Protein/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "ほとんどのタンパク質は、最大20種類の<small>L</small>-α-アミノ酸からなる直鎖状のポリマーから構成されている。すべてのタンパク質性アミノ酸は、α-炭素にアミノ基、カルボキシル基、および可変の側鎖が|結合してい..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "ペプチド結合には2つの共鳴形があり、二重結合の性質を助長し、軸周りの回転を抑制するので、α炭素はほぼコプラナーになる。ペプチド結合の他の2つの二面角は、タンパク質の骨格の局所的な形状を決定する。遊離アミノ基を持つ末端はN末端またはアミノ末端として知られ..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
ポリペプチド鎖のアミノ酸は[[peptide bond/ja|ペプチド結合]]によって結合している。タンパク質鎖に連結された個々のアミノ酸は''残基''と呼ばれ、連結された一連の炭素、窒素、酸素原子は''主鎖''または''タンパク質骨格''と呼ばれる。 | ポリペプチド鎖のアミノ酸は[[peptide bond/ja|ペプチド結合]]によって結合している。タンパク質鎖に連結された個々のアミノ酸は''残基''と呼ばれ、連結された一連の炭素、窒素、酸素原子は''主鎖''または''タンパク質骨格''と呼ばれる。 | ||
ペプチド結合には2つの[[resonance (chemistry)/ja|共鳴]]形があり、[[double-bond/ja|二重結合]]の性質を助長し、軸周りの回転を抑制するので、α炭素はほぼ[[coplanar/ja|コプラナー]]になる。ペプチド結合の他の2つの[[dihedral angle/ja|二面角]]は、タンパク質の骨格の局所的な形状を決定する。遊離アミノ基を持つ末端は[[N-terminus/ja|N末端]]またはアミノ末端として知られ、遊離カルボキシル基を持つタンパク質の末端は[[C-terminus/ja|C末端]]またはカルボキシ末端として知られる(タンパク質の配列はN末端からC末端まで、左から右に書かれる)。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 21:25, 23 February 2024

タンパク質は、アミノ酸残基の1本以上の長い鎖からなる大きな大きな生体分子であり、高分子である。タンパク質は、代謝反応の触媒、DNA複製、刺激への応答、細胞への構造および生物の提供、およびある場所から別の場所への分子の輸送など、生物内で膨大な機能を果たす。タンパク質は主にアミノ酸の配列において互いに異なっており、それは遺伝子のヌクレオチド配列によって決定され、その結果、通常、タンパク質はその活性を決定する特定の3次元構造に折り畳まれる。
アミノ酸残基の直鎖をポリペプチドと呼ぶ。タンパク質は少なくとも1つの長いポリペプチドを含む。20-30残基以下の短いポリペプチドはタンパク質とみなされることはほとんどなく、一般にペプチドと呼ばれる。個々のアミノ酸残基はペプチド結合と隣接するアミノ酸残基によって結合されている。タンパク質中のアミノ酸残基の配列は、遺伝暗号にコードされた遺伝子の配列によって定義される。一般的に、遺伝暗号は20の標準アミノ酸を規定しているが、ある種の生物では遺伝暗号にセレノシステインや、ある種のarchaea/ja古細菌ではピロリジンが含まれることがある。合成後まもなく、あるいは合成中であっても、タンパク質中の残基はしばしば翻訳後修飾によって化学的に修飾される。タンパク質の中には、補欠基または補因子と呼ばれる、ペプチド以外の基が結合しているものもある。タンパク質はまた、特定の機能を達成するために協働することができ、しばしば会合して安定したタンパク質複合体を形成する。
一度形成されたタンパク質は一定期間しか存在せず、その後分解され、タンパク質のターンオーバーのプロセスを通じて細胞の機械によって再利用される。タンパク質の寿命は半減期で測定され、その範囲は広い。哺乳類の細胞では平均寿命は1〜2日で、数分間存在することもあれば数年間存在することもある。異常なタンパク質や誤った折り畳み方をしたタンパク質は、破壊の対象となるためか、不安定であるためか、より急速に分解される。
タンパク質は、多糖類や核酸などの他の生体高分子と同様に、生物にとって不可欠な部分であり、細胞内のほぼすべてのプロセスに関与している。多くのタンパク質は生化学反応を触媒する酵素であり、代謝に不可欠である。タンパク質はまた、構造的あるいは機械的な機能も持っている。例えば、筋肉のアクチンとミオシン、細胞の形を維持する足場のシステムを形成する細胞骨格のタンパク質などである。その他のタンパク質は、細胞シグナル伝達、免疫応答、細胞接着、細胞周期において重要である。動物では、タンパク質は合成できない必須アミノ酸を供給するためにダイエットに必要である。消化によってタンパク質は分解され、代謝に利用される。
タンパク質は、超遠心分離、沈殿、電気泳動、クロマトグラフィーなどの様々な技術を用いて、他の細胞成分から精製することができる。タンパク質の構造と機能を研究するために一般的に用いられる方法には、免疫組織化学、部位特異的突然変異誘発、X線結晶構造解析、核磁気共鳴、質量分析などがある。
歴史と語源
タンパク質は18世紀にAntoine Fourcroyらによって生物学的分子の別個のクラスとして認識され、熱や酸による処理下で凝固または凝集する分子の能力によって区別された。当時の有名な例としては、卵白のアルブミン、血液の血清アルブミン、フィブリン、小麦のグルテンなどが挙げられる。
タンパク質は1838年にオランダの化学者Gerardus Johannes Mulderによって初めて記述され、スウェーデンの化学者Jöns Jacob Berzeliusによって命名された。Mulderは一般的なタンパク質の元素分析を行い、ほぼすべてのタンパク質が同じ実験式、C400H620N100O120P1S1を持っていることを発見した。彼は、タンパク質は1種類の(非常に大きな)分子で構成されているのではないかという誤った結論に達した。これらの分子を表す「タンパク質」という用語は、Mulderの同僚であるBerzeliusによって提案された。タンパク質はギリシア語のπρώτειοςに由来する。(proteios)、「第一の」、「先頭に立つ」、「前に立つ」を意味し、-inに由来する。Mulderはさらに、アミノ酸などのタンパク質分解産物を特定した。ロイシンの分子量は131Daであった。「タンパク質」以前には、「アルブミン」や「アルブミン質」(ドイツ語では「Eiweisskörper」)といった別の名称が使われていた。
ドイツのカール・フォン・ヴォイトのような初期の栄養学者は、"肉は肉を作る"と一般的に信じられていたため、タンパク質が身体の構造を維持するために最も重要な栄養素であると信じていた。カール・ハインリッヒ・リトハウゼンは、グルタミン酸の同定によって、既知のタンパク質の形態を拡張した。コネチカット農業試験場で、植物性タンパク質の詳細なレビューがトーマス・バー・オズボーンによってまとめられた。ラファイエット・メンデルと協力し、実験用ラットの摂食にリービッヒの最小の法則を適用して、栄養学的に必須アミノ酸が確立された。この研究はウィリアム・カミング・ローズによって継続され、伝えられた。1902年、フランツ・ホフマイスターとヘルマン・エミール・フィッシャーの研究によって、ポリペプチドとしてのタンパク質が理解された。生物における酵素としてのタンパク質の中心的役割は、1926年にジェームズ・B・サムナーがウレアーゼという酵素が実際にタンパク質であることを示すまで、完全には理解されなかった。
タンパク質を大量に精製することは困難であったため、初期のタンパク質生化学者にとっては、非常に研究しにくいものであった。従って、初期の研究は、大量に精製できるタンパク質、例えば、血液、卵白、様々な毒素、食肉処理場から得られる消化・代謝酵素に焦点を当てた。1950年代、アーマー・ホットドッグ社は1 kgの純粋なウシ膵臓リボヌクレアーゼAを精製し、科学者が自由に利用できるようにした。このジェスチャーによって、リボヌクレアーゼAはその後数十年間、生化学研究の主要なターゲットとなった。
ライナス・ポーリングは、1933年にウィリアム・アストベリーによって初めて提唱された水素結合に基づく規則的なタンパク質の二次構造の予測に成功したことで知られている。その後、ウォルター・カウズマンによる変性に関する研究は、カイ・ウリンデルストローム=ラングによる以前の研究を部分的に基にしたものであり、疎水性相互作用によって媒介されるタンパク質の折り畳みと構造の理解に貢献した。
最初に配列されたタンパク質は、1949年、フレデリック・サンガーによるインスリンであった。サンガーはインスリンのアミノ酸配列を正確に決定し、タンパク質が分岐鎖、コロイド、シクロールではなく、アミノ酸の直鎖ポリマーから構成されていることを決定的に証明した。1958年、彼はこの功績によりノーベル賞を受賞した。

X線結晶学の発展により、タンパク質の構造配列を決定することが可能になった。最初にタンパク質構造が解明されたのは、1958年のマックス・ペルッツによるヘモグロビンとジョン・ケンドリューによるミオグロビンであった。コンピュータの使用と計算能力の向上も、複雑なタンパク質の配列決定を支えた。1999年、ロジャー・コーンバーグはシンクロトロンからの高強度X線を用いてRNAポリメラーゼの非常に複雑な構造の配列決定に成功した。
それ以来、大きな高分子集合体のクライオ電子顕微鏡(クライオEM)が開発された。クライオ電子顕微鏡は、結晶ではなく凍結したタンパク質サンプルを用い、X線ではなく電子ビームを用いる。試料へのダメージが少ないため、科学者はより多くの情報を得ることができ、より大きな構造を解析することができる。小さなタンパク質のドメインの計算によるタンパク質構造予測も、研究者がタンパク質構造の原子レベルの分解能に近づくのに役立っている。 2017年現在、プロテインデータバンクには126,060以上の原子分解能のタンパク質構造が登録されている。
ゲノムにコードされるタンパク質の数
ゲノムにコードされているタンパク質の数は、おおよそ遺伝子の数に対応する(ただし、タンパク質のRNAをコードする遺伝子、例えばリボソームRNAの数もかなり多いかもしれない)。ウイルスは通常数個から数百個、古細菌やバクテリアは数百個から数千個、真核生物は通常数千個から数万個のタンパク質をコードしている(例についてはゲノムサイズを参照)。
分類
タンパク質は主に配列と構造によって分類されるが、その他の分類も一般的に用いられている。特に酵素については、EC番号システムが機能的な分類スキームを提供している。同様に、Gene Ontology/ja遺伝子オントロジーでは、遺伝子とタンパク質の両方を生物学的・生化学的機能によって分類しているが、細胞内の位置によっても分類している。
配列の類似性は、進化的類似性と機能的類似性の両方の観点からタンパク質を分類するために使用される。特にマルチドメインタンパク質では、タンパク質全体またはタンパク質ドメインのいずれかを使用することができる。タンパク質ドメインは、配列、構造、機能の組み合わせによるタンパク質の分類を可能にし、それらは多くの異なる方法で組み合わせることができる。17万個のタンパク質を対象とした初期の研究では、約3分の2のタンパク質に少なくとも1つのドメインが割り当てられ、より大きなタンパク質ほど多くのドメインを含んでいた(例えば、600アミノ酸以上のタンパク質は平均5つ以上のドメインを持つ)。
生化学


ほとんどのタンパク質は、最大20種類のL-α-アミノ酸からなる直鎖状のポリマーから構成されている。すべてのタンパク質性アミノ酸は、α-炭素にアミノ基、カルボキシル基、および可変の側鎖が|結合しているα-炭素を含む共通の構造的特徴を持っている。プロリンだけはこの基本構造とは異なり、N末端のアミン基に変わった環を持ち、CO-NHアミド部分を固定したコンフォメーションにする。標準アミノ酸の側鎖は、標準アミノ酸リストに詳述されているが、実に多様な化学構造と性質を持っている。タンパク質の立体構造と化学反応性を最終的に決定するのは、タンパク質中のアミノ酸側鎖すべての複合効果である。 ポリペプチド鎖のアミノ酸はペプチド結合によって結合している。タンパク質鎖に連結された個々のアミノ酸は残基と呼ばれ、連結された一連の炭素、窒素、酸素原子は主鎖またはタンパク質骨格と呼ばれる。
ペプチド結合には2つの共鳴形があり、二重結合の性質を助長し、軸周りの回転を抑制するので、α炭素はほぼコプラナーになる。ペプチド結合の他の2つの二面角は、タンパク質の骨格の局所的な形状を決定する。遊離アミノ基を持つ末端はN末端またはアミノ末端として知られ、遊離カルボキシル基を持つタンパク質の末端はC末端またはカルボキシ末端として知られる(タンパク質の配列はN末端からC末端まで、左から右に書かれる)。
The words protein, polypeptide, and peptide are a little ambiguous and can overlap in meaning. Protein is generally used to refer to the complete biological molecule in a stable conformation, whereas peptide is generally reserved for a short amino acid oligomers often lacking a stable 3D structure. But the boundary between the two is not well defined and usually lies near 20–30 residues. Polypeptide can refer to any single linear chain of amino acids, usually regardless of length, but often implies an absence of a defined conformation.
Interactions
Proteins can interact with many types of molecules, including with other proteins, with lipids, with carbohydrates, and with DNA.
Abundance in cells
It has been estimated that average-sized bacteria contain about 2 million proteins per cell (e.g. E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus). Smaller bacteria, such as Mycoplasma or spirochetes contain fewer molecules, on the order of 50,000 to 1 million. By contrast, eukaryotic cells are larger and thus contain much more protein. For instance, yeast cells have been estimated to contain about 50 million proteins and human cells on the order of 1 to 3 billion. The concentration of individual protein copies ranges from a few molecules per cell up to 20 million. Not all genes coding proteins are expressed in most cells and their number depends on, for example, cell type and external stimuli. For instance, of the 20,000 or so proteins encoded by the human genome, only 6,000 are detected in lymphoblastoid cells.
合成
Biosynthesis
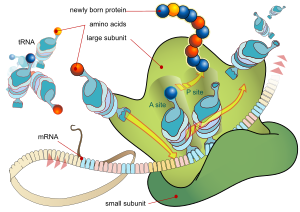

Proteins are assembled from amino acids using information encoded in genes. Each protein has its own unique amino acid sequence that is specified by the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding this protein. The genetic code is a set of three-nucleotide sets called codons and each three-nucleotide combination designates an amino acid, for example AUG (adenine–uracil–guanine) is the code for methionine. Because DNA contains four nucleotides, the total number of possible codons is 64; hence, there is some redundancy in the genetic code, with some amino acids specified by more than one codon. Genes encoded in DNA are first transcribed into pre-messenger RNA (mRNA) by proteins such as RNA polymerase. Most organisms then process the pre-mRNA (also known as a primary transcript) using various forms of post-transcriptional modification to form the mature mRNA, which is then used as a template for protein synthesis by the ribosome. In prokaryotes the mRNA may either be used as soon as it is produced, or be bound by a ribosome after having moved away from the nucleoid. In contrast, eukaryotes make mRNA in the cell nucleus and then translocate it across the nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis then takes place. The rate of protein synthesis is higher in prokaryotes than eukaryotes and can reach up to 20 amino acids per second.
The process of synthesizing a protein from an mRNA template is known as translation. The mRNA is loaded onto the ribosome and is read three nucleotides at a time by matching each codon to its base pairing anticodon located on a transfer RNA molecule, which carries the amino acid corresponding to the codon it recognizes. The enzyme aminoacyl tRNA synthetase "charges" the tRNA molecules with the correct amino acids. The growing polypeptide is often termed the nascent chain. Proteins are always biosynthesized from N-terminus to C-terminus.
The size of a synthesized protein can be measured by the number of amino acids it contains and by its total molecular mass, which is normally reported in units of daltons (synonymous with atomic mass units), or the derivative unit kilodalton (kDa). The average size of a protein increases from Archaea to Bacteria to Eukaryote (283, 311, 438 residues and 31, 34, 49 kDa respectively) due to a bigger number of protein domains constituting proteins in higher organisms. For instance, yeast proteins are on average 466 amino acids long and 53 kDa in mass. The largest known proteins are the titins, a component of the muscle sarcomere, with a molecular mass of almost 3,000 kDa and a total length of almost 27,000 amino acids.
Chemical synthesis
Short proteins can also be synthesized chemically by a family of methods known as peptide synthesis, which rely on organic synthesis techniques such as chemical ligation to produce peptides in high yield. Chemical synthesis allows for the introduction of non-natural amino acids into polypeptide chains, such as attachment of fluorescent probes to amino acid side chains. These methods are useful in laboratory biochemistry and cell biology, though generally not for commercial applications. Chemical synthesis is inefficient for polypeptides longer than about 300 amino acids, and the synthesized proteins may not readily assume their native tertiary structure. Most chemical synthesis methods proceed from C-terminus to N-terminus, opposite the biological reaction.
Structure

Most proteins fold into unique 3D structures. The shape into which a protein naturally folds is known as its native conformation. Although many proteins can fold unassisted, simply through the chemical properties of their amino acids, others require the aid of molecular chaperones to fold into their native states. Biochemists often refer to four distinct aspects of a protein's structure:
- Primary structure: the amino acid sequence. A protein is a polyamide.
- Secondary structure: regularly repeating local structures stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The most common examples are the α-helix, β-sheet and turns. Because secondary structures are local, many regions of different secondary structure can be present in the same protein molecule.
- Tertiary structure: the overall shape of a single protein molecule; the spatial relationship of the secondary structures to one another. Tertiary structure is generally stabilized by nonlocal interactions, most commonly the formation of a hydrophobic core, but also through salt bridges, hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds, and even post-translational modifications. The term "tertiary structure" is often used as synonymous with the term fold. The tertiary structure is what controls the basic function of the protein.
- Quaternary structure: the structure formed by several protein molecules (polypeptide chains), usually called protein subunits in this context, which function as a single protein complex.
- Quinary structure: the signatures of protein surface that organize the crowded cellular interior. Quinary structure is dependent on transient, yet essential, macromolecular interactions that occur inside living cells.
Proteins are not entirely rigid molecules. In addition to these levels of structure, proteins may shift between several related structures while they perform their functions. In the context of these functional rearrangements, these tertiary or quaternary structures are usually referred to as "conformations", and transitions between them are called conformational changes. Such changes are often induced by the binding of a substrate molecule to an enzyme's active site, or the physical region of the protein that participates in chemical catalysis. In solution, proteins also undergo variation in structure through thermal vibration and the collision with other molecules.

Proteins can be informally divided into three main classes, which correlate with typical tertiary structures: globular proteins, fibrous proteins, and membrane proteins. Almost all globular proteins are soluble and many are enzymes. Fibrous proteins are often structural, such as collagen, the major component of connective tissue, or keratin, the protein component of hair and nails. Membrane proteins often serve as receptors or provide channels for polar or charged molecules to pass through the cell membrane.
A special case of intramolecular hydrogen bonds within proteins, poorly shielded from water attack and hence promoting their own dehydration, are called dehydrons.
Protein domains
Many proteins are composed of several protein domains, i.e. segments of a protein that fold into distinct structural units. Domains usually also have specific functions, such as enzymatic activities (e.g. kinase) or they serve as binding modules (e.g. the SH3 domain binds to proline-rich sequences in other proteins).
Sequence motif
Short amino acid sequences within proteins often act as recognition sites for other proteins. For instance, SH3 domains typically bind to short PxxP motifs (i.e. 2 prolines [P], separated by two unspecified amino acids [x], although the surrounding amino acids may determine the exact binding specificity). Many such motifs has been collected in the Eukaryotic Linear Motif (ELM) database.
Protein topology
Topology of a protein describes the entanglement of the backbone and the arrangement of contacts within the folded chain. Two theoretical frameworks of knot theory and Circuit topology have been applied to characterise protein topology. Being able to describe protein topology opens up new pathways for protein engineering and pharmaceutical development, and adds to our understanding of protein misfolding diseases such as neuromuscular disorders and cancer.
細胞機能
Proteins are the chief actors within the cell, said to be carrying out the duties specified by the information encoded in genes. With the exception of certain types of RNA, most other biological molecules are relatively inert elements upon which proteins act. Proteins make up half the dry weight of an Escherichia coli cell, whereas other macromolecules such as DNA and RNA make up only 3% and 20%, respectively. The set of proteins expressed in a particular cell or cell type is known as its proteome.

The chief characteristic of proteins that also allows their diverse set of functions is their ability to bind other molecules specifically and tightly. The region of the protein responsible for binding another molecule is known as the binding site and is often a depression or "pocket" on the molecular surface. This binding ability is mediated by the tertiary structure of the protein, which defines the binding site pocket, and by the chemical properties of the surrounding amino acids' side chains. Protein binding can be extraordinarily tight and specific; for example, the ribonuclease inhibitor protein binds to human angiogenin with a sub-femtomolar dissociation constant (<10−15 M) but does not bind at all to its amphibian homolog onconase (>1 M). Extremely minor chemical changes such as the addition of a single methyl group to a binding partner can sometimes suffice to nearly eliminate binding; for example, the aminoacyl tRNA synthetase specific to the amino acid valine discriminates against the very similar side chain of the amino acid isoleucine.
Proteins can bind to other proteins as well as to small-molecule substrates. When proteins bind specifically to other copies of the same molecule, they can oligomerize to form fibrils; this process occurs often in structural proteins that consist of globular monomers that self-associate to form rigid fibers. Protein–protein interactions also regulate enzymatic activity, control progression through the cell cycle, and allow the assembly of large protein complexes that carry out many closely related reactions with a common biological function. Proteins can also bind to, or even be integrated into, cell membranes. The ability of binding partners to induce conformational changes in proteins allows the construction of enormously complex signaling networks. As interactions between proteins are reversible, and depend heavily on the availability of different groups of partner proteins to form aggregates that are capable to carry out discrete sets of function, study of the interactions between specific proteins is a key to understand important aspects of cellular function, and ultimately the properties that distinguish particular cell types.
Enzymes
The best-known role of proteins in the cell is as enzymes, which catalyse chemical reactions. Enzymes are usually highly specific and accelerate only one or a few chemical reactions. Enzymes carry out most of the reactions involved in metabolism, as well as manipulating DNA in processes such as DNA replication, DNA repair, and transcription. Some enzymes act on other proteins to add or remove chemical groups in a process known as posttranslational modification. About 4,000 reactions are known to be catalysed by enzymes. The rate acceleration conferred by enzymatic catalysis is often enormous—as much as 1017-fold increase in rate over the uncatalysed reaction in the case of orotate decarboxylase (78 million years without the enzyme, 18 milliseconds with the enzyme).
The molecules bound and acted upon by enzymes are called substrates. Although enzymes can consist of hundreds of amino acids, it is usually only a small fraction of the residues that come in contact with the substrate, and an even smaller fraction—three to four residues on average—that are directly involved in catalysis. The region of the enzyme that binds the substrate and contains the catalytic residues is known as the active site.
Dirigent proteins are members of a class of proteins that dictate the stereochemistry of a compound synthesized by other enzymes.
Cell signaling and ligand binding

Many proteins are involved in the process of cell signaling and signal transduction. Some proteins, such as insulin, are extracellular proteins that transmit a signal from the cell in which they were synthesized to other cells in distant tissues. Others are membrane proteins that act as receptors whose main function is to bind a signaling molecule and induce a biochemical response in the cell. Many receptors have a binding site exposed on the cell surface and an effector domain within the cell, which may have enzymatic activity or may undergo a conformational change detected by other proteins within the cell.
Antibodies are protein components of an adaptive immune system whose main function is to bind antigens, or foreign substances in the body, and target them for destruction. Antibodies can be secreted into the extracellular environment or anchored in the membranes of specialized B cells known as plasma cells. Whereas enzymes are limited in their binding affinity for their substrates by the necessity of conducting their reaction, antibodies have no such constraints. An antibody's binding affinity to its target is extraordinarily high.
Many ligand transport proteins bind particular small biomolecules and transport them to other locations in the body of a multicellular organism. These proteins must have a high binding affinity when their ligand is present in high concentrations, but must also release the ligand when it is present at low concentrations in the target tissues. The canonical example of a ligand-binding protein is haemoglobin, which transports oxygen from the lungs to other organs and tissues in all vertebrates and has close homologs in every biological kingdom. Lectins are sugar-binding proteins which are highly specific for their sugar moieties. Lectins typically play a role in biological recognition phenomena involving cells and proteins. Receptors and hormones are highly specific binding proteins.
Transmembrane proteins can also serve as ligand transport proteins that alter the permeability of the cell membrane to small molecules and ions. The membrane alone has a hydrophobic core through which polar or charged molecules cannot diffuse. Membrane proteins contain internal channels that allow such molecules to enter and exit the cell. Many ion channel proteins are specialized to select for only a particular ion; for example, potassium and sodium channels often discriminate for only one of the two ions.
構造タンパク質
Structural proteins confer stiffness and rigidity to otherwise-fluid biological components. Most structural proteins are fibrous proteins; for example, collagen and elastin are critical components of connective tissue such as cartilage, and keratin is found in hard or filamentous structures such as hair, nails, feathers, hooves, and some animal shells. Some globular proteins can also play structural functions, for example, actin and tubulin are globular and soluble as monomers, but polymerize to form long, stiff fibers that make up the cytoskeleton, which allows the cell to maintain its shape and size.
Other proteins that serve structural functions are motor proteins such as myosin, kinesin, and dynein, which are capable of generating mechanical forces. These proteins are crucial for cellular motility of single celled organisms and the sperm of many multicellular organisms which reproduce sexually. They also generate the forces exerted by contracting muscles and play essential roles in intracellular transport.
Protein evolution
A key question in molecular biology is how proteins evolve, i.e. how can mutations (or rather changes in amino acid sequence) lead to new structures and functions? Most amino acids in a protein can be changed without disrupting activity or function, as can be seen from numerous homologous proteins across species (as collected in specialized databases for protein families, e.g. PFAM). In order to prevent dramatic consequences of mutations, a gene may be duplicated before it can mutate freely. However, this can also lead to complete loss of gene function and thus pseudo-genes. More commonly, single amino acid changes have limited consequences although some can change protein function substantially, especially in enzymes. For instance, many enzymes can change their substrate specificity by one or a few mutations. Changes in substrate specificity are facilitated by substrate promiscuity, i.e. the ability of many enzymes to bind and process multiple substrates. When mutations occur, the specificity of an enzyme can increase (or decrease) and thus its enzymatic activity. Thus, bacteria (or other organisms) can adapt to different food sources, including unnatural substrates such as plastic.
Methods of study
The activities and structures of proteins may be examined in vitro, in vivo, and in silico. In vitro studies of purified proteins in controlled environments are useful for learning how a protein carries out its function: for example, enzyme kinetics studies explore the chemical mechanism of an enzyme's catalytic activity and its relative affinity for various possible substrate molecules. By contrast, in vivo experiments can provide information about the physiological role of a protein in the context of a cell or even a whole organism. In silico studies use computational methods to study proteins.
Protein purification
To perform in vitro analysis, a protein must be purified away from other cellular components. This process usually begins with cell lysis, in which a cell's membrane is disrupted and its internal contents released into a solution known as a crude lysate. The resulting mixture can be purified using ultracentrifugation, which fractionates the various cellular components into fractions containing soluble proteins; membrane lipids and proteins; cellular organelles, and nucleic acids. Precipitation by a method known as salting out can concentrate the proteins from this lysate. Various types of chromatography are then used to isolate the protein or proteins of interest based on properties such as molecular weight, net charge and binding affinity. The level of purification can be monitored using various types of gel electrophoresis if the desired protein's molecular weight and isoelectric point are known, by spectroscopy if the protein has distinguishable spectroscopic features, or by enzyme assays if the protein has enzymatic activity. Additionally, proteins can be isolated according to their charge using electrofocusing.
For natural proteins, a series of purification steps may be necessary to obtain protein sufficiently pure for laboratory applications. To simplify this process, genetic engineering is often used to add chemical features to proteins that make them easier to purify without affecting their structure or activity. Here, a "tag" consisting of a specific amino acid sequence, often a series of histidine residues (a "His-tag"), is attached to one terminus of the protein. As a result, when the lysate is passed over a chromatography column containing nickel, the histidine residues ligate the nickel and attach to the column while the untagged components of the lysate pass unimpeded. A number of different tags have been developed to help researchers purify specific proteins from complex mixtures.
Cellular localization

The study of proteins in vivo is often concerned with the synthesis and localization of the protein within the cell. Although many intracellular proteins are synthesized in the cytoplasm and membrane-bound or secreted proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, the specifics of how proteins are targeted to specific organelles or cellular structures is often unclear. A useful technique for assessing cellular localization uses genetic engineering to express in a cell a fusion protein or chimera consisting of the natural protein of interest linked to a "reporter" such as green fluorescent protein (GFP). The fused protein's position within the cell can then be cleanly and efficiently visualized using microscopy, as shown in the figure opposite.
Other methods for elucidating the cellular location of proteins requires the use of known compartmental markers for regions such as the ER, the Golgi, lysosomes or vacuoles, mitochondria, chloroplasts, plasma membrane, etc. With the use of fluorescently tagged versions of these markers or of antibodies to known markers, it becomes much simpler to identify the localization of a protein of interest. For example, indirect immunofluorescence will allow for fluorescence colocalization and demonstration of location. Fluorescent dyes are used to label cellular compartments for a similar purpose.
Other possibilities exist, as well. For example, immunohistochemistry usually uses an antibody to one or more proteins of interest that are conjugated to enzymes yielding either luminescent or chromogenic signals that can be compared between samples, allowing for localization information. Another applicable technique is cofractionation in sucrose (or other material) gradients using isopycnic centrifugation. While this technique does not prove colocalization of a compartment of known density and the protein of interest, it does increase the likelihood, and is more amenable to large-scale studies.
Finally, the gold-standard method of cellular localization is immunoelectron microscopy. This technique also uses an antibody to the protein of interest, along with classical electron microscopy techniques. The sample is prepared for normal electron microscopic examination, and then treated with an antibody to the protein of interest that is conjugated to an extremely electro-dense material, usually gold. This allows for the localization of both ultrastructural details as well as the protein of interest.
Through another genetic engineering application known as site-directed mutagenesis, researchers can alter the protein sequence and hence its structure, cellular localization, and susceptibility to regulation. This technique even allows the incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins, using modified tRNAs, and may allow the rational design of new proteins with novel properties.
Proteomics
The total complement of proteins present at a time in a cell or cell type is known as its proteome, and the study of such large-scale data sets defines the field of proteomics, named by analogy to the related field of genomics. Key experimental techniques in proteomics include 2D electrophoresis, which allows the separation of many proteins, mass spectrometry, which allows rapid high-throughput identification of proteins and sequencing of peptides (most often after in-gel digestion), protein microarrays, which allow the detection of the relative levels of the various proteins present in a cell, and two-hybrid screening, which allows the systematic exploration of protein–protein interactions. The total complement of biologically possible such interactions is known as the interactome. A systematic attempt to determine the structures of proteins representing every possible fold is known as structural genomics.
Structure determination
Discovering the tertiary structure of a protein, or the quaternary structure of its complexes, can provide important clues about how the protein performs its function and how it can be affected, i.e. in drug design. As proteins are too small to be seen under a light microscope, other methods have to be employed to determine their structure. Common experimental methods include X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy, both of which can produce structural information at atomic resolution. However, NMR experiments are able to provide information from which a subset of distances between pairs of atoms can be estimated, and the final possible conformations for a protein are determined by solving a distance geometry problem. Dual polarisation interferometry is a quantitative analytical method for measuring the overall protein conformation and conformational changes due to interactions or other stimulus. Circular dichroism is another laboratory technique for determining internal β-sheet / α-helical composition of proteins. Cryoelectron microscopy is used to produce lower-resolution structural information about very large protein complexes, including assembled viruses; a variant known as electron crystallography can also produce high-resolution information in some cases, especially for two-dimensional crystals of membrane proteins. Solved structures are usually deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), a freely available resource from which structural data about thousands of proteins can be obtained in the form of Cartesian coordinates for each atom in the protein.
Many more gene sequences are known than protein structures. Further, the set of solved structures is biased toward proteins that can be easily subjected to the conditions required in X-ray crystallography, one of the major structure determination methods. In particular, globular proteins are comparatively easy to crystallize in preparation for X-ray crystallography. Membrane proteins and large protein complexes, by contrast, are difficult to crystallize and are underrepresented in the PDB. Structural genomics initiatives have attempted to remedy these deficiencies by systematically solving representative structures of major fold classes. Protein structure prediction methods attempt to provide a means of generating a plausible structure for proteins whose structures have not been experimentally determined.
Structure prediction

Complementary to the field of structural genomics, protein structure prediction develops efficient mathematical models of proteins to computationally predict the molecular formations in theory, instead of detecting structures with laboratory observation. The most successful type of structure prediction, known as homology modeling, relies on the existence of a "template" structure with sequence similarity to the protein being modeled; structural genomics' goal is to provide sufficient representation in solved structures to model most of those that remain. Although producing accurate models remains a challenge when only distantly related template structures are available, it has been suggested that sequence alignment is the bottleneck in this process, as quite accurate models can be produced if a "perfect" sequence alignment is known. Many structure prediction methods have served to inform the emerging field of protein engineering, in which novel protein folds have already been designed. Also proteins (in eukaryotes ~33%) contain large unstructured but biologically functional segments and can be classified as intrinsically disordered proteins. Predicting and analysing protein disorder is, therefore, an important part of protein structure characterisation.
Bioinformatics
A vast array of computational methods have been developed to analyze the structure, function and evolution of proteins. The development of such tools has been driven by the large amount of genomic and proteomic data available for a variety of organisms, including the human genome. It is simply impossible to study all proteins experimentally, hence only a few are subjected to laboratory experiments while computational tools are used to extrapolate to similar proteins. Such homologous proteins can be efficiently identified in distantly related organisms by sequence alignment. Genome and gene sequences can be searched by a variety of tools for certain properties. Sequence profiling tools can find restriction enzyme sites, open reading frames in nucleotide sequences, and predict secondary structures. Phylogenetic trees can be constructed and evolutionary hypotheses developed using special software like ClustalW regarding the ancestry of modern organisms and the genes they express. The field of bioinformatics is now indispensable for the analysis of genes and proteins.
動的過程のインシリコシミュレーション
A more complex computational problem is the prediction of intermolecular interactions, such as in molecular docking, protein folding, protein–protein interaction and chemical reactivity. Mathematical models to simulate these dynamical processes involve molecular mechanics, in particular, molecular dynamics. In this regard, in silico simulations discovered the folding of small α-helical protein domains such as the villin headpiece, the HIV accessory protein and hybrid methods combining standard molecular dynamics with quantum mechanical mathematics have explored the electronic states of rhodopsins.
Beyond classical molecular dynamics, quantum dynamics methods allow the simulation of proteins in atomistic detail with an accurate description of quantum mechanical effects. Examples include the multi-layer multi-configuration time-dependent Hartree (MCTDH) method and the hierarchical equations of motion (HEOM) approach, which have been applied to plant cryptochromes and bacteria light-harvesting complexes, respectively. Both quantum and classical mechanical simulations of biological-scale systems are extremely computationally demanding, so distributed computing initiatives (for example, the Folding@home project) facilitate the molecular modeling by exploiting advances in GPU parallel processing and Monte Carlo techniques.
化学分析
The total nitrogen content of organic matter is mainly formed by the amino groups in proteins. The Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) is a measure of nitrogen widely used in the analysis of (waste) water, soil, food, feed and organic matter in general. As the name suggests, the Kjeldahl method is applied. More sensitive methods are available.
Nutrition
Most microorganisms and plants can biosynthesize all 20 standard amino acids, while animals (including humans) must obtain some of the amino acids from the diet. The amino acids that an organism cannot synthesize on its own are referred to as essential amino acids. Key enzymes that synthesize certain amino acids are not present in animals—such as aspartokinase, which catalyses the first step in the synthesis of lysine, methionine, and threonine from aspartate. If amino acids are present in the environment, microorganisms can conserve energy by taking up the amino acids from their surroundings and downregulating their biosynthetic pathways.
In animals, amino acids are obtained through the consumption of foods containing protein. Ingested proteins are then broken down into amino acids through digestion, which typically involves denaturation of the protein through exposure to acid and hydrolysis by enzymes called proteases. Some ingested amino acids are used for protein biosynthesis, while others are converted to glucose through gluconeogenesis, or fed into the citric acid cycle. This use of protein as a fuel is particularly important under starvation conditions as it allows the body's own proteins to be used to support life, particularly those found in muscle.
In animals such as dogs and cats, protein maintains the health and quality of the skin by promoting hair follicle growth and keratinization, and thus reducing the likelihood of skin problems producing malodours. Poor-quality proteins also have a role regarding gastrointestinal health, increasing the potential for flatulence and odorous compounds in dogs because when proteins reach the colon in an undigested state, they are fermented producing hydrogen sulfide gas, indole, and skatole. Dogs and cats digest animal proteins better than those from plants, but products of low-quality animal origin are poorly digested, including skin, feathers, and connective tissue.
こちらも参照
さらに読む
- 教科書
- Branden C, Tooze J (1999). Introduction to Protein Structure. New York: Garland Pub. ISBN 978-0-8153-2305-1.
- Murray RF, Harper HW, Granner DK, Mayes PA, Rodwell VW (2006). Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry. New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-146197-9.
- Van Holde KE, Mathews CK (1996). Biochemistry. Menlo Park, California: Benjamin/Cummings Pub. Co., Inc. ISBN 978-0-8053-3931-4.
外部リンク
データベースとプロジェクト
- NCBI Entrez Protein database
- NCBI Protein Structure database
- Human Protein Reference Database
- Human Proteinpedia
- Folding@Home (Stanford University) Archived 2012-09-08 at the Wayback Machine
- Protein Databank in Europe (see also PDBeQuips, short articles and tutorials on interesting PDB structures)
- Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (see also Molecule of the Month Archived 2020-07-24 at the Wayback Machine, presenting short accounts on selected proteins from the PDB)
- Proteopedia – Life in 3D: rotatable, zoomable 3D model with wiki annotations for every known protein molecular structure.
- UniProt the Universal Protein Resource
チュートリアルと教育ウェブサイト
- "An Introduction to Proteins" from HOPES (Huntington's Disease Outreach Project for Education at Stanford)
- Proteins: Biogenesis to Degradation – The Virtual Library of Biochemistry and Cell Biology