Metformin/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "メトホルミンは、ほとんどの人に無欲作用を及ぼし、カロリー摂取を減少させる。メトホルミンは、肝臓での糖新生(グルコース産生)を減少させる。メトホルミンは、下垂体からの成長ホルモン、副腎皮質刺激ホルモン、卵胞刺激ホルモンの基礎分..." |
Created page with "肝グルコース産生に対するメトホルミンの抑制効果には、AMPKの活性化が必要であった。AMPKは、インスリンシグナル伝達、全身のエネルギーバランス、グルコースと脂肪の代謝において重要な役割を果たす酵素である。AMPKの活性化は、スモールヘテロダイマーパートナーの発現増加に必要であり、その結果、肝グルコネ..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 189: | Line 189: | ||
メトホルミンは、ほとんどの人に無欲作用を及ぼし、カロリー摂取を減少させる。メトホルミンは、肝臓での[[gluconeogenesis/ja|糖新生]](グルコース産生)を減少させる。メトホルミンは、[[pituitary gland/ja|下垂体]]からの[[growth hormone/ja|成長ホルモン]]、[[adrenocorticotropic hormone/ja|副腎皮質刺激ホルモン]]、[[follicle stimulating hormone/ja|卵胞刺激ホルモン]]の基礎分泌、および[[proopiomelanocortin/ja|プロオピオメラノコルチン]]の発現を阻害し、このことが、肝臓、骨格筋、内皮、脂肪組織、および卵巣を含む組織に対する複数の作用を有するインスリン感作作用の一因となっている。平均的な2型糖尿病患者は、正常の3倍の糖新生速度を持っている。メトホルミンの治療は、これを3分の1以上減少させる。 | メトホルミンは、ほとんどの人に無欲作用を及ぼし、カロリー摂取を減少させる。メトホルミンは、肝臓での[[gluconeogenesis/ja|糖新生]](グルコース産生)を減少させる。メトホルミンは、[[pituitary gland/ja|下垂体]]からの[[growth hormone/ja|成長ホルモン]]、[[adrenocorticotropic hormone/ja|副腎皮質刺激ホルモン]]、[[follicle stimulating hormone/ja|卵胞刺激ホルモン]]の基礎分泌、および[[proopiomelanocortin/ja|プロオピオメラノコルチン]]の発現を阻害し、このことが、肝臓、骨格筋、内皮、脂肪組織、および卵巣を含む組織に対する複数の作用を有するインスリン感作作用の一因となっている。平均的な2型糖尿病患者は、正常の3倍の糖新生速度を持っている。メトホルミンの治療は、これを3分の1以上減少させる。 | ||
肝グルコース産生に対するメトホルミンの抑制効果には、AMPKの活性化が必要であった。AMPKは、インスリンシグナル伝達、全身のエネルギーバランス、グルコースと[[lipid/ja|脂肪]]の代謝において重要な役割を果たす酵素である。AMPKの活性化は、[[small heterodimer partner/ja|スモールヘテロダイマーパートナー]]の発現増加に必要であり、その結果、肝グルコネーシス遺伝子[[phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase/ja|ホスホエノールピルビン酸カルボキシキナーゼ]]および[[glucose 6-phosphatase/ja|グルコース6-ホスファターゼ]]の[[gene expression/ja|発現]]が阻害された。メトホルミンは、AMPKアゴニストとして[[AICA ribonucleotide/ja|AICAリボヌクレオチド]]とともに研究において頻繁に使用されている。メトホルミンは、[[cytosol/ja|細胞質]]の[[adenosine monophosphate/ja|アデノシン一リン酸]](AMP)濃度を上昇させる(総AMPまたは総AMP/[[adenosine triphosphate/ja|アデノシン三リン酸]]の変化とは異なる)。メトホルミンは、サイクリックAMP産生を阻害し、[[グルカゴン]]の作用を阻害し、それによって空腹時グルコースレベルを低下させる。メトホルミンはまた、糖尿病マウスの糞便微生物群集プロフィールの大きな変化を誘導し、これはおそらく[[glucagon-like peptide-1/ja|グルカゴン様ペプチド-1]]分泌への影響を通してその作用様式に寄与している可能性がある。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 08:56, 12 March 2024
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /mɛtˈfɔːrmɪn/, met-FOR-min |
| Trade names | フォルタメット, グルコファージ, グルメッツァ, その他 |
| Other names | N,N-dimethylbiguanide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a696005 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | 経口 |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50–60% |
| Protein binding | Minimal |
| Metabolism | 肝臓ではない |
| Elimination half-life | 4–8.7 時間 |
| Excretion | 尿中 (90%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
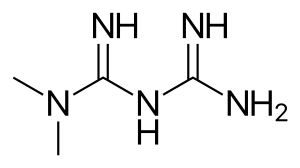
| Formula | C4H11N5 |
| Molar mass | 129.167 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| |
| |
メトホルミン(Metformin)は、グルコファージ(Glucophage)などの商品名で販売されており、特に太りすぎの2型糖尿病の治療のための主要な第一選択医薬品である。また、多嚢胞性卵巣症候群の治療にも用いられる。抗精神病薬を服用している人のメタボリックシンドロームのリスクを軽減するために、適応外の補助薬として使用されることもある。
メトホルミンは一般的に忍容性が高い。一般的な副作用には、下痢、吐き気、腹痛などがある。メトホルミンは低血糖を引き起こすリスクが小さい。高血中乳酸値(アシドーシス)は、医薬品を過度に大量に使用したり、重度の腎障害のある人に処方した場合に懸念される。
メトホルミンはビグアナイド系抗高血糖薬である。肝臓におけるグルコース産生を減少させ、体組織のインスリン感受性を高めることによって作用する。
メトホルミンは、1922年にEmil WernerとJames Bellによって初めて科学文献に記載された。フランスの医師ジャン・スターン(Jean Sterne)は1950年代にヒトでの研究を開始した。フランスでは1957年に、米国では1995年に医薬品として導入された。メトホルミンは世界保健機関の必須医薬品リストに掲載されており、口から服用する糖尿病治療薬として最も広く使用されている。ジェネリック医薬品としても販売されている。2021年には、米国で2番目に多く処方された医薬品であり、91 万以上の処方があった。
医療用途
メトホルミンは、2型糖尿病患者の血糖を低下させるために使用される。また、多嚢胞性卵巣症候群の不妊症の第二選択薬としても用いられる。
2型糖尿病
米国糖尿病学会と米国内科学会はともに、メトホルミンを2型糖尿病治療の第一選択薬として推奨している。メトホルミンはレパグリニドと同程度に有効であり、2型糖尿病に対する他のすべての経口薬物よりも有効である。
有効性
欧州糖尿病学会、欧州心臓病学会、米国糖尿病学会などの主要な専門学会の治療ガイドラインでは、メトホルミンの心血管ベネフィットに関するエビデンスは曖昧であると記述されている。2020年のコクランでは システマティックレビューでは、メトホルミン単剤療法を他の糖低下薬物、行動変容介入、プラセボ、介入なしと比較した場合、心血管死亡率、非致死的心筋梗塞、非致死的脳卒中の減少を示す十分なエビデンスは認められなかった。
メトホルミンの使用は、体重増加と関連するスルホニル尿素とは対照的に、2型糖尿病患者の体重を減少させる。メトホルミンが糖尿病がない肥満の体重減少に関連することを示す証拠もある。メトホルミンはスルホニル尿素系薬剤よりも低血糖のリスクが低いが、低血糖は激しい運動、カロリー不足、または血糖を低下させる他の薬剤との併用時に起こることがまれである。メトホルミンは、低密度リポ蛋白およびトリグリセリド値を緩やかに低下させる。
糖尿病予備軍の個人において、2019年に行われた2型糖尿病の発症リスク低下におけるメトホルミンと他の介入との効果を比較したシステマティックレビューでは、メトホルミンが食事療法や運動療法、またはプラセボと比較した場合に2型糖尿病の発症リスクを低下させるという中程度の質のエビデンスが認められた。しかし、メトホルミンと集中的な食事療法または運動療法を比較した場合、メトホルミンは2型糖尿病の発症リスクを減少させないという中等度の質のエビデンスが得られ、集中的な食事療法または運動療法にメトホルミンを追加しても、集中的な運動療法と食事療法のみと比較した場合、2型糖尿病のリスクを減少させるという利点も欠点も示さないという非常に質の低いエビデンスが得られた。同レビューでは、糖尿病予備軍における2型糖尿病発症リスクの低下におけるメトホルミンとスルホニル尿素の効果を比較した適切な試験も1件見つかったが、この試験では患者に関連するアウトカムは報告されていない。
多嚢胞性卵巣症候群
多嚢胞性卵巣症候群(PCOS)では、メトホルミンの使用により生児出生率が増加するという暫定的なエビデンスがある。これには、クロミフェンで妊娠できなかった人も含まれる。メトホルミンは流産のリスクを変化させないようである。その他にも、妊娠中および非妊娠中のPCOS女性において、多くの有益性が認められている。PCOS女性におけるIVF/ICSI前または治療中のメトホルミン対プラセボ/無治療に関するコクラン(2020年)の最新レビューでは、生児出生率の改善に関する決定的な証拠は見つかっていない。長時間のGnRHアゴニストプロトコールでは、生児出生率改善のエビデンスには不確実性があったが、臨床的妊娠率の増加はあり得た。要するに、GnRHアンタゴニストプロトコールのメトホルミンは、臨床的妊娠率への影響については不確実であるが、生児出生率を低下させる可能性がある。メトホルミンはOHSSの減少をもたらすかもしれないが、副作用の頻度が高くなる可能性がある。流産に対するメトホルミンの影響については不明確であった。エビデンスは、肥満女性の母体および乳児の転帰を改善するための妊娠中の一般的な使用を支持していない。
イギリスの米国国立医療技術評価機構は2004年に、PCOSで肥満度が25を超える女性に対して、他の治療法で効果が得られない場合に無排卵と不妊のためにメトホルミンを投与することを推奨した。英国および国際的な臨床実践ガイドラインでは、耐糖能異常のある女性を除き、メトホルミンを第一選択治療として推奨していないか、まったく推奨していない。ガイドラインでは、クロミフェンを第一選択医薬品として推奨し、内科的治療とは別に生活習慣の改善を強調している。メトホルミン治療は、ベースライン時に耐糖能障害を示したPCOS女性における2型糖尿病の発症リスクを低下させる。
胃癌
胃癌(GC)は、その高い有病率と死亡率から、世界的な健康上の大きな問題となっている。様々な治療法がある中で、2型糖尿病(T2DM)の一般的な医薬品であるメトホルミンは、その潜在的な抗がん作用が注目されている。GCに対するメトホルミンの有効性については議論の的となってきたが、最近の臨床研究では、GC患者のリスクを低減し生存率を向上させるというメトホルミンの保護作用が優勢に支持されている。メトホルミンの抗癌作用は、複数の経路、特にAMPKの活性化とIGF-1Rの調節を介すると考えられている。有望な知見にもかかわらず、GCの予防と治療におけるメトホルミンの応用に関するコンセンサスは得られていないため、その治療的役割を確認するためには、さらなる臨床的およびメカニズム的研究が必要である。
糖尿病と妊娠
妊娠中のメトホルミン使用について、インスリン単独と比較した総説では、母児ともに短期的な安全性は良好であったが、長期的な安全性は不明であった。いくつかの観察研究およびランダム化比較試験では、メトホルミンは妊娠糖尿病の管理においてインスリンと同様に有効かつ安全であることが明らかにされた。それにもかかわらず、いくつかの懸念が提起されており、母子双方に対するメトホルミンの長期安全性に関するエビデンスは不足している。インスリンと比較して、メトホルミンを投与された妊娠糖尿病の女性は体重増加が少なく、妊娠中に子癇前症を発症する可能性が低い。メトホルミンを投与された女性から生まれた赤ちゃんは内臓脂肪が少なく、そのため、その後の人生でインスリン抵抗性になりにくい可能性がある。妊娠糖尿病にメトホルミンを使用すると、インスリンによる治療と比較して赤ちゃんが小さくなる。しかし、妊娠中にメトホルミンを投与された子どもは、当初は出生体重が低かったにもかかわらず、出生後の成長が促進され、妊娠中にインスリンを投与された子どもよりも小児期半ばまでに体重が増加した。このように、出生時低体重の後、比較対照児を上回るキャッチアップ成長というパターンは、長期的な心代謝疾患と関連している。
体重の変化
メトホルミンの使用は一般的に体重減少を伴う。メトホルミンは、抗精神病薬であるオランザピンおよびクロザピンによって引き起こされる体重増加を打ち消すのに安全かつ有効であるようである。メトホルミンによりクロザピンによる体重増加の緩やかな逆転が認められるが、体重増加の一次予防の方がより価値がある。
インスリンとの併用
メトホルミンは、低血糖のリスクは増加するものの、1型糖尿病におけるインスリン必要量を減少させる可能性がある。
寿命延長
メトホルミンは、健康な人でも寿命延長に役立つ可能性があることを示す証拠がいくつかある。メトホルミンは、おそらく糖尿病治療(インスリンと糖質調節)と同様のメカニズムで老化を遅らせる薬剤として大きな関心を集めている。
アルツハイマー病
予備研究では、メトホルミンがアルツハイマー病のリスクを低下させるかどうか、2型糖尿病とアルツハイマー病のリスクに相関があるかどうかが検討されている。
禁忌事項
メトホルミンは以下の併用禁忌である:
- 重度の腎機能障害(推定糸球体濾過量(eGFR)が30 mL/分/1.73 m2未満)。
- メトホルミンに対する既知の過敏症
- 糖尿病性ケトアシドーシス(コントロールされていない糖尿病による)を含む急性または慢性の代謝性アシドーシスで、昏睡を伴うか伴わない。
副作用
メトホルミンの最も一般的な副作用は、下痢、けいれん、吐き気、嘔吐、および鼓腸の増加などの消化管刺激である。メトホルミンは、他のほとんどの抗糖尿病医薬品よりも一般的に消化器系の副作用と関連している。メトホルミンの最も重篤な潜在的副作用は乳酸アシドーシスである;この合併症はまれであり、肝機能または腎機能の低下に関連しているようである。メトホルミンは重度の腎臓病患者への使用は承認されていないが、腎臓に問題のある患者には低用量で使用することができる。
胃腸
胃腸の不調は激しい不快感を引き起こすことがある;メトホルミンの初回投与時または増量時に最もよくみられる。低用量(1.0~1.7g/日)から開始し、徐々に増量することで不快感を回避できることが多いが、低用量でも5%の人はメトホルミンに耐えられないことがある。徐放性製剤または徐放性製剤を用いると、忍容性が改善することがある。
メトホルミンの長期使用は、ホモシステイン値の上昇およびビタミンB12の吸収不良と関連している。高用量や長期間の使用はビタミンB12欠乏症の発生率の増加と関連しており、スクリーニングや予防戦略を推奨する研究者もいる。
乳酸アシドーシス
日常診療でメトホルミンに曝露しても乳酸アシドーシスが起こることはほとんどない。メトホルミンに関連した乳酸アシドーシスの発生率は、10万人/年あたり約9人であり、これは一般集団における乳酸アシドーシスの背景率と同様である。システマティックレビューでは、メトホルミンと乳酸アシドーシスを決定的に関連づけるデータは存在しないと結論づけている。
メトホルミンは一般に軽度から中等度の慢性腎臓病において安全であり、推算糸球体濾過量(eGFR)の重症度に応じてメトホルミンの投与量を比例的に減量し、腎機能を定期的に評価する(例えば、定期的な血漿クレアチニン測定)。米国食品医薬品局(FDA)は、eGFRのカットオフ値である30mL/分/1.73m2未満の、より重症の慢性腎臓病ではメトホルミンの使用を避けるよう推奨している。乳酸は肝糖新生の基質であり、メトホルミンが阻害するプロセスであるため、メトホルミンの使用により肝臓での乳酸取り込みが減少する。健常者では、このわずかな過剰は他の機序(障害のない腎臓による取り込みを含む)によって排出され、乳酸の血中濃度の有意な上昇は起こらない。腎機能が著しく低下している場合は、メトホルミンと乳酸のクリアランスが低下し、両方の濃度が上昇し、乳酸が蓄積する可能性がある。メトホルミンは乳酸の肝臓への取り込みを減少させるため、乳酸アシドーシスを誘発するような病態は禁忌である。一般的な原因としては、アルコール中毒(NAD+貯蔵量の枯渇による)、心不全、呼吸器疾患(組織の酸素化が不十分なため)などが挙げられる;最も一般的な原因は腎疾患である。
メトホルミンに伴う乳酸産生は大腸でも起こる可能性があり、危険因子を有する患者では乳酸アシドーシスの一因となる可能性がある。しかし、このことの臨床的意義は不明であり、メトホルミン関連乳酸アシドーシスのリスクは、腸での産生増加よりもむしろ肝での取り込み減少に起因することが最も一般的である。
過剰摂取
過量投与後の最も一般的な症状としては、嘔吐、下痢、腹痛、頻脈、眠気、まれに低血糖または高血糖がある。メトホルミン過剰摂取の治療は、特異的な解毒剤が知られていないため、一般に支持療法である。重度の過量投与では、体外治療が推奨される。メトホルミンは分子量が低く、血漿蛋白結合がないため、これらの手技にはメトホルミンを血漿から除去し、さらなる乳酸の過剰産生を防ぐという利点がある。
メトホルミンは、治療のモニタリング、中毒の診断の確認、または法医学的死亡調査の補助のために、血液、血漿、または血清で定量することができる。血中または血漿中のメトホルミン濃度は通常、治療用量の投与を受けている人で1~4 mg/L、急性過剰摂取の犠牲者で40~120 mg/L、死亡例で80~200 mg/Lの範囲である。クロマトグラフィー技術が一般的に採用されている。
メトホルミンに関連した乳酸アシドーシスのリスクは、メトホルミンの大量過剰投与によっても高まるが、かなり大量のメトホルミンを投与しても致命的にならないことが多い。
相互作用
H2受容体拮抗薬はメトホルミンの血漿中濃度を上昇させる。シメチジンは、腎臓によるメトホルミンのクリアランスを低下させることにより、メトホルミンの血漿中濃度の上昇を引き起こす;メトホルミンとシメチジンはどちらも尿細管分泌によって体外に排出され、両者、特にシメチジンの陽イオン(正の電荷を帯びた)型は、同じ輸送機序で競合する可能性がある。小規模な二重盲検のランダム化試験で、抗生物質である セファレキシンも同様の機序でメトホルミン濃度を上昇させることがわかった;理論的には、他の陽イオン医薬品も同じ効果をもたらす可能性がある。
メトホルミンはまた、胃運動への影響により抗コリン薬とも相互作用する。抗コリン薬は胃の運動性を低下させ、薬が消化管に留まる時間を延長させる。この障害により、抗コリン薬が存在しない場合よりもメトホルミンが多く吸収され、血漿中のメトホルミン濃度が上昇し、副作用のリスクが高まる可能性がある。
薬理学
作用機序
メトホルミンの分子メカニズムは完全には解明されていない。複数の潜在的な作用機序が提唱されている: ミトコンドリア呼吸鎖(複合体I)の阻害、AMP活性化プロテインキナーゼ(AMPK)の活性化、プロテインキナーゼA(PKA)の活性化の減少を伴うグルカゴン誘導性のgut microbiota/ja|環状アデノシン一リン酸(cAMP)の上昇の阻害、 ミトコンドリアグリセロール-3-リン酸デヒドロゲナーゼのGPD2変異体の複合体IV媒介阻害(それにより、グリセロール由来の肝グルコネシン生成を減少させる)、および腸内細菌叢への影響。
メトホルミンは、ほとんどの人に無欲作用を及ぼし、カロリー摂取を減少させる。メトホルミンは、肝臓での糖新生(グルコース産生)を減少させる。メトホルミンは、下垂体からの成長ホルモン、副腎皮質刺激ホルモン、卵胞刺激ホルモンの基礎分泌、およびプロオピオメラノコルチンの発現を阻害し、このことが、肝臓、骨格筋、内皮、脂肪組織、および卵巣を含む組織に対する複数の作用を有するインスリン感作作用の一因となっている。平均的な2型糖尿病患者は、正常の3倍の糖新生速度を持っている。メトホルミンの治療は、これを3分の1以上減少させる。
肝グルコース産生に対するメトホルミンの抑制効果には、AMPKの活性化が必要であった。AMPKは、インスリンシグナル伝達、全身のエネルギーバランス、グルコースと脂肪の代謝において重要な役割を果たす酵素である。AMPKの活性化は、スモールヘテロダイマーパートナーの発現増加に必要であり、その結果、肝グルコネーシス遺伝子ホスホエノールピルビン酸カルボキシキナーゼおよびグルコース6-ホスファターゼの発現が阻害された。メトホルミンは、AMPKアゴニストとしてAICAリボヌクレオチドとともに研究において頻繁に使用されている。メトホルミンは、細胞質のアデノシン一リン酸(AMP)濃度を上昇させる(総AMPまたは総AMP/アデノシン三リン酸の変化とは異なる)。メトホルミンは、サイクリックAMP産生を阻害し、グルカゴンの作用を阻害し、それによって空腹時グルコースレベルを低下させる。メトホルミンはまた、糖尿病マウスの糞便微生物群集プロフィールの大きな変化を誘導し、これはおそらくグルカゴン様ペプチド-1分泌への影響を通してその作用様式に寄与している可能性がある。
In addition to suppressing hepatic glucose production, metformin increases insulin sensitivity, enhances peripheral glucose uptake (by inducing the phosphorylation of GLUT4 enhancer factor), decreases insulin-induced suppression of fatty acid oxidation, and decreases the absorption of glucose from the gastrointestinal tract. Increased peripheral use of glucose may be due to improved insulin binding to insulin receptors. The increase in insulin binding after metformin treatment has also been demonstrated in patients with type 2 diabetes.
AMPK probably also plays a role in increased peripheral insulin sensitivity, as metformin administration increases AMPK activity in skeletal muscle. AMPK is known to cause GLUT4 deployment to the plasma membrane, resulting in insulin-independent glucose uptake. Some metabolic actions of metformin do appear to occur by AMPK-independent mechanisms, however AMPK likely has a modest overall effect and its activity is not likely to directly decrease gluconeogenesis in the liver.
Metformin has indirect antiandrogenic effects in women with insulin resistance, such as those with PCOS, due to its beneficial effects on insulin sensitivity. It may reduce testosterone levels in such women by as much as 50%. A Cochrane review, though, found that metformin was only slightly effective for decreasing androgen levels in women with PCOS.
Metformin also has significant effects on the gut microbiome, such as its effect on increasing agmatine production by gut bacteria, but the relative importance of this mechanism compared to other mechanisms is uncertain.
Due to its effect on GLUT4 and AMPK, metformin has been described as an exercise mimetic.
Pharmacokinetics
Metformin has an oral bioavailability of 50–60% under fasting conditions, and is absorbed slowly. Peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) are reached within 1–3 hours of taking immediate-release metformin and 4–8 hours with extended-release formulations. The plasma protein binding of metformin is negligible, as reflected by its very high apparent volume of distribution (300–1000 L after a single dose). Steady state is usually reached in 1–2 days.
Metformin has acid dissociation constant values (pKa) of 2.8 and 11.5, so it exists very largely as the hydrophilic cationic species at physiological pH values. The metformin pKa values make it a stronger base than most other basic medications with less than 0.01% nonionized in blood. Furthermore, the lipid solubility of the nonionized species is slight as shown by its low logP value (log(10) of the distribution coefficient of the nonionized form between octanol and water) of −1.43. These chemical parameters indicate low lipophilicity and, consequently, rapid passive diffusion of metformin through cell membranes is unlikely. As a result of its low lipid solubility it requires the transporter SLC22A1 in order for it to enter cells. The logP of metformin is less than that of phenformin (−0.84) because two methyl substituents on metformin impart lesser lipophilicity than the larger phenylethyl side chain in phenformin. More lipophilic derivatives of metformin are presently under investigation with the aim of producing prodrugs with superior oral absorption than metformin.
Metformin is not metabolized. It is cleared from the body by tubular secretion and excreted unchanged in the urine; it is undetectable in blood plasma within 24 hours of a single oral dose. The average elimination half-life in plasma is 6.2 hours. Metformin is distributed to (and appears to accumulate in) red blood cells, with a much longer elimination half-life: 17.6 hours (reported as ranging from 18.5 to 31.5 hours in a single-dose study of nondiabetics).
Some evidence indicates that liver concentrations of metformin in humans may be two to three times higher than plasma concentrations, due to portal vein absorption and first-pass uptake by the liver in oral administration.
Chemistry
Metformin hydrochloride (1,1-dimethylbiguanide hydrochloride) is freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, but almost insoluble in acetone, ether, or chloroform. The pKa of metformin is 12.4. The usual synthesis of metformin, originally described in 1922, involves the one-pot reaction of dimethylamine hydrochloride and 2-cyanoguanidine over heat.
According to the procedure described in the 1975 Aron patent, and the Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, equimolar amounts of dimethylamine and 2-cyanoguanidine are dissolved in toluene with cooling to make a concentrated solution, and an equimolar amount of hydrogen chloride is slowly added. The mixture begins to boil on its own, and after cooling, metformin hydrochloride precipitates with a 96% yield.
Derivatives
A new derivative HL156A, also known as IM156, is a potential new drug for medical use.
The biguanide class of antidiabetic medications, which also includes the withdrawn agents phenformin and buformin, originates from the French lilac or goat's rue (Galega officinalis), a plant used in folk medicine for several centuries. G. officinalis itself does not contain any of these medications, but isoamylene guanidine; phenformin, buformin, and metformin are chemically synthesized compounds composed of two guanidine molecules, and are more lipophilic than the plant-derived parent compound.
Metformin was first described in the scientific literature in 1922, by Emil Werner and James Bell, as a product in the synthesis of N,N-dimethylguanidine. In 1929, Slotta and Tschesche discovered its sugar-lowering action in rabbits, finding it the most potent biguanide analog they studied. This result was ignored, as other guanidine analogs such as the synthalins, took over and were themselves soon overshadowed by insulin.
Interest in metformin resumed at the end of the 1940s. In 1950, metformin, unlike some other similar compounds, was found not to decrease blood pressure and heart rate in animals. That year, Filipino physician Eusebio Y. Garcia used metformin (he named it Fluamine) to treat influenza; he noted the medication "lowered the blood sugar to minimum physiological limit" and was not toxic. Garcia believed metformin to have bacteriostatic, antiviral, antimalarial, antipyretic, and analgesic actions. In a series of articles in 1954, Polish pharmacologist Janusz Supniewski was unable to confirm most of these effects, including lowered blood sugar. Instead he observed antiviral effects in humans.
French diabetologist Jean Sterne studied the antihyperglycemic properties of galegine, an alkaloid isolated from G. officinalis, which is related in structure to metformin, and had seen brief use as an antidiabetic before the synthalins were developed. Later, working at Laboratoires Aron in Paris, he was prompted by Garcia's report to reinvestigate the blood sugar-lowering activity of metformin and several biguanide analogs. Sterne was the first to try metformin on humans for the treatment of diabetes; he coined the name "Glucophage" (glucose eater) for the medication and published his results in 1957.
Metformin became available in the British National Formulary in 1958. It was sold in the UK by a small Aron subsidiary called Rona.
Broad interest in metformin was not rekindled until the withdrawal of the other biguanides in the 1970s. Metformin was approved in Canada in 1972, but did not receive approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for type 2 diabetes until 1994. Produced under license by Bristol-Myers Squibb, Glucophage was the first branded formulation of metformin to be marketed in the U.S., beginning on 3 March 1995. Generic formulations are available in several countries, and metformin is believed to have become the world's most widely prescribed antidiabetic medication.
Society and culture
Environmental
Metformin and its major transformation product guanylurea are present in wastewater treatment plant effluents and regularly detected in surface waters. Guanylurea concentrations above 200 μg/L have been measured in the German river Erpe, which are amongst the highest reported for pharmaceutical transformation products in aquatic environments.
The name "Metformin" is the BAN, USAN, and INN for this medication, and is sold under several trade names. Common brand names include Glucophage, Riomet, Fortamet, and Glumetza in the US. In other areas of the world, there is also Obimet, Gluformin, Dianben, Diabex, Diaformin, Metsol, Siofor, Metfogamma and Glifor. There are several formulations of Metformin available to the market, and all but the liquid form have generic equivalents. Metformin IR (immediate release) is available in 500-, 850-, and 1000-mg tablets, while Metformin XR (extended release) is available in 500-, 750-, and 1000-mg strengths (also sold as Fortamet, Glumetza, and Glucophage XR in the US). Also available is liquid metformin (sold as Riomet in the US), where 5 mL of solution contains the same amount of drug as a 500-mg tablet.
Combination with other medications
When used for type 2 diabetes, metformin is often prescribed in combination with other medications.
Several are available as fixed-dose combinations, with the potential to reduce pill burden, decrease cost, and simplify administration.
Thiazolidinediones (glitazones)
Rosiglitazone
A combination of metformin and rosiglitazone was released in 2002, and sold as Avandamet by GlaxoSmithKline, or as a generic medication. Formulations are 500/1, 500/2, 500/4, 1000/2, and 1000 mg/4 mg of metformin/rosiglitazone.
By 2009, it had become the most popular metformin combination.
In 2005, the stock of Avandamet was removed from the market, after inspections showed the factory where it was produced was violating good manufacturing practices. The medication pair continued to be prescribed separately, and Avandamet was again available by the end of that year. A generic formulation of metformin/rosiglitazone from Teva received tentative approval from the FDA and reached the market in early 2012.
However, following a meta-analysis in 2007 that linked the medication's use to an increased risk of heart attack, concerns were raised over the safety of medicines containing rosiglitazone. In September 2010, the European Medicines Agency recommended that the medication be suspended from the European market because the benefits of rosiglitazone no longer outweighed the risks.
It was withdrawn from the market in the UK and India in 2010, and in New Zealand and South Africa in 2011. did not allow rosiglitazone or metformin/rosiglitazone to be sold without a prescription; moreover, makers were required to notify patients of the risks associated with its use, and the drug had to be purchased by mail order through specified pharmacies.
In November 2013, the FDA lifted its earlier restrictions on rosiglitazone after reviewing the results of the 2009 RECORD clinical trial (a six-year, open-label randomized control trial), which failed to show elevated risk of heart attack or death associated with the medication.
Pioglitazone
The combination of metformin and pioglitazone (Actoplus Met, Piomet, Politor, Glubrava) is available in the US and the European Union.
DPP-4 inhibitors
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors inhibit dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and thus reduce glucagon and blood glucose levels.
DPP-4 inhibitors combined with metformin include a sitagliptin/metformin combination (Janumet), a saxagliptin/metformin combination (Kombiglyze XR, Komboglyze), and an alogliptin/metformin combination (Kazano, Vipdomet).
Linagliptin combined with metformin hydrochloride is sold under the brand name Jentadueto. As of August 2021, linagliptin/metformin is available as a generic medicine in the US.
SGLT-2 inhibitors
There are combinations of metformin with the SGLT-2 inhibitors dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, and canagliflozin.
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas act by increasing insulin release from the beta cells in the pancreas.
A 2019 systematic review suggested that there is limited evidence if the combined used of metformin with sulfonylurea compared to the combination of metformin plus another glucose-lowering intervention, provides benefit or harm in mortality, severe adverse events, macrovascular and microvascular complications. Combined metformin and sulfonylurea therapy did appear to lead to higher risk of hypoglicaemia.
Metformin is available combined with the sulfonylureas glipizide (Metaglip) and glibenclamide (US: glyburide) (Glucovance). Generic formulations of metformin/glipizide and metformin/glibenclamide are available (the latter is more popular).
Meglitinide
Meglitinides are similar to sulfonylureas, as they bind to beta cells in the pancreas, but differ by the site of binding to the intended receptor and the drugs' affinities to the receptor. As a result, they have a shorter duration of action compared to sulfonylureas, and require higher blood glucose levels to begin to secrete insulin. Both meglitinides, known as nateglinide and repanglinide, is sold in formulations combined with metformin. A repaglinide/metformin combination is sold as Prandimet, or as its generic equivalent.
Triple combination
The combination of metformin with dapagliflozen and saxagliptin is available in the United States as Qternmet XR.
The combination of metformin with pioglitazone and glibenclamide is available in India as Accuglim-MP, Adglim MP, and Alnamet-GP, along with the Philippines as Tri-Senza.
The combination of metformin with pioglitazone and lipoic acid is available in Turkey as Pional.
Impurities
In December 2019, the US FDA announced that it learned that some metformin medicines manufactured outside the United States might contain a nitrosamine impurity called N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), classified as a probable human carcinogen, at low levels. Health Canada announced that it was assessing NDMA levels in metformin.
In February 2020, the FDA found NDMA levels in some tested metformin samples that did not exceed the acceptable daily intake.
In February 2020, Health Canada announced a recall of Apotex immediate-release metformin, followed in March by recalls of Ranbaxy metformin and in March by Jamp metformin.
In May 2020, the FDA asked five companies to voluntarily recall their sustained-release metformin products. The five companies were not named, but they were revealed to be Amneal Pharmaceuticals, Actavis Pharma, Apotex Corp, Lupin Pharma, and Marksans Pharma Limited in a letter sent to Valisure, the pharmacy that had first alerted the FDA to this contaminant in metformin via a Citizen Petition.
In June 2020, the FDA posted its laboratory results showing NDMA amounts in metformin products it tested. It found NDMA in certain lots of ER metformin, and is recommending companies recall lots with levels of NDMA above the acceptable intake limit of 96 nanograms per day. The FDA is also collaborating with international regulators to share testing results for metformin.
In July 2020, Lupin Pharmaceuticals pulled all lots (batches) of metformin after discovering unacceptably high levels of NDMA in tested samples.
In August 2020, Bayshore Pharmaceuticals recalled two lots of tablets.
Research
Metformin has been studied for its effects on multiple other conditions, including:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Premature puberty
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular disease in people with diabetes
- Aging
While metformin may reduce body weight in persons with fragile X syndrome, whether it improves neurological or psychiatric symptoms is uncertain. Metformin has been studied in vivo (C. elegans and crickets) for effects on aging. A 2017 review found that people with diabetes who were taking metformin had lower all-cause mortality. They also had reduced cancer and cardiovascular disease compared with those on other therapies.
There is also some research suggesting that although metformin prevents diabetes, it does not reduce the risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease and thus does not extend lifespan in non-diabetic individuals. Furthermore, some studies suggest that long-term chronic use of metformin by healthy individuals may develop vitamin B12 deficiency.
さらに読む
- Markowicz-Piasecka M, Huttunen KM, Mateusiak L, Mikiciuk-Olasik E, Sikora J (2017). "Is Metformin a Perfect Drug? Updates in Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 23 (17): 2532–2550. doi:10.2174/1381612822666161201152941. PMID 27908266.
- McCreight LJ, Bailey CJ, Pearson ER (March 2016). "Metformin and the gastrointestinal tract". Diabetologia. 59 (3): 426–35. doi:10.1007/s00125-015-3844-9. PMC 4742508. PMID 26780750.
- Moin T, Schmittdiel JA, Flory JH, Yeh J, Karter AJ, Kruge LE, Schillinger D, Mangione CM, Herman WH, Walker EA (October 2018). "Review of Metformin Use for Type 2 Diabetes Prevention". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 55 (4): 565–574. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.04.038. PMC 6613947. PMID 30126667.
- Rena G, Hardie DG, Pearson ER (September 2017). "The mechanisms of action of metformin". Diabetologia. 60 (9): 1577–1585. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4342-z. PMC 5552828. PMID 28776086.
- Sanchez-Rangel E, Inzucchi SE (September 2017). "Metformin: clinical use in type 2 diabetes". Diabetologia. 60 (9): 1586–1593. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4336-x. PMID 28770321.
- Zhou J, Massey S, Story D, Li L (September 2018). "Metformin: An Old Drug with New Applications". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 19 (10): 2863. doi:10.3390/ijms19102863. PMC 6213209. PMID 30241400.
- Zhou T, Xu X, Du M, Zhao T, Wang J (October 2018). "A preclinical overview of metformin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes". Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 106: 1227–1235. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.085. PMID 30119191. S2CID 52031602.
外部リンク
- "Nitrosamine impurities in medications: Guidance". Health Canada. 4 April 2022.


