Renin–angiotensin system/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "==活性化== {{Anchor|Activation}} {{Further/ja|Autoregulation/ja#Renal regulation}} thumb|center|700px|RAAS概略図 この系は、血液量の減少や血圧の低下(出血や脱水など)があると活性化する。この圧力の低下は頸動脈洞の圧受容器によって解釈され..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "# 腎臓の黄斑部にある傍糸球体装置の灌流が低下すると、傍糸球体細胞(糸球体毛細血管にある顆粒細胞、変化した周皮細胞)が酵素レニンを放出する。 # レニンは、球状タンパク質であるアンジオテンシノーゲンからデカペプチド..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
この系は、[[blood volume/ja|血液量]]の減少や[[blood pressure/ja|血圧]]の低下([[hemorrhage/ja|出血]]や[[dehydration/ja|脱水]]など)があると活性化する。この圧力の低下は[[carotid sinus/ja|頸動脈洞]]の[[baroreceptor/ja|圧受容器]]によって解釈される。また、濾液[[sodium chloride/ja|塩化ナトリウム]](NaCl)濃度の低下や濾液流量の低下によっても活性化され、[[macula densa/ja|黄斑円錐体]]を刺激して[[juxtaglomerular cell/ja|次糸球体細胞]]にレニンを放出するように信号を送る。 | この系は、[[blood volume/ja|血液量]]の減少や[[blood pressure/ja|血圧]]の低下([[hemorrhage/ja|出血]]や[[dehydration/ja|脱水]]など)があると活性化する。この圧力の低下は[[carotid sinus/ja|頸動脈洞]]の[[baroreceptor/ja|圧受容器]]によって解釈される。また、濾液[[sodium chloride/ja|塩化ナトリウム]](NaCl)濃度の低下や濾液流量の低下によっても活性化され、[[macula densa/ja|黄斑円錐体]]を刺激して[[juxtaglomerular cell/ja|次糸球体細胞]]にレニンを放出するように信号を送る。 | ||
# 腎臓の[[macula densa/ja|黄斑部]]にある[[juxtaglomerular apparatus/ja|傍糸球体装置]]の灌流が低下すると、傍糸球体細胞(糸球体毛細血管にある顆粒細胞、変化した周皮細胞)が[[enzyme/ja|酵素]][[renin/ja|レニン]]を放出する。 | |||
# | # レニンは、[[globular protein/ja|球状タンパク質]]である[[angiotensinogen/ja|アンジオテンシノーゲン]]から[[Peptide/ja#Notes on terminology|デカペプチド]]を[[Proteolysis/ja#Cleavage of precursor proteins|分解]]する。このデカペプチドは[[Angiotensin/ja#Angiotensin I|アンジオテンシンI]]として知られている。 | ||
# | # アンジオテンシンIはその後、[[angiotensin-converting enzyme/ja|アンジオテンシン変換酵素]](ACE)によって[[Peptide/ja#Notes on terminology|オクタペプチド]]である''[[angiotensin/ja|アンジオテンシンII]]''に変換されるが、ACEは主に全身の[[capillary/ja|毛細血管]]の内皮細胞、肺、腎臓の上皮細胞に存在すると考えられている。1992年のある研究では、すべての血管内皮細胞にACEが存在することが発見された。 | ||
# | # アンジオテンシンIIは、レニン-アンジオテンシン系の主要な生理活性産物であり、[[intraglomerular mesangial cells/ja|糸球体内メサンギウム細胞]]上の受容体に結合し、これらの細胞を周囲の血管とともに収縮させる;また糸球体座細胞上の受容体に結合し、[[adrenal cortex/ja|副腎皮質]]の[[zona glomerulosa/ja|糸球体座]]から[[aldosterone/ja|アルドステロン]]の放出を引き起こす。アンジオテンシンIIは、[[endocrine system/ja|内分泌系|内分泌]]、[[autocrine signalling/ja|オートクリン]]/[[paracrine signalling/ja|パラクリン]]、[[intracrine/ja|イントラクリン]]ホルモンとして作用する。 | ||
# | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 17:24, 27 March 2024

レニン-アンジオテンシン系(RAS)、またはレニン-アンジオテンシン-アルドステロン系(RAAS)は、血圧、体液バランス、電解質バランス、および全身の血管抵抗を調節するホルモン系である。
腎血流が減少すると、腎臓の次糸球体細胞は前駆体であるプロレニン(すでに血液中に存在する)をレニンに変換し、直接体循環に分泌する。血漿レニンは次に、肝臓から放出されたアンジオテンシノーゲンをアンジオテンシンIと呼ばれるデカペプチドに変換する。アンジオテンシンIはその後、主に肺の血管内皮細胞表面に存在するアンジオテンシン変換酵素(ACE)によってアンジオテンシンII(オクタペプチド)に変換される。アンジオテンシンIIの寿命は約1~2分と短い。その後、多くの組織の赤血球や血管床に存在するアンジオテンシナーゼによって、アンジオテンシンIIIと呼ばれるヘプタペプチドに急速に分解される。
アンジオテンシンIIIは血圧を上昇させ、副腎皮質からのアルドステロン分泌を刺激する。副腎皮質刺激活性は100%で、血管圧迫活性はアンジオテンシンIIの40%である。
アンジオテンシンIVはまた、副腎皮質作用と血管圧制御作用を持つ。
アンジオテンシンIIは強力な血管収縮ペプチドであり、血管を狭窄させて血圧を上昇させる。アンジオテンシンIIはまた、副腎皮質からのホルモンアルドステロンの分泌を刺激する。アルドステロンは腎尿細管のナトリウムの再吸収を増加させ、その結果、血液中への水分の再吸収を引き起こすと同時に、(電解質バランスを維持するために)カリウムの排泄を引き起こす。これにより体内の細胞外液の体積が増加し、血圧も上昇する。
RASが異常に活性化すると血圧が高くなりすぎる。ACE阻害薬、アンジオテンシンⅡ受容体拮抗薬(ARB)、レニン阻害薬など、血圧を改善するためにこのシステムのさまざまな段階を阻害する薬物がいくつかある。これらの薬物は、高血圧、心不全、腎不全、および糖尿病の有害な影響を制御するための主要な方法の1つである。
活性化
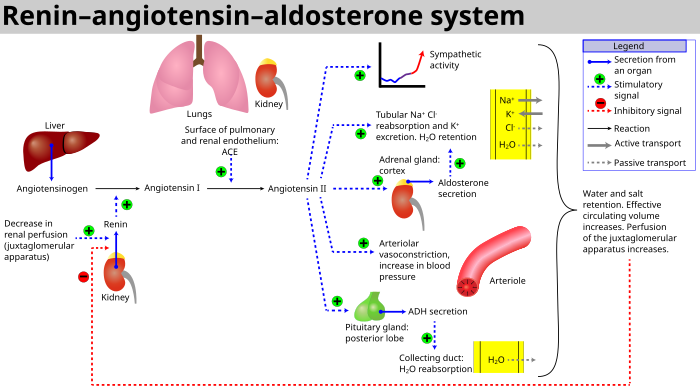
この系は、血液量の減少や血圧の低下(出血や脱水など)があると活性化する。この圧力の低下は頸動脈洞の圧受容器によって解釈される。また、濾液塩化ナトリウム(NaCl)濃度の低下や濾液流量の低下によっても活性化され、黄斑円錐体を刺激して次糸球体細胞にレニンを放出するように信号を送る。
- 腎臓の黄斑部にある傍糸球体装置の灌流が低下すると、傍糸球体細胞(糸球体毛細血管にある顆粒細胞、変化した周皮細胞)が酵素レニンを放出する。
- レニンは、球状タンパク質であるアンジオテンシノーゲンからデカペプチドを分解する。このデカペプチドはアンジオテンシンIとして知られている。
- アンジオテンシンIはその後、アンジオテンシン変換酵素(ACE)によってオクタペプチドであるアンジオテンシンIIに変換されるが、ACEは主に全身の毛細血管の内皮細胞、肺、腎臓の上皮細胞に存在すると考えられている。1992年のある研究では、すべての血管内皮細胞にACEが存在することが発見された。
- アンジオテンシンIIは、レニン-アンジオテンシン系の主要な生理活性産物であり、糸球体内メサンギウム細胞上の受容体に結合し、これらの細胞を周囲の血管とともに収縮させる;また糸球体座細胞上の受容体に結合し、副腎皮質の糸球体座からアルドステロンの放出を引き起こす。アンジオテンシンIIは、内分泌系|内分泌、オートクリン/パラクリン、イントラクリンホルモンとして作用する。
Angiotensin I may have some minor activity, but angiotensin II is the major bio-active product. Angiotensin II has a variety of effects on the body:
- Throughout the body, angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor of arterioles.
- In the kidneys, angiotensin II constricts glomerular arterioles, having a greater effect on efferent arterioles than afferent. As with most other capillary beds in the body, the constriction of afferent arterioles increases the arteriolar resistance, raising systemic arterial blood pressure and decreasing the blood flow. However, the kidneys must continue to filter enough blood despite this drop in blood flow, necessitating mechanisms to keep glomerular blood pressure up. To do this, angiotensin II constricts efferent arterioles, which forces blood to build up in the glomerulus, increasing glomerular pressure. The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is thus maintained, and blood filtration can continue despite lowered overall kidney blood flow. Because the filtration fraction, which is the ratio of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) to the renal plasma flow (RPF), has increased, there is less plasma fluid in the downstream peritubular capillaries. This in turn leads to a decreased hydrostatic pressure and increased oncotic pressure (due to unfiltered plasma proteins) in the peritubular capillaries. The effect of decreased hydrostatic pressure and increased oncotic pressure in the peritubular capillaries will facilitate increased reabsorption of tubular fluid.
- Angiotensin II decreases medullary blood flow through the vasa recta. This decreases the washout of NaCl and urea in the kidney medullary space. Thus, higher concentrations of NaCl and urea in the medulla facilitate increased absorption of tubular fluid. Furthermore, increased reabsorption of fluid into the medulla will increase passive reabsorption of sodium along the thick ascending limb of the Loop of Henle.
- Angiotensin II stimulates Na+
/H+
exchangers located on the apical membranes (faces the tubular lumen) of cells in the proximal tubule and thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle in addition to Na+
channels in the collecting ducts. This will ultimately lead to increased sodium reabsorption. - Angiotensin II stimulates the hypertrophy of renal tubule cells, leading to further sodium reabsorption.
- In the adrenal cortex, angiotensin II acts to cause the release of aldosterone. Aldosterone acts on the tubules (e.g., the distal convoluted tubules and the cortical collecting ducts) in the kidneys, causing them to reabsorb more sodium and water from the urine. This increases blood volume and, therefore, increases blood pressure. In exchange for the reabsorbing of sodium to blood, potassium is secreted into the tubules, becomes part of urine and is excreted.
- Angiotensin II causes the release of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), also called vasopressin – ADH is made in the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary gland. As its name suggests, it also exhibits vaso-constrictive properties, but its main course of action is to stimulate reabsorption of water in the kidneys. ADH also acts on the central nervous system to increase an individual's appetite for salt, and to stimulate the sensation of thirst.
These effects directly act together to increase blood pressure and are opposed by atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP).
Local renin–angiotensin systems
Locally expressed renin–angiotensin systems have been found in a number of tissues, including the kidneys, adrenal glands, the heart, vasculature and nervous system, and have a variety of functions, including local cardiovascular regulation, in association or independently of the systemic renin–angiotensin system, as well as non-cardiovascular functions. Outside the kidneys, renin is predominantly picked up from the circulation but may be secreted locally in some tissues; its precursor prorenin is highly expressed in tissues and more than half of circulating prorenin is of extrarenal origin, but its physiological role besides serving as precursor to renin is still unclear. Outside the liver, angiotensinogen is picked up from the circulation or expressed locally in some tissues; with renin they form angiotensin I, and locally expressed angiotensin-converting enzyme, chymase or other enzymes can transform it into angiotensin II. This process can be intracellular or interstitial.
In the adrenal glands, it is likely involved in the paracrine regulation of aldosterone secretion; in the heart and vasculature, it may be involved in remodeling or vascular tone; and in the brain, where it is largely independent of the circulatory RAS, it may be involved in local blood pressure regulation. In addition, both the central and peripheral nervous systems can use angiotensin for sympathetic neurotransmission. Other places of expression include the reproductive system, the skin and digestive organs. Medications aimed at the systemic system may affect the expression of those local systems, beneficially or adversely.
Fetal renin–angiotensin system
In the fetus, the renin–angiotensin system is predominantly a sodium-losing system, as angiotensin II has little or no effect on aldosterone levels. Renin levels are high in the fetus, while angiotensin II levels are significantly lower; this is due to the limited pulmonary blood flow, preventing ACE (found predominantly in the pulmonary circulation) from having its maximum effect.
臨床的意義

- アンジオテンシン変換酵素阻害薬のACE阻害薬は、より強力なアンジオテンシンⅡの生成を抑えるためによく使われる。カプトプリルはACE阻害薬の一例である。ACEは他の多くのペプチドを切断し、この能力においてキニン・カリクレイン系の重要な調節因子であり、ACEを阻害することは副作用につながる可能性がある。
- アンジオテンシンII受容体拮抗薬は、アンジオテンシン受容体遮断薬としても知られ、アンジオテンシンIIが受容体に作用するのを防ぐために使用できる。
- 直接的なレニン阻害薬も高血圧に使用できる。レニンを阻害する薬物にはアリスキレンと治験中のレミキレンがある。
- アンジオテンシンIIに対するワクチン、例えばCYT006-AngQbが研究されている。
こちらも参照
さらに読む
外部リンク
- Renin-Angiotensin+System at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
