| 妊婦 | (vs. 5) | 6 mg |
| 授乳中の女性 | (vs. 5) | 7 mg |
多くの栄養素について、米国農務省は食品成分データと食品消費調査の結果を組み合わせて平均消費量を推定しているが、調査や報告書にはパントテン酸は分析に含まれていない。成人の1日摂取量に関するあまり正式でない推定値では、約4~7 mg/日と報告されている。
欧州食品安全機関(EFSA)は、これらの情報をまとめて食事摂取基準値(Dietary Reference Values)と呼んでおり、RDAの代わりに人口摂取基準(Population Reference Intake:PRI)、EARの代わりに平均必要量(Average Requirement)を用いている。AIとULの定義は米国と同じである。11歳以上の女性と男性については、十分摂取量(AI)は5 mg/日とされている。妊娠中のAIは5 mg/日、授乳期は7 mg/日である。1~10歳の子供のAIは4 mg/日である。これらのAIは米国のAIと同様である。
安全性
安全性に関しては、IOMは十分なエビデンスがある場合、ビタミンとミネラルの耐容上限摂取量レベル(UL)を設定している。パントテン酸の場合、高用量摂取による副作用に関するヒトでのデータがないため、ULは設定されていない。EFSAも安全性の問題を検討し、パントテン酸のULを設定するには十分な証拠がないという、米国と同じ結論に達した。
表示要件
米国の食品および栄養補助食品の表示目的では、1食あたりの摂取量は1日当たりの摂取価値(Daily Value)のパーセンテージ(%DV)で表される。パントテン酸の表示目的では、デイリーバリューの100%は10 mgであったが、2016年5月27日付でAIと一致させるために5 mgに改訂された。 更新された表示規制への準拠は、年間食品売上高がUS$10 百万以上の製造業者については2020年1月1日までに、それ以下の製造業者については2021年1月1日までに義務付けられた。新旧の成人一日摂取量の表は基準一日摂取量に掲載されている。
摂取源
食事
パントテン酸を含む食品としては、乳製品や卵などの動物性食品がある。植物性食品では、ジャガイモ、トマト製品、オート麦、ひまわりの種、アボカドなどがよい。キノコ類もよい摂取源となる。全粒穀物もビタミンの供給源だが、白米や白玉粉を作るために製粉すると、全粒穀物の外層に含まれるパントテン酸の多くが除去されてしまう。動物用飼料では、アルファルファ、穀類、フィッシュミール、ピーナッツミール、糖蜜、米ぬか、小麦ふすま、酵母が最も重要な供給源である。
Supplements
Dietary supplements of pantothenic acid commonly use pantothenol (or panthenol), a shelf-stable analog, which is converted to pantothenic acid once consumed. Calcium pantothenate – a salt – may be used in manufacturing because it is more resistant than pantothenic acid to factors that deteriorate stability, such as acid, alkali or heat. The amount of pantothenic acid in dietary supplement products may contain up to 1,000 mg (200 times the Adequate Intake level for adults), without evidence that such large amounts provide any benefit. According to WebMD, pantothenic acid supplements have a long list of claimed uses, but there is insufficient scientific evidence to support any of them.
As a dietary supplement, pantothenic acid is not the same as pantethine, which is composed of two pantothenic acid molecules linked by a disulfide bridge. Sold as a high-dose supplement (600 mg), pantethine may be effective for lowering blood levels of LDL cholesterol – a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases – but its long-term effects are unknown, requiring that its use be supervised by a physician. Dietary supplementation with pantothenic acid does not have the same effect on LDL.
Fortification
According to the Global Fortification Data Exchange, pantothenic acid deficiency is so rare that no countries require that foods be fortified.
Absorption, metabolism and excretion
When found in foods, most pantothenic acid is in the form of CoA or bound to acyl carrier protein (ACP). For the intestinal cells to absorb this vitamin, it must be converted into free pantothenic acid. Within the lumen of the intestine, CoA and ACP are hydrolyzed into 4'-phosphopantetheine. The 4'-phosphopantetheine is then dephosphorylated into pantetheine. Pantetheinase, an intestinal enzyme, then hydrolyzes pantetheine into free pantothenic acid. Free pantothenic acid is absorbed into intestinal cells via a saturable, sodium-dependent active transport system. At high levels of intake, when this mechanism is saturated, some pantothenic acid may also be additionally absorbed via passive diffusion. As a whole, when intake increases 10-fold, absorption rate decreases to 10%.
Pantothenic acid is excreted in urine. This occurs after its release from CoA. Urinary amounts are on the order of 2.6 mg/day, but decreased to negligible amounts when subjects in multi-week experimental situations were fed diets devoid of the vitamin.
Deficiency
Pantothenic acid deficiency in humans is very rare and has not been thoroughly studied. In the few cases where deficiency has been seen (prisoners of war during World War II, victims of starvation, or limited volunteer trials), nearly all symptoms were reversed with orally administered pantothenic acid. Symptoms of deficiency are similar to other vitamin B deficiencies. There is impaired energy production, due to low CoA levels, which could cause symptoms of irritability, fatigue, and apathy. Acetylcholine synthesis is also impaired; therefore, neurological symptoms can also appear in deficiency; they include sensation of numbness in hands and feet, paresthesia and muscle cramps. Additional symptoms could include restlessness, malaise, sleep disturbances, nausea, vomiting and abdominal cramps.
In animals, symptoms include disorders of the nervous, gastrointestinal, and immune systems, reduced growth rate, decreased food intake, skin lesions and changes in hair coat, and alterations in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. In rodents, there can be loss of hair color, which led to marketing of pantothenic acid as a dietary supplement which could prevent or treat graying of hair in humans (despite the lack of any human trial evidence).
Pantothenic acid status can be assessed by measuring either whole blood concentration or 24-hour urinary excretion. In humans, whole blood values less than 1 μmol/L are considered low, as is urinary excretion of less than 4.56 mmol/day.
Animal nutrition
Calcium pantothenate and dexpanthenol (D-panthenol) are European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) approved additives to animal feed. Supplementation is on the order of 8–20 mg/kg for pigs, 10–15 mg/kg for poultry, 30–50 mg/kg for fish and 8–14 mg/kg feed for pets. These are recommended concentrations, designed to be higher than what are thought to be requirements. There is some evidence that feed supplementation increases pantothenic acid concentration in tissues, i.e., meat, consumed by humans, and also for eggs, but this raises no concerns for consumer safety.
No dietary requirement for pantothenic acid has been established in ruminant species. Synthesis of pantothenic acid by ruminal microorganisms appears to be 20 to 30 times more than dietary amounts. Net microbial synthesis of pantothenic acid in the rumen of steer calves has been estimated to be 2.2 mg/kg of digestible organic matter consumed per day. Supplementation of pantothenic acid at 5 to 10 times theoretical requirements did not improve growth performance of feedlot cattle.
Synthesis
Biosynthesis
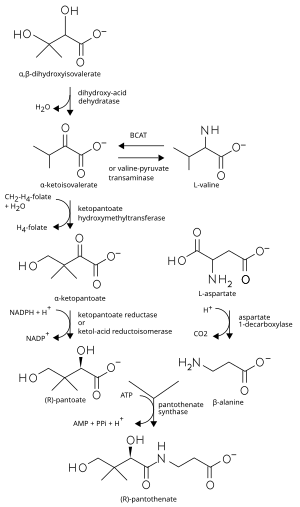
Bacteria synthesize pantothenic acid from the amino acids aspartate and a precursor to the amino acid valine. Aspartate is converted to β-alanine. The amino group of valine is replaced by a keto-moiety to yield α-ketoisovalerate, which, in turn, forms α-ketopantoate following transfer of a methyl group, then D-pantoate (also known as pantoic acid) following reduction. β-alanine and pantoic acid are then condensed to form pantothenic acid (see figure).
Industrial synthesis
The industrial synthesis of pantothenic acid starts with the aldol condensation of isobutyraldehyde and formaldehyde. The resulting hydroxypivaldehyde is converted to its cyanohydrin derivative. which is cyclised to give racemic pantolactone. This sequence of reactions was first published in 1904.
Synthesis of the vitamin is completed by resolution of the lactone using quinine, for example, followed by treatment with the calcium or sodium salt of β-alanine.
History
The term vitamin is derived from the word vitamine, which was coined in 1912 by Polish biochemist Casimir Funk, who isolated a complex of water-soluble micronutrients essential to life, all of which he presumed to be amines. When this presumption was later determined not to be true, the "e" was dropped from the name, hence "vitamin". Vitamin nomenclature was alphabetical, with Elmer McCollum calling these fat-soluble A and water-soluble B. Over time, eight chemically distinct, water-soluble B vitamins were isolated and numbered, with pantothenic acid as vitamin B5.
The essential nature of pantothenic acid was discovered by Roger J. Williams in 1933 by showing it was required for the growth of yeast. Three years later Elvehjem and Jukes demonstrated that it was a growth and anti-dermatitis factor in chickens. Williams dubbed the compound "pantothenic acid", deriving the name from the Greek word pantothen, which translates as "from everywhere". His reason was that he found it to be present in almost every food he tested. Williams went on to determine the chemical structure in 1940. In 1953, Fritz Lipmann shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for his discovery of co-enzyme A and its importance for intermediary metabolism", work he had published in 1946.
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Pantothenic acid/ja(27 January 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Lua error in Module:Itemnumber at line 91: attempt to concatenate local 'qid' (a nil value). |

