Protein/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "抗体は適応免疫系のタンパク質成分であり、その主な機能は抗原、すなわち体内の異物と結合し、破壊の対象とすることである。抗体は細胞外環境に分泌されるか、形質細胞として知られる特殊なB細胞の膜に固定される。酵素が反応を行う必要性から基質との結合親和性..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "多くのリガンド輸送タンパク質は、特定の|低分子生体分子と結合し、多細胞生物の体内の別の場所に輸送する。これらのタンパク質は、リガンドが高濃度で存在するときには高い結合親和性を持たなければならないが、標的組織中に低濃度で存在するときにはリガンドを放出しなければならない。リガンド結合タンパク質の典..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
[[Antibodies/ja|抗体]]は[[adaptive immune system/ja|適応免疫系]]のタンパク質成分であり、その主な機能は[[antigen/ja|抗原]]、すなわち体内の異物と結合し、破壊の対象とすることである。抗体は細胞外環境に[[secrete/ja|分泌]]されるか、[[plasma cell/ja|形質細胞]]として知られる特殊な[[B cell/ja|B細胞]]の膜に固定される。酵素が反応を行う必要性から基質との結合親和性に制約があるのに対し、抗体にはそのような制約はない。抗体の標的に対する結合親和性は非常に高い。 | [[Antibodies/ja|抗体]]は[[adaptive immune system/ja|適応免疫系]]のタンパク質成分であり、その主な機能は[[antigen/ja|抗原]]、すなわち体内の異物と結合し、破壊の対象とすることである。抗体は細胞外環境に[[secrete/ja|分泌]]されるか、[[plasma cell/ja|形質細胞]]として知られる特殊な[[B cell/ja|B細胞]]の膜に固定される。酵素が反応を行う必要性から基質との結合親和性に制約があるのに対し、抗体にはそのような制約はない。抗体の標的に対する結合親和性は非常に高い。 | ||
多くのリガンド輸送タンパク質は、特定の[[Small molecule/ja||低分子生体分子]]と結合し、多細胞生物の体内の別の場所に輸送する。これらのタンパク質は、[[ligand/ja|リガンド]]が高濃度で存在するときには高い結合親和性を持たなければならないが、標的組織中に低濃度で存在するときにはリガンドを放出しなければならない。リガンド結合タンパク質の典型例は[[hemoglobin/ja|ヘモグロビン]]であり、すべての[[vertebrate/ja|脊椎動物]]の[[lung/ja|肺]]から他の臓器や組織に[[oxygen/ja|酸素]]を輸送する。[[lectins/ja|レクチン]]は[[Glycan-protein interactions/ja|糖結合タンパク質]]であり、その糖鎖部分に非常に特異的である。[[lectins/ja|レクチン]]は通常、細胞やタンパク質が関与する生物学的な[[Molecular recognition/ja|認識]]現象において役割を果たす。[[Receptor (biochemistry)/ja|受容体]]や[[hormone/ja|ホルモン]]は特異性の高い結合タンパク質である。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 21:47, 24 February 2024

タンパク質は、アミノ酸残基の1本以上の長い鎖からなる大きな大きな生体分子であり、高分子である。タンパク質は、代謝反応の触媒、DNA複製、刺激への応答、細胞への構造および生物の提供、およびある場所から別の場所への分子の輸送など、生物内で膨大な機能を果たす。タンパク質は主にアミノ酸の配列において互いに異なっており、それは遺伝子のヌクレオチド配列によって決定され、その結果、通常、タンパク質はその活性を決定する特定の3次元構造に折り畳まれる。
アミノ酸残基の直鎖をポリペプチドと呼ぶ。タンパク質は少なくとも1つの長いポリペプチドを含む。20-30残基以下の短いポリペプチドはタンパク質とみなされることはほとんどなく、一般にペプチドと呼ばれる。個々のアミノ酸残基はペプチド結合と隣接するアミノ酸残基によって結合されている。タンパク質中のアミノ酸残基の配列は、遺伝暗号にコードされた遺伝子の配列によって定義される。一般的に、遺伝暗号は20の標準アミノ酸を規定しているが、ある種の生物では遺伝暗号にセレノシステインや、ある種のarchaea/ja古細菌ではピロリジンが含まれることがある。合成後まもなく、あるいは合成中であっても、タンパク質中の残基はしばしば翻訳後修飾によって化学的に修飾される。タンパク質の中には、補欠基または補因子と呼ばれる、ペプチド以外の基が結合しているものもある。タンパク質はまた、特定の機能を達成するために協働することができ、しばしば会合して安定したタンパク質複合体を形成する。
一度形成されたタンパク質は一定期間しか存在せず、その後分解され、タンパク質のターンオーバーのプロセスを通じて細胞の機械によって再利用される。タンパク質の寿命は半減期で測定され、その範囲は広い。哺乳類の細胞では平均寿命は1〜2日で、数分間存在することもあれば数年間存在することもある。異常なタンパク質や誤った折り畳み方をしたタンパク質は、破壊の対象となるためか、不安定であるためか、より急速に分解される。
タンパク質は、多糖類や核酸などの他の生体高分子と同様に、生物にとって不可欠な部分であり、細胞内のほぼすべてのプロセスに関与している。多くのタンパク質は生化学反応を触媒する酵素であり、代謝に不可欠である。タンパク質はまた、構造的あるいは機械的な機能も持っている。例えば、筋肉のアクチンとミオシン、細胞の形を維持する足場のシステムを形成する細胞骨格のタンパク質などである。その他のタンパク質は、細胞シグナル伝達、免疫応答、細胞接着、細胞周期において重要である。動物では、タンパク質は合成できない必須アミノ酸を供給するためにダイエットに必要である。消化によってタンパク質は分解され、代謝に利用される。
タンパク質は、超遠心分離、沈殿、電気泳動、クロマトグラフィーなどの様々な技術を用いて、他の細胞成分から精製することができる。タンパク質の構造と機能を研究するために一般的に用いられる方法には、免疫組織化学、部位特異的突然変異誘発、X線結晶構造解析、核磁気共鳴、質量分析などがある。
歴史と語源
タンパク質は18世紀にAntoine Fourcroyらによって生物学的分子の別個のクラスとして認識され、熱や酸による処理下で凝固または凝集する分子の能力によって区別された。当時の有名な例としては、卵白のアルブミン、血液の血清アルブミン、フィブリン、小麦のグルテンなどが挙げられる。
タンパク質は1838年にオランダの化学者Gerardus Johannes Mulderによって初めて記述され、スウェーデンの化学者Jöns Jacob Berzeliusによって命名された。Mulderは一般的なタンパク質の元素分析を行い、ほぼすべてのタンパク質が同じ実験式、C400H620N100O120P1S1を持っていることを発見した。彼は、タンパク質は1種類の(非常に大きな)分子で構成されているのではないかという誤った結論に達した。これらの分子を表す「タンパク質」という用語は、Mulderの同僚であるBerzeliusによって提案された。タンパク質はギリシア語のπρώτειοςに由来する。(proteios)、「第一の」、「先頭に立つ」、「前に立つ」を意味し、-inに由来する。Mulderはさらに、アミノ酸などのタンパク質分解産物を特定した。ロイシンの分子量は131Daであった。「タンパク質」以前には、「アルブミン」や「アルブミン質」(ドイツ語では「Eiweisskörper」)といった別の名称が使われていた。
ドイツのカール・フォン・ヴォイトのような初期の栄養学者は、"肉は肉を作る"と一般的に信じられていたため、タンパク質が身体の構造を維持するために最も重要な栄養素であると信じていた。カール・ハインリッヒ・リトハウゼンは、グルタミン酸の同定によって、既知のタンパク質の形態を拡張した。コネチカット農業試験場で、植物性タンパク質の詳細なレビューがトーマス・バー・オズボーンによってまとめられた。ラファイエット・メンデルと協力し、実験用ラットの摂食にリービッヒの最小の法則を適用して、栄養学的に必須アミノ酸が確立された。この研究はウィリアム・カミング・ローズによって継続され、伝えられた。1902年、フランツ・ホフマイスターとヘルマン・エミール・フィッシャーの研究によって、ポリペプチドとしてのタンパク質が理解された。生物における酵素としてのタンパク質の中心的役割は、1926年にジェームズ・B・サムナーがウレアーゼという酵素が実際にタンパク質であることを示すまで、完全には理解されなかった。
タンパク質を大量に精製することは困難であったため、初期のタンパク質生化学者にとっては、非常に研究しにくいものであった。従って、初期の研究は、大量に精製できるタンパク質、例えば、血液、卵白、様々な毒素、食肉処理場から得られる消化・代謝酵素に焦点を当てた。1950年代、アーマー・ホットドッグ社は1 kgの純粋なウシ膵臓リボヌクレアーゼAを精製し、科学者が自由に利用できるようにした。このジェスチャーによって、リボヌクレアーゼAはその後数十年間、生化学研究の主要なターゲットとなった。
ライナス・ポーリングは、1933年にウィリアム・アストベリーによって初めて提唱された水素結合に基づく規則的なタンパク質の二次構造の予測に成功したことで知られている。その後、ウォルター・カウズマンによる変性に関する研究は、カイ・ウリンデルストローム=ラングによる以前の研究を部分的に基にしたものであり、疎水性相互作用によって媒介されるタンパク質の折り畳みと構造の理解に貢献した。
最初に配列されたタンパク質は、1949年、フレデリック・サンガーによるインスリンであった。サンガーはインスリンのアミノ酸配列を正確に決定し、タンパク質が分岐鎖、コロイド、シクロールではなく、アミノ酸の直鎖ポリマーから構成されていることを決定的に証明した。1958年、彼はこの功績によりノーベル賞を受賞した。

X線結晶学の発展により、タンパク質の構造配列を決定することが可能になった。最初にタンパク質構造が解明されたのは、1958年のマックス・ペルッツによるヘモグロビンとジョン・ケンドリューによるミオグロビンであった。コンピュータの使用と計算能力の向上も、複雑なタンパク質の配列決定を支えた。1999年、ロジャー・コーンバーグはシンクロトロンからの高強度X線を用いてRNAポリメラーゼの非常に複雑な構造の配列決定に成功した。
それ以来、大きな高分子集合体のクライオ電子顕微鏡(クライオEM)が開発された。クライオ電子顕微鏡は、結晶ではなく凍結したタンパク質サンプルを用い、X線ではなく電子ビームを用いる。試料へのダメージが少ないため、科学者はより多くの情報を得ることができ、より大きな構造を解析することができる。小さなタンパク質のドメインの計算によるタンパク質構造予測も、研究者がタンパク質構造の原子レベルの分解能に近づくのに役立っている。 2017年現在、プロテインデータバンクには126,060以上の原子分解能のタンパク質構造が登録されている。
ゲノムにコードされるタンパク質の数
ゲノムにコードされているタンパク質の数は、おおよそ遺伝子の数に対応する(ただし、タンパク質のRNAをコードする遺伝子、例えばリボソームRNAの数もかなり多いかもしれない)。ウイルスは通常数個から数百個、古細菌やバクテリアは数百個から数千個、真核生物は通常数千個から数万個のタンパク質をコードしている(例についてはゲノムサイズを参照)。
分類
タンパク質は主に配列と構造によって分類されるが、その他の分類も一般的に用いられている。特に酵素については、EC番号システムが機能的な分類スキームを提供している。同様に、Gene Ontology/ja遺伝子オントロジーでは、遺伝子とタンパク質の両方を生物学的・生化学的機能によって分類しているが、細胞内の位置によっても分類している。
配列の類似性は、進化的類似性と機能的類似性の両方の観点からタンパク質を分類するために使用される。特にマルチドメインタンパク質では、タンパク質全体またはタンパク質ドメインのいずれかを使用することができる。タンパク質ドメインは、配列、構造、機能の組み合わせによるタンパク質の分類を可能にし、それらは多くの異なる方法で組み合わせることができる。17万個のタンパク質を対象とした初期の研究では、約3分の2のタンパク質に少なくとも1つのドメインが割り当てられ、より大きなタンパク質ほど多くのドメインを含んでいた(例えば、600アミノ酸以上のタンパク質は平均5つ以上のドメインを持つ)。
生化学


ほとんどのタンパク質は、最大20種類のL-α-アミノ酸からなる直鎖状のポリマーから構成されている。すべてのタンパク質性アミノ酸は、α-炭素にアミノ基、カルボキシル基、および可変の側鎖が|結合しているα-炭素を含む共通の構造的特徴を持っている。プロリンだけはこの基本構造とは異なり、N末端のアミン基に変わった環を持ち、CO-NHアミド部分を固定したコンフォメーションにする。標準アミノ酸の側鎖は、標準アミノ酸リストに詳述されているが、実に多様な化学構造と性質を持っている。タンパク質の立体構造と化学反応性を最終的に決定するのは、タンパク質中のアミノ酸側鎖すべての複合効果である。 ポリペプチド鎖のアミノ酸はペプチド結合によって結合している。タンパク質鎖に連結された個々のアミノ酸は残基と呼ばれ、連結された一連の炭素、窒素、酸素原子は主鎖またはタンパク質骨格と呼ばれる。
ペプチド結合には2つの共鳴形があり、二重結合の性質を助長し、軸周りの回転を抑制するので、α炭素はほぼコプラナーになる。ペプチド結合の他の2つの二面角は、タンパク質の骨格の局所的な形状を決定する。遊離アミノ基を持つ末端はN末端またはアミノ末端として知られ、遊離カルボキシル基を持つタンパク質の末端はC末端またはカルボキシ末端として知られる(タンパク質の配列はN末端からC末端まで、左から右に書かれる)。
タンパク質、ポリペプチド、ペプチド'という言葉は少し曖昧で、意味が重複することがある。一般的にタンパク質は安定したコンフォメーションを持つ完全な生物学的分子を指すのに使われ、ペプチドは一般的に安定した三次元構造を持たないことが多い短いアミノ酸オリゴマーを指す。しかし、両者の境界は明確ではなく、通常20-30残基付近にある。ポリペプチドは、通常、長さに関係なく、アミノ酸の一本の直鎖を指すことができるが、しばしば、定義された立体構造がないことを意味する。
相互作用
タンパク質は、他のタンパク質との相互作用、脂質との相互作用、炭水化物との相互作用、DNAとの相互作用など、多くの種類の分子と相互作用することができる。
細胞内の存在量
平均的な大きさの細菌は、細胞あたり約200万個のタンパク質を含むと推定されている(例えば大腸菌や黄色ブドウ球菌)。より小さな細菌、例えばマイコプラズマやスピロヘータは、5万から100万のオーダーで、より少ない分子を含んでいる。対照的に、真核生物の細胞は大きく、そのためより多くのタンパク質を含んでいる。例えば、酵母細胞は約5000万個のタンパク質を含み、ヒト細胞は10億から30億個のオーダーであると推定されている。個々のタンパク質コピーの濃度は、細胞あたり数分子から2000万個に及ぶ。タンパク質をコードする遺伝子のすべてがほとんどの細胞で発現しているわけではなく、その数は例えば細胞の種類や外部からの刺激に左右される。例えば、ヒトゲノムがコードする20,000ほどのタンパク質のうち、リンパ芽球細胞で検出されるのは6,000だけである。
合成
生合成
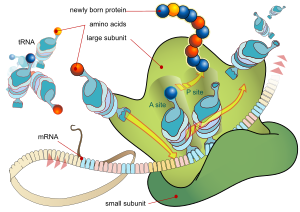

タンパク質は遺伝子にコードされた情報を使ってアミノ酸から組み立てられる。各タンパク質は、そのタンパク質をコードする遺伝子のヌクレオチド配列によって規定される独自のアミノ酸配列を持っている。遺伝コードはコドンと呼ばれる3塩基の集合であり、それぞれの3塩基の組み合わせがアミノ酸を指定する。例えば、AUG(アデニン-ウラシル-グアニン)はメチオニンのコードである。DNAには4つのヌクレオチドが含まれているため、可能なコドンの総数は64である。したがって、遺伝コードには冗長性があり、複数のコドンで指定されるアミノ酸もある。DNAにコードされた遺伝子は、まずRNAポリメラーゼなどのタンパク質によってプレメッセンジャーRNA(mRNA)に転写される。ほとんどの生物はその後、様々な形の転写後修飾を用いてプレmRNA(一次転写産物とも呼ばれる)を処理して成熟mRNAを形成し、これをテンプレートとしてリボソームによるタンパク質合成を行う。原核生物では、mRNAは産生されるとすぐに使われるか、あるいはヌクレオイドから離れた後にリボソームによって結合される。一方、真核生物は細胞核でmRNAを作り、それを核膜を越えて細胞質に転移させ、そこでタンパク質生合成を行う。タンパク質合成の速度は、真核生物よりも原核生物の方が速く、1秒間に20個のアミノ酸が合成されることもある。
mRNAを鋳型としてタンパク質を合成する過程は、翻訳として知られている。mRNAはリボソームにロードされ、転移RNA分子上にあるアンチコドンと塩基対になっているコドンを一致させることで、一度に3つのヌクレオチドを読み取る。酵素アミノアシルtRNA合成酵素はtRNA分子にアミノ酸を「チャージ」する。tRNA分子に正しいアミノ酸を「チャージ」する。成長するポリペプチドはしばしば新生鎖と呼ばれる。タンパク質は常にN末端からC末端まで生合成される。
合成されたタンパク質の大きさは、含まれるアミノ酸の数とその総分子量によって測定することができ、通常はダルトン(原子質量単位と同義)または誘導体単位キロダルトン(kDa)の単位で報告される。高等生物ではタンパク質を構成するタンパク質ドメインの数が多くなるため、タンパク質の平均サイズは古細菌から細菌、真核生物へと増加する(それぞれ283, 311, 438残基、31, 34, 49 kDa)。例えば、酵母のタンパク質は平均466アミノ酸長で53kDaである。知られている最大のタンパク質は、筋肉サルコメアの構成要素であるタイチンである。分子量はほぼ3,000kDa、全長はほぼ27,000アミノ酸である。
化学合成
短いタンパク質はペプチド合成と呼ばれる一連の方法によって化学的に合成することもできる。これは化学ライゲーションなどの有機合成技術に依存して高収率でペプチドを生産する。化学合成では、アミノ酸側鎖に蛍光プローブを結合させるなど、ポリペプチド鎖に非天然アミノ酸を導入することができる。これらの方法は実験室での生化学や細胞生物学に有用であるが、しかし、一般的には商業用には使われない。化学合成は約300アミノ酸より長いポリペプチドでは効率が悪く、合成されたタンパク質は本来の三次構造をなかなかとらない。ほとんどの化学合成法は、生物学的反応とは逆に、C末端からN末端へと進む。
構造

ほとんどのタンパク質は折りたたみ独特の3次元構造になる。タンパク質が自然に折り畳まれる形は、そのネイティブコンフォメーションとして知られている。多くのタンパク質は、アミノ酸の化学的性質によって、何もしなくても折り畳むことができるが、他のタンパク質は、分子シャペロンの助けを借りなければ、本来の状態に折り畳むことができない。生化学者はしばしば、タンパク質の構造について4つの異なる側面に言及する:
- 一次構造:アミノ酸配列のことである。タンパク質はポリアミドである。
- 二次構造:水素結合によって安定化された、規則的に繰り返される局所構造。最も一般的な例は、αヘリックス、βシート、ターンである。二次構造は局所的であるため、同じタンパク質分子内に異なる二次構造の領域が多数存在しうる。
- 三次構造: タンパク質1分子の全体的な形;二次構造の空間的な相互関係。三次構造は一般に非局所的相互作用によって安定化される。最も一般的なのは疎水性コアの形成であるが、塩橋、水素結合、ジスルフィド結合、さらには翻訳後修飾によっても安定化される。三次構造という用語は、しばしばフォールドという用語と同義語として使われる。三次構造はタンパク質の基本的な機能を制御するものである。
- 四次構造: この文脈では通常タンパク質サブユニットと呼ばれる複数のタンパク質分子(ポリペプチド鎖)によって形成される構造であり、それらは単一のタンパク質複合体として機能する。
- 二項構造: 混雑した細胞内部を組織化するタンパク質表面のサインである。四大構造は、生きた細胞内で起こる、一過性でありながら不可欠な高分子相互作用に依存している。
タンパク質は完全に硬い分子ではない。これらの構造レベルに加え、タンパク質はその機能を果たす間に、いくつかの関連した構造の間を移動することがある。このような機能的転位の文脈において、これらの三次構造や四次構造は通常「コンフォーメーション」と呼ばれ、それらの間の遷移はコンフォーメーション変化と呼ばれる。このような変化は、酵素の活性部位、すなわち化学的触媒作用に関与するタンパク質の物理的領域に基質分子が結合することによって誘発されることが多い。溶液中では、タンパク質は熱振動や他の分子との衝突によっても構造が変化する。

タンパク質は非公式に3つの主要なクラスに分けることができる: 球状タンパク質、繊維状タンパク質、膜タンパク質である。ほとんどの球状タンパク質は可溶性であり、多くは酵素である。繊維状タンパク質は、結合組織の主成分であるコラーゲンや、髪や爪のタンパク質成分であるケラチンなど、構造的なタンパク質であることが多い。膜タンパク質は、しばしばレセプターとして機能したり、極性分子や荷電分子が細胞膜を通過するためのチャネルを提供したりする。
タンパク質内の分子内水素結合の特殊な例として、水からの攻撃を受けにくく、それゆえに自身の脱水を促進する、デヒドロンと呼ばれるものがある。
タンパク質ドメイン
多くのタンパク質はいくつかのタンパク質ドメインから構成されている。ドメインは通常、酵素的活性(例えば、キナーゼ)などの特定の機能も持つか、結合モジュール(例えば、SH3ドメインは他のタンパク質のプロリンに富んだ配列に結合する)として機能する。
配列モチーフ
タンパク質内の短いアミノ酸配列は、しばしば他のタンパク質の認識部位として働く。例えば、SH3ドメインは通常、短いPxxPモチーフ(すなわち、2つのプロリン[P]と2つの不特定のアミノ酸[x]で隔てられているが、周囲のアミノ酸が正確な結合特異性を決定するかもしれない)に結合する。このようなモチーフは真核生物の線形モチーフ(ELM)データベースに多数収集されている。
===タンパク質のトポロジー タンパク質のトポロジーは、骨格のもつれや折り畳まれた鎖内の接点の配置を記述する。タンパク質のトポロジーを特徴付けるために、結び目理論と回路トポロジーの2つの理論的枠組みが適用されている。タンパク質のトポロジーを記述できるようになることで、タンパク質工学や医薬品開発に新たな道が開かれ、神経筋疾患やがんなどのタンパク質のミスフォールディング疾患に対する理解が深まる。
細胞機能
タンパク質は細胞内の主役であり、遺伝子にコードされた情報によって指定された任務を遂行していると言われている。ある種のRNAを除いて、他のほとんどの生体分子はタンパク質が作用する比較的不活性な要素である。タンパク質は、大腸菌細胞の乾燥重量の半分を占めるが、DNAやRNAのような他の高分子はそれぞれ3%と20%に過ぎない。特定の細胞や細胞型で発現するタンパク質の集合は、そのプロテオームとして知られている。

タンパク質の最大の特徴は、他の分子と特異的かつ強固に結合できることである。他の分子と結合するタンパク質の領域は結合部位と呼ばれ、多くの場合、分子表面の窪みや「ポケット」である。この結合能力は、結合部位ポケットを規定するタンパク質の三次構造と、周囲のアミノ酸側鎖の化学的性質によって媒介される。例えば、リボヌクレアーゼ阻害剤タンパク質はヒトのアンジオジェニンとはフェムトモル以下の解離定数(<10-15 M)で結合するが、両生類のホモログであるオンコナーゼ(>1 M)とは全く結合しない。例えば、アミノ酸バリンに特異的なアミノアシルtRNA合成酵素は、アミノ酸イソロイシンの非常によく似た側鎖を識別する。
タンパク質は低分子基質だけでなく、他のタンパク質とも結合することができる。タンパク質が同じ分子の他のコピーと特異的に結合すると、オリゴマー化して線維を形成することができる。この過程は、自己会合して硬い線維を形成する球状モノマーからなる構造タンパク質でしばしば起こる。タンパク質-タンパク質相互作用はまた、酵素活性を調節し、細胞周期の進行を制御し、共通の生物学的機能を持つ多くの密接に関連した反応を実行する大きなタンパク質複合体の集合を可能にする。タンパク質はまた、細胞膜に結合したり、細胞膜に組み込まれたりすることもある。結合パートナーはタンパク質の構造変化を引き起こすことができるため、非常に複雑なシグナル伝達ネットワークを構築することができる。 タンパク質間の相互作用は可逆的であり、個別の機能を実行することができる凝集体を形成するために、異なるグループのパートナータンパク質が利用できるかどうかに大きく依存するため、特定のタンパク質間の相互作用を研究することは、細胞機能の重要な側面、ひいては特定の細胞タイプを区別する特性を理解するための鍵となる。
酵素
細胞内におけるタンパク質の最もよく知られた役割は、化学反応を触媒する酵素としての役割である。酵素は通常、非常に特異的であり、1つまたは少数の化学反応のみを促進する。酵素は代謝に関わる反応のほとんどを行うだけでなく、DNA複製、DNA修復、転写などの過程でDNAを操作する。一部の酵素は、翻訳後修飾として知られるプロセスにおいて、他のタンパク質に作用して化学基を付加したり除去したりする。約4,000の反応が酵素によって触媒されることが知られている。酵素触媒作用によってもたらされる反応速度の加速は、しばしば莫大なものであり、オロチン酸脱炭酸酵素の場合、触媒作用のない反応に比べて1017倍の速度増加が見られる(酵素なしでは7800万年、酵素ありでは18ミリ秒)。
酵素が結合し作用する分子はSubstrate (biochemistry)/ja基質と呼ばれる。酵素は何百ものアミノ酸から構成されることがあるが、通常、基質と接触する残基はごく一部であり、触媒反応に直接関与する残基はさらにごく一部である。 基質と結合し、触媒残基を含む酵素の領域は活性部位として知られている。
ディリゲントタンパク質は、他の酵素によって合成された化合物の立体化学を決定するタンパク質の一種である。
細胞シグナル伝達とリガンド結合

多くのタンパク質が細胞シグナル伝達やシグナル伝達の過程に関与している。インスリンのようないくつかのタンパク質は、それが合成された細胞から離れた組織の他の細胞にシグナルを伝達する細胞外タンパク質である。他のものは膜タンパク質で、レセプターとして働き、その主な機能はシグナル伝達分子と結合して細胞内の生化学的反応を誘導することである。多くのレセプターは、細胞表面に露出した結合部位と細胞内のエフェクタードメインを持ち、酵素活性を持つこともあれば、細胞内の他のタンパク質によって検出される構造変化を起こすこともある。
抗体は適応免疫系のタンパク質成分であり、その主な機能は抗原、すなわち体内の異物と結合し、破壊の対象とすることである。抗体は細胞外環境に分泌されるか、形質細胞として知られる特殊なB細胞の膜に固定される。酵素が反応を行う必要性から基質との結合親和性に制約があるのに対し、抗体にはそのような制約はない。抗体の標的に対する結合親和性は非常に高い。
多くのリガンド輸送タンパク質は、特定の|低分子生体分子と結合し、多細胞生物の体内の別の場所に輸送する。これらのタンパク質は、リガンドが高濃度で存在するときには高い結合親和性を持たなければならないが、標的組織中に低濃度で存在するときにはリガンドを放出しなければならない。リガンド結合タンパク質の典型例はヘモグロビンであり、すべての脊椎動物の肺から他の臓器や組織に酸素を輸送する。レクチンは糖結合タンパク質であり、その糖鎖部分に非常に特異的である。レクチンは通常、細胞やタンパク質が関与する生物学的な認識現象において役割を果たす。受容体やホルモンは特異性の高い結合タンパク質である。
Transmembrane proteins can also serve as ligand transport proteins that alter the permeability of the cell membrane to small molecules and ions. The membrane alone has a hydrophobic core through which polar or charged molecules cannot diffuse. Membrane proteins contain internal channels that allow such molecules to enter and exit the cell. Many ion channel proteins are specialized to select for only a particular ion; for example, potassium and sodium channels often discriminate for only one of the two ions.
構造タンパク質
Structural proteins confer stiffness and rigidity to otherwise-fluid biological components. Most structural proteins are fibrous proteins; for example, collagen and elastin are critical components of connective tissue such as cartilage, and keratin is found in hard or filamentous structures such as hair, nails, feathers, hooves, and some animal shells. Some globular proteins can also play structural functions, for example, actin and tubulin are globular and soluble as monomers, but polymerize to form long, stiff fibers that make up the cytoskeleton, which allows the cell to maintain its shape and size.
Other proteins that serve structural functions are motor proteins such as myosin, kinesin, and dynein, which are capable of generating mechanical forces. These proteins are crucial for cellular motility of single celled organisms and the sperm of many multicellular organisms which reproduce sexually. They also generate the forces exerted by contracting muscles and play essential roles in intracellular transport.
Protein evolution
A key question in molecular biology is how proteins evolve, i.e. how can mutations (or rather changes in amino acid sequence) lead to new structures and functions? Most amino acids in a protein can be changed without disrupting activity or function, as can be seen from numerous homologous proteins across species (as collected in specialized databases for protein families, e.g. PFAM). In order to prevent dramatic consequences of mutations, a gene may be duplicated before it can mutate freely. However, this can also lead to complete loss of gene function and thus pseudo-genes. More commonly, single amino acid changes have limited consequences although some can change protein function substantially, especially in enzymes. For instance, many enzymes can change their substrate specificity by one or a few mutations. Changes in substrate specificity are facilitated by substrate promiscuity, i.e. the ability of many enzymes to bind and process multiple substrates. When mutations occur, the specificity of an enzyme can increase (or decrease) and thus its enzymatic activity. Thus, bacteria (or other organisms) can adapt to different food sources, including unnatural substrates such as plastic.
Methods of study
The activities and structures of proteins may be examined in vitro, in vivo, and in silico. In vitro studies of purified proteins in controlled environments are useful for learning how a protein carries out its function: for example, enzyme kinetics studies explore the chemical mechanism of an enzyme's catalytic activity and its relative affinity for various possible substrate molecules. By contrast, in vivo experiments can provide information about the physiological role of a protein in the context of a cell or even a whole organism. In silico studies use computational methods to study proteins.
Protein purification
To perform in vitro analysis, a protein must be purified away from other cellular components. This process usually begins with cell lysis, in which a cell's membrane is disrupted and its internal contents released into a solution known as a crude lysate. The resulting mixture can be purified using ultracentrifugation, which fractionates the various cellular components into fractions containing soluble proteins; membrane lipids and proteins; cellular organelles, and nucleic acids. Precipitation by a method known as salting out can concentrate the proteins from this lysate. Various types of chromatography are then used to isolate the protein or proteins of interest based on properties such as molecular weight, net charge and binding affinity. The level of purification can be monitored using various types of gel electrophoresis if the desired protein's molecular weight and isoelectric point are known, by spectroscopy if the protein has distinguishable spectroscopic features, or by enzyme assays if the protein has enzymatic activity. Additionally, proteins can be isolated according to their charge using electrofocusing.
For natural proteins, a series of purification steps may be necessary to obtain protein sufficiently pure for laboratory applications. To simplify this process, genetic engineering is often used to add chemical features to proteins that make them easier to purify without affecting their structure or activity. Here, a "tag" consisting of a specific amino acid sequence, often a series of histidine residues (a "His-tag"), is attached to one terminus of the protein. As a result, when the lysate is passed over a chromatography column containing nickel, the histidine residues ligate the nickel and attach to the column while the untagged components of the lysate pass unimpeded. A number of different tags have been developed to help researchers purify specific proteins from complex mixtures.
Cellular localization

The study of proteins in vivo is often concerned with the synthesis and localization of the protein within the cell. Although many intracellular proteins are synthesized in the cytoplasm and membrane-bound or secreted proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, the specifics of how proteins are targeted to specific organelles or cellular structures is often unclear. A useful technique for assessing cellular localization uses genetic engineering to express in a cell a fusion protein or chimera consisting of the natural protein of interest linked to a "reporter" such as green fluorescent protein (GFP). The fused protein's position within the cell can then be cleanly and efficiently visualized using microscopy, as shown in the figure opposite.
Other methods for elucidating the cellular location of proteins requires the use of known compartmental markers for regions such as the ER, the Golgi, lysosomes or vacuoles, mitochondria, chloroplasts, plasma membrane, etc. With the use of fluorescently tagged versions of these markers or of antibodies to known markers, it becomes much simpler to identify the localization of a protein of interest. For example, indirect immunofluorescence will allow for fluorescence colocalization and demonstration of location. Fluorescent dyes are used to label cellular compartments for a similar purpose.
Other possibilities exist, as well. For example, immunohistochemistry usually uses an antibody to one or more proteins of interest that are conjugated to enzymes yielding either luminescent or chromogenic signals that can be compared between samples, allowing for localization information. Another applicable technique is cofractionation in sucrose (or other material) gradients using isopycnic centrifugation. While this technique does not prove colocalization of a compartment of known density and the protein of interest, it does increase the likelihood, and is more amenable to large-scale studies.
Finally, the gold-standard method of cellular localization is immunoelectron microscopy. This technique also uses an antibody to the protein of interest, along with classical electron microscopy techniques. The sample is prepared for normal electron microscopic examination, and then treated with an antibody to the protein of interest that is conjugated to an extremely electro-dense material, usually gold. This allows for the localization of both ultrastructural details as well as the protein of interest.
Through another genetic engineering application known as site-directed mutagenesis, researchers can alter the protein sequence and hence its structure, cellular localization, and susceptibility to regulation. This technique even allows the incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins, using modified tRNAs, and may allow the rational design of new proteins with novel properties.
Proteomics
The total complement of proteins present at a time in a cell or cell type is known as its proteome, and the study of such large-scale data sets defines the field of proteomics, named by analogy to the related field of genomics. Key experimental techniques in proteomics include 2D electrophoresis, which allows the separation of many proteins, mass spectrometry, which allows rapid high-throughput identification of proteins and sequencing of peptides (most often after in-gel digestion), protein microarrays, which allow the detection of the relative levels of the various proteins present in a cell, and two-hybrid screening, which allows the systematic exploration of protein–protein interactions. The total complement of biologically possible such interactions is known as the interactome. A systematic attempt to determine the structures of proteins representing every possible fold is known as structural genomics.
Structure determination
Discovering the tertiary structure of a protein, or the quaternary structure of its complexes, can provide important clues about how the protein performs its function and how it can be affected, i.e. in drug design. As proteins are too small to be seen under a light microscope, other methods have to be employed to determine their structure. Common experimental methods include X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy, both of which can produce structural information at atomic resolution. However, NMR experiments are able to provide information from which a subset of distances between pairs of atoms can be estimated, and the final possible conformations for a protein are determined by solving a distance geometry problem. Dual polarisation interferometry is a quantitative analytical method for measuring the overall protein conformation and conformational changes due to interactions or other stimulus. Circular dichroism is another laboratory technique for determining internal β-sheet / α-helical composition of proteins. Cryoelectron microscopy is used to produce lower-resolution structural information about very large protein complexes, including assembled viruses; a variant known as electron crystallography can also produce high-resolution information in some cases, especially for two-dimensional crystals of membrane proteins. Solved structures are usually deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), a freely available resource from which structural data about thousands of proteins can be obtained in the form of Cartesian coordinates for each atom in the protein.
Many more gene sequences are known than protein structures. Further, the set of solved structures is biased toward proteins that can be easily subjected to the conditions required in X-ray crystallography, one of the major structure determination methods. In particular, globular proteins are comparatively easy to crystallize in preparation for X-ray crystallography. Membrane proteins and large protein complexes, by contrast, are difficult to crystallize and are underrepresented in the PDB. Structural genomics initiatives have attempted to remedy these deficiencies by systematically solving representative structures of major fold classes. Protein structure prediction methods attempt to provide a means of generating a plausible structure for proteins whose structures have not been experimentally determined.
Structure prediction

Complementary to the field of structural genomics, protein structure prediction develops efficient mathematical models of proteins to computationally predict the molecular formations in theory, instead of detecting structures with laboratory observation. The most successful type of structure prediction, known as homology modeling, relies on the existence of a "template" structure with sequence similarity to the protein being modeled; structural genomics' goal is to provide sufficient representation in solved structures to model most of those that remain. Although producing accurate models remains a challenge when only distantly related template structures are available, it has been suggested that sequence alignment is the bottleneck in this process, as quite accurate models can be produced if a "perfect" sequence alignment is known. Many structure prediction methods have served to inform the emerging field of protein engineering, in which novel protein folds have already been designed. Also proteins (in eukaryotes ~33%) contain large unstructured but biologically functional segments and can be classified as intrinsically disordered proteins. Predicting and analysing protein disorder is, therefore, an important part of protein structure characterisation.
Bioinformatics
A vast array of computational methods have been developed to analyze the structure, function and evolution of proteins. The development of such tools has been driven by the large amount of genomic and proteomic data available for a variety of organisms, including the human genome. It is simply impossible to study all proteins experimentally, hence only a few are subjected to laboratory experiments while computational tools are used to extrapolate to similar proteins. Such homologous proteins can be efficiently identified in distantly related organisms by sequence alignment. Genome and gene sequences can be searched by a variety of tools for certain properties. Sequence profiling tools can find restriction enzyme sites, open reading frames in nucleotide sequences, and predict secondary structures. Phylogenetic trees can be constructed and evolutionary hypotheses developed using special software like ClustalW regarding the ancestry of modern organisms and the genes they express. The field of bioinformatics is now indispensable for the analysis of genes and proteins.
動的過程のインシリコシミュレーション
A more complex computational problem is the prediction of intermolecular interactions, such as in molecular docking, protein folding, protein–protein interaction and chemical reactivity. Mathematical models to simulate these dynamical processes involve molecular mechanics, in particular, molecular dynamics. In this regard, in silico simulations discovered the folding of small α-helical protein domains such as the villin headpiece, the HIV accessory protein and hybrid methods combining standard molecular dynamics with quantum mechanical mathematics have explored the electronic states of rhodopsins.
Beyond classical molecular dynamics, quantum dynamics methods allow the simulation of proteins in atomistic detail with an accurate description of quantum mechanical effects. Examples include the multi-layer multi-configuration time-dependent Hartree (MCTDH) method and the hierarchical equations of motion (HEOM) approach, which have been applied to plant cryptochromes and bacteria light-harvesting complexes, respectively. Both quantum and classical mechanical simulations of biological-scale systems are extremely computationally demanding, so distributed computing initiatives (for example, the Folding@home project) facilitate the molecular modeling by exploiting advances in GPU parallel processing and Monte Carlo techniques.
化学分析
The total nitrogen content of organic matter is mainly formed by the amino groups in proteins. The Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) is a measure of nitrogen widely used in the analysis of (waste) water, soil, food, feed and organic matter in general. As the name suggests, the Kjeldahl method is applied. More sensitive methods are available.
Nutrition
Most microorganisms and plants can biosynthesize all 20 standard amino acids, while animals (including humans) must obtain some of the amino acids from the diet. The amino acids that an organism cannot synthesize on its own are referred to as essential amino acids. Key enzymes that synthesize certain amino acids are not present in animals—such as aspartokinase, which catalyses the first step in the synthesis of lysine, methionine, and threonine from aspartate. If amino acids are present in the environment, microorganisms can conserve energy by taking up the amino acids from their surroundings and downregulating their biosynthetic pathways.
動物では、アミノ酸はタンパク質を含む食物を摂取することで得られる。摂取されたタンパク質は消化によってアミノ酸に分解されるが、この消化には通常、酸にさらされることによるタンパク質の変性と、プロテアーゼと呼ばれる酵素による加水分解が含まれる。摂取されたアミノ酸の一部はタンパク質の生合成に使われ、他のアミノ酸は糖新生によってグルコースに変換されるか、クエン酸サイクルに供給される。このようにタンパク質を燃料として利用することは、飢餓状態において特に重要である。特に筋肉に含まれるタンパク質がそうである。
犬や猫などの動物では、タンパク質は毛包の成長と角化を促進することで皮膚の健康と質を維持し、悪臭を発生させる皮膚トラブルの可能性を減らす。質の悪いタンパク質は胃腸の健康にも関与し、犬の鼓腸や悪臭の可能性を高める。タンパク質が未消化の状態で大腸に到達すると、発酵して硫化水素ガス、インドール、スカトールが発生するからだ。犬や猫の動物性タンパク質は植物性タンパク質よりも消化が良いが、低品質の動物性タンパク質は消化が悪く、皮膚、羽毛、結合組織などが含まれる。
こちらも参照
さらに読む
- 教科書
- Branden C, Tooze J (1999). Introduction to Protein Structure. New York: Garland Pub. ISBN 978-0-8153-2305-1.
- Murray RF, Harper HW, Granner DK, Mayes PA, Rodwell VW (2006). Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-146197-9.
- Van Holde KE, Mathews CK (1996). Biochemistry. Menlo Park, California: Benjamin/Cummings Pub. Co., Inc. ISBN 978-0-8053-3931-4.
外部リンク
データベースとプロジェクト
- NCBI Entrez Protein database
- NCBI Protein Structure database
- Human Protein Reference Database
- Human Proteinpedia
- Folding@Home (Stanford University) Archived 2012-09-08 at the Wayback Machine
- Protein Databank in Europe (see also PDBeQuips, short articles and tutorials on interesting PDB structures)
- Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (see also Molecule of the Month Archived 2020-07-24 at the Wayback Machine, presenting short accounts on selected proteins from the PDB)
- Proteopedia – Life in 3D: rotatable, zoomable 3D model with wiki annotations for every known protein molecular structure.
- UniProt the Universal Protein Resource
チュートリアルと教育ウェブサイト
- "An Introduction to Proteins" from HOPES (Huntington's Disease Outreach Project for Education at Stanford)
- Proteins: Biogenesis to Degradation – The Virtual Library of Biochemistry and Cell Biology