Zinc/ja: Difference between revisions
| Line 301: | Line 301: | ||
亜鉛はヒトや他の動物、植物、[[microorganism/ja|微生物]]にとって必須の[[trace element/ja|微量元素]]である。亜鉛は300を超える[[enzyme/ja|酵素]]と1000を超える[[transcription factor/ja|転写因子]]の機能に必要であり、[[metallothionein/ja|メタロチオネイン]]に貯蔵され移動する。亜鉛は鉄に次いでヒトに多く含まれる微量金属であり、すべての[[Enzyme/ja#Naming conventions|酵素クラス]]に現れる唯一の金属である。 | 亜鉛はヒトや他の動物、植物、[[microorganism/ja|微生物]]にとって必須の[[trace element/ja|微量元素]]である。亜鉛は300を超える[[enzyme/ja|酵素]]と1000を超える[[transcription factor/ja|転写因子]]の機能に必要であり、[[metallothionein/ja|メタロチオネイン]]に貯蔵され移動する。亜鉛は鉄に次いでヒトに多く含まれる微量金属であり、すべての[[Enzyme/ja#Naming conventions|酵素クラス]]に現れる唯一の金属である。 | ||
タンパク質では、亜鉛イオンはしばしば[[aspartic acid/ja|アスパラギン酸]]、[[glutamic acid/ja|グルタミン酸]]、[[cysteine/ja|システイン]]、[[histidine/ja|ヒスチジン]]などのアミノ酸側鎖に配位する。タンパク質におけるこの亜鉛結合(他の遷移金属と同様)の理論的・計算的記述は困難である。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 20 April 2024
Page Template:Infobox element/styles.css has no content.
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zinc | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | silver-gray | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(Zn) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zinc in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 692.68 K (419.53 °C, 787.15 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 1180 K (907 °C, 1665 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 7.14 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 6.57 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 7.32 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 115 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.470 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −2, 0, +1, +2 (an amphoteric oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 134 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 122±4 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 139 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | hexagonal close-packed (hcp) (hP2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lattice constants | a = 266.46 pm c = 494.55 pm (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 30.2 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 116 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 59.0 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −11.4×10−6 cm3/mol (298 K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 108 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 43 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 70 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 3850 m/s (at r.t.) (rolled) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 2.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 327–412 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-66-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Indian metallurgists (before 1000 BCE) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Andreas Sigismund Marggraf (1746) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognized as a unique metal by | Rasaratna Samuccaya (1300) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of zinc | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
亜鉛は化学元素の一つであり、シンボルはZn、原子番号は30である。室温ではやや脆い金属であり、酸化を取り除くと光沢のある灰色がかった外観を持つ。周期表の12族 (IIB)の最初の元素である。いくつかの点で、マグネシウムと化学的に似ている:両元素とも通常の酸化状態は1つだけ(+2)であり、Zn2+とMg2+のイオンの大きさは似ている。亜鉛は24番目に豊富な地殻中の元素であり、5つの安定な同位体を持っている。最も一般的な亜鉛鉱石は閃亜鉛鉱(zinc blende)で、硫化亜鉛鉱物である。加工可能な最大の鉱脈はオーストラリア、アジア、アメリカにある。亜鉛は鉱石の泡沫浮遊、焙焼、そして最終的に電気(電解)を用いた抽出によって精製される。
亜鉛はヒト、動物、植物、微生物にとって必須の微量元素であり、出生前と出生後の発育に必要である。人間にとって鉄に次いで2番目に多い微量金属であり、すべての酵素クラスに登場する唯一の金属である。また、多くの酵素の重要な補因子であるため、サンゴの成長に不可欠な栄養元素でもある。
亜鉛欠乏症は発展途上国の約20億人に影響を及ぼし、多くの病気と関連している。子どもの場合、欠乏は成長遅延、性成熟遅延、感染症感受性、下痢を引き起こす。亜鉛原子を反応中心に持つ酵素は、ヒトのアルコールデヒドロゲナーゼなど、生化学に広く存在する。過剰な亜鉛の摂取は運動失調、嗜眠、銅欠乏を引き起こすことがある。海洋生物群、特に極域では、亜鉛が不足すると一次藻類群集の活力が損なわれ、複雑な海洋栄養構造を不安定にし、結果として生物多様性に影響を与える可能性がある。
真鍮は銅と亜鉛を様々な割合で混ぜた合金であり、紀元前3千年紀には早くもエーゲ海地域と現在のイラク、アラブ首長国連邦、カルムイキア、トルクメニスタン、ジョージアを含む地域で使用されていた。紀元前2千年紀には、現在西インド、ウズベキスタン、イラン、シリア、イラク、イスラエルを含む地域で使用されていた。ラジャスタンの鉱山は、紀元前6世紀まで遡る亜鉛生産の明確な証拠を与えている。現在までに、純粋な亜鉛の最古の証拠は、純粋な亜鉛を作るために蒸留プロセスが採用された紀元後9世紀には、ラジャスタン州のザワールから来ている。錬金術師たちは空気中で亜鉛を燃やし、「哲学者の羊毛」または「白い雪」と呼ばれるものを形成した。
この元素はおそらく錬金術師パラケルススによってドイツ語のZinke(突起、歯)にちなんで命名された。ドイツの化学者アンドレアス・シギスムント・マルグラーフは1746年に純粋な金属亜鉛を発見したとされている。1800年までにルイジ・ガルヴァーニとアレッサンドロ・ボルタによって亜鉛の電気化学的特性が明らかにされた。鉄の腐食に対する亜鉛めっき(溶融亜鉛メッキ)は、亜鉛の主要な用途である。その他の用途としては、電気電池、小さな非構造鋳造品、そして真鍮などの合金があります。亜鉛化合物はさまざまな用途で一般的に使用されており、亜鉛炭酸塩や亜鉛グルコン酸塩(栄養補助剤として)、塩化亜鉛(制汗剤に)、ピリチオン亜鉛(抗フケシャンプーに)、亜鉛硫化物(蛍光ペイントに)、そしてジメチル亜鉛やジエチル亜鉛(有機実験室で)が含まれる。
特徴
物理的性質
亜鉛は青みがかった白色で光沢のある反磁性金属であるが、一般的な市販グレードの多くはくすんだ仕上げが施されている。密度は鉄よりもやや低く、六角形の結晶構造を持ち、歪んだ形の六角クローズパッキングを持つ。この金属はほとんどの温度で硬く脆いが、100~150 °Cの間では可鍛性になる。210 °Cを超えると再び脆くなり、叩いて粉砕することができる。亜鉛はかなりの電気伝導体である。金属としては融点(419.5 °C)と沸点(907 °C)が比較的低い。融点は水銀とカドミウムを除けばd-ブロック金属の中で最も低く、このため亜鉛、カドミウム、水銀は他のd-ブロック金属と同様に遷移金属とは見なされないことが多い。
真鍮を含む多くの合金が亜鉛を含む。亜鉛と二元合金を形成することが古くから知られている他の金属は、アルミニウム、アンチモン、ビスマス、金、鉄、鉛、水銀、銀、錫、マグネシウム、コバルト、ニッケル、テルル、ナトリウムである。亜鉛もジルコニウムも強磁性ではないが、それらの合金であるZrZn
2は35 K以下で強磁性を示す。
出現率
亜鉛は地殻の約75 ppm(0.0075%)を占め、24番目に豊富な元素である。亜鉛の典型的なバックグラウンド濃度は、大気中では1 μg/m3、土壌中では300 mg/kg、植生中では100 mg/kg、淡水中では20 μg/L、海水中では5 μg/Lを超えない。この元素は通常、銅や鉛などの他の卑金属と結びついて鉱石に含まれている。亜鉛は好塩基性であり、鉱物中では酸素のような軽いカルコゲンやハロゲンのような非カルコゲンの電気陰性元素よりもむしろ、硫黄や他の重いカルコゲンと共に発見されやすい。硫化物は、初期の地球大気の還元条件下で地殻が固化する際に形成された。硫化亜鉛の一種である閃亜鉛鉱は、その精鉱が亜鉛を60~62%含むため、亜鉛を含む鉱石の中で最も多く採掘されている。
他の亜鉛源鉱物には、スミソナイト(亜鉛炭酸塩)、ヘミモルファイト(亜鉛ケイ酸塩)、ウルツァイト(別の硫化亜鉛)、時にはハイドロ亜鉛鉱(塩基性炭酸亜鉛)がある。ウルツァイトを除いて、これら他の鉱物はすべて原初の硫化亜鉛の風化によって形成されたものである。
確認されている世界の亜鉛資源は合計約19億~28億トンである。大規模な鉱床はオーストラリア、カナダ、アメリカにあり、最大の埋蔵量はイランにある。一方、亜鉛の埋蔵量とは、地質学的に確認された鉱体のうち、回収の適否が決定時の経済性(位置、品位、質、量)に基づいているものを指す。探鉱と鉱山開発は現在進行中のプロセスであるため、亜鉛埋蔵量は固定された数字ではなく、現在の亜鉛鉱山の鉱山寿命を単純に外挿することで亜鉛鉱石供給の持続可能性を判断することはできない。この考え方は、米国地質調査所(USGS)のデータによって裏付けられている。USGSによると、1990年から2010年の間に亜鉛精錬生産量は80%増加したが、亜鉛の埋蔵量は変わっていない。2002年までの歴史を通じて約3億4600万トンが採掘され、学者たちは約1億900万トンから3億500万トンが使用されていると推定している。

同位体
自然界には亜鉛の5つの安定な同位体が存在し、64Znが最も豊富な同位体である(49.17%自然存在量)。自然界に存在する他の同位体は66
Znである。(27.73%), 67
Zn である。(4.04%), 68
Zn である。(18.45%)、70
Znである。(0.61%).
数十種類の放射性同位体が特徴づけられている。半減期が243.66 日の65
Znは最も活性の低い放射性同位体であり、半減期が46.5 時間の72
Znがそれに続く。亜鉛には10個の核異性体があり、そのうち69mZnの半減期は13.76時間と最も長い。上付き文字mは準安定同位体を示す。準安定同位体の原子核は励起状態にあり、ガンマ線の形で光子を放出することで基底状態に戻る。61
Znには3つの励起準安定状態があり、73
Znには2つの励起準安定状態がある。同位体65
Zn、71
Zn、77
Zn、78
Znはそれぞれ1つの励起準安定状態しか持たない。
質量数が66より小さい亜鉛の放射性同位体の最も一般的な崩壊様式は陽電子放出(β+)であり、銅の同位体が生じる。
質量数66以上の亜鉛の放射性同位体の最も一般的な崩壊様式はβ崩壊(β-)であり、ガリウムの同位体を生成する。
化合物と化学
反応性
亜鉛は電子配置が[Ar]3d104s2であり、周期表の12族の一員である。中程度の反応性を持つ金属であり、強い還元剤である。純金属の表面は変色が早く、最終的には大気中の二酸化炭素との反応によって塩基性の炭酸亜鉛、Zn
5(OH)
6(CO3)
2の保護不動態化層を形成する。
亜鉛は空気中で明るい青緑色の炎で燃え、酸化亜鉛の煙霧を出す。亜鉛は酸やアルカリ、その他の非金属と容易に反応する。極めて純粋な亜鉛は室温では酸とゆっくりとしか反応しない。塩酸や硫酸のような強い酸は不動態化層を除去することができ、その後の酸との反応によって水素ガスが放出される。
亜鉛の化学的性質は+2酸化状態が支配的である。この酸化状態の化合物が形成されると、外側のシェルのs電子が失われ、電子配置[Ar]3d10の裸の亜鉛イオンが生じる。水溶液中では八面体錯体[Zn(H
2O)6]2+
が優勢な種である。285 °C以上の温度で塩化亜鉛と組み合わせた亜鉛の揮発は、酸化状態が+1の亜鉛化合物Zn
2Cl
2の形成を示す。1または+2以外の正の酸化状態の亜鉛化合物は知られていない。計算では、+4の酸化状態の亜鉛化合物は存在しそうにない。Zn(III)は電気陰性度の強いトリアニオンの存在下で存在すると予測されているが、この可能性には疑問がある。しかし2021年、ZnBeB11(CN)12という式で表される、酸化状態が+3である別の化合物が、より多くの証拠とともに報告された。
亜鉛の化学的性質は後期第一遷移金属であるニッケルと銅の化学的性質に似ているが、充填d殻を持ち、化合物は反磁性でほとんどが無色である。亜鉛とマグネシウムのイオン半径は偶然にもほぼ同じである。このため、等価塩の中には同じ結晶構造を持つものもあり、イオン半径が決定要因となる他の状況では、亜鉛の化学はマグネシウムの化学と共通点が多い。他の点では、後期第一遷移金属との類似性はほとんどない。亜鉛は、NおよびSドナーと、より高度な共有結合性を持ち、はるかに安定な錯体を形成する傾向がある。亜鉛の錯体は5配位錯体も知られているが、ほとんどが4配位または6配位の配位錯体である。
亜鉛(I)化合物
亜鉛(I)化合物は非常に稀である。[Zn2]2+イオンは、溶融ZnCl2に金属亜鉛を溶かすと黄色い反磁性ガラスが形成されることから示唆されている。[Zn2]2+コアは、水銀(I)化合物に存在する[Hg2]2+カチオンと類似している。このイオンの反磁的な性質は、その二量体構造を裏付けている。Zn-Zn結合を含む最初の亜鉛(I)化合物(η5-C5Me5)2Zn2である。
亜鉛(II)化合物

3CO
2)
2

亜鉛の二元化合物は、ほとんどのメタロイドと希ガスを除くすべての非金属で知られている。酸化物ZnOは白色の粉末で、中性の水溶液にはほとんど溶けないが、両性であり、強い塩基性溶液にも酸性溶液にも溶ける。他のカルコゲン化物(ZnS、ZnSe、ZnTe)は電子工学や光学で様々な用途がある。また、[[Zinc nitride/ja|Zn
3N
2]、[[zinc phosphide/ja|Zn
3P
2]、[[zinc arsenide/ja|{chem|Zn|3|As|2}}]などのニクトゲン化物材料もある、また、[[zinc antimonide/ja|{chem|Zn|3|Sb|2}}]、過酸化物([[zinc peroxide/ja|ZnO
2])、水素化物([[zinc hydride/ja|{Chem|ZnH|2}}])、炭化物(ZnC
2)も知られている。4つのハロゲン化物のうち、[[zinc fluoride/ja|Template:化学式]は最もイオン的な性質を持ち、他のもの([[zinc chloride/ja|Template:化学式]、[[zinc bromide/ja|Template:化学式]、[[zinc iodide/ja|Template:化学式])は比較的融点が低く、共有結合的な性質が強いと考えられている。
Zn2+
イオンを含む弱い塩基性溶液では、水酸化物Zn(OH)
2が白色の沈殿物を形成する。より強いアルカリ溶液では、この水酸化物は溶解して亜鉛酸塩([Zn(OH)4]2−
)を形成する。) 硝酸塩Zn(NO3)
2、塩素酸塩Zn(ClO3)
2、硫酸塩ZnSO
4、リン酸塩Zn
3(PO4)
2、モリブデン酸塩ZnMoO
4、シアン化物[[Zinc cyanide/ja|Template:化学式]]、亜ヒ酸Zn(AsO2)
2、 ヒ酸塩Zn(AsO4)
2-8H
2Oやクロム酸塩ZnCrO
4(数少ない有色亜鉛化合物のひとつ)は、亜鉛の他の一般的な無機化合物のいくつかの例である。
有機亜鉛化合物は亜鉛-炭素共有結合を含む化合物である。ジエチル亜鉛((C
2H5)
2Zn)は合成化学の試薬である。1848年に亜鉛とヨウ化エチルの反応から初めて報告され、金属-炭素シグマ結合を含む最初の化合物として知られている。
亜鉛の検査
亜鉛の化学的指示薬として、コバルトシアニド紙(リンマンの亜鉛試験)を用いることができる。4 gのK3Co(CN)6と1 gのKClO3を100 mlの水に溶かす。紙を溶液に浸し、100℃で乾燥させる。試料を1滴、乾燥した紙の上に滴下し、加熱する。緑色の円盤が亜鉛の存在を示す。
歴史
古代の利用
古代に不純物のない亜鉛が使用されていた例はいくつか発見されている。亜鉛が別の元素として発見される何千年も前に、亜鉛と銅の合金黄銅を作るために亜鉛鉱石が使われていた。紀元前14世紀から10世紀のユダの黄銅には亜鉛が23%含まれている。
紀元前7世紀までに古代ギリシアに真鍮の製造方法が広まったが、作られた種類は少なかった。亜鉛を80〜90%含み、残りを鉛、鉄、アンチモン、その他の金属が占める合金で作られた2500年前の装飾品が発見されている。
紀元前1世紀に書かれたStrabo(ただし、紀元前4世紀の歴史家Theopompusの失われた著作を引用している)は、銅と混ぜると真鍮を作る「偽銀の滴」について言及している。これは硫化物鉱石の製錬の副産物である少量の亜鉛を指しているのかもしれない。
真鍮の製造は紀元前30年頃にはローマ人に知られていた。彼らは粉末状のカラミン(亜鉛珪酸塩または炭酸塩)と木炭と銅を坩堝で加熱して真鍮を作った。出来上がったカラミン真鍮は鋳造されるか、槌で打たれて武器に使われた。キリスト教時代のローマ人によって鋳造されたコインの中には、おそらくカラミン黄銅で作られたものがある。

最古の錠剤は、炭酸亜鉛のハイドロジンカイトとスミソナイトで作られていた。この丸薬は目の痛みに使用され、紀元前140年に難破したローマ船Relitto del Pozzinoから発見された。
ベルンの亜鉛板はローマ・ゴール時代に作られた奉納額で、ほとんどが亜鉛の合金でできている。
紀元300年から500年の間に書かれたと考えられているチャラカ・サムヒターには、酸化されると酸化亜鉛と思われるプッシュパンジャンを生成する金属が記載されている。インドのウダイプール近郊にあるザワールの亜鉛鉱山は、マウリヤ朝(c. 322 and 187 BC)から活動している。しかし、ここでの金属亜鉛の製錬は紀元12世紀頃に始まったようである。ある推定によれば、この場所では12世紀から16世紀にかけて推定100万トンの金属亜鉛と酸化亜鉛が生産されたという。別の推定では、この期間の金属亜鉛の総生産量は6万トンとされている。紀元13世紀頃に書かれたRasaratna Samuccayaには、2種類の亜鉛含有鉱石について言及されている。
初期の研究と命名
亜鉛は、1374年頃に書かれたヒンドゥー教のマダナパーラ王(タカ朝)の医学書『医学用語集』において、YasadaまたはJasadaという呼称で明確に金属として認識されていた。カラミンを羊毛やその他の有機物で還元して不純物の亜鉛を製錬・抽出することは、13世紀にインドで実現された。中国がこの技術を学んだのは17世紀になってからである。

錬金術師は金属亜鉛を空気中で燃焼させ、コンデンサーに酸化亜鉛を集めた。ある錬金術師はこの酸化亜鉛をlana philosophica、ラテン語で「哲学者の羊毛」を意味するlana philosophicaと呼んだ。
この金属の名称は、16世紀にスイス生まれのドイツの錬金術師であるパラケルススが著書Liber Mineralium IIの中で「zincum」または「zinken」として言及したのが最初と思われる。この語はおそらくドイツ語のzinkeに由来し、「歯のような、尖った、ギザギザした」という意味であると思われる(金属亜鉛結晶は針のような外観を持つ)。また、Zinkはドイツ語で錫を意味するzinnとの関係から、「錫のような」という意味もある。さらにもう一つの可能性は、この単語がペルシア語のسنگに由来するということである。sengは石を意味する。この金属は、Indian tin、tutanego、calamine、spinterとも呼ばれた。
ドイツの冶金学者アンドレアス・リバヴィウスは、1596年にポルトガル人から拿捕した貨物船からマラバル産の「カライ」(マレー語またはヒンディー語の錫の意味から)と呼ばれる量を受け取った。リバビウスは、亜鉛であった可能性のあるサンプルの特性を記述した。亜鉛は17世紀から18世紀初頭にかけてオリエントからヨーロッパに定期的に輸入されていたが、非常に高価であった。
単離

。
金属亜鉛は西暦1300年までにインドで単離された。ヨーロッパで分離される前に、西暦1600年頃にインドから輸入された。ヨーロッパの技術情報を提供する現代の資料であるPostlewaytのUniversal Dictionaryには1751年以前に亜鉛は記載されていないが、それ以前にこの元素は研究されていた。
フランドルの冶金学者であり錬金術師でもあった。P. M. de Respourは1668年に酸化亜鉛から金属亜鉛を抽出したと報告している。18世紀初頭には、エティエンヌ・フランソワ・ジェフロワが製錬中の亜鉛鉱石の上に置かれた鉄の棒の上で酸化亜鉛が黄色の結晶として凝結する様子を記述した。イギリスでは、ジョン・レインが1726年に破産する前に、おそらくランドールで亜鉛の製錬実験を行ったと言われている。
1738年にイギリスでウィリアム・チャンピオンが、縦型のレトルト式製錬所でカラミンから亜鉛を抽出するプロセスの特許を取得した。彼の技術はラジャスタンのザワール亜鉛鉱山で使われていたものに似ていたが、彼が東洋を訪れたことを示す証拠はない。チャンピオンの製法は1851年まで使用された。
ドイツの化学者アンドレアス・マルグラーフは通常、西洋で純粋な金属亜鉛を単離した功績を認められているが、その4年前にはスウェーデンの化学者アントン・フォン・スワブがカラミンから亜鉛を蒸留していた。1746年の実験では、マルグラフはカラミンと木炭の混合物を銅の入っていない密閉容器で加熱し、金属を得た。
その後の仕事
ウィリアム・チャンピオンの弟ジョンは、1758年に硫化亜鉛をレトルト処理で使用可能な酸化物に焼成するプロセスの特許を取得した。それ以前は、亜鉛の製造にはカラミンしか使用できなかった。1798年、ヨハン・クリスチャン・ルーベルグが最初の水平レトルト製錬所を建設して製錬プロセスを改良した。ジャン・ジャック・ダニエル・ドニーは、ベルギーにさらに多くの亜鉛を処理する別の種類の水平亜鉛製錬所を建設した。
イタリアの医師ルイジ・ガルヴァーニは1780年に、解剖したばかりのカエルの脊髄を真鍮のフックで取り付けた鉄のレールに接続すると、カエルの足が痙攣することを発見した。彼は誤って、神経と筋肉が電気を作り出す能力を発見したと考え、その効果を「動物電気」と呼んだ。ガルバニ電池と亜鉛メッキのプロセスはどちらもルイジ・ガルヴァーニにちなんで命名され、彼の発見は電気電池、亜鉛メッキ、カソード保護への道を開いた。
ガルヴァーニの友人であったアレッサンドロ・ボルタはこの効果の研究を続け、1800年にボルタの杭を発明した。ヴォルタの杭は簡略化されたガルバニックセルの積み重ねで構成されており、それぞれが1枚の銅板と1枚の亜鉛板を電解液で接続していた。これらのユニットを直列に積み重ねることで、ヴォルタの山(または「電池」)は全体としてより高い電圧を持ち、単セルよりも簡単に使用することができた。電気が発生するのは、2枚の金属板の間のボルタ電位によって電子が亜鉛から銅に流れ、亜鉛を腐食させるからである。
亜鉛は磁性を持たず、溶液中で色を持たないため、生化学や栄養学における重要性の発見が遅れた。1940年、血液から二酸化炭素を除去する酵素である炭酸脱水酵素の活性部位に亜鉛があることが示されると、この状況は一変した。
生産
採掘と加工
| ランク | 国 | トン |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 中国 | 4,210,000 |
| 2 | ペルー | 1,400,000 |
| 3 | オーストラリア | 1,330,000 |
| 4 | アメリカ | 753,000 |
| 5 | インド | 720,000 |
| 6 | メキシコ | 677,000 |




27°57′17″S 016°46′00″E / 27.95472°S 16.76667°E

27°49′09″S 016°36′28″E / 27.81917°S 16.60778°E
亜鉛は鉄、アルミニウム、銅に次いで4番目に多く使用されている金属で、年間生産量は約13 百万トンである。世界最大の亜鉛生産者は、オーストラリアのOZ MineralsとベルギーのUmicoreが合併したNyrstarである。世界の亜鉛の約70%は採掘によるもので、残りの30%は二次亜鉛のリサイクルによるものである。
商業的に純度の高い亜鉛はスペシャル・ハイグレードと呼ばれ、しばしばSHGと略される。
世界中で、新しい亜鉛の95%は硫化鉱鉱床から採掘され、その鉱床では、閃亜鉛鉱(ZnS)はほぼ常に銅、鉛、鉄の硫化物と混合している。亜鉛鉱山は世界中に点在しており、主な産地は中国、オーストラリア、ペルーである。中国は2014年に世界の亜鉛生産量の38%を生産した。
金属亜鉛は抽出冶金を用いて生産される。鉱石を細かく粉砕し、フロス浮遊法にかけて(疎水性の性質を利用して)鉱物とガングエを分離し、亜鉛約50%、硫黄32%、鉄13%、SiO
25%からなる硫化亜鉛鉱精鉱を得る。
焙焼は硫化亜鉛精鉱を酸化亜鉛に変える:
二酸化硫黄は、浸出プロセスに必要な硫酸の生産に使用される。炭酸亜鉛、ケイ酸亜鉛、またはジンクスピネル(ナミビアのスコーピオン鉱床のような)の鉱床を亜鉛生産に使用する場合は、焙焼を省略することができる。
さらなる処理には、2つの基本的な方法が用いられる: 高温冶金または電解である。乾式冶金では、950 °C (1,740 °F)で酸化亜鉛を炭素または一酸化炭素で還元して金属にし、それを亜鉛蒸気として蒸留して、その温度では揮発しない他の金属から分離する。亜鉛蒸気はコンデンサーに集められる。以下の式がこのプロセスを説明している:
電解では、硫酸によって鉱石精鉱から亜鉛が溶出し、不純物が沈殿する:
最後に、亜鉛は電気分解によって還元される。
硫酸は再生され、浸出工程に再利用される。
亜鉛めっきされた原料が電気アーク炉に供給されると、多くのプロセス、主にWaelzプロセス(2014年時点で90%)によってダストから亜鉛が回収される。
環境への影響
硫化亜鉛鉱石の精錬は大量の二酸化硫黄とカドミウム蒸気を発生させる。製錬所のスラグやその他の残渣にはかなりの量の金属が含まれている。ベルギーの町ラ・カラミンとプロンビエールでは、1806年から1882年の間に約110万トンの金属亜鉛と13万トンの鉛が採掘・製錬された。過去の採掘の投棄物からは亜鉛とカドミウムが溶出し、ゴール川の堆積物には微量の金属が含まれている。約2000年前、採掘と製錬による亜鉛の排出量は年間1万トンだった。1850年から10倍に増加した後、亜鉛の排出量は1980年代に年間340万トンでピークを迎え、1990年代には270万トンまで減少したが、 2005年の北極対流圏の研究では、北極の濃度は減少を反映していないことがわかった。 人為的排出と自然排出の割合は20対1である。
工業地帯や鉱業地帯を流れる河川の亜鉛濃度は20 ppmにもなる。効果的な下水処理はこれを大幅に減少させる。例えばライン川沿いの処理では、亜鉛濃度は50 ppbまで低下した。2 ppmという低濃度の亜鉛は、魚が血液中に運べる酸素の量に悪影響を与える。
亜鉛を含む汚泥の採掘、精製、施肥によって亜鉛に汚染された土壌には、乾燥土壌1kgあたり数グラムの亜鉛が含まれることがある。土壌中の亜鉛濃度が500 ppmを超えると、植物が鉄やマンガンなどの他の必須金属を吸収する能力が阻害される。いくつかの土壌サンプルでは、2000 ppmから180,000 ppm(18%)の亜鉛レベルが記録されている。欧州土壌観測所(European Soil Observatory)は、欧州における表土の亜鉛(Zn)濃度の初の高解像度空間評価を発表した。表土中の亜鉛の平均濃度は47mg/kgで、測定された22,000サンプルのうち1%は167mg/kg以上の高濃度であった。
用途
亜鉛の主な用途(米国での比率)は以下の通りである。
防錆とバッテリー


亜鉛は抗腐食剤として最も一般的に使用され、亜鉛メッキ(鉄または鋼鉄へのコーティング)が最も身近な形態である。2009年の米国では、亜鉛金属の55%にあたる89万3,000トンが亜鉛めっきに使用された。
亜鉛は鉄や鋼よりも反応性が高いため、完全に腐食しきるまで、ほとんどすべての局所的な酸化を引き寄せる。亜鉛が腐食すると、酸化物と炭酸塩の保護表面層(Zn
5(OH)
6(CO
3)
2)が形成される。この保護機能は亜鉛層に傷がついても持続するが、亜鉛が腐食するにつれて時間と共に劣化する。亜鉛は電気化学的に、または溶融亜鉛として溶融亜鉛メッキやスプレーで施される。亜鉛メッキはチェーン・リンク・フェンス、ガード・レール、吊り橋、電柱、金属屋根、熱交換器、自動車の車体などに使用される。
亜鉛の相対的な反応性とそれ自体に酸化を引き寄せる能力により、亜鉛はカソード保護(CP)における効率的な犠牲陽極となっている。例えば、埋設パイプラインのカソード保護は、亜鉛で作られた陽極をパイプに接続することで達成できる。亜鉛は鋼管に電流を流すと徐々に腐食し、陽極(負の終端)として機能する。亜鉛は、海水にさらされる金属の陰極保護にも使われる。船の鉄製舵に取り付けられた亜鉛ディスクは、舵が無傷のままゆっくりと腐食していく。同様に、プロペラや船のキールの金属製保護ガードに取り付けられた亜鉛プラグは、一時的な保護を提供する。
標準電極電位(SEP)は-0.76ボルトであり、亜鉛は電池の負極材料として使用される。(より反応性の高いリチウム(SEP -3.04V)はリチウム電池の負極に使用される)。粉末亜鉛はアルカリ乾電池でこのように使用され、亜鉛-炭素電池のケース(負極としても機能する)は板状の亜鉛から形成される。亜鉛は空気亜鉛電池/燃料電池の負極または燃料として使用される。亜鉛-セリウム電池レドックスフロー電池も亜鉛ベースの負極ハーフセルに依存している。
合金
広く使われている亜鉛合金は黄銅で、黄銅の種類にもよるが、銅に3%から45%の亜鉛を合金化したものである。真鍮は一般に銅よりも延性があり強度が高く、優れた耐食性を持つ。これらの特性により、通信機器、金物、楽器、水道バルブなどに有用である。

他に広く使われている亜鉛合金には、洋白、タイプライターメタル、軟質およびアルミニウムのはんだ、市販の青銅などがある。亜鉛は現代のパイプオルガンでも、パイプの伝統的な鉛/錫合金の代用として使用されている。亜鉛85~88%、銅4~10%、アルミニウム2~8%の合金は、ある種の機械ベアリングに限定的に使用されている。亜鉛は1982年以来アメリカの1セント硬貨(ペニー)の主金属である。亜鉛のコアは、銅貨の外観を与えるために銅の薄い層でコーティングされている。1994年には、33,200 tonnes (36,600 short tons)の亜鉛が、アメリカで136 億のペニーを製造するために使用された。
亜鉛に少量の銅、アルミニウム、マグネシウムを加えた合金は、ダイカストやスピンキャスティング、特に自動車、電気、ハードウェア産業で有用である。これらの合金はザマックという名前で販売されている。その一例が亜鉛アルミニウムである。融点が低く粘性が低いため、小さく複雑な形状の製造が可能である。低い作業温度は、鋳造製品の急速な冷却と組立のための迅速な生産につながる。プレスタールというブランド名で販売されている別の合金は、78%の亜鉛と22%のアルミニウムを含み、鋼とほぼ同等の強度を持ちながらプラスチックのように可鍛性であると報告されている。この合金の超塑性により、セラミックやセメントでできたダイカストを使って成形することができる。
少量の鉛を加えた同様の合金は、冷間圧延して板状にすることができる。亜鉛96%とアルミニウム4%の合金は、鉄の金型では高価すぎる少量生産用途のプレス金型に使われる。深絞り、ロール成形、ベンディングで成形されるシートメタルの建築ファサード、屋根、その他の用途には、チタンや銅を含む亜鉛合金が使われる。未合金の亜鉛はこれらの製造工程には脆すぎる。
密度が高く、安価で加工しやすい材料として、亜鉛は鉛の代替品として使われる。鉛懸念の後、亜鉛は釣りからタイヤバランスやフライホイールに至るまで様々な用途の錘に登場する。
カドミウム亜鉛テルル化物(CZT)は半導電性合金であり、小さなセンシングデバイスのアレイに分割することができる。これらのデバイスは集積回路に似ており、入射ガンマ線光子のエネルギーを検出することができる。吸収マスクの背後にあるとき、CZTセンサーアレイは光線の方向を決定することができる。
その他の工業的用途

2009年の米国における全亜鉛産出量のおよそ4分の1は亜鉛化合物として消費された。酸化亜鉛は塗料の白色顔料として、またゴムの製造において熱を分散させる触媒として広く使用されている。酸化亜鉛はゴムポリマーやプラスチックを紫外線(UV)から保護するために使われる。酸化亜鉛の半導体特性はバリスタやコピー製品に有用である。亜鉛-酸化亜鉛サイクルは、亜鉛と酸化亜鉛に基づく2段階の熱化学プロセスで、水素製造を行う。
塩化亜鉛は難燃剤として木材に添加されることが多い。他の化学物質の製造にも使われる。亜鉛メチル(Zn(CH3)
2)は多くの有機合成で使われる。硫化亜鉛(ZnS)は、時計の針、X線やテレビの画面、夜光塗料などの発光顔料に使用される。ZnSの結晶は、スペクトルの中赤外部分で動作するレーザーに使用される。硫酸亜鉛は染料や顔料に含まれる化学物質である。ジンクピリチオンは防汚塗料に使われる。
亜鉛パウダーは模型ロケットの推進剤として使われることがある。亜鉛70%と硫黄30%の粉末を圧縮した混合物に点火すると激しい化学反応が起こる。大量の高温ガス、熱、光とともに硫化亜鉛が生成される。
亜鉛板金は屋根、壁、カウンターの耐久性のあるカバーとして使われ、最後はビストロやオイスターバーでよく見られ、使用中に表面が酸化して青灰色のパティナになり、傷がつきやすくなることで素朴な外観を与えることで知られている。
亜鉛の最も豊富な同位体である64
Znは中性子放射化の影響を非常に受けやすく、半減期が244日で強烈なγ線を発生する高放射能の65
Znに核変換される。このため、原子炉の防錆剤として使用される酸化亜鉛は、使用前に64
Znが取り除かれ、これを劣化酸化亜鉛と呼ぶ。同じ理由から、亜鉛は核兵器の塩漬け材料として提案されている(コバルトもよく知られた塩漬け材料である)。同位体濃縮された64
Znのジャケットは、爆発する熱核兵器からの強烈な高エネルギー中性子束によって照射され、大量の65
Znを形成し、兵器の降下物の放射能を著しく増加させる。
亜鉛
65はトレーサーとして、亜鉛を含む合金がどのように摩耗するか、または生物における亜鉛の経路と役割を研究するために使用される。
ジチオカルバミン酸亜鉛錯体は農業用殺菌剤として使用されている。これらにはジネブ、メチラム、プロピネブ、ジラムが含まれる。亜鉛はZDDPの形で、エンジンオイル中の金属部品の摩耗防止添加剤として使用される。
有機化学

有機化学は、炭素-亜鉛結合を含む化合物の物性、合成、化学反応を記述する科学である。多くの有機亜鉛化合物は商業的に重要である。重要な用途には以下のようなものがある:
- Frankland-Duppa反応では、オキシレートエステル(ROCOCOOR)がアルキルハライドR'X、亜鉛、塩酸と反応して、α-ヒドロキシカルボン酸エステルRR'COHCOORが生成する。
- オルガノ亜鉛はグリニャール試薬と類似した反応性を持ちますが、非常に求核性が低く、高価で取り扱いが難しいです。オルガノ亜鉛は通常、アルデヒドなどの求電子剤に求核的付加を行い、それらをアルコールに還元する。市販のジオルガノ亜鉛化合物には、ジメチル亜鉛、ジエチル亜鉛、ジフェニル亜鉛などが含まれます。グリニャール試薬と同様に、オルガノ亜鉛は一般的に有機臭素前駆体から合成される。
亜鉛はエナンチオ選択的合成を含む有機合成の触媒反応において多くの用途を見出しており、貴金属錯体に代わる安価で入手しやすい触媒である。キラル亜鉛触媒で得られる定量的結果(収率およびエナンチオマー過剰)は、パラジウム、ルテニウム、イリジウムなどで得られる結果に匹敵する。
栄養補助食品

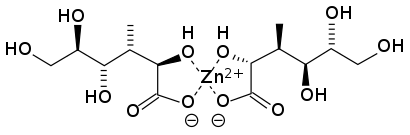
重要な微量ミネラルである亜鉛は、体内に大量に貯蔵されることはないため、最適な健康のためには定期的な食事からの摂取が必要となる。細胞代謝(亜鉛は人体内の300以上の酵素の機能に不可欠である)、免疫機能、タンパク質合成、DNA合成、細胞分裂など、亜鉛が人間の健康に広く関与していることを考えると、定期的な摂取は特に重要である。
ほとんどの1錠タイプの市販の日用ビタミン・ミネラルサプリメントでは、亜鉛は酸化亜鉛、酢酸亜鉛、グルコン酸亜鉛、または亜鉛アミノ酸キレートなどの形で含まれている。
一般に、亜鉛欠乏症のリスクが高い場合(低・中所得国など)には、予防策として亜鉛サプリメントが推奨される。一般的には硫酸亜鉛がよく使われるが、クエン酸 亜鉛、グルコン酸亜鉛、ピコリン酸亜鉛も有効な選 択肢となる。これらの形態は酸化亜鉛よりも吸収がよい。
胃腸炎
亜鉛は、開発途上国の子どもたちの下痢の治療において、安価で効果的である。亜鉛は下痢の際に体内で枯渇するため、10~14日間 の治療で亜鉛を補給することで、下痢エピソードの期間 と重症度を軽減することができ、また、将来のエピソード を3ヵ月も予防することができる。胃腸炎は亜鉛の摂取によって強力に減弱するが、これはおそらく消化管でのイオンの直接的な抗菌作用、または亜鉛の吸収と免疫細胞からの再放出(すべての顆粒球は亜鉛を分泌する)、またはその両方によるものであろう。
風邪
亜鉛サプリメント(酢酸亜鉛やグルコン酸亜鉛が多い)ロゼンジは、common cold/jaの治療に一般的に使用される一群の栄養補助食品である。症状の発現から24時間以内に75 mg/日を超える用量の亜鉛サプリメントを使用すると、成人では風邪症状の持続期間が約1 日短縮することが示されている。亜鉛サプリメントの口から副作用には、悪味と吐き気がある。亜鉛を含む点鼻薬の経鼻使用は、嗅覚の喪失と関連している;その結果、2009年6月、米国食品医薬品局(USFDA)は、経鼻亜鉛の使用を中止するよう消費者に警告した。
ヒトライノウイルス -ヒトで最も一般的なウイルス病原体 -は、風邪の主な原因である。亜鉛が風邪症状の重症度および/または持続時間を減少させる作用機序は、鼻の炎症の抑制と、鼻粘膜におけるライノウイルス受容体結合およびライノウイルスの増殖の直接的阻害であると仮説されている。
体重増加
亜鉛欠乏症は食欲不振を引き起こすことがある。食欲不振の治療に亜鉛を用いることは、1979年以来提唱されている。少なくとも15の臨床試験で、亜鉛が食欲不振の体重増加を改善することが示されている。1994年の試験では、神経性食欲不振症の治療において、亜鉛が体重増加率を2倍にすることが示された。チロシン、トリプトファン、チアミンなどの他の栄養素の欠乏は、この「栄養失調による栄養不良」現象に寄与している可能性がある。 多くの国々で実施された亜鉛の補給と子どもの成長に対するその効果に関する33の前向き介入試験のメタアナリシスによると、亜鉛の補給のみでは直線的な成長と体重増加に統計的に有意な効果があり、存在する可能性のある他の欠乏が成長遅延の原因ではないことが示された。
その他
2023年のコクラン・レビューでは、亜鉛サプリメントを摂取している人は加齢黄斑変性症に進行しにくい可能性があると述べられている。亜鉛サプリメントは腸性肢端皮膚炎の効果的な治療法であり、亜鉛の吸収に影響する遺伝的疾患で、以前は罹患した乳児は致命的であった。亜鉛欠乏は大うつ病性障害(MDD)と関連しており、亜鉛サプリメントは効果的な治療法となりうる。亜鉛は個人の睡眠を助けるかもしれない。
局所的使用
亜鉛の局所製剤には、皮膚に使用するものがあり、多くの場合酸化亜鉛の形で使用される。酸化亜鉛は一般的に安全で効果的であるとFDAに認められており、非常に光安定性が高いと考えられている。酸化亜鉛は、日焼けを軽減するために日焼け止めに配合される最も一般的な有効成分のひとつである。おむつ交換のたびに赤ちゃんのおむつ部分(会陰)に薄く塗ると、おむつかぶれを防ぐことができる。
キレート化亜鉛は、口臭を予防するために歯磨き粉や洗口液に使われる。クエン酸亜鉛は、歯石の蓄積を抑えるのに役立つ。
ジンクピリチオンは、フケを防ぐためのシャンプーに広く含まれている。
局所亜鉛はまた、性器ヘルペスを効果的に治療し、寛解を延長することが示されている。
生物学的役割
亜鉛はヒトや他の動物、植物、微生物にとって必須の微量元素である。亜鉛は300を超える酵素と1000を超える転写因子の機能に必要であり、メタロチオネインに貯蔵され移動する。亜鉛は鉄に次いでヒトに多く含まれる微量金属であり、すべての酵素クラスに現れる唯一の金属である。
タンパク質では、亜鉛イオンはしばしばアスパラギン酸、グルタミン酸、システイン、ヒスチジンなどのアミノ酸側鎖に配位する。タンパク質におけるこの亜鉛結合(他の遷移金属と同様)の理論的・計算的記述は困難である。
Roughly 2–4 grams of zinc are distributed throughout the human body. Most zinc is in the brain, muscle, bones, kidney, and liver, with the highest concentrations in the prostate and parts of the eye. Semen is particularly rich in zinc, a key factor in prostate gland function and reproductive organ growth.
Zinc homeostasis of the body is mainly controlled by the intestine. Here, ZIP4 and especially TRPM7 were linked to intestinal zinc uptake essential for postnatal survival.
In humans, the biological roles of zinc are ubiquitous. It interacts with "a wide range of organic ligands", and has roles in the metabolism of RNA and DNA, signal transduction, and gene expression. It also regulates apoptosis. A review from 2015 indicated that about 10% of human proteins (~3000) bind zinc, in addition to hundreds more that transport and traffic zinc; a similar in silico study in the plant Arabidopsis thaliana found 2367 zinc-related proteins.
In the brain, zinc is stored in specific synaptic vesicles by glutamatergic neurons and can modulate neuronal excitability. It plays a key role in synaptic plasticity and so in learning. Zinc homeostasis also plays a critical role in the functional regulation of the central nervous system. Dysregulation of zinc homeostasis in the central nervous system that results in excessive synaptic zinc concentrations is believed to induce neurotoxicity through mitochondrial oxidative stress (e.g., by disrupting certain enzymes involved in the electron transport chain, including complex I, complex III, and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase), the dysregulation of calcium homeostasis, glutamatergic neuronal excitotoxicity, and interference with intraneuronal signal transduction. L- and D-histidine facilitate brain zinc uptake. SLC30A3 is the primary zinc transporter involved in cerebral zinc homeostasis.
Enzymes


Zinc is an efficient Lewis acid, making it a useful catalytic agent in hydroxylation and other enzymatic reactions. The metal also has a flexible coordination geometry, which allows proteins using it to rapidly shift conformations to perform biological reactions. Two examples of zinc-containing enzymes are carbonic anhydrase and carboxypeptidase, which are vital to the processes of carbon dioxide (CO
2) regulation and digestion of proteins, respectively.
In vertebrate blood, carbonic anhydrase converts CO
2 into bicarbonate and the same enzyme transforms the bicarbonate back into CO
2 for exhalation through the lungs. Without this enzyme, this conversion would occur about one million times slower at the normal blood pH of 7 or would require a pH of 10 or more. The non-related β-carbonic anhydrase is required in plants for leaf formation, the synthesis of indole acetic acid (auxin) and alcoholic fermentation.
Carboxypeptidase cleaves peptide linkages during digestion of proteins. A coordinate covalent bond is formed between the terminal peptide and a C=O group attached to zinc, which gives the carbon a positive charge. This helps to create a hydrophobic pocket on the enzyme near the zinc, which attracts the non-polar part of the protein being digested.
Signalling
Zinc has been recognized as a messenger, able to activate signalling pathways. Many of these pathways provide the driving force in aberrant cancer growth. They can be targeted through ZIP transporters.
Other proteins
Zinc serves a purely structural role in zinc fingers, twists and clusters. Zinc fingers form parts of some transcription factors, which are proteins that recognize DNA base sequences during the replication and transcription of DNA. Each of the nine or ten Zn2+
ions in a zinc finger helps maintain the finger's structure by coordinately binding to four amino acids in the transcription factor.
In blood plasma, zinc is bound to and transported by albumin (60%, low-affinity) and transferrin (10%). Because transferrin also transports iron, excessive iron reduces zinc absorption, and vice versa. A similar antagonism exists with copper. The concentration of zinc in blood plasma stays relatively constant regardless of zinc intake. Cells in the salivary gland, prostate, immune system, and intestine use zinc signaling to communicate with other cells.
Zinc may be held in metallothionein reserves within microorganisms or in the intestines or liver of animals. However, inadequate or excessive zinc intake can be harmful; excess zinc particularly impairs copper absorption because metallothionein absorbs both metals.
The human dopamine transporter contains a high affinity extracellular zinc binding site which, upon zinc binding, inhibits dopamine reuptake and amplifies amphetamine-induced dopamine efflux in vitro. The human serotonin transporter and norepinephrine transporter do not contain zinc binding sites. Some EF-hand calcium binding proteins such as S100 or NCS-1 are also able to bind zinc ions.
Nutrition
Dietary recommendations
The U.S. Institute of Medicine (IOM) updated Estimated Average Requirements (EARs) and Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for zinc in 2001. The current EARs for zinc for women and men ages 14 and up is 6.8 and 9.4 mg/day, respectively. The RDAs are 8 and 11 mg/day. RDAs are higher than EARs so as to identify amounts that will cover people with higher than average requirements. RDA for pregnancy is 11 mg/day. RDA for lactation is 12 mg/day. For infants up to 12 months the RDA is 3 mg/day. For children ages 1–13 years the RDA increases with age from 3 to 8 mg/day. As for safety, the IOM sets Tolerable upper intake levels (ULs) for vitamins and minerals when evidence is sufficient. In the case of zinc the adult UL is 40 mg/day including both food and supplements combined (lower for children). Collectively the EARs, RDAs, AIs and ULs are referred to as Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs).
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) refers to the collective set of information as Dietary Reference Values, with Population Reference Intake (PRI) instead of RDA, and Average Requirement instead of EAR. AI and UL are defined the same as in the United States. For people ages 18 and older the PRI calculations are complex, as the EFSA has set higher and higher values as the phytate content of the diet increases. For women, PRIs increase from 7.5 to 12.7 mg/day as phytate intake increases from 300 to 1200 mg/day; for men the range is 9.4 to 16.3 mg/day. These PRIs are higher than the U.S. RDAs. The EFSA reviewed the same safety question and set its UL at 25 mg/day, which is much lower than the U.S. value.
For U.S. food and dietary supplement labeling purposes the amount in a serving is expressed as a percent of Daily Value (%DV). For zinc labeling purposes 100% of the Daily Value was 15 mg, but on May 27, 2016, it was revised to 11 mg. A table of the old and new adult daily values is provided at Reference Daily Intake.
Dietary intake

Animal products such as meat, fish, shellfish, fowl, eggs, and dairy contain zinc. The concentration of zinc in plants varies with the level in the soil. With adequate zinc in the soil, the food plants that contain the most zinc are wheat (germ and bran) and various seeds, including sesame, poppy, alfalfa, celery, and mustard. Zinc is also found in beans, nuts, almonds, whole grains, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, and blackcurrant.
Other sources include fortified food and dietary supplements in various forms. A 1998 review concluded that zinc oxide, one of the most common supplements in the United States, and zinc carbonate are nearly insoluble and poorly absorbed in the body. This review cited studies that found lower plasma zinc concentrations in the subjects who consumed zinc oxide and zinc carbonate than in those who took zinc acetate and sulfate salts. For fortification, however, a 2003 review recommended cereals (containing zinc oxide) as a cheap, stable source that is as easily absorbed as the more expensive forms. A 2005 study found that various compounds of zinc, including oxide and sulfate, did not show statistically significant differences in absorption when added as fortificants to maize tortillas.
Deficiency
Nearly two billion people in the developing world are deficient in zinc. Groups at risk include children in developing countries and elderly with chronic illnesses. In children, it causes an increase in infection and diarrhea and contributes to the death of about 800,000 children worldwide per year. The World Health Organization advocates zinc supplementation for severe malnutrition and diarrhea. Zinc supplements help prevent disease and reduce mortality, especially among children with low birth weight or stunted growth. However, zinc supplements should not be administered alone, because many in the developing world have several deficiencies, and zinc interacts with other micronutrients. While zinc deficiency is usually due to insufficient dietary intake, it can be associated with malabsorption, acrodermatitis enteropathica, chronic liver disease, chronic renal disease, sickle cell disease, diabetes, malignancy, and other chronic illnesses.
In the United States, a federal survey of food consumption determined that for women and men over the age of 19, average consumption was 9.7 and 14.2 mg/day, respectively. For women, 17% consumed less than the EAR, for men 11%. The percentages below EAR increased with age. The most recent published update of the survey (NHANES 2013–2014) reported lower averages – 9.3 and 13.2 mg/day – again with intake decreasing with age.
Symptoms of mild zinc deficiency are diverse. Clinical outcomes include depressed growth, diarrhea, impotence and delayed sexual maturation, alopecia, eye and skin lesions, impaired appetite, altered cognition, impaired immune functions, defects in carbohydrate use, and reproductive teratogenesis. but excessive zinc does also.
Despite some concerns, western vegetarians and vegans do not suffer any more from overt zinc deficiency than meat-eaters. Major plant sources of zinc include cooked dried beans, sea vegetables, fortified cereals, soy foods, nuts, peas, and seeds. However, phytates in many whole-grains and fibers may interfere with zinc absorption and marginal zinc intake has poorly understood effects. The zinc chelator phytate, found in seeds and cereal bran, can contribute to zinc malabsorption. Some evidence suggests that more than the US RDA (8 mg/day for adult women; 11 mg/day for adult men) may be needed in those whose diet is high in phytates, such as some vegetarians. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) guidelines attempt to compensate for this by recommending higher zinc intake when dietary phytate intake is greater. These considerations must be balanced against the paucity of adequate zinc biomarkers, and the most widely used indicator, plasma zinc, has poor sensitivity and specificity.
土壌浄化
カルーナ、エリカ、ワクシニウムなどは、エリコイド菌根菌の働きによって有害イオンの移動が阻止されるため、亜鉛メタル土壌でも生育することができる。
農業
亜鉛欠乏症は作物植物における最も一般的な微量栄養素欠乏症のようである。亜鉛欠乏土壌は、トルコとインドの約半分、中国の3分の1、西オーストラリアのほとんどの農地で耕作されている。これらの地域では、亜鉛施肥に対する実質的な反応が報告されている。亜鉛が欠乏した土壌で生育する植物は、病気にかかりやすくなる。亜鉛は主に岩石の風化によって土壌に添加されるが、化石燃料の燃焼、鉱山廃棄物、リン酸肥料、農薬(リン化亜鉛)、石灰石、糞尿、下水汚泥、亜鉛メッキ表面の粒子などによっても、人間が亜鉛を添加している。過剰な亜鉛は植物に有毒であるが、亜鉛の毒性ははるかに少ない。
注意事項
毒性
亜鉛は健康に不可欠な栄養素だが、過剰摂取は有害である。亜鉛の過剰吸収は銅と鉄の吸収を抑制する。溶液中の遊離亜鉛イオンは、植物、無脊椎動物、脊椎動物の魚類にさえ強い毒性を示す。遊離イオン活性モデルは文献的に確立されており、マイクロモル量の遊離イオンがある種の生物を殺すことを示している。最近の例では、6マイクロモルで水中のミジンコ'の93%が死んだ。
遊離の亜鉛イオンは腐食性に至るまで強力なルイス酸である。胃酸には塩酸が含まれており、金属亜鉛は容易に溶けて腐食性の塩化亜鉛を与える。1982年以降のアメリカの1セント片(亜鉛97.5%)を飲み込むと、酸性の胃の中で亜鉛イオンの溶解度が高いため、胃粘膜に損傷を与えることがある。
亜鉛を1日100~300mg摂取している人は、誘発性の銅欠乏症に悩まされる可能性があるという証拠がある。2007年の試験では、1日80 mgを摂取している高齢男性は、プラセボを摂取している人よりも泌尿器系の合併症で入院する頻度が高いことが観察された。100~300 mgのレベルでは、銅や鉄の使用を妨げたり、コレステロールに悪影響を及ぼす可能性がある。土壌中の亜鉛が500 ppmを超えると、鉄やマンガンなど他の必須金属の植物吸収を妨げる。亜鉛をろう付けするときや亜鉛メッキされた材料を溶接するときに亜鉛のヒュームを吸い込むと、亜鉛シェイクや亜鉛チルと呼ばれる症状が誘発されることがある。亜鉛は義歯クリームの一般的な成分であり、1グラムあたり17~38mgの亜鉛が含まれている。これらの製品の過剰使用による障害や死亡さえも主張されている。
米国食品医薬品局(FDA)は、亜鉛が鼻の神経受容体を損傷し、無嗅覚症を引き起こすとしている。アノスミアの報告は、1930年代にポリオ感染を予防するために亜鉛製剤を使用して失敗した際にも観察された。2009年6月16日、FDAは亜鉛ベースの鼻腔内風邪薬の店頭からの撤去を命じた。FDAによると、嗅覚が損なわれると、ガスや煙の漏れを感知できなくなり、食べる前に食品が腐っているかどうかがわからなくなるため、生命を脅かす可能性があるという。
最近の研究では、外用抗菌剤ジンクピリチオンが強力な熱ショック応答誘導物質であり、培養ヒトケラチノサイトやメラノサイトにおいてPARP依存性のエネルギー危機を誘導してゲノムの完全性を損なう可能性が示唆されている。
中毒
1982年、アメリカ合衆国造幣局は、銅でコーティングされているが、主に亜鉛を含むペニーの鋳造を開始した。亜鉛硬貨は亜鉛中毒の危険性があり、死に至ることもある。425ペニー(1 kg以上の亜鉛)を慢性的に摂取したある報告例は、消化管細菌および真菌による敗血症で死亡した。12 グラムの亜鉛を摂取した別の患者では、嗜眠と運動失調(筋肉の動きの協調性が著しく欠如している)のみがみられた。亜鉛硬貨の摂取によって亜鉛中毒に陥った症例が他にもいくつか報告されている。
小銭やその他の小さな硬貨を犬が食べてしまうことがあり、獣医による異物の除去が必要となる。硬貨に含まれる亜鉛は亜鉛中毒を引き起こすことがあり、犬では重度の溶血性貧血と肝臓または腎臓の損傷によって致死的となる。亜鉛はオウムに強い毒性を示し、中毒はしばしば致命的となる。亜鉛メッキ缶に保存されたフルーツジュースの消費により、亜鉛によるオウムの大量中毒が発生している。
こちらも参照
- List of countries by zinc production/ja
- Spelter/ja
- Wet storage stain/ja
- Zinc alloy electroplating/ja
- Metal fume fever/ja
- Piotr Steinkeller/ja
参考文献
- Chambers, William and Robert (1901). Chambers's Encyclopaedia: A Dictionary of Universal Knowledge (Revised ed.). London and Edinburgh: J. B. Lippincott Company. Archived from the original on March 17, 2024. Retrieved September 27, 2020.
- Cotton, F. Albert; Wilkinson, Geoffrey; Murillo, Carlos A.; Bochmann, Manfred (1999). Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (6th ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 978-0-471-19957-1.
- David R. Lide, ed. (2006). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group. ISBN 978-0-8493-0487-3. Archived from the original on March 17, 2024. Retrieved September 27, 2020.
- Emsley, John (2001). "Zinc". Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements. Oxford, England, UK: Oxford University Press. pp. 499–505. ISBN 978-0-19-850340-8.
- Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-3365-9.
- Heiserman, David L. (1992). "Element 30: Zinc". Exploring Chemical Elements and their Compounds. New York: TAB Books. ISBN 978-0-8306-3018-9.
- Lehto, R. S. (1968). "Zinc". In Clifford A. Hampel (ed.). The Encyclopedia of the Chemical Elements. New York: Reinhold Book Corporation. pp. 822–830. ISBN 978-0-442-15598-8. LCCN 68-29938.
- Stwertka, Albert (1998). "Zinc". Guide to the Elements (Revised ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-508083-4.
- Weeks, Mary Elvira (1933). "III. Some Eighteenth-Century Metals". The Discovery of the Elements. Easton, PA: Journal of Chemical Education. ISBN 978-0-7661-3872-8.
外部リンク
- Zinc: Fact Sheet for Health Professionals from the U.S. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements
- Zinc Statistics and Information from the U.S. Geological Survey's National Minerals Information Center
- Zinc.org - official website of the International Zinc Association, a zinc industry association
- Zinc video from the Periodic Videos series (University of Nottingham)
- ZincBind.net – a database identifying biological zinc binding sites from within the Protein Data Bank