Potassium/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "カリウム塩を沈殿させるための試薬としては、テトラフェニルホウ酸ナトリウム、ヘキサクロロ白金酸、コバルト亜硝酸ナトリウムをそれぞれテトラフェニルホウ酸カリウム、ヘキサクロロ白金酸カリウム、potassium cobaltinitrite/ja|..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
|||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
コバルト亜硝酸カリウムは黄色の固体として得られる。 | コバルト亜硝酸カリウムは黄色の固体として得られる。 | ||
==商業的利用{{Anchor|Commercial uses}}== | |||
==Commercial uses== | ===肥料=== | ||
=== | [[File:Patentkali (Potassium sulfate with magnesium).jpg|thumb|硫酸カリウム・硫酸マグネシウム肥料]] | ||
[[File:Patentkali (Potassium sulfate with magnesium).jpg|thumb| | カリウムイオンは[[plant/ja|植物]]の栄養に不可欠な成分であり、ほとんどの[[soil/ja|土壌]]に含まれている。それらは[[potassium chloride/ja|塩化物]](KCl)の形で[[agriculture/ja|農業]]、[[horticulture/ja|園芸]]、[[hydroponic/ja|水耕栽培]]の[[fertilizer/ja|肥料]]として使用される、 [[potassium sulfate/ja|硫酸塩]]({{chem2|K2SO4}})、または[[potassium nitrate|nitrate/ja|硝酸塩]]({{chem2|KNO3}})の形で、「K」[[labeling of fertilizer/ja|肥料の表示|in "NPK"]]を表す。農業用肥料は世界のカリウム化学生産量の95%を消費しており、このカリウムの約90%はKClとして供給されている。ほとんどの植物のカリウム含有量は、作物の収穫重量の0.5%から2%の範囲であり、従来は{{chem2|K2O}}の量で表されていた。現代の高[[:en:Crop yield|収量]]農業は、収穫時に失われるカリウムを補うための肥料に依存している。ほとんどの農業用肥料は塩化カリウムを含むが、硫酸カリウムは塩化カリウムに敏感な作物や、より高い硫黄含有量を必要とする作物に使用される。硫酸カリウムは、主に複雑な鉱物である[[kainite/ja|カイナイト]]({{chem2|MgSO4*KCl*3H2O}})と[[langbeinite/ja|ラングベーナイト]]({{chem2|MgSO4*K2SO4}})の分解によって生成される。硝酸カリウムを含む肥料はごくわずかである。2005年には、世界のカリウム生産量の約93%が肥料産業によって消費された。さらに、カリウムはリターの組成をコントロールすることによって、栄養循環において重要な役割を果たすことができる。 | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 11:31, 22 April 2024
Page Template:Infobox element/styles.css has no content.
 Potassium pearls (in paraffin oil, ~5 mm each) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Potassium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | silvery white, faint bluish-purple hue when exposed to air | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Potassium in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 4s1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 8, 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 336.7 K (63.5 °C, 146.3 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 1030.793 K (757.643 °C, 1395.757 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at 20° C) | 0.8590 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 0.82948 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 2223 K, 16 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 2.33 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 76.9 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 29.6 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −1, +1 (a strongly basic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 0.82 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 227 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 203±12 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 275 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | body-centered cubic (bcc) (cI2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice constant | a = 532.69 pm (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 77.37×10−6/K (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 102.5 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 72 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | +20.8×10−6 cm3/mol (298 K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 3.53 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 1.3 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 3.1 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 2000 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 0.363 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-09-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery and first isolation | Humphry Davy (1807) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symbol | "K": from New Latin kalium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of potassium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
カリウムは化学元素の一つであり、記号はK(新ラテン語kaliumから)、原子番号 は19である。銀白色の金属で、ナイフで簡単に切れるほど柔らかい。金属カリウムは大気中の酸素と急速に反応し、わずか数秒の暴露で薄片状の白い過酸化カリウムを形成する。カリウムは植物の灰であるカリから初めて単離された。周期表では、カリウムはアルカリ金属の1つであり、すべての金属は外側の電子殻に1個の価電子を持ち、この価電子は容易に除去されて正電荷を持つイオン(陰イオンと結合して塩を形成する)を作る。自然界では、カリウムはイオン塩でのみ存在する。元素のカリウムは水と激しく反応し、反応で放出される水素に引火するのに十分な熱を発生し、薄紫色の色のついた炎で燃焼する。カリウムは花崗岩や他の火成岩の一般的な成分である斜長石など、多くの鉱物に含まれている。
カリウムはナトリウムと化学的に非常によく似ている。周期表の1族の前の元素である。両者は最初のイオン化エネルギーが似ており、各原子が唯一の外側の電子を手放すことができる。1702年に初めて、それらは同じ陰イオンと結合して類似の塩を作る別個の元素であることが示唆され、1807年に元素カリウムが初めて電気分解によって単離されたときに実証された。天然に存在するカリウムは3つの同位体から構成されており、そのうち40
Kは放射性である。40
Kの痕跡はすべてのカリウムに含まれており、人体で最も一般的な放射性同位体である。
カリウムイオンは、すべての生きた細胞の機能に不可欠である。神経細胞膜を介したカリウムイオンの移動は、正常な神経伝達に必要である。カリウムの欠乏と過剰はそれぞれ、心臓のリズム異常や様々な心電図異常など、多くの徴候や症状を引き起こす。新鮮な果物や野菜は、カリウムのよい食事源である。身体は、カリウムを細胞外から細胞内に移動させ、腎臓からのカリウム排泄を増加させることによって、血清カリウム濃度を上昇させる食事性カリウムの流入に反応する。
カリウムの工業的用途のほとんどは、塩水石鹸のような水に対するカリウム化合物の高い溶解性を利用したものである。農作物の大量生産は土壌のカリウムを急速に枯渇させるが、これはカリウムを含む農業用肥料で改善することができ、世界のカリウム化学生産の95%を占めている。
語源
カリウムの英語名はpotashという語に由来する。これは、様々なカリウム塩を抽出する初期の方法を指しており、'potに灰(ash)を入れ、水を加えて加熱し、溶液を蒸発させるというものである。1807年にハンフリー・デイヴィーが初めて電気分解を用いて純粋な元素を単離したとき、彼はそれをpotashという語に由来するpotassiumと命名した。
記号Kはkaliに由来し、語源はアルカリ(alkali)であり、alkaliはArabic: القَلْيَه「植物の灰」に由来する。1797年、ドイツの化学者マルティン・クラプロスが鉱物リューサイトとレピドライトの中に「kali」を発見し、「kali」は植物の成長の産物ではなく、実際には新しい元素を含んでいることに気づき、それをkaliと呼ぶことを提案した。1807年、ハンフリー・デイヴィは電気分解によってこの元素を生成した。1809年、ルートヴィヒ・ヴィルヘルム・ジルベルトはデイヴィの「カリウム」にKaliumという名称を提案した。1814年、スウェーデンの化学者ヨンス・ヤコブ・ベルゼリウスは化学記号Kでカリウムをkaliumと呼ぶことを提唱した。
英語圏とフランス語圏ではデイヴィとフランスの化学者ジョセフ・ルイ・ゲイ=リュサックとルイ・ジャック・テナールが好んだカリウムという名称が採用され、他のゲルマン諸国ではギルバートとクラプロスのカリウムという名称が採用された。国際純正・応用化学連合の「ゴールドブック」では、公式の化学記号をKと定めている。
特性
物理的

カリウムはリチウムに次いで密度の低い金属である。融点が低く柔らかい固体であり、ナイフで簡単に切ることができる。カリウムの外観は銀色であるが、空気に触れるとすぐに灰色に変色し始める。火炎試験では、カリウムとその化合物は766.5ナノメートルに発光ピーク波長を持つライラック色を発する。
中性のカリウム原子は19個の電子を持ち、希ガスアルゴンの配置よりも1個多い。最初のイオン化エネルギーが418.8 kJ/molと低いため、カリウム原子は最後の電子を失って正電荷を帯びる可能性が高いが、負電荷を帯びたアルカリドK−
イオンも不可能ではない。対照的に、第二イオン化エネルギーは非常に高い(3052 kJ/mol)。
化学的
カリウムは空気中の酸素、水、二酸化炭素成分と反応する。酸素とは過酸化カリウムを形成する。水とカリウムは水酸化カリウム(KOH)を形成する。カリウムと水の反応は激しく発熱することがあり、特に共生した水素ガスが発火することがある。このため、カリウムと液体のナトリウム-カリウム(NaK)合金は強力な乾燥剤であるが、現在ではそのように使用されることはない。
化合物
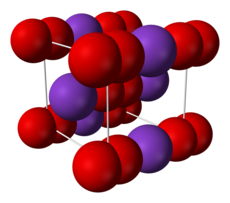
2)の構造
酸化カリウム(K
2O)、過酸化カリウム(K
2O
2)、過酸化カリウム(KO
2)、オゾン化カリウム(KO
3)である。カリウムと酸素の二元化合物は、水と反応してKOHを形成する。
KOHは強塩基である。その親水性を示すように、1.21kgものKOHが1リットルの水に溶けることがある。無水KOHに遭遇することは稀である。KOHは二酸化炭素(CO
2)と容易に反応して炭酸カリウム(K
2CO
3)を生成し、原理的には空気中のガスの痕跡を除去するために使用することができる。密接に関連する水酸化ナトリウムと同様に、KOHは脂肪と反応して石鹸を生成する。
一般に、カリウム化合物はイオン性であり、K+
イオンの水和エネルギーが高いため、優れた水溶性を持つ。水溶液中の主な種はアクオ錯体である。[K(H
2O)
n]+
で、n=6と7である。
ヘプタフルオロタンタル酸カリウム(K
2[TaF
7])は、ニオブの難分解性汚染物質からタンタルを精製する際の中間体である。
有機カリウム化合物はカリウムの非イオン性化合物を示す。それらは高度に極性共有結合を特徴とする。K-C結合を持つ。例えば、ベンジルカリウムKCH
2C
6H
5がある。カリウムのインターカレートはグラファイト中に挿入され、KC
8を含む様々なグラファイトインターカレーション化合物を与える。
同位体
カリウムの同位体は25種類知られているが、そのうち3種類は天然に存在する: 39
K(93.3%)、40
K(0.0117%)、41
K(6.7%)(モル分率)である。天然に存在する40
Kの半減期は1.250×109年である。電子捕獲または陽電子放出(11.2%)によって安定な{chem|40|Ar}}に崩壊するか、ベータ崩壊(88.8%)によって安定な{chem|40|Ca}}に崩壊する。40
Kから40
Arへの崩壊は、岩石の年代測定の一般的な方法の基礎となっている。従来のK-Ar年代測定法は、岩石が形成された時点ではアルゴンを含んでおらず、その後の放射性アルゴン(40
Ar)はすべて定量的に保持されていたという仮定に依存している。鉱物の年代測定は、カリウムの濃度と蓄積された放射性40
Arの量を測定することによって行われる。年代測定に最適な鉱物には、黒雲母、白雲母、変成角閃石、火山性の長石などがある。:火山流や浅い貫入岩の全岩試料も、変化していなければ年代測定が可能である。年代測定とは別に、カリウム同位体は風化の研究や、カリウムが地球上の生命に必要な大栄養素であることから、栄養塩循環の研究にトレーサーとして用いられてきた。
40
Kは天然のカリウム(したがっていくつかの市販の代用塩)中に十分な量含まれており、それらの代用塩の大きな袋を教室での実演のための放射源として使用することができる。40
Kは人体中で最も存在量の多い放射性同位体である。健康な動物や人間では、40
Kは最大の放射能源であり、{chem|14|C}}よりも大きい。体重70kgの人体では、1秒間に約4,400個の40
Kの原子核が崩壊する。天然カリウムの放射能は31Bq/gである。
歴史
ポターシュ
ポターシュは主にカリウム塩の混合物である。なぜなら、植物にはナトリウムがほとんど、あるいはまったく含まれておらず、植物の主要ミネラルの残りは、水への溶解度が比較的低いカルシウム塩で構成されているからである。カリは古代から使用されてきたが、その組成は解明されていなかった。1702年にゲオルク・エルンスト・シュタールがナトリウム塩とカリウム塩の基本的な違いを示唆する実験的証拠を得たが、カリウム化合物とナトリウム化合物の正確な化学組成、およびカリウムとナトリウムの化学元素としての地位は当時知られていなかったため、アントワーヌ・ラヴォアジエは1789年にアルカリを化学元素リストに含めなかった。長い間、カリの重要な用途はガラス、漂白剤、石鹸、硝酸カリウムとしての火薬の製造だけであった。動物性油脂や植物性油脂から作られるカリウム石鹸は、水溶性が高く、質感が柔らかいため、特に珍重された。1840年にユストゥス・リービッヒがカリウムは植物にとって必要な元素であり、ほとんどの種類の土壌にはカリウムが不足していることを発見したことで、カリウム塩の需要が急増した。当初はモミの木の木灰が肥料用のカリウム塩の原料として使われていたが、1868年にドイツのシュタイスフルト近郊で塩化カリウムを含む鉱床が発見され、カリウムを含む肥料の生産が工業的規模で始まった。他のカリ鉱床も発見され、1960年代にはカナダが主要な生産国になった。
金属


カリウム金属は1807年にハンフリー・デイヴィーによって初めて単離された。彼は溶融した苛性カリ(KOH)を新しく発見されたボルタ杭で電気分解することによってカリウムを得た。カリウムは電気分解によって単離された最初の金属であった。同年末、デイヴィは同様の手法で植物塩ではなく鉱物誘導体(苛性ソーダ、NaOH、灰汁)から金属ナトリウムを抽出することを報告し、元素、ひいては塩が異なることを実証した。金属カリウムと金属ナトリウムの生成は、どちらも元素であることを示すはずであったが、この見解が普遍的に受け入れられるまでには時間がかかった。
カリウムは水や空気に敏感であるため、この元素の取り扱いには通常空気を使わない技術が用いられる。窒素や鉱物油や灯油のような飽和炭化水素には反応しない。液体アンモニアに容易に溶解し、0 ℃でアンモニア1000gあたり480gまで溶解する。濃度にもよるが、アンモニア溶液は青から黄色であり、その電気伝導率は液体金属に似ている。カリウムはアンモニアとゆっくりと反応してKNH
2を形成するが、この反応は微量の遷移金属塩によって加速される。カリウムは塩を金属に還元することができるので、Rieke法によって微分された金属をその塩から調製する際に還元剤としてよく使われる。マグネシウムの調製がその例である:
- MgCl
2 + 2 K → Mg + 2 KCl
発生

カリウムは超新星において、より軽い原子からの核合成によって生成される。カリウムは主にII型超新星において爆発的酸素燃焼過程を経て生成される。これらは核融合反応であり、酸素中でのカリウムの化学的燃焼と混同してはならない。40
Kはs-process核合成やネオン燃焼過程でも生成される。
カリウムは太陽系で20番目に多い元素であり、地球では17番目に多い元素である。地殻の重量の約2.6%を占め、地殻中で7番目に豊富な元素である。海水中のカリウム濃度は0.39 g/L(0.039 wt/v%)で、ナトリウム濃度の約27分の1である。
地質学
カリウムは反応性が高いため、自然界には存在しない。水と激しく反応し、酸素とも反応する。正斜長石(カリウム長石)は一般的な造岩鉱物である。例えば花崗岩には5%のカリウムが含まれており、これは地殻の平均を大きく上回っている。シルバイト(KCl)、カルナライト(KCl·MgCl
2·6H2O)、カイナイト(MgSO
4·KCl·3H2O)、ラングベーナイト(MgSO
4·K
2SO
4)は、世界中の大規模なエバポライト鉱床で見られる鉱物である。鉱床はしばしば、最も溶解度の低いものが底部に、最も溶解度の高いものが上部にある層を示す。ナイター(硝酸カリウム)の鉱床は、大気と接触した有機物の分解によって形成される。
商業生産
採掘


カルナライト、ラングベーナイト、ポリハライト、シルバイトなどのカリウム塩は、古代の湖底や海底に広範なエバポライト鉱床を形成しており、このような環境でのカリウム塩の抽出は商業的に実行可能である。カリウムの主要な供給源であるカリは、カナダ、ロシア、ベラルーシ、カザフスタン、ドイツ、イスラエル、アメリカ、ヨルダン、その他世界中で採掘されている。最初に採掘された鉱床はドイツのシュタイスフルト近郊にあったが、鉱床はイギリスからドイツを越えてポーランドにまで及んでいる。それらはゼクシュタインにあり、中期から後期のペルム紀に堆積したものである。これまでに発見された中で最大の鉱床は、カナダのサスカチュワン州の地下1,000 meters (3,300 feet)にある。鉱床は中期デボン紀に産出するエルク・ポイント層群にある。サスカチュワン州では、1960年代からいくつかの大規模な鉱山が操業しており、湿った砂(ブレアモア層)を凍らせて坑道を掘る技術を開拓した。合併するまでサスカチュワン州の主要なカリ鉱山会社はポタッシュ・コーポレーション・オブ・サスカチュワンであり、現在はニュートリエンである。死海の水はイスラエルとヨルダンがカリの供給源として使用しているが、通常の海洋の濃度は現在の価格では商業生産には低すぎる。
化学的抽出
カリウム塩をナトリウム化合物やマグネシウム化合物から分離するには、いくつかの方法が用いられる。最もよく使われる方法は、塩の溶解度の違いを利用した分別沈殿である。一部の鉱山では、地中の混合塩を静電分離する方法も用いられている。得られたナトリウムとマグネシウムの廃棄物は地下に貯蔵されるか、スラグヒープに積み上げられる。採掘されたカリウム鉱物の大部分は、加工後に塩化カリウムになる。鉱物業界では、塩化カリウムをカリ、カリ酸ムリエート、または単にMOPと呼ぶ。
純粋な金属カリウムは、その水酸化物を電気分解することによって単離することができる。電解法は1920年代に開発され工業的に使用されるようになったが、1950年代にはナトリウムと塩化カリウムを化学平衡反応させる熱法が主流となった。
- Na + KCl → NaCl + K
ナトリウムカリウム合金の製造は、反応時間と反応に使用するナトリウムの量を変えることによって達成される。フッ化カリウムと炭化カルシウムの反応を利用したグリースハイマー法もカリウムの製造に用いられた。
- 2 KF + CaC
2 → 2 K + CaF
2 + 2 C
試薬グレードのカリウム金属は、トン単位で購入した場合、2010年には1|ポンドあたり約10.00ドル(1kgあたり22ドル)である。純度の低い金属はかなり安い。金属の長期保管が難しいため、市場は不安定である。傷がつくと起爆する感圧性の爆薬である過酸化カリウムの表面層の形成を防ぐために、乾燥した不活性ガス雰囲気または無水の鉱油中で保管しなければならない。その結果、爆発はしばしば消火困難な火災を引き起こす。
陽イオンの同定
カリウムは現在ではイオン化技術によって定量されるが、かつては重量分析によって定量されていた。
カリウム塩を沈殿させるための試薬としては、テトラフェニルホウ酸ナトリウム、ヘキサクロロ白金酸、コバルト亜硝酸ナトリウムをそれぞれテトラフェニルホウ酸カリウム、ヘキサクロロ白金酸カリウム、コバルト亜硝酸カリウムに変換するものがある。 コバルト亜硝酸ナトリウムとの反応がその例である:
- 3 K+
+ Na
3[Co(NO
2)
6] → K
3[Co(NO
2)
6] + 3 Na+
コバルト亜硝酸カリウムは黄色の固体として得られる。
商業的利用
肥料

カリウムイオンは植物の栄養に不可欠な成分であり、ほとんどの土壌に含まれている。それらは塩化物(KCl)の形で農業、園芸、水耕栽培の肥料として使用される、 硫酸塩(K
2SO
4)、またはnitrate/ja|硝酸塩(KNO
3)の形で、「K」肥料の表示|in "NPK"を表す。農業用肥料は世界のカリウム化学生産量の95%を消費しており、このカリウムの約90%はKClとして供給されている。ほとんどの植物のカリウム含有量は、作物の収穫重量の0.5%から2%の範囲であり、従来はK
2Oの量で表されていた。現代の高収量農業は、収穫時に失われるカリウムを補うための肥料に依存している。ほとんどの農業用肥料は塩化カリウムを含むが、硫酸カリウムは塩化カリウムに敏感な作物や、より高い硫黄含有量を必要とする作物に使用される。硫酸カリウムは、主に複雑な鉱物であるカイナイト(MgSO
4·KCl·3H2O)とラングベーナイト(MgSO
4·K
2SO
4)の分解によって生成される。硝酸カリウムを含む肥料はごくわずかである。2005年には、世界のカリウム生産量の約93%が肥料産業によって消費された。さらに、カリウムはリターの組成をコントロールすることによって、栄養循環において重要な役割を果たすことができる。
Medical use
Potassium citrate
Potassium citrate is used to treat a kidney stone condition called renal tubular acidosis.
Potassium chloride
Potassium, in the form of potassium chloride is used as a medication to treat and prevent low blood potassium. Low blood potassium may occur due to vomiting, diarrhea, or certain medications. It is given by slow injection into a vein or by mouth.
Food additives
Potassium sodium tartrate (KNaC
4H
4O
6, Rochelle salt) is a main constituent of some varieties of baking powder; it is also used in the silvering of mirrors. Potassium bromate (KBrO
3) is a strong oxidizer (E924), used to improve dough strength and rise height. Potassium bisulfite (KHSO
3) is used as a food preservative, for example in wine and beer-making (but not in meats). It is also used to bleach textiles and straw, and in the tanning of leathers.
Industrial
Major potassium chemicals are potassium hydroxide, potassium carbonate, potassium sulfate, and potassium chloride. Megatons of these compounds are produced annually.
KOH is a strong base, which is used in industry to neutralize strong and weak acids, to control pH and to manufacture potassium salts. It is also used to saponify fats and oils, in industrial cleaners, and in hydrolysis reactions, for example of esters.
Potassium nitrate (KNO
3) or saltpeter is obtained from natural sources such as guano and evaporites or manufactured via the Haber process; it is the oxidant in gunpowder (black powder) and an important agricultural fertilizer. Potassium cyanide (KCN) is used industrially to dissolve copper and precious metals, in particular silver and gold, by forming complexes. Its applications include gold mining, electroplating, and electroforming of these metals; it is also used in organic synthesis to make nitriles. Potassium carbonate (K
2CO
3 or potash) is used in the manufacture of glass, soap, color TV tubes, fluorescent lamps, textile dyes and pigments. Potassium permanganate (KMnO
4) is an oxidizing, bleaching and purification substance and is used for production of saccharin. Potassium chlorate (KClO
3) is added to matches and explosives. Potassium bromide (KBr) was formerly used as a sedative and in photography.
While potassium chromate (K
2CrO
4) is used in the manufacture of a host of different commercial products such as inks, dyes, wood stains (by reacting with the tannic acid in wood), explosives, fireworks, fly paper, and safety matches, as well as in the tanning of leather, all of these uses are due to the chemistry of the chromate ion rather than to that of the potassium ion.
Niche uses
There are thousands of uses of various potassium compounds. One example is potassium superoxide, KO
2, an orange solid that acts as a portable source of oxygen and a carbon dioxide absorber. It is widely used in respiration systems in mines, submarines and spacecraft as it takes less volume than the gaseous oxygen.
- 4 KO
2 + 2 CO
2 → 2 K
2CO
3 + 3 O
2
Another example is potassium cobaltinitrite, K
3[Co(NO
2)
6], which is used as artist's pigment under the name of Aureolin or Cobalt Yellow.
The stable isotopes of potassium can be laser cooled and used to probe fundamental and technological problems in quantum physics. The two bosonic isotopes possess convenient Feshbach resonances to enable studies requiring tunable interactions, while 40
K is one of only two stable fermions amongst the alkali metals.
Laboratory uses
An alloy of sodium and potassium, NaK is a liquid used as a heat-transfer medium and a desiccant for producing dry and air-free solvents. It can also be used in reactive distillation. The ternary alloy of 12% Na, 47% K and 41% Cs has the lowest melting point of −78 °C of any metallic compound.
Metallic potassium is used in several types of magnetometers.
Biological role
Potassium is the eighth or ninth most common element by mass (0.2%) in the human body, so that a 60 kg adult contains a total of about 120 g of potassium. The body has about as much potassium as sulfur and chlorine, and only calcium and phosphorus are more abundant (with the exception of the ubiquitous CHON elements).
Biochemical function
Potassium levels influence multiple physiological processes, including
- resting cellular-membrane potential and the propagation of action potentials in neuronal, muscular, and cardiac tissue. Due to the electrostatic and chemical properties, K+
ions are larger than Na+
ions, and ion channels and pumps in cell membranes can differentiate between the two ions, actively pumping or passively passing one of the two ions while blocking the other. - hormone secretion and action
- vascular tone
- systemic blood pressure control
- gastrointestinal motility
- acid–base homeostasis
- glucose and insulin metabolism
- mineralocorticoid action
- renal concentrating ability
- fluid and electrolyte balance
- local cortical monoaminergic norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine levels, and through them, sleep/wake balance, and spontaneous activity.
Homeostasis
Potassium homeostasis denotes the maintenance of the total body potassium content, plasma potassium level, and the ratio of the intracellular to extracellular potassium concentrations within narrow limits, in the face of pulsatile intake (meals), obligatory renal excretion, and shifts between intracellular and extracellular compartments.
Plasma levels
Plasma potassium is normally kept at 3.5 to 5.5 millimoles (mmol) [or milliequivalents (mEq)] per liter by multiple mechanisms. Levels outside this range are associated with an increasing rate of death from multiple causes, and some cardiac, kidney, and lung diseases progress more rapidly if serum potassium levels are not maintained within the normal range.
An average meal of 40–50 mmol presents the body with more potassium than is present in all plasma (20–25 mmol). This surge causes the plasma potassium to rise up to 10% before clearance by renal and extrarenal mechanisms.
Hypokalemia, a deficiency of potassium in the plasma, can be fatal if severe. Common causes are increased gastrointestinal loss (vomiting, diarrhea), and increased renal loss (diuresis). Deficiency symptoms include muscle weakness, paralytic ileus, ECG abnormalities, decreased reflex response; and in severe cases, respiratory paralysis, alkalosis, and cardiac arrhythmia.
Control mechanisms
Potassium content in the plasma is tightly controlled by four basic mechanisms, which have various names and classifications. These are:
- a reactive negative-feedback system,
- a reactive feed-forward system,
- a predictive or circadian system, and
- an internal or cell membrane transport system.
Collectively, the first three are sometimes termed the "external potassium homeostasis system"; and the first two, the "reactive potassium homeostasis system".
- The reactive negative-feedback system refers to the system that induces renal secretion of potassium in response to a rise in the plasma potassium (potassium ingestion, shift out of cells, or intravenous infusion.)
- The reactive feed-forward system refers to an incompletely understood system that induces renal potassium secretion in response to potassium ingestion prior to any rise in the plasma potassium. This is probably initiated by gut cell potassium receptors that detect ingested potassium and trigger vagal afferent signals to the pituitary gland.
- The predictive or circadian system increases renal secretion of potassium during mealtime hours (e.g. daytime for humans, nighttime for rodents) independent of the presence, amount, or absence of potassium ingestion. It is mediated by a circadian oscillator in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the brain (central clock), which causes the kidney (peripheral clock) to secrete potassium in this rhythmic circadian fashion.

The action of the sodium-potassium pump is an example of primary active transport. The two carrier proteins embedded in the cell membrane on the left are using ATP to move sodium out of the cell against the concentration gradient; The two proteins on the right are using secondary active transport to move potassium into the cell. This process results in reconstitution of ATP. - The ion transport system moves potassium across the cell membrane using two mechanisms. One is active and pumps sodium out of, and potassium into, the cell. The other is passive and allows potassium to leak out of the cell. Potassium and sodium cations influence fluid distribution between intracellular and extracellular compartments by osmotic forces. The movement of potassium and sodium through the cell membrane is mediated by the Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase pump. This ion pump uses ATP to pump three sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell, creating an electrochemical gradient and electromotive force across the cell membrane. The highly selective potassium ion channels (which are tetramers) are crucial for hyperpolarization inside neurons after an action potential is triggered, to cite one example. The most recently discovered potassium ion channel is KirBac3.1, which makes a total of five potassium ion channels (KcsA, KirBac1.1, KirBac3.1, KvAP, and MthK) with a determined structure. All five are from prokaryotic species.
Renal filtration, reabsorption, and excretion
Renal handling of potassium is closely connected to sodium handling. Potassium is the major cation (positive ion) inside animal cells (150 mmol/L, 4.8 g/L), while sodium is the major cation of extracellular fluid (150 mmol/L, 3.345 g/L). In the kidneys, about 180 liters of plasma is filtered through the glomeruli and into the renal tubules per day. This filtering involves about 600 mg of sodium and 33 mg of potassium. Since only 1–10 mg of sodium and 1–4 mg of potassium are likely to be replaced by diet, renal filtering must efficiently reabsorb the remainder from the plasma.
Sodium is reabsorbed to maintain extracellular volume, osmotic pressure, and serum sodium concentration within narrow limits. Potassium is reabsorbed to maintain serum potassium concentration within narrow limits. Sodium pumps in the renal tubules operate to reabsorb sodium. Potassium must be conserved, but because the amount of potassium in the blood plasma is very small and the pool of potassium in the cells is about 30 times as large, the situation is not so critical for potassium. Since potassium is moved passively in counter flow to sodium in response to an apparent (but not actual) Donnan equilibrium, the urine can never sink below the concentration of potassium in serum except sometimes by actively excreting water at the end of the processing. Potassium is excreted twice and reabsorbed three times before the urine reaches the collecting tubules. At that point, urine usually has about the same potassium concentration as plasma. At the end of the processing, potassium is secreted one more time if the serum levels are too high.
With no potassium intake, it is excreted at about 200 mg per day until, in about a week, potassium in the serum declines to a mildly deficient level of 3.0–3.5 mmol/L. If potassium is still withheld, the concentration continues to fall until a severe deficiency causes eventual death.
The potassium moves passively through pores in the cell membrane. When ions move through ion transporters (pumps) there is a gate in the pumps on both sides of the cell membrane and only one gate can be open at once. As a result, approximately 100 ions are forced through per second. Ion channels have only one gate, and there only one kind of ion can stream through, at 10 million to 100 million ions per second. Calcium is required to open the pores, although calcium may work in reverse by blocking at least one of the pores. Carbonyl groups inside the pore on the amino acids mimic the water hydration that takes place in water solution by the nature of the electrostatic charges on four carbonyl groups inside the pore.
Nutrition
Dietary recommendations
The U.S. National Academy of Medicine (NAM), on behalf of both the U.S. and Canada, sets Dietary Reference Intakes, including Estimated Average Requirements (EARs) and Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs), or Adequate Intakes (AIs) for when there is not sufficient information to set EARs and RDAs.
For both males and females under 9 years of age, the AIs for potassium are: 400 mg of potassium for 0 to 6-month-old infants, 860 mg of potassium for 7 to 12-month-old infants, 2,000 mg of potassium for 1 to 3-year-old children, and 2,300 mg of potassium for 4 to 8-year-old children.
For males 9 years of age and older, the AIs for potassium are: 2,500 mg of potassium for 9 to 13-year-old males, 3,000 mg of potassium for 14 to 18-year-old males, and 3,400 mg for males that are 19 years of age and older.
For females 9 years of age and older, the AIs for potassium are: 2,300 mg of potassium for 9 to 18-year-old females, and 2,600 mg of potassium for females that are 19 years of age and older.
For pregnant and lactating females, the AIs for potassium are: 2,600 mg of potassium for 14 to 18-year-old pregnant females, 2,900 mg for pregnant females that are 19 years of age and older; furthermore, 2,500 mg of potassium for 14 to 18-year-old lactating females, and 2,800 mg for lactating females that are 19 years of age and older. As for safety, the NAM also sets tolerable upper intake levels (ULs) for vitamins and minerals, but for potassium the evidence was insufficient, so no UL was established.
As of 2004, most Americans adults consume less than 3,000 mg.
Likewise, in the European Union, in particular in Germany, and Italy, insufficient potassium intake is somewhat common. The British National Health Service recommends a similar intake, saying that adults need 3,500 mg per day and that excess amounts may cause health problems such as stomach pain and diarrhea.
In 2019, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine revised the Adequate Intake for potassium to 2,600 mg/day for females 19 years of age and older who are not pregnant or lactating, and 3,400 mg/day for males 19 years of age and older.
食物摂取源
カリウムはすべての果物、野菜、肉、魚に含まれている。カリウムを多く含む食品としては、ヤム、パセリ、干しアプリコット、牛乳、チョコレートなどがある、 ナッツ類(特にアーモンドとピスタチオ)、ジャガイモ、タケノコ、バナナ、アボカド、ココナッツウォーター、大豆、ふすまなどである。
米国農務省はまた、トマトペースト、オレンジジュース、ビートグリーン、白いんげん豆、プランタン、その他多くのカリウムの食事供給源を、カリウム含有量の多い順にリストアップしている。1日分のカリウムは、プランタン5個分またはバナナ11本分に含まれる。
摂取不足
カリウムの少ない食事は、高血圧や低カリウム血症の原因となる。
サプリメント化
カリウムのサプリメントは、遠位尿細管の上流でナトリウムと水の再吸収を阻害する利尿薬(サイアザイドおよびループ利尿薬)と併用するのが最も広く用いられている。さまざまな処方薬や市販のサプリメントが利用できる。塩化カリウムは水に溶かしてもよいが、塩辛い/苦い味がするため、液体のサプリメントは口に合わない。一般的な用量は10 mmol(400 mg)から20 mmol(800 mg)である。固形錠剤に隣接して発生する非常に高濃度のカリウムイオンは、胃や腸の粘膜を傷つける可能性があるため、カリウムがマトリックスからゆっくりと溶出するように処方されている。このため、米国では非処方のカリウム錠剤は、法律で最大99 mgのカリウムに制限されている。
カリウムの補給は、クエン酸塩や塩化物などの他の代謝産物と組み合わせて、特定の臨床効果を得ることもできる。
カリウムサプリメントは高血圧の影響を緩和し、心血管リスクを軽減するために採用されることがある。塩化カリウムと炭酸水素カリウムは軽度の高血圧をコントロールするのに有用であろう。2020年には、カリウムは米国で33番目に多く処方された医薬品であり、17 万以上の処方があった。カリウムの補給は、本態性高血圧患者の収縮期血圧と拡張期血圧の両方を低下させることが示されている。
さらに、放置すると腎合併症を引き起こす可能性のある腎結石の形成を予防する目的で、カリウムサプリメントが採用されることもある。カリウム濃度が低いと、腎臓でのカルシウム再吸収が低下し、尿中カルシウムの上昇や腎結石の形成リスクが高まる。適切なカリウム濃度を維持することで、このリスクを減らすことができる。
カリウムの作用機序には、細胞膜を横切るカリウムの移動を促進する様々な種類のトランスポーターやチャネルが関与している。このプロセスは、水素イオンの汲み出しを増加させる。その結果、胃酸の分泌が促進され、胃潰瘍の発症につながる可能性がある。
カリウムは骨の健康に関与している。体内の酸塩基平衡に寄与し、骨組織の保護に役立つ。カリウム塩は、骨の健康維持を助けるアルカリ成分を生成する。
糖尿病患者には、特に2型糖尿病患者にはカリウムの補給が必要かもしれない。カリウムは膵臓のβ細胞によるインスリンの分泌に不可欠であり、グルコースレベルを調節するのに役立っている。カリウムが十分でないと、インスリンの分泌が悪くなり、高血糖や糖尿病の悪化につながる。
カリウムの過剰摂取は、胃腸の不快感や心臓のリズムの乱れといった悪影響を及ぼす可能性がある。
カリウムの補給は潰瘍、特に消化性潰瘍疾患に関連して副作用をもたらす可能性がある。カリウムチャネルは胃酸分泌を増加させる可能性があり、潰瘍のリスクを高めることにつながる。消化性潰瘍疾患に使用される医薬品は「プロトンポンプ阻害薬」として知られ、H/K ATPaseを活性化するカリウムポンプを阻害することによって作用する。この阻害作用により、塩酸の胃壁細胞への分泌が抑制され、酸性合成が減少し、潰瘍のリスクが低下する。虚血性心疾患の治療に用いられる薬物であるニコランジルは、硝酸塩およびカリウムATPチャネルを刺激する可能性があり、その結果、消化管潰瘍、口腔潰瘍、肛門潰瘍などの副作用と関連している。カリウムサプリメントの長期的かつ慢性的な使用は、消化管(GI)以外の潰瘍など、より重篤な副作用に関連している。アンジオテンシノーゲン変換酵素阻害薬、アンジオテンシン受容体拮抗薬、カリウム温存利尿薬を服用している患者には、厳重な監視が必要である。
味蕾による検出
カリウムは、濃度に応じて5種類の味覚のうち3種類を誘発するため、味覚で感知することができる。カリウムイオンの希薄溶液は甘味を感じ、牛乳やジュースに適度な濃度で含まれるようになるが、高濃度になると苦味やアルカリ性が増し、最後には塩味も感じるようになる。高濃度カリウム溶液の苦味と塩味の組み合わせは、液体飲料による高用量カリウム補給を嗜好上の難題にしている。
注意事項
| Hazards | |
|---|---|
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H260, H314 | |
| P223, P231+P232, P280, P305+P351+P338, P370+P378, P422 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
金属カリウムは水と激しく反応し、KOHと水素ガスを発生させる。
- 2 K(s) + 2 H
2O(l) → 2 KOH(aq) + H
2(g)↑

この反応は発熱性で、酸素の存在下、生成した水素を発火させるのに十分な熱を放出する。微粉末のカリウムは室温の空気中で発火する。バルクの金属は加熱すると空気中で発火する。密度は0.89 g/cm3であるため、燃焼したカリウムは大気中の酸素にさらされた水に浮く。水を含む多くの一般的な消火剤は効果がないか、カリウム火災を悪化させる。窒素、アルゴン、塩化ナトリウム(食卓塩)、炭酸ナトリウム(ソーダ灰)、二酸化ケイ素(砂)は乾燥していれば有効である。金属火災用のクラスD粉末消火器も有効である。これらの薬剤は火から酸素を奪い、カリウム金属を冷却する。
貯蔵中、カリウムは過酸化物やスーパーオキシドを形成する。これらの過酸化物は油などの有機化合物と激しく反応することがある。過酸化物も過酸化物も金属カリウムと爆発的に反応することがある。
カリウムは空気中の水蒸気と反応するため、通常、無水鉱物油または灯油の下で保管される。リチウムやナトリウムと異なり、カリウムは、不活性(酸素を含まない)雰囲気または真空下でない限り、6ヶ月を超えて油の下で保管すべきではない。空気中で長期間保管すると、衝撃に弱い危険な過酸化物が金属上や容器の蓋の下に形成され、開封時に爆発する恐れがある。
大量のカリウム化合物を摂取すると高カリウム血症を引き起こし、心血管系に強い影響を与える。塩化カリウムはアメリカでは致死注射の処刑に使われる。
こちらも参照
参考文献
- Burkhardt, Elizabeth R. (2006). "Potassium and Potassium Alloys". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. A22. pp. 31–38. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_031.pub2. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (2007). "Potassium". Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (in German) (91–100 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1.
- Schultz, H.; Bauer, G.; Schachl, E.; Hagedorn, F.; Schmittinger, P. (2006). "Potassium compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. A22. pp. 39–103. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_031.pub2. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- National Nutrient Database Archived 2014-08-10 at the Wayback Machine at USDA Website
外部リンク
- CID Potassium from PubChem