Calcipotriol: Difference between revisions
Marked this version for translation |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages /> | <languages /> | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
<!--T:1--> | |||
{{Short description|Chemical compound}} | {{Short description|Chemical compound}} | ||
{{Drugbox | {{Drugbox | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
| USAN = calcipotriene | | USAN = calcipotriene | ||
<!--T:2--> | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | <!--Clinical data--> | ||
| tradename = Daivonex, Dovonex, Sorilux | | tradename = Daivonex, Dovonex, Sorilux | ||
| Line 27: | Line 29: | ||
| ATC_suffix = AX02 | | ATC_suffix = AX02 | ||
<!--T:3--> | |||
| legal_AU = S4 | | legal_AU = S4 | ||
| legal_CA = Rx-only | | legal_CA = Rx-only | ||
| Line 33: | Line 36: | ||
| legal_status = | | legal_status = | ||
<!--T:4--> | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | ||
| bioavailability = 5 to 6% | | bioavailability = 5 to 6% | ||
| Line 38: | Line 42: | ||
| excretion = Biliary | | excretion = Biliary | ||
<!--T:5--> | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | <!--Identifiers--> | ||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | ||
| Line 56: | Line 61: | ||
| ChEMBL = 100918 | | ChEMBL = 100918 | ||
<!--T:6--> | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | <!--Chemical data--> | ||
| IUPAC_name = (1''R'',3''S'',5''E''<nowiki>)-5-{2-[(1</nowiki>''R'',3a''S'',4''Z'',7a''R'')-1-[(2''R'',3''E'')-5-cyclopropyl-5-hydroxypent-3-en-2-yl]-7a-methyl-octahydro-1''H''-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene}-4-methylidenecyclohexane-1,3-diol | | IUPAC_name = (1''R'',3''S'',5''E''<nowiki>)-5-{2-[(1</nowiki>''R'',3a''S'',4''Z'',7a''R'')-1-[(2''R'',3''E'')-5-cyclopropyl-5-hydroxypent-3-en-2-yl]-7a-methyl-octahydro-1''H''-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene}-4-methylidenecyclohexane-1,3-diol | ||
| Line 68: | Line 74: | ||
}} | }} | ||
<!--T:7--> | |||
<!-- Definition and medical uses --> | <!-- Definition and medical uses --> | ||
'''Calcipotriol''', also known as '''calcipotriene''', is a synthetic [[derivative (chemistry)|derivative]] of [[calcitriol]], a form of [[vitamin D]]. It is used in the treatment of [[psoriasis]]. It is safe for long-term application in psoriatic skin conditions. | '''Calcipotriol''', also known as '''calcipotriene''', is a synthetic [[derivative (chemistry)|derivative]] of [[calcitriol]], a form of [[vitamin D]]. It is used in the treatment of [[psoriasis]]. It is safe for long-term application in psoriatic skin conditions. | ||
<!--T:8--> | |||
<!-- Society and culture --> | <!-- Society and culture --> | ||
It was patented in 1985 and approved for medical use in 1991. It is marketed under the trade name "Dovonex" in the United States, "Daivonex" outside North America, and "Psorcutan" in Germany. | It was patented in 1985 and approved for medical use in 1991. It is marketed under the trade name "Dovonex" in the United States, "Daivonex" outside North America, and "Psorcutan" in Germany. | ||
<!--T:9--> | |||
It is on the [[WHO Model List of Essential Medicines|World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines]]. | It is on the [[WHO Model List of Essential Medicines|World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines]]. | ||
<!--T:10--> | |||
Calcipotriol is also available as [[Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate]], a fixed-dose [[combination medication]] with the synthetic [[corticosteroid]] [[betamethasone dipropionate]] for the treatment of [[plaque psoriasis]]. | Calcipotriol is also available as [[Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate]], a fixed-dose [[combination medication]] with the synthetic [[corticosteroid]] [[betamethasone dipropionate]] for the treatment of [[plaque psoriasis]]. | ||
<!--T:11--> | |||
==Medical uses== | ==Medical uses== | ||
Chronic plaque psoriasis is the chief medical use of calcipotriol. It has also been used successfully in the treatment of [[alopecia areata]]. | Chronic plaque psoriasis is the chief medical use of calcipotriol. It has also been used successfully in the treatment of [[alopecia areata]]. | ||
<!--T:12--> | |||
==Contraindications== | ==Contraindications== | ||
Hypersensitivity, use on face, hypercalcaemia, or evidence of vitamin D toxicity are the only [[contraindications]] for calcipotriol use. | Hypersensitivity, use on face, hypercalcaemia, or evidence of vitamin D toxicity are the only [[contraindications]] for calcipotriol use. | ||
<!--T:13--> | |||
Cautions include exposure to excessive natural or artificial light, due to the potential for calcipotriol to cause photosensitivity. | Cautions include exposure to excessive natural or artificial light, due to the potential for calcipotriol to cause photosensitivity. | ||
<!--T:14--> | |||
==Adverse effects== | ==Adverse effects== | ||
Adverse effects by frequency: | Adverse effects by frequency: | ||
| Line 93: | Line 107: | ||
* Skin irritation | * Skin irritation | ||
<!--T:15--> | |||
;Common (1–10% frequency): | ;Common (1–10% frequency): | ||
{{div col|colwidth=18em}} | {{div col|colwidth=18em}} | ||
| Line 103: | Line 118: | ||
{{div col end}} | {{div col end}} | ||
<!--T:16--> | |||
;Uncommon (0.1–1% frequency): | ;Uncommon (0.1–1% frequency): | ||
* Exacerbation of [[psoriasis]] | * Exacerbation of [[psoriasis]] | ||
<!--T:17--> | |||
;Rare (< 0.1% frequency): | ;Rare (< 0.1% frequency): | ||
{{div col|colwidth=18em}} | {{div col|colwidth=18em}} | ||
| Line 115: | Line 132: | ||
{{div col end}} | {{div col end}} | ||
== Interactions == | == Interactions == <!--T:18--> | ||
<!--T:19--> | |||
No drug interactions are known. | No drug interactions are known. | ||
==Pharmacology== | ==Pharmacology== <!--T:20--> | ||
<!--T:21--> | |||
===Mechanism of action=== | ===Mechanism of action=== | ||
The efficacy of calcipotriol in the treatment of psoriasis was first noticed by the observation of patients receiving various forms of vitamin D in an osteoporosis study. Unexpectedly, some patients who also had psoriasis experienced dramatic reductions in lesion counts. | The efficacy of calcipotriol in the treatment of psoriasis was first noticed by the observation of patients receiving various forms of vitamin D in an osteoporosis study. Unexpectedly, some patients who also had psoriasis experienced dramatic reductions in lesion counts. | ||
<!--T:22--> | |||
The precise mechanism of calcipotriol in remitting psoriasis is not well understood. However, it has been shown to have comparable affinity with calcitriol for the [[vitamin D receptor]] (VDR), while being less than 1% as active as the calcitriol in regulating [[calcium metabolism]]. The vitamin D receptor belongs to the steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily, and is found on the cells of many different tissues including the thyroid, bone, kidney, and [[T cell]]s of the immune system. T cells are known to play a role in psoriasis, and it is thought that the binding of calcipotriol to the VDR modulates the T cells gene transcription of cell differentiation and proliferation related genes. | The precise mechanism of calcipotriol in remitting psoriasis is not well understood. However, it has been shown to have comparable affinity with calcitriol for the [[vitamin D receptor]] (VDR), while being less than 1% as active as the calcitriol in regulating [[calcium metabolism]]. The vitamin D receptor belongs to the steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily, and is found on the cells of many different tissues including the thyroid, bone, kidney, and [[T cell]]s of the immune system. T cells are known to play a role in psoriasis, and it is thought that the binding of calcipotriol to the VDR modulates the T cells gene transcription of cell differentiation and proliferation related genes. | ||
<!--T:23--> | |||
In mouse studies, topical calcipotriol administration to the ear and dorsal skin led to a dose-dependent increase in the production of the epithelial cell-derived cytokine [[Thymic stromal lymphopoietin|TSLP]] by [[keratinocyte]]s, and triggered [[atopic dermatitis]] at high concentrations. This upregulation of TSLP production due to calcipotriol application is thought to be mediated through the [[Coactivation (Transcription)|coactivation]] of [[Calcitriol receptor|vitamin D receptor]]/[[Retinoid X receptor alpha|RXRα]] and vitamin D receptor/[[Retinoid X receptor beta|RXRβ]] heterodimers. As psoriasis is typically thought to be partially driven by [[T helper cell|Th1]]/[[T helper 17 cell|Th17]] inflammatory cytokines, calcipotriol treatment at appropriate concentrations may alleviate psoriasis symptoms by repressing Th1/Th17 inflammation through TSLP production, which is linked to a [[T helper cell|Th2]] response. However, it is important to note that this has not yet been confirmed. | In mouse studies, topical calcipotriol administration to the ear and dorsal skin led to a dose-dependent increase in the production of the epithelial cell-derived cytokine [[Thymic stromal lymphopoietin|TSLP]] by [[keratinocyte]]s, and triggered [[atopic dermatitis]] at high concentrations. This upregulation of TSLP production due to calcipotriol application is thought to be mediated through the [[Coactivation (Transcription)|coactivation]] of [[Calcitriol receptor|vitamin D receptor]]/[[Retinoid X receptor alpha|RXRα]] and vitamin D receptor/[[Retinoid X receptor beta|RXRβ]] heterodimers. As psoriasis is typically thought to be partially driven by [[T helper cell|Th1]]/[[T helper 17 cell|Th17]] inflammatory cytokines, calcipotriol treatment at appropriate concentrations may alleviate psoriasis symptoms by repressing Th1/Th17 inflammation through TSLP production, which is linked to a [[T helper cell|Th2]] response. However, it is important to note that this has not yet been confirmed. | ||
<!--T:24--> | |||
===Pharmacokinetics=== | ===Pharmacokinetics=== | ||
After application and systemic uptake, calcipotriol undergoes rapid [[hepatic]] metabolism. Calcipotriol is metabolized to MC1046 (the α,β−unsaturated ketone analog), which is subsequently metabolized to its primary metabolite, the saturated ketone analog MC1080. MC1080 is then slowly metabolized to [[calcitroic acid]]. | After application and systemic uptake, calcipotriol undergoes rapid [[hepatic]] metabolism. Calcipotriol is metabolized to MC1046 (the α,β−unsaturated ketone analog), which is subsequently metabolized to its primary metabolite, the saturated ketone analog MC1080. MC1080 is then slowly metabolized to [[calcitroic acid]]. | ||
<!--T:25--> | |||
The metabolites of calcipotriol are less potent than the parent compound. | The metabolites of calcipotriol are less potent than the parent compound. | ||
<!--T:26--> | |||
==Chemistry== | ==Chemistry== | ||
Calcipotriol is a white to almost white crystalline compound. | Calcipotriol is a white to almost white crystalline compound. | ||
<!--T:27--> | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
* {{cite web | url = https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/calcipotriene | publisher = U.S. National Library of Medicine | work = Drug Information Portal | title = Calcipotriene }} | * {{cite web | url = https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/calcipotriene | publisher = U.S. National Library of Medicine | work = Drug Information Portal | title = Calcipotriene }} | ||
<!--T:28--> | |||
{{Antipsoriatics}} | {{Antipsoriatics}} | ||
{{Vitamins}} | {{Vitamins}} | ||
| Line 144: | Line 170: | ||
{{Portal bar | Medicine}} | {{Portal bar | Medicine}} | ||
<!--T:29--> | |||
{{二次利用|date=20 February 2024}} | {{二次利用|date=20 February 2024}} | ||
[[Category:Vitamin D]] | [[Category:Vitamin D]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:40, 12 April 2024
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Daivonex, Dovonex, Sorilux |
| Other names | calcipotriene (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608018 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Topical administration |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 5 to 6% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Excretion | Biliary |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H40O3 |
| Molar mass | 412.614 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
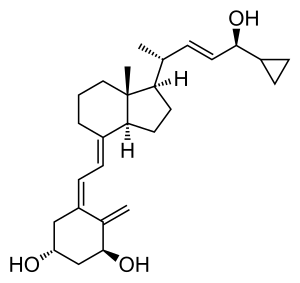
Calcipotriol, also known as calcipotriene, is a synthetic derivative of calcitriol, a form of vitamin D. It is used in the treatment of psoriasis. It is safe for long-term application in psoriatic skin conditions.
It was patented in 1985 and approved for medical use in 1991. It is marketed under the trade name "Dovonex" in the United States, "Daivonex" outside North America, and "Psorcutan" in Germany.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
Calcipotriol is also available as Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate, a fixed-dose combination medication with the synthetic corticosteroid betamethasone dipropionate for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
Medical uses
Chronic plaque psoriasis is the chief medical use of calcipotriol. It has also been used successfully in the treatment of alopecia areata.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, use on face, hypercalcaemia, or evidence of vitamin D toxicity are the only contraindications for calcipotriol use.
Cautions include exposure to excessive natural or artificial light, due to the potential for calcipotriol to cause photosensitivity.
Adverse effects
Adverse effects by frequency:
- Very common (> 10% frequency)
- Burning
- Itchiness
- Skin irritation
- Common (1–10% frequency)
- Dermatitis
- Dry skin
- Erythema
- Peeling
- Worsening of psoriasis including facial/scalp
- Rash
- Uncommon (0.1–1% frequency)
- Exacerbation of psoriasis
- Rare (< 0.1% frequency)
- Allergic contact dermatitis
- Hypercalcaemia
- Photosensitivity
- Changes in pigmentation
- Skin atrophy
Interactions
No drug interactions are known.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
The efficacy of calcipotriol in the treatment of psoriasis was first noticed by the observation of patients receiving various forms of vitamin D in an osteoporosis study. Unexpectedly, some patients who also had psoriasis experienced dramatic reductions in lesion counts.
The precise mechanism of calcipotriol in remitting psoriasis is not well understood. However, it has been shown to have comparable affinity with calcitriol for the vitamin D receptor (VDR), while being less than 1% as active as the calcitriol in regulating calcium metabolism. The vitamin D receptor belongs to the steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily, and is found on the cells of many different tissues including the thyroid, bone, kidney, and T cells of the immune system. T cells are known to play a role in psoriasis, and it is thought that the binding of calcipotriol to the VDR modulates the T cells gene transcription of cell differentiation and proliferation related genes.
In mouse studies, topical calcipotriol administration to the ear and dorsal skin led to a dose-dependent increase in the production of the epithelial cell-derived cytokine TSLP by keratinocytes, and triggered atopic dermatitis at high concentrations. This upregulation of TSLP production due to calcipotriol application is thought to be mediated through the coactivation of vitamin D receptor/RXRα and vitamin D receptor/RXRβ heterodimers. As psoriasis is typically thought to be partially driven by Th1/Th17 inflammatory cytokines, calcipotriol treatment at appropriate concentrations may alleviate psoriasis symptoms by repressing Th1/Th17 inflammation through TSLP production, which is linked to a Th2 response. However, it is important to note that this has not yet been confirmed.
Pharmacokinetics
After application and systemic uptake, calcipotriol undergoes rapid hepatic metabolism. Calcipotriol is metabolized to MC1046 (the α,β−unsaturated ketone analog), which is subsequently metabolized to its primary metabolite, the saturated ketone analog MC1080. MC1080 is then slowly metabolized to calcitroic acid.
The metabolites of calcipotriol are less potent than the parent compound.
Chemistry
Calcipotriol is a white to almost white crystalline compound.
External links
- "Calcipotriene". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Calcipotriol(20 February 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Item:Q22023 |