Flavin adenine dinucleotide/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "グルコースオキシダーゼ(GOX)は、β-D-グルコースのD-グルコノ-δ-ラクトンへの酸化を触媒し、同時に酵素結合フラビンを還元する。GOXはホモ二量体として存在し、各サブユニットが1個のFAD分子を結合している。結晶構造から、FADは二量体界面近くの酵素の深いポケットに結合していることがわかった。研究により、FADを8-ヒドロキシ-5-..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with ":650px" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
==== 炭素-硫黄 ==== | ==== 炭素-硫黄 ==== | ||
プレニルシステインリアーゼ(PCLase)は、プレニルシステイン(タンパク質修飾)の切断を触媒し、イソプレノイドアルデヒドとタンパク質標的上の遊離システイン残基を形成する。FADはPCLaseと非共有結合している。フラビンの反応を調べるメカニズム研究はあまり行われていないが、提案されているメカニズムを以下に示す。プレニル部分のC1からFADへのヒドリド転移が提案され、その結果フラビンはFADH<sub>2</sub>に還元される。 COformEDは隣の硫黄原子によって安定化された[[carbocation/ja|カルボカチオン]]である。その後、FADH<sub>2</sub>は分子状酸素と反応して酸化酵素を回復させる。 | |||
:[[Image:Prenylcysteine lyase mechanism.png|650px]] | :[[Image:Prenylcysteine lyase mechanism.png|650px]] | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 20:44, 10 April 2024
| |

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1208946 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| 108834 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Flavin-Adenine+Dinucleotide |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H33N9O15P2 | |
| Molar mass | 785.557 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White, vitreous crystals |
| log P | -1.336 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.128 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 12.8689 |
生化学において、フラビンアデニンジヌクレオチド(FAD)は、様々なタンパク質に付随する酸化還元活性の補酵素であり、代謝におけるいくつかの酵素反応に関与する。フラボタンパク質はフラビン基を持つタンパク質であり、FADまたはフラビンモノヌクレオチド(FMN)の形をとる。コハク酸デヒドロゲナーゼ複合体の構成要素、α-ケトグルタル酸デヒドロゲナーゼ、ピルビン酸デヒドロゲナーゼ複合体の構成要素など、多くのフラボタンパク質が知られている。
FADは、フラビン-N(5)-オキシド、キノン、セミキノン、ヒドロキノンの4つの酸化還元状態で存在することができる。FADは電子を受容したり供与したりすることによって、これらの状態の間で変換される。FADは完全に酸化された形、すなわちキノン形では、2個の電子と2個のプロトンを受け入れてFADH2(ハイドロキノン形)となる。セミキノン(FADH-)は、FADの還元か、FADH2の酸化のどちらかによって、それぞれ1個の電子と1個のプロトンを受容するか供与することで形成される。しかし、タンパク質によっては、フラビン補因子の過酸化型、フラビン-N(5)-オキシドを生成し、維持するものもある。
歴史
フラボタンパク質は、1879年に牛乳の成分を分離することによって初めて発見された。当初はその乳由来と黄色の色素からラクトクロムと呼ばれていた。科学界が黄色い色素の原因分子を特定するのに実質的な進歩を遂げるには50年かかった。1930年代には、多くのフラビンとニコチンアミドの誘導体構造が発表され、酸化還元触媒反応におけるそれらの義務的な役割が明らかになり、補酵素の研究分野が始まった。ドイツの科学者オットー・ヴァールブルクとウォルター・クリスチャンは1932年に細胞呼吸に必要な酵母由来の黄色いタンパク質を発見した。彼らの同僚ユーゴ・セオレルはこの黄色い酵素をアポ酵素と黄色い色素に分離し、酵素も色素もNADHを酸化する能力がないが、両者を混ぜ合わせると活性が回復することを示した。テオレルは1937年にこの色素がリボフラビンのリン酸エステルであることを確認した(フラビンモノヌクレオチド(FMN))。それは、酵素補因子の最初の直接的な証拠となった。ワールブルグとクリスチャンは、1938年にも同様の実験を行い、FADがD-アミノ酸オキシダーゼの補因子であることを発見した。ニコチンアミドをヒドリド基転移に結びつけたワールブルグの仕事とフラビンの発見は、40年代から50年代にかけて多くの科学者が大量の酸化還元生化学を発見し、クエン酸サイクルやATP合成などの経路でそれらを結びつける道を開いた。
特性
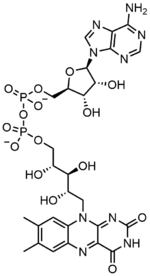
フラビンアデニンジヌクレオチドは2つの部分からなる:アデニンヌクレオチド(アデノシン一リン酸)とフラビンモノヌクレオチド(FMN)の2つの部分がリン酸基を介して橋渡しされている。アデニンは1'炭素で環状リボースと結合し、リン酸は5'炭素でリボースと結合してアデニンヌクレオチドを形成する。リボフラビンは、イソアロキサジンとリビトールとの間の炭素-窒素(C-N)結合によって形成される。その後、リン酸基は末端のリボース炭素に結合し、FMNを形成する。イソアロキサジンとリビトールの結合はグリコシド結合ではないと考えられているため、フラビンモノヌクレオチドは真のヌクレオチドではない。このため、ジヌクレオチドという名称は誤解を招く。しかし、フラビンモノヌクレオチド基は、その構造と化学的性質において、依然としてヌクレオチドに非常に近い。


FADは2H+と2e-の付加によってFADH2に還元される。FADH2はまた、1つのH+と1つのe-の損失によって酸化され、FADHを形成することができる。FADの形は、1H+と1e-のさらなる損失によって再形成される。FADの形成は、フラビン-N(5)-オキシドの還元と脱水によっても起こりうる。酸化状態に基づいて、フラビンは水溶液中で特定の色をとる。 フラビン-N(5)-オキシド(超酸化型)は黄橙色、FAD(完全酸化型)は黄色、FADH(半還元型)はpHに基づいて青色または赤色、完全還元型は無色である。形を変えると、他の化学的性質に大きな影響を与えることがある。例えば、完全酸化型のFADは求核攻撃を受け、完全還元型のFADH2は高い分極率を持ち、半還元型は水溶液中で不安定である。FADは芳香環系であるが、FADH2はそうではない。これは、芳香族構造がもたらす共鳴による安定化がなく、FADH2のエネルギーが著しく高いことを意味する。 FADH2は、酸化されると芳香族性を取り戻し、この安定化によって表されるエネルギーを放出するので、エネルギーを運ぶ分子である。
FADとその変異体の分光特性は、UV-VIS吸収と蛍光分光法を使用することによる反応のモニタリングを可能にする。FADの各形態は明確な吸光度スペクトルを持ち、酸化状態の変化を容易に観察することができる。FADの主な局所吸光度極大は450 nmに観測され、消衰係数は11,300 M-1cm-1である。フラビンは一般に、結合していないときに蛍光活性を示す(フラビン核酸誘導体と結合したタンパク質はフラボタンパク質と呼ばれる)。この性質は、タンパク質の結合を調べる際に利用することができ、結合状態にすると蛍光活性が失われることを観察することができる。酸化フラビンは約450 nmの高い吸光度を持ち、約515-520 nmで蛍光を発する。
化学状態
生物学的システムでは、FADは完全に酸化された形態ではH+とe-の受容体として、FADHの形態では受容体または供与体として、還元されたFADH2の形態では供与体として働く。下の図は、この物質が受ける可能性のある変化をまとめたものである。
上に見たものの他に、FADの他の反応性形態が形成されたり消費されたりすることもある。これらの反応は、電子の移動と化学結合の生成/切断を伴う。反応機構を通して、FADは生物システム内の化学活動に貢献することができる。以下の写真は、FADが関与しうるいくつかの作用の一般的な形を表している。
メカニズム1と2はヒドリド獲得を表し、分子は1つのヒドリドイオンとなるものを獲得する。メカニズム3と4はラジカル生成とヒドリド喪失を表す。ラジカル種は不対電子原子を含み、非常に化学的に活性である。ヒドリド損失は、前に見たヒドリド獲得の逆過程である。最後の2つの機構は、求核付加と炭素ラジカルを用いた反応である。
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
生合成
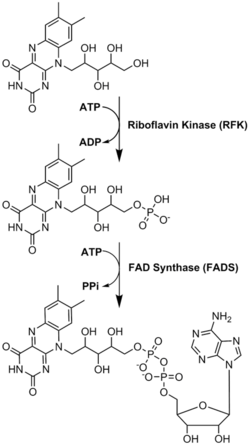
FADは、リボフラビンに由来するもう一つの分子であるフラビンモノヌクレオチドとともに、酵素補因子として主要な役割を果たしている。細菌、菌類、植物はリボフラビンを作ることができるが、ヒトのような他の真核生物は作る能力を失っている。そのため、ヒトはビタミンB2としても知られるリボフラビンを食事から摂取しなければならない。リボフラビンは一般的に小腸で摂取され、その後キャリアタンパク質を介して細胞に輸送される。リボフラビンキナーゼ(EC 2.7.1.26)は、リボフラビンにリン酸基を付加してフラビンモノヌクレオチドを生成し、次に|FAD合成酵素がアデニンヌクレオチドを付加する;両ステップともATPを必要とする。細菌は通常1つの2機能酵素を持つが、古細菌や真核生物は通常2つの異なる酵素を用いる。現在の研究では、異なるアイソフォームが細胞質とミトコンドリアに存在することが示されている。FADは両方の場所で合成され、必要な場所に運ばれる可能性があるようだ。
機能
フラビンタンパク質は、フラビン部分のユニークで多様な構造を利用して、難しい酸化還元反応を触媒する。 フラビンは複数の酸化還元状態を持つため、1個または2個の電子、水素原子、またはヒドロニウムイオンの移動を伴うプロセスに関与することができる。 完全に酸化されたフラビン環のN5とC4aは求核攻撃を受けやすい。フラビン部分のこのような多様なイオン化と修飾は、イソアロキサジン環系と、フラビンアデニンジヌクレオチド(FAD)を含むフラビンの結合時の速度論的パラメーターを劇的に変化させるフラビンタンパク質の能力に起因している。
ゲノム(フラボプロテオーム)中のフラビン依存性タンパク質をコードする遺伝子の数は種によって異なり、0.1%〜3.5%で、ヒトは90のフラボプロテインをコードする遺伝子を持つ。FADはフラビンのより複雑で豊富な形態であり、フラボプロテオーム全体の75%、ヒトがコードするフラボタンパク質の84%に結合していると報告されている。 様々な哺乳類培養細胞株における遊離または非共有結合フラビンの細胞内濃度は、FAD(2.2-17.0 amol/cell)とFMN(0.46-3.4 amol/cell)で報告されている。
FADはNAD+よりも正の還元電位を持ち、非常に強い酸化剤である。細胞はこれを、C-C結合のアルケンへの脱水素反応など、エネルギー的に困難な多くの酸化反応に利用する。FAD依存性タンパク質は、電子輸送、DNA修復、ヌクレオチド生合成、脂肪酸のβ酸化、アミノ酸異化、さらにCoA、CoQ、ヘム基などの他の補因子の合成など、多種多様な代謝経路で機能している。 よく知られている反応の1つはクエン酸サイクル(TCAまたはクレブスサイクルとしても知られている)の一部である。コハク酸デヒドロゲナーゼ(電子伝達系の複合体II)は、ユビキノンのユビキノールへの還元と結合させることによってコハク酸のフマル酸への酸化を触媒するために共有結合したFADを必要とする。この酸化による高エネルギー電子は、FADをFADH2に還元することによって一時的に蓄えられる。FADH2はその後FADに戻り、その2つの高エネルギー電子を電子伝達系に送る。FADH2のエネルギーは、酸化的リン酸化によって1.5当量のATPを生成するのに十分である。いくつかの酸化還元フラボ蛋白質は、アセチルCoAデヒドロゲナーゼのようにFADと非共有結合し、脂肪酸のβ酸化やロイシンのようなアミノ酸の異化に関与する(イソバレリルCoAデヒドロゲナーゼ)、 イソロイシン(短鎖/分岐鎖アシル-CoAデヒドロゲナーゼ)、バリン(イソブチリル-CoAデヒドロゲナーゼ)、およびリジン(グルタリル-CoAデヒドロゲナーゼ)のようなアミノ酸の異化を行う。 代謝を制御するFAD依存性酵素のその他の例としては、グリセロール-3-リン酸デヒドロゲナーゼ(トリグリセリド合成)とプリンヌクレオチド異化に関与するキサンチンオキシダーゼがある。 フラボタンパク質においてFADが果たしうる非触媒的機能としては、構造的役割、あるいは生物時計や発生を制御する青感受性の光光受容体への関与、生物発光細菌における光の発生などがある。
フラボタンパク質
フラボタンパク質は、FMNまたはFAD分子を補欠基として持ち、この補欠基は強固に結合しているか共有結合している。共有結合したFADを持つフラボ蛋白質は5-10%程度しかないが、これらの酵素はより強い酸化還元力を持つ。場合によっては、FADは活性部位を構造的に支持したり、触媒反応中の中間体を安定化させたりする。利用可能な構造データに基づいて、既知のFAD結合部位は200以上のタイプに分けられる。
ヒトゲノムには90のフラボタンパク質がコードされており、約84%はFADを、約16%はFMNを必要とする。フラボタンパク質は主にミトコンドリアに存在する。フラボタンパク質のうち90%は酸化還元反応を行い、残りの10%は転移酵素、リアーゼ、異性化酵素、リガーゼである。
炭素-ヘテロ原子結合の酸化
炭素-窒素
モノアミン酸化酵素(MAO)は、ノルエピネフリン、セロトニン、ドーパミンの異化における生物学的重要性から、広く研究されているフラボ酵素である。MAOは一級、二級、三級アミンを酸化し、非酵素的にイミンからアルデヒドやケトンに加水分解する。このクラスの酵素は広く研究されているが、その作用機序についてはまだ議論が続いている。ラジカル機構と求核機構である。ラジカル機構は、ラジカル中間体の存在を示すスペクトルや電子常磁性共鳴の証拠が存在しないため、あまり一般的には受け入れられていない。求核機構は、基質の求核性を高めると予想される2つのチロシン残基を変異させた部位特異的突然変異誘発研究によって支持されているため、より支持されている。
炭素-酸素
グルコースオキシダーゼ(GOX)は、β-D-グルコースのD-グルコノ-δ-ラクトンへの酸化を触媒し、同時に酵素結合フラビンを還元する。GOXはホモ二量体として存在し、各サブユニットが1個のFAD分子を結合している。結晶構造から、FADは二量体界面近くの酵素の深いポケットに結合していることがわかった。研究により、FADを8-ヒドロキシ-5-カルバ-5-デアザFADで置換すると、フラビンのre面と反応して反応の立体化学が決定されることが示された。ターンオーバーの際、中性および陰イオンのセミキノンが観察され、ラジカル機構が示唆された。
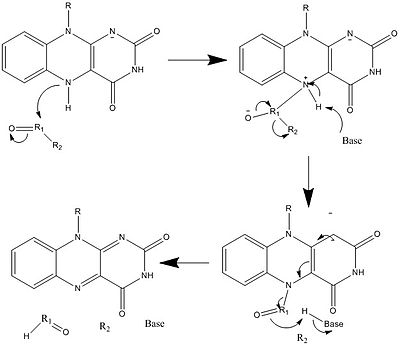
炭素-硫黄
プレニルシステインリアーゼ(PCLase)は、プレニルシステイン(タンパク質修飾)の切断を触媒し、イソプレノイドアルデヒドとタンパク質標的上の遊離システイン残基を形成する。FADはPCLaseと非共有結合している。フラビンの反応を調べるメカニズム研究はあまり行われていないが、提案されているメカニズムを以下に示す。プレニル部分のC1からFADへのヒドリド転移が提案され、その結果フラビンはFADH2に還元される。 COformEDは隣の硫黄原子によって安定化されたカルボカチオンである。その後、FADH2は分子状酸素と反応して酸化酵素を回復させる。
Carbon-carbon
UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvylglucosamine Reductase (MurB) is an enzyme that catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of enolpyruvyl-UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (substrate) to the corresponding D-lactyl compound UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid (product). MurB is a monomer and contains one FAD molecule. Before the substrate can be converted to product, NADPH must first reduce FAD. Once NADP+ dissociates, the substrate can bind and the reduced flavin can reduce the product.
Thiol/disulfide chemistry
Glutathione reductase (GR) catalyzes the reduction of glutathione disulfide (GSSG) to glutathione (GSH). GR requires FAD and NADPH to facilitate this reaction; first a hydride must be transferred from NADPH to FAD. The reduced flavin can then act as a nucleophile to attack the disulfide, this forms the C4a-cysteine adduct. Elimination of this adduct results in a flavin-thiolate charge-transfer complex.
Electron transfer reactions
Cytochrome P450 type enzymes that catalyze monooxygenase (hydroxylation) reactions are dependent on the transfer of two electrons from FAD to the P450. Two types of P450 systems are found in eukaryotes. The P450 systems that are located in the endoplasmic reticulum are dependent on a cytochrome P-450 reductase (CPR) that contains both an FAD and an FMN. The two electrons on reduced FAD (FADH2) are transferred one at a time to FMN and then a single electron is passed from FMN to the heme of the P450.
The P450 systems that are located in the mitochondria are dependent on two electron transfer proteins: An FAD containing adrenodoxin reductase (AR) and a small iron-sulfur group containing protein named adrenodoxin. FAD is embedded in the FAD-binding domain of AR. The FAD of AR is reduced to FADH2 by transfer of two electrons from NADPH that binds in the NADP-binding domain of AR. The structure of this enzyme is highly conserved to maintain precisely the alignment of electron donor NADPH and acceptor FAD for efficient electron transfer. The two electrons in reduced FAD are transferred one a time to adrenodoxin which in turn donates the single electron to the heme group of the mitochondrial P450.
The structures of the reductase of the microsomal versus reductase of the mitochondrial P450 systems are completely different and show no homology.
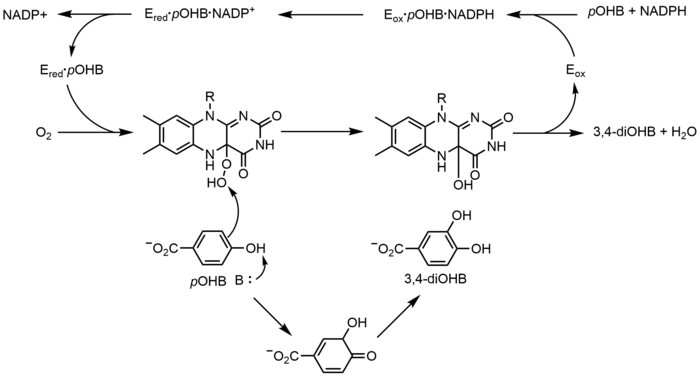
Redox
p-Hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase (PHBH) catalyzes the oxygenation of p-hydroxybenzoate (pOHB) to 3,4-dihyroxybenzoate (3,4-diOHB); FAD, NADPH and molecular oxygen are all required for this reaction. NADPH first transfers a hydride equivalent to FAD, creating FADH−, and then NADP+ dissociates from the enzyme. Reduced PHBH then reacts with molecular oxygen to form the flavin-C(4a)-hydroperoxide. The flavin hydroperoxide quickly hydroxylates pOHB, and then eliminates water to regenerate oxidized flavin. An alternative flavin-mediated oxygenation mechanism involves the use of a flavin-N(5)-oxide rather than a flavin-C(4a)-(hydro)peroxide.
Nonredox
Chorismate synthase (CS) catalyzes the last step in the shikimate pathway—the formation of chorismate. Two classes of CS are known, both of which require FMN, but are divided on their need for NADPH as a reducing agent. The proposed mechanism for CS involves radical species. The radical flavin species has not been detected spectroscopically without using a substrate analogue, which suggests that it is short-lived. However, when using a fluorinated substrate, a neutral flavin semiquinone was detected.
Complex flavoenzymes
Glutamate synthase catalyzes the conversion of 2-oxoglutarate into L-glutamate with L-glutamine serving as the nitrogen source for the reaction. All glutamate syntheses are iron-sulfur flavoproteins containing an iron-sulfur cluster and FMN. The three classes of glutamate syntheses are categorized based on their sequences and biochemical properties. Even though there are three classes of this enzyme, it is believed that they all operate through the same mechanism, only differing by what first reduces the FMN. The enzyme produces two glutamate molecules: one by the hydrolysis of glutamine (forming glutamate and ammonia), and the second by the ammonia produced from the first reaction attacking 2-oxoglutarate, which is reduced by FMN to glutamate.
Clinical significance
Due to the importance of flavoproteins, it is unsurprising that approximately 60% of human flavoproteins cause human disease when mutated. In some cases, this is due to a decreased affinity for FAD or FMN and so excess riboflavin intake may lessen disease symptoms, such as for multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. In addition, riboflavin deficiency itself (and the resulting lack of FAD and FMN) can cause health issues. For example, in ALS patients, there are decreased levels of FAD synthesis. Both of these paths can result in a variety of symptoms, including developmental or gastrointestinal abnormalities, faulty fat break-down, anemia, neurological problems, cancer or heart disease, migraine, worsened vision and skin lesions. The pharmaceutical industry therefore produces riboflavin to supplement diet in certain cases. In 2008, the global need for riboflavin was 6,000 tons per year, with production capacity of 10,000 tons. This $150 to 500 million market is not only for medical applications, but is also used as a supplement to animal food in the agricultural industry and as a food colorant.
Drug design
New design of anti-bacterial medications is of continuing importance in scientific research as bacterial antibiotic resistance to common antibiotics increases. A specific metabolic protein that uses FAD (Complex II) is vital for bacterial virulence, and so targeting FAD synthesis or creating FAD analogs could be a useful area of investigation. Already, scientists have determined the two structures FAD usually assumes once bound: either an extended or a butterfly conformation, in which the molecule essentially folds in half, resulting in the stacking of the adenine and isoalloxazine rings. FAD imitators that are able to bind in a similar manner but do not permit protein function could be useful mechanisms of inhibiting bacterial infection. Alternatively, drugs blocking FAD synthesis could achieve the same goal; this is especially intriguing because human and bacterial FAD synthesis relies on very different enzymes, meaning that a drug made to target bacterial FAD synthase would be unlikely to interfere with the human FAD synthase enzymes.
Optogenetics
Optogenetics allows control of biological events in a non-invasive manner. The field has advanced in recent years with a number of new tools, including those to trigger light sensitivity, such as the Blue-Light-Utilizing FAD domains (BLUF). BLUFs encode a 100 to 140 amino acid sequence that was derived from photoreceptors in plants and bacteria. Similar to other photoreceptors, the light causes structural changes in the BLUF domain that results in disruption of downstream interactions. Current research investigates proteins with the appended BLUF domain and how different external factors can impact the proteins.
治療モニタリング
体内には、トリプトファン、collagen/jaコラーゲン、FAD、NADH、ポルフィリンなど、固有の蛍光を持つ分子が数多く存在する。 科学者たちはこれを利用して、病気の進行や治療効果をモニターしたり、診断に役立てたりしている。 例えば、FADとNADHのネイティブ蛍光は正常組織と口腔粘膜下線維症で異なる。これは浸潤性口腔癌の初期徴候である。そのため医師は、標準的な生検とは対照的に、診断の補助や治療のモニタリングに蛍光を採用している。
その他の画像
-
FADH2
こちらも参照
外部リンク
- FAD bound to proteins in the PDB
- FAD entry in the NIH Chemical Database