Fertilizer/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "気候変動に関する政府間パネル(IPCC)の気候変動と土地に関する特別報告書によると、これらの肥料の生産と関連する土地利用慣行は、地球温暖化の推進要因である。肥料の使用はまた、多くの直接的な環境への影響を引き起こしている。:en:agricul..." |
Created page with "環境および食料安全保障への懸念を軽減するため、国際社会は持続可能な開発目標2に食料システムを組み込んでおり、これは気候変動に配慮した持続可能な食料生産システムの構築に焦点を当てている。これらの問題に対処するためのほとんどの..." |
||
| Line 266: | Line 266: | ||
[[:en:Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change|気候変動に関する政府間パネル(IPCC)]]の[[:en:Special Report on Climate Change and Land|気候変動と土地に関する特別報告書]]によると、これらの肥料の生産と関連する[[:en:land use|土地利用]]慣行は、[[:en:global warming|地球温暖化]]の推進要因である。肥料の使用はまた、多くの直接的な環境への影響を引き起こしている。[[:en:agricultural runoff|農業排水]]による[[:en:Dead zone (ecology)|海洋のデッドゾーン]]や水路汚染といった下流への影響、[[:en:soil microbiome|土壌微生物叢]]の劣化、生態系における毒素の蓄積などである。間接的な環境への影響としては、[[:en:Haber process|ハーバー・ボッシュ法]]で使用される[[natural gas/ja|天然ガス]]の[[:en:Hydraulic fracturing|水圧破砕による環境への影響]]、農業のブームが[[:en:Human population growth|人口の急速な増加]]の一因となっていること、大規模な工業的農業慣行が[[:en:habitat destruction|生息地の破壊]]、[[:en:Biodiversity loss|生物多様性への圧力]]、農業[[:en:soil loss|土壌損失]]と関連していることが挙げられる。 | [[:en:Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change|気候変動に関する政府間パネル(IPCC)]]の[[:en:Special Report on Climate Change and Land|気候変動と土地に関する特別報告書]]によると、これらの肥料の生産と関連する[[:en:land use|土地利用]]慣行は、[[:en:global warming|地球温暖化]]の推進要因である。肥料の使用はまた、多くの直接的な環境への影響を引き起こしている。[[:en:agricultural runoff|農業排水]]による[[:en:Dead zone (ecology)|海洋のデッドゾーン]]や水路汚染といった下流への影響、[[:en:soil microbiome|土壌微生物叢]]の劣化、生態系における毒素の蓄積などである。間接的な環境への影響としては、[[:en:Haber process|ハーバー・ボッシュ法]]で使用される[[natural gas/ja|天然ガス]]の[[:en:Hydraulic fracturing|水圧破砕による環境への影響]]、農業のブームが[[:en:Human population growth|人口の急速な増加]]の一因となっていること、大規模な工業的農業慣行が[[:en:habitat destruction|生息地の破壊]]、[[:en:Biodiversity loss|生物多様性への圧力]]、農業[[:en:soil loss|土壌損失]]と関連していることが挙げられる。 | ||
環境および[[:en:food security|食料安全保障]]への懸念を軽減するため、国際社会は[[:en:Sustainable Development Goal 2|持続可能な開発目標2]]に食料システムを組み込んでおり、これは[[:en:Effects of climate change on agriculture|気候変動に配慮した]][[:en:sustainable food system|持続可能な食料生産システム]]の構築に焦点を当てている。これらの問題に対処するためのほとんどの政策的・規制的アプローチは、農業慣行を[[:en:Sustainable agriculture|持続可能な農業]]または[[:en:Regenerative agriculture|再生型農業]]の慣行へと転換することに焦点を当てている。これらは、合成肥料の使用量を減らし、より良い[[:en:soil management|土壌管理]](例えば[[:en:No-till farming|不耕起農業]])を行い、より多くの有機肥料を使用する。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 14:12, 16 July 2025

肥料は、植物の栄養を供給するために土壌または植物組織に適用される、天然または合成由来のあらゆる物質である。肥料は、石灰質資材やその他の非栄養土壌改良材とは異なる場合がある。肥料の供給源は、天然のものも工業的に生産されるものも多数存在する。現代のほとんどの農業慣行では、施肥は窒素(N)、リン(P)、カリウム(K)の3つの主要な多量栄養素に焦点を当てており、微量栄養素のためにロックフラワーのような補助剤が時折追加される。農家はこれらの肥料を、大規模な農業機械を使用したり、手作業の方法を使用したりして、乾燥またはペレット状、あるいは液体施用プロセスを通じて、さまざまな方法で施用する。
歴史的に、施肥は天然または有機源から行われてきた。すなわち、堆肥、動物の糞尿、人間の糞尿、採取された鉱物、輪作、そして人間と自然の産業の副産物(例:魚粉、血粉)である。しかし、19世紀以降、植物栄養の革新後、合成的に作られた農業化学肥料を中心とした農業産業が発展した。この転換は、世界の食料システムを変革し、大規模な集約農業による高収量を可能にする上で重要であった。

20世紀初頭に発明され、第二次世界大戦中に生まれた生産能力によって増幅された窒素固定化学プロセス、例えばハーバー・ボッシュ法は、窒素肥料の使用ブームにつながった。20世紀後半には、窒素肥料の使用量の増加(1961年から2019年の間に800%増加)が、いわゆる「緑の革命」の一環として、従来の食料システムの生産性向上(一人当たり30%以上)の重要な要素となっている。
人工肥料および工業的に施用される肥料の使用は、栄養素の流出による水質汚染や富栄養化、肥料の生産および採掘による炭素その他の排出、そして土壌の汚染などの環境問題を引き起こしている。肥料や農薬の使用による悪影響や工業的農業による環境破壊を減らすために、様々な持続可能な農業慣行が実施され得る。
歴史




土壌の肥沃度管理は、農業が始まって以来、農民の関心事であった。中東、中国、メソアメリカ、中央アンデスの文化はすべて、農業の初期採用者であった。これにより、これらの文化の人口が急速に増加し、隣接する狩猟採集民グループへの文化の輸出が可能になったと考えられている(P Bellwood - 2023)。エジプト人、ローマ人、バビロニア人、初期のドイツ人は皆、農地の生産性を高めるために鉱物や肥料を使用していたと記録されている。植物栄養に関する科学的研究は、ドイツの化学者ユストゥス・フォン・リービッヒの業績よりもずっと前に始まっていたが、彼の名前は「肥料産業の父」として最もよく言及されている。ニコラ・テオドール・ド・ソシュールと当時の科学者たちは、フォン・リービッヒの単純化をすぐに否定した。フォン・リービッヒが影響を受けた著名な科学者には、カール・ルートヴィヒ・シュプレンガーとヘルマン・ヘルリーゲルがいる。この分野では、経済学と研究の混交が部分的に拍車をかけた「知識の浸食」が起こった。イギリスの起業家であるジョン・ベネット・ローズは、1837年に鉢植え植物に対する様々な肥料の効果を実験し始め、1、2年後にはその実験を畑の作物にまで拡大した。その直接の結果として、1842年にリン酸塩を硫酸で処理して形成される肥料の特許を取得し、人工肥料産業を最初に創設した人物となった。翌年、彼はジョセフ・ヘンリー・ギルバートの協力を得て、ローザムステッド研究センターで作物実験を行った。
ビルケランド・アイデ法は、窒素系肥料生産開始時の競合する工業プロセスの一つであった。このプロセスは、大気中の窒素(N2)を硝酸(HNO3)に固定するために使用され、これは窒素固定と呼ばれるいくつかの化学プロセスの1つである。生成された硝酸は、その後硝酸塩(NO3−)の供給源として使用された。このプロセスに基づく工場はノルウェーのリューカンとノトデンに建設され、大規模な水力発電施設も建設された。
1910年代から1920年代にかけて、ハーバー法とオストワルド法が台頭した。ハーバー法は、メタン(CH4)(天然ガス)と空気中の分子状窒素(N2)からアンモニア(NH3)を生成する。ハーバー法で得られたアンモニアは、オストワルド法で部分的に硝酸(HNO3)に変換される。世界の年間食料生産の3分の1はハーバー・ボッシュ法によるアンモニアを使用しており、これが世界の人口のほぼ半分を支えていると推定されている。第二次世界大戦後、戦時中の爆弾製造のために増強された窒素生産工場は、農業用途に転換された。合成窒素肥料の使用は過去50年間着実に増加し、現在の年間1億トンの窒素という割合まで約20倍に増加している。
合成窒素肥料の開発は、世界の人口増加を著しく支えてきた。現在、地球上のほぼ半分の人々が合成窒素肥料の使用によって食料を供給されていると推定されている。リン酸肥料の使用も、1960年の年間900万トンから2000年には年間4000万トンに増加している。
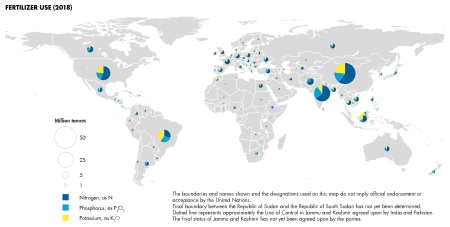
2021年の無機肥料の農業利用量は1億9500万トンの養分であり、そのうち56%が窒素であった。2021年の世界の無機肥料の総農業利用量のうち、アジアが53%を占め、次いでアメリカ大陸(29%)、ヨーロッパ(12%)、アフリカ(4%)、オセアニア(2%)であった。これらの地域の順位はすべての養分で同じである。無機肥料の主要な使用国は、降順に中国、インド、ブラジル、およびアメリカ合衆国である(表15参照)。中国は各養分の最大の使用者である。
1ヘクタール(2.5 acres)あたり6〜9トンの穀物を収穫するトウモロコシ畑では、リン酸塩肥料を31–50 kilograms (68–110 lb)施用する必要がある。大豆畑ではその約半分、1ヘクタールあたり20〜25kgが必要である。
メカニズム


肥料は植物の成長を促進する。この目標は2つの方法で達成され、伝統的な方法は養分を供給する添加物である。肥料が作用する2番目の方法は、保水性と通気性を変更することで土壌の効果を高めることである。この記事では、多くの肥料に関する記事と同様に、栄養面に重点を置いている。 肥料は通常、様々な割合で以下を提供する。
- 3つの主要多量栄養素(NPK):
- 3つの二次多量栄養素:カルシウム(Ca)、マグネシウム(Mg)、硫黄(S)
- 微量栄養素:銅(Cu)、鉄(Fe)、マンガン(Mn)、モリブデン(Mo)、亜鉛(Zn)、ホウ素(B)。時折重要なものとしては、ケイ素(Si)、コバルト(Co)、バナジウム(V)がある。
健全な植物の生命に必要な養分は元素によって分類されるが、元素は肥料としては使用されない。代わりに、これらの元素を含む化合物が肥料の基礎となる。多量栄養素はより大量に消費され、乾燥物質(DM)(水分0%)基準で0.15%から6.0%の量で植物組織に存在する。植物は主に水素、酸素、炭素、窒素の4つの元素で構成されている。炭素、水素、酸素はそれぞれ二酸化炭素と水中に広く存在する。窒素は大気の大部分を占めているが、植物が利用できない形態である。窒素はタンパク質(アミノ酸間のアミド結合)、DNA(プリン塩基とピリミジン塩基)、およびその他の成分(例:クロロフィル中のテトラピロールヘム)中に存在するため、最も重要な肥料である。植物にとって栄養価を高めるためには、窒素を「固定された」形態で利用可能にする必要がある。一部の細菌とその宿主植物(特にマメ科植物)のみが、大気中の窒素(N2)をアンモニア(NH3)に変換することで固定できる。リン酸塩(PO43−)は、DNA(遺伝暗号)とATP(細胞の主要なエネルギーキャリア)、ならびに特定の脂質(細胞膜の脂質二重層の主要成分であるリン脂質)の生産に必要である。
微生物学的考察
2組の酵素反応は、窒素系肥料の効率に非常に密接に関連している。
- ウレアーゼ
1つ目は、尿素(CO(NH2)2)の加水分解(水との反応)である。多くの土壌細菌はウレアーゼという酵素を持っており、これは尿素をアンモニウムイオン(NH4+)と炭酸水素イオン(HCO3−)に変換する触媒作用をする。
- アンモニア酸化
ニトロソモナス属のようなアンモニア酸化細菌(AOB)は、アンモニア(NH3)を亜硝酸塩(NO2−)に酸化する。このプロセスは硝化と呼ばれる。亜硝酸酸化細菌、特にニトロバクターは、亜硝酸塩(NO2−)を硝酸塩(NO3−)に酸化する。硝酸塩は極めて溶解度が高く移動性があり、富栄養化やアオコの主要な原因となる。
分類
肥料はいくつかの方法で分類される。単一の養分(例:K、P、またはN)を供給するかどうかに応じて分類され、その場合は「単肥」と分類される。「複合肥料」(または「複合肥料」)は、例えばNとPのように2つ以上の養分を供給する。肥料はまた、無機肥料(この記事のほとんどのトピック)と有機肥料に分類されることもある。無機肥料は尿素を除く炭素含有物質を含まない。有機肥料は通常、(リサイクルされた)植物または動物由来の物質である。無機肥料は、その製造に様々な化学的処理が必要とされるため、合成肥料と呼ばれることもある。
単一養分(「単肥」)肥料
主な窒素ベースの単肥は、アンモニア(NH3)アンモニウム(NH4+)またはその溶液であり、以下を含む。
- 硝酸アンモニウム(NH4NO3)は窒素を34〜35%含み、広く使用されている。
- 尿素(CO(NH2)2)は窒素を45〜46%含み、もう一つの人気のある窒素源であり、アンモニアや硝酸アンモニウムとは異なり、固体で非爆発性であるという利点がある。
- 硝酸アンモニウム石灰は、20〜30%の石灰石CaCO3またはドロマイト(Ca,Mg)CO3と、70〜80%の硝酸アンモニウムを混合したもので、窒素を24〜28%含む。
- 硝酸カルシウムは窒素を15.5%、カルシウムを19%含み、窒素肥料市場の小さなシェア(2007年には4%)を占めていると報告されている。
主な単一リン酸肥料は過リン酸石灰である。
- 「過リン酸一石灰」(SSP)は14〜18%のP2O5を含み、これもCa(H2PO4)2の形態であるが、リン酸石膏(CaSO4 • 2 H2O)も含む。
- 重過リン酸石灰(TSP)は通常44〜48%のP2O5を含み、石膏は含まない。
過リン酸一石灰と重過リン酸石灰の混合物は、倍過リン酸石灰と呼ばれる。一般的な過リン酸石灰肥料の90%以上は水溶性である。
主なカリウムベースの単肥は、塩化カリウム(MOP、95〜99% KCl)である。通常、0-0-60または0-0-62肥料として利用可能である。
多量養分肥料
これらの肥料は一般的である。これらは2つ以上の養分成分から構成される。
- 二成分(NP、NK、PK)肥料
主要な二成分肥料は、窒素とリンの両方を植物に供給する。これらはNP肥料と呼ばれる。主なNP肥料は次の通りである。
- リン酸一アンモニウム(MAP)NH4H2PO4。窒素11%、P2O5 48%を含む。
- リン酸二アンモニウム(DAP)。(NH4)2HPO4。窒素18%、P2O5 46%を含む。
MAPおよびDAP肥料の約85%は水溶性である。
- NPK肥料
{{multiple image | width = 200 | footer = | image1 = Compound fertiliser.jpg | alt1 = Compound fertiliser | caption1 = 化成肥料 | image2 = Bulk-blend fertiliser.jpg | alt2 = Bulk-blend fertiliser | caption2 = バルクブレンド肥料
}}NPK肥料は、窒素、リン、カリウムを供給する三成分肥料である。NPK肥料には、化成肥料と配合肥料の2種類がある。化成NPK肥料は化学的に結合した成分を含み、配合NPK肥料は単一養分成分の物理的混合物である。
NPK表示は、肥料中の窒素、リン、カリウムの量を記述する評価システムである。NPK表示は、ダッシュで区切られた3つの数字(例:10-10-10または16-4-8)で構成され、肥料の化学成分を記述する。最初の数字は製品中の窒素の割合、2番目の数字はP2O5、3番目の数字はK2Oを表す。肥料には実際にはP2O5やK2Oは含まれていないが、このシステムは肥料中のリン(P)またはカリウム(K)の量を表す慣習的な略記である。16-4-8と表示された50-pound (23 kg)の肥料袋には、窒素が8 lb (3.6 kg)(50ポンドの16%)、P2O5 2ポンドに含まれるリンに相当する量(50ポンドの4%)、K2O 4ポンド(50ポンドの8%)が含まれている。ほとんどの肥料はこのN-P-K表示に従って表示されているが、オーストラリアの慣習ではN-P-K-Sシステムに従い、硫黄のために4番目の数字を追加し、PとKを含むすべての値に元素値を使用している。
微量養分
微量養分は少量消費され、植物組織中にはppm単位で存在する。これは0.15から400ppm、または乾燥物質で0.04%未満の範囲である。これらの元素は、植物の代謝に不可欠な酵素にしばしば必要とされる。これらの元素が触媒(酵素)を可能にするため、その影響は重量パーセントをはるかに超える。典型的な微量養分は、ホウ素、亜鉛、モリブデン、鉄、マンガンである。これらの元素は水溶性塩として供給される。鉄は、中程度の土壌pHおよびリン酸塩濃度で不溶性(生体利用不可能)化合物に変化するため、特殊な問題を引き起こす。このため、鉄はしばしばキレート錯体として、例えばEDTAやEDDHA誘導体として投与される。微量養分の必要性は、植物と環境によって異なる。例えば、テンサイはホウ素を必要とし、マメ科植物はコバルトを必要とするとされる。
生産
合成肥料、すなわち無機肥料の生産には調製された化学物質が必要であるが、有機肥料は生化学的プロセスを用いて植物や動物の有機プロセスから派生する。
窒素肥料

窒素肥料は、ハーバー・ボッシュ法によって生産されるアンモニア(NH3)から作られる。このエネルギー集約的なプロセスでは、天然ガス(CH4)が通常水素を供給し、窒素(N2)は空気から派生する。このアンモニアは、無水硝酸アンモニウム(NH4NO3)や尿素(CO(NH2)2)など、他のすべての窒素肥料の原料として使用される。
硝酸ナトリウム(NaNO3)(チリ硝石)の鉱床はチリのアタカマ砂漠にも見られ、使用された元々の(1830年)窒素豊富な肥料の一つであった。現在も肥料として採掘されている。硝酸塩はオストワルド法によってアンモニアからも生産される。
リン酸肥料

リン酸肥料は、2つの主要なリン含有鉱物であるフッ素アパタイトCa5(PO4)3F(CFA)と水酸アパタイトCa5(PO4)3OHを含むリン鉱石から抽出されることで得られる。毎年数十億kgのリン鉱石が採掘されているが、残存する鉱石の規模と品質は低下している。これらの鉱物は、酸で処理することにより水溶性リン酸塩に変換される。硫酸の大量生産は、主にこの用途によって動機付けられている。ニトロリン酸法またはオッダ法(1927年発明)では、最大20%のリン(P)含有量を持つリン鉱石が硝酸(HNO3)で溶解され、リン酸(H3PO4)と硝酸カルシウム(Ca(NO3)2)の混合物が生成される。この混合物はカリウム肥料と組み合わせて、3つの多量栄養素N、P、Kを容易に溶解する形で含む「複合肥料」を生産することができる。
カリウム肥料
カリウムは、カリウム(化学記号:K)肥料を作るために使用されるカリウム鉱物の混合物である。カリウムは水に可溶であるため、鉱石からこの養分を生産する主な努力は、塩化ナトリウム(NaCl)(一般的な塩)を除去するなどのいくつかの精製段階を含む。カリウムは、カリウム含有量を記述する人々の便宜上、K2Oとして言及されることがある。実際には、カリウム肥料は通常、塩化カリウム、硫酸カリウム、炭酸カリウム、または硝酸カリウムである。
NPK肥料
NPK肥料(主要成分である窒素(N)、リン(P)、カリウム(K)にちなんで名付けられた)を製造する主な方法は3つある。
- バルクブレンド。個々の肥料を所望の栄養比で組み合わせる。
| 配合成分 | NPK 17-17-17 | NPK 19-19-19 | NPK 9-23-30 | NPK 8-32-16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硝酸アンモニウム | 310 | |||
| 尿素 | 256 | |||
| リン酸二アンモニウム(DAP) | 376 | 421 | 500 | 462 |
| 重過リン酸石灰 | 261 | |||
| 塩化カリウム | 288 | 323 | 500 | 277 |
| 充填材 | 26 |
- ニトロリン酸法。ステップ1。ニトロリン酸塩は、硝酸でリン鉱石を酸性化することによって作られる。
- 硝酸 + リン鉱石 → リン酸 + 硫酸カルシウム + 六フッ化ケイ酸。
- Ca5F(PO4)3 + 10 HNO3 →6 H3PO4 + 5 Ca(NO3)2 + HF
- 6 HF + SiO2 →H2SiF6 + 2 H2O
ステップ2。硝酸カルシウムの除去。硝酸カルシウムは極めて吸湿性が高いため、硝酸カルシウムを除去することが重要である。
- 方法1。(オッダ法)硝酸カルシウム結晶は遠心分離によって除去される。
- 方法2。スルホ硝酸法 Ca(NO3)2 + H2SO4 + 2NH3 → CaSO4 + 2NH4NO3
- 方法3。ホスホ硝酸法 Ca(NO3)2 + H3PO4 + 2NH3 → CaHPO4 + 2NH4NO3
- 方法4。カルボ硝酸法 Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 + H2O + 2NH3 → CaCO3 + 2NH4NO3
有機肥料


「有機肥料」は、生物学的起源を持つ肥料、すなわち生きている物質またはかつて生きていた物質から派生した肥料を記述できる。有機肥料はまた、「有機農業」や「環境に優しい」園芸(合成肥料や農薬の使用を大幅に制限または厳密に避ける食品および植物生産関連システム)によって採用された期待と制限に従うように努める市販の、そしてしばしば包装された製品を記述することもできる。「有機肥料」製品は通常、いくつかの有機材料と、栄養豊富な岩石粉末、粉砕された貝殻(カニ、カキなど)、種子粕やケルプなどの他の調製製品、および培養された微生物とその誘導体などの許容される添加物の両方を含む。
有機起源の肥料(最初の定義)には、動物の排泄物、農業からの植物性廃棄物、海藻、堆肥、処理された下水汚泥(バイオソリッド)が含まれる。肥料以外にも、動物源には動物の屠殺による製品が含まれる。血粉、骨粉、フェザーミール、皮、ひづめ、角はすべて典型的な成分である。下水汚泥のような産業で利用可能な有機由来の物質は、残留汚染物質から世間の認識に至るまでの要因により、有機農業や園芸の許容される成分ではないかもしれない。一方、市販されている「有機肥料」は、その材料が消費者のアピール力を持つため、加工された有機物を意図的に含み、宣伝することもある。定義や組成に関わらず、これらの製品のほとんどは濃度の低い栄養素を含み、その栄養素は容易に定量化できない。これらは土壌構築の利点を提供するとともに、「より自然に」農業/園芸を行おうとする人々にとって魅力的である。
体積の観点から、泥炭は最も広く使用されている包装された有機土壌改良材である。これは石炭の未熟な形態であり、通気と吸水によって土壌を改善するが、植物に栄養価を与えない。したがって、これは記事の冒頭で定義された肥料ではなく、むしろ改良材である。コイア(ココナッツの殻に由来)、樹皮、おがくずは、土壌に添加されるとすべて泥炭と同様に(ただし同一ではない)作用し、栄養素の投入が限られているため、有機土壌改良材、またはテクスチャー材と見なされる。一部の有機添加物は、栄養素に逆の効果を持つ可能性がある。新鮮なおがくずは、分解する際に土壌栄養素を消費し、土壌pHを下げる可能性がある。しかし、これらの同じ有機テクスチャー材(および堆肥など)は、陽イオン交換の改善や、特定の植物栄養素の利用可能性を増加させる微生物の成長の増加を通じて、栄養素の利用可能性を高める可能性がある。堆肥や糞尿などの有機肥料は、産業生産を経ずに地域で流通する可能性があり、実際の消費量を定量化することがより困難になる。
肥料消費量

| 国 | 窒素総使用量 (百万トン/年) |
飼料・牧草用 窒素使用量 (百万トン/年) |
|---|---|---|
| 中国 | 18.7 | 3.0 |
| インド | 11.9 | n/a |
| 米国 | 9.1 | 4.7 |
| フランス | 2.5 | 1.3 |
| ドイツ | 2.0 | 1.2 |
| ブラジル | 1.7 | 0.7 |
| カナダ | 1.6 | 0.9 |
| トルコ | 1.5 | 0.3 |
| 英国 | 1.3 | 0.9 |
| メキシコ | 1.3 | 0.3 |
| スペイン | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| アルゼンチン | 0.4 | 0.1 |
中国は窒素肥料の最大の生産国および消費国となっており、一方アフリカでは窒素肥料への依存度が低い。農業用および化学鉱物は、約2,000億ドルの価値がある肥料の工業的使用において非常に重要である。窒素は世界の鉱物使用に大きな影響を与えており、それにカリウムとリン酸が続く。窒素の生産は1960年代以降劇的に増加している。リン酸とカリウムの価格は1960年代以降上昇しており、これは消費者物価指数よりも大きい。カリウムはカナダ、ロシア、ベラルーシで生産され、これらを合わせると世界の生産量の半分以上を占める。カナダのカリウム生産量は2017年と2018年に18.6%増加した。控えめな推定では、作物収量の30〜50%は天然または合成の市販肥料によるものと報告されている。肥料消費量は米国の農地面積を上回っている。
2012年の耕地1ヘクタールあたりの肥料消費量データは世界銀行によって公表されている。下の図は、欧州連合(EU)諸国による肥料消費量を1ヘクタールあたりキログラム(1エーカーあたりポンド)で示している。EU全体の肥料消費量は、1億500万ヘクタールの耕地面積に対し1590万トン(別の推定によると1億700万ヘクタールの耕地面積)である。この数値は、EU諸国で平均して耕地1ヘクタールあたり151kgの肥料が消費されていることに相当する。
施用



肥料は通常、すべての作物栽培に使用され、施用量は土壌肥沃度(通常は土壌検査によって測定される)および特定の作物に応じて決定される。例えば、マメ科植物は空気中の窒素を固定するため、一般的に窒素肥料を必要としない。
液体肥料と固体肥料
肥料は固体としても液体としても作物に施用される。肥料の約90%は固体として施用される。最も広く使用されている固体無機肥料は尿素、リン酸二アンモニウム、塩化カリウムである。固体肥料は通常、粒状または粉末状である。しばしば固体はプリル(固体の小球)として利用可能である。液体肥料は、無水アンモニア、アンモニア水溶液、硝酸アンモニウムまたは尿素の水溶液からなる。これらの濃縮製品は水で希釈して濃縮液体肥料(例:尿素硝酸アンモニウム)を形成することができる。液体肥料の利点は、より迅速な効果と容易な散布である。灌漑用水への肥料添加は「液肥混入」と呼ばれる。
尿素
尿素は水溶性が高く、そのため肥料溶液(硝酸アンモニウムとの組み合わせ:UAN)での使用、例えば「葉面散布肥料」での使用にも非常に適している。肥料用途では、機械施用において有利な狭い粒度分布を持つため、プリルよりも顆粒が好まれる。
尿素は通常、40〜300kg/ha(35〜270lbs/エーカー)の割合で散布されるが、その割合は様々である。少量施用の場合、浸出による損失が少ない。夏期には、揮発(窒素がアンモニアガスとして大気中に失われるプロセス)による損失を最小限に抑えるため、尿素は雨の直前または降雨中に散布されることが多い。
尿素の窒素濃度が高いため、均一な散布を達成することが非常に重要である。発芽損傷のリスクがあるため、種子に接触または近接して施用してはならない。尿素は水に溶解して、スプレーとして、または灌漑システムを通じて施用される。
穀物作物や綿花作物では、尿素はしばしば播種前の最後の耕うん時に施用される。降雨量の多い地域や砂質土壌(窒素が浸出によって失われる可能性がある場所)で、生育期の良好な降雨が期待される場合、尿素は生育期中に側条施肥または追肥として施用できる。追肥は牧草地や飼料作物でも人気がある。サトウキビ栽培では、尿素は植え付け後に側条施肥され、各ひこばえ作物に施用される。
尿素は空気中の水分を吸収するため、密閉容器に保管されることが多い。
過剰施用や種子の近くに尿素を置くことは有害である。
緩効性肥料および制御放出性肥料
葉面散布
葉面肥料は葉に直接施用される。この方法はほとんど例外なく水溶性のストレート窒素肥料を施用するために使用され、特に果物などの高価値作物に利用される。尿素は最も一般的な葉面肥料である。

窒素吸収に影響を与える化学物質

窒素系肥料の効率を高めるために、様々な化学物質が使用される。この方法により、農家は窒素流出による汚染効果を抑制することができる。硝化抑制剤(窒素安定剤とも呼ばれる)は、アンモニアが硝酸塩(浸出しやすい陰イオン)に変換されるのを抑制する。1-カルバモイル-3-メチルピラゾール(CMP)、ジシアンジアミド、ニトラピリン(2-クロロ-6-トリクロロメチルピリジン)、3,4-ジメチルピラゾールリン酸(DMPP)が一般的である。ウレアーゼ阻害剤は、尿素がアンモニアに加水分解されるのを遅らせるために使用される。アンモニアは蒸発しやすく、硝化も起こりやすい。尿素がウレアーゼと呼ばれる酵素によって触媒されるアンモニアへの変換を抑制する。ウレアーゼの一般的な阻害剤はN-(n-ブチル)チオホスホリルトリアミド(NBPT)である。
過剰施肥
栄養素の過剰は有害となる可能性があるため、施肥技術を慎重に使用することが重要である。肥料の施用量が多すぎると、肥料焼けが発生し、植物に損傷を与えたり、枯死させたりすることさえある。肥料は、その塩類指数にほぼ比例して、肥料焼けの傾向が異なる。
環境への影響

農業で使用される合成肥料は、広範囲にわたる環境への影響を及ぼす。
気候変動に関する政府間パネル(IPCC)の気候変動と土地に関する特別報告書によると、これらの肥料の生産と関連する土地利用慣行は、地球温暖化の推進要因である。肥料の使用はまた、多くの直接的な環境への影響を引き起こしている。農業排水による海洋のデッドゾーンや水路汚染といった下流への影響、土壌微生物叢の劣化、生態系における毒素の蓄積などである。間接的な環境への影響としては、ハーバー・ボッシュ法で使用される天然ガスの水圧破砕による環境への影響、農業のブームが人口の急速な増加の一因となっていること、大規模な工業的農業慣行が生息地の破壊、生物多様性への圧力、農業土壌損失と関連していることが挙げられる。
環境および食料安全保障への懸念を軽減するため、国際社会は持続可能な開発目標2に食料システムを組み込んでおり、これは気候変動に配慮した持続可能な食料生産システムの構築に焦点を当てている。これらの問題に対処するためのほとんどの政策的・規制的アプローチは、農業慣行を持続可能な農業または再生型農業の慣行へと転換することに焦点を当てている。これらは、合成肥料の使用量を減らし、より良い土壌管理(例えば不耕起農業)を行い、より多くの有機肥料を使用する。

For each ton of phosphoric acid produced by the processing of phosphate rock, five tons of waste are generated. This waste takes the form of impure, useless, radioactive solid called phosphogypsum. Estimates range from 100,000,000 and 280,000,000 tons of phosphogypsum waste produced annually worldwide.
Water
Phosphorus and nitrogen fertilizers can affect soil, surface water, and groundwater due to the dispersion of minerals into waterways due to high rainfall, snowmelt and can leaching into groundwater over time. Agricultural run-off is a major contributor to the eutrophication of freshwater bodies. For example, in the US, about half of all the lakes are eutrophic. The main contributor to eutrophication is phosphate, which is normally a limiting nutrient; high concentrations promote the growth of cyanobacteria and algae, the demise of which consumes oxygen. Cyanobacteria blooms ('algal blooms') can also produce harmful toxins that can accumulate in the food chain, and can be harmful to humans. Fertilizer run-off can be reduced by using weather-optimized fertilization strategies.
The nitrogen-rich compounds found in fertilizer runoff are the primary cause of serious oxygen depletion in many parts of oceans, especially in coastal zones, lakes and rivers. The resulting lack of dissolved oxygen greatly reduces the ability of these areas to sustain oceanic fauna. The number of oceanic dead zones near inhabited coastlines is increasing.
As of 2006, the application of nitrogen fertilizer is being increasingly controlled in northwestern Europe and the United States. In cases where eutrophication can be reversed, it may nevertheless take decades and significant soil management before the accumulated nitrates in groundwater can be broken down by natural processes.
Nitrate pollution
Only a fraction of the nitrogen-based fertilizers is converted to plant matter. The remainder accumulates in the soil or is lost as run-off. High application rates of nitrogen-containing fertilizers combined with the high water solubility of nitrate leads to increased runoff into surface water as well as leaching into groundwater, thereby causing groundwater pollution. The excessive use of nitrogen-containing fertilizers (be they synthetic or natural) is particularly damaging, as much of the nitrogen that is not taken up by plants is transformed into nitrate which is easily leached.
Nitrate levels above 10 mg/L (10 ppm) in groundwater can cause 'blue baby syndrome' (acquired methemoglobinemia). Run-off can lead to fertilizing blooms of algae that use up all the oxygen and leave huge "dead zones" behind where other fish and aquatic life can not live.
Soil
Acidification
Soil acidification refers to the process by which the pH level of soil becomes more acidic over time. Soil pH is a measure of the soil's acidity or alkalinity and is determined on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH value below 7 indicates acidic soil, while a pH value above 7 indicates alkaline or basic soil.
Nitrogen-containing fertilizers can cause soil acidification when added. This may lead to decrease in nutrient availability which may be offset by liming. These fertilizers release ammonium or nitrate ions, which can acidify the soil as they undergo chemical reactions.
When these nitrogen-containing fertilizers are added to the soil, they increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the soil solution, which lowers the pH of the soil.
Accumulation of toxic elements
Cadmium
The concentration of cadmium in phosphorus-containing fertilizers varies considerably and can be problematic. For example, mono-ammonium phosphate fertilizer may have a cadmium content of as low as 0.14 mg/kg or as high as 50.9 mg/kg. The phosphate rock used in their manufacture can contain as much as 188 mg/kg cadmium (examples are deposits on Nauru and the Christmas Islands). Continuous use of high-cadmium fertilizer can contaminate soil (as shown in New Zealand) and plants. Limits to the cadmium content of phosphate fertilizers has been considered by the European Commission. Producers of phosphorus-containing fertilizers now select phosphate rock based on the cadmium content.
Fluoride
Phosphate rocks contain high levels of fluoride. Consequently, the widespread use of phosphate fertilizers has increased soil fluoride concentrations. It has been found that food contamination from fertilizer is of little concern as plants accumulate little fluoride from the soil; of greater concern is the possibility of fluoride toxicity to livestock that ingest contaminated soils. Also of possible concern are the effects of fluoride on soil microorganisms.
Radioactive elements
The radioactive content of the fertilizers varies considerably and depends both on their concentrations in the parent mineral and on the fertilizer production process. Uranium-238 concentrations can range from 7 to 100 pCi/g (picocuries per gram) in phosphate rock and from 1 to 67 pCi/g in phosphate fertilizers. Where high annual rates of phosphorus fertilizer are used, this can result in uranium-238 concentrations in soils and drainage waters that are several times greater than are normally present. However, the impact of these increases on the risk to human health from radinuclide contamination of foods is very small (less than 0.05 mSv/y).
Other metals
Steel industry wastes, recycled into fertilizers for their high levels of zinc (essential to plant growth), wastes can include the following toxic metals: lead arsenic, cadmium, chromium, and nickel. The most common toxic elements in this type of fertilizer are mercury, lead, and arsenic. These potentially harmful impurities can be removed; however, this significantly increases cost. Highly pure fertilizers are widely available and perhaps best known as the highly water-soluble fertilizers containing blue dyes used around households, such as Miracle-Gro. These highly water-soluble fertilizers are used in the plant nursery business and are available in larger packages at significantly less cost than retail quantities. Some inexpensive retail granular garden fertilizers are made with high purity ingredients.
Trace mineral depletion
Attention has been addressed to the decreasing concentrations of elements such as iron, zinc, copper and magnesium in many foods over the last 50–60 years. Intensive farming practices, including the use of synthetic fertilizers are frequently suggested as reasons for these declines and organic farming is often suggested as a solution. Although improved crop yields resulting from NPK fertilizers are known to dilute the concentrations of other nutrients in plants, much of the measured decline can be attributed to the use of progressively higher-yielding crop varieties that produce foods with lower mineral concentrations than their less-productive ancestors. It is, therefore, unlikely that organic farming or reduced use of fertilizers will solve the problem; foods with high nutrient density are posited to be achieved using older, lower-yielding varieties or the development of new high-yield, nutrient-dense varieties.
Fertilizers are, in fact, more likely to solve trace mineral deficiency problems than cause them: In Western Australia deficiencies of zinc, copper, manganese, iron and molybdenum were identified as limiting the growth of broad-acre crops and pastures in the 1940s and 1950s. Soils in Western Australia are very old, highly weathered and deficient in many of the major nutrients and trace elements. Since this time these trace elements are routinely added to fertilizers used in agriculture in this state. Many other soils around the world are deficient in zinc, leading to deficiency in both plants and humans, and zinc fertilizers are widely used to solve this problem.
Changes in soil biology
High levels of fertilizer may cause the breakdown of the symbiotic relationships between plant roots and mycorrhizal fungi.
Organic agriculture
Two types of agricultural management practices include organic agriculture and conventional agriculture. The former encourages soil fertility using local resources to maximize efficiency. Organic agriculture avoids synthetic agrochemicals. Conventional agriculture uses all the components that organic agriculture does not use.
Hydrogen consumption and sustainability
Most fertilizer is made from dirty hydrogen. Ammonia is produced from natural gas and air. The cost of natural gas makes up about 90% of the cost of producing ammonia. The increase in price of natural gases over the past decade, along with other factors such as increasing demand, have contributed to an increase in fertilizer price.
Contribution to climate change
The amount of greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide produced during the manufacture and use of nitrogen fertilizer is estimated as around 5% of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. One third is produced during the production and two thirds during the use of fertilizers. Nitrous oxide emissions by humans, most of which are from fertilizer, between 2007 and 2016 have been estimated at 7 million tonnes per year, which is incompatible with limiting global warming to below 2 °C.
Atmosphere

Through the increasing use of nitrogen fertilizer, which was used at a rate of about 110 million tons (of N) per year in 2012, adding to the already existing amount of reactive nitrogen, nitrous oxide (N2O) has become the third most important greenhouse gas after carbon dioxide and methane. It has a global warming potential 296 times larger than an equal mass of carbon dioxide and it also contributes to stratospheric ozone depletion. By changing processes and procedures, it is possible to mitigate some, but not all, of these effects on anthropogenic climate change.
Methane emissions from crop fields (notably rice paddy fields) are increased by the application of ammonium-based fertilizers. These emissions contribute to global climate change as methane is a potent greenhouse gas.
Policy
Regulation
In Europe, problems with high nitrate concentrations in runoff are being addressed by the European Union's Nitrates Directive. Within Britain, farmers are encouraged to manage their land more sustainably in 'catchment-sensitive farming'. In the US, high concentrations of nitrate and phosphorus in runoff and drainage water are classified as nonpoint source pollutants due to their diffuse origin; this pollution is regulated at the state level. Oregon and Washington, both in the United States, have fertilizer registration programs with on-line databases listing chemical analyses of fertilizers. Carbon emission trading and eco-tariffs affect the production and price of fertilizer.
Subsidies
In China, regulations have been implemented to control the use of N fertilizers in farming. In 2008, Chinese governments began to partially withdraw fertilizer subsidies, including subsidies to fertilizer transportation and to electricity and natural gas use in the industry. In consequence, the price of fertilizer has gone up and large-scale farms have begun to use less fertilizer. If large-scale farms keep reducing their use of fertilizer subsidies, they have no choice but to optimize the fertilizer they have which would therefore gain an increase in both grain yield and profit.
In March 2022, the United States Department of Agriculture announced a new $250M grant to promote American fertilizer production. Part of the Commodity Credit Corporation, the grant program will support fertilizer production that is independent of dominant fertilizer suppliers, made in America, and utilizing innovative production techniques to jumpstart future competition.
関連項目
外部リンク
- 私たちの食物を養うための窒素、その地球の起源、ハーバープロセス Archived 11 January 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA)|国際肥料工業会(IFA)
- Agriculture Guide, Complete Guide to Fertilizers and Fertilization|農業ガイド、肥料と施肥の完全ガイド (archived 6 October 2011)
- Nitrogen-Phosphorus-Potassium Values of Organic Fertilizers|有機肥料の窒素-リン-カリウム値。Archived 26 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Fertilizer(9 July 2025, at 16:59編集記事参照)を翻訳して二次利用しています。 |