Enzyme/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "{{main/ja|Activation energy/ja|Thermodynamic equilibrium/ja|Chemical equilibrium/ja}}" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "{{NumBlk|:| <chem>CO2{} + H2O ->[\text{Carbonic anhydrase}] H2CO3</chem> ( 組織内; 高 CO<sub>2</sub> 濃度)|{{EquationRef|1}}}}" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 149: | Line 149: | ||
{{main/ja|Activation energy/ja|Thermodynamic equilibrium/ja|Chemical equilibrium/ja}} | {{main/ja|Activation energy/ja|Thermodynamic equilibrium/ja|Chemical equilibrium/ja}} | ||
すべての触媒と同様、酵素は反応の化学平衡の位置を変えることはない。酵素の存在下では、反応は酵素がない場合と同じ方向に進むが、より速く進むだけである。例えば、[[carbonic anhydrase/ja|炭酸脱水酵素]]は反応物の濃度に応じて、どちらの方向にも反応を触媒する: | |||
{{NumBlk|:| <chem>CO2{} + H2O ->[\text{Carbonic anhydrase}] H2CO3</chem> ( [[Tissue (biology)/ja|組織内]]; 高 CO<sub>2</sub> 濃度)|{{EquationRef|1}}}} | |||
{{NumBlk|:| <chem>CO2{} + H2O ->[\text{Carbonic anhydrase}] H2CO3</chem> ( | |||
{{NumBlk|:| <chem>CO2{} + H2O <-[\text{Carbonic anhydrase}] H2CO3</chem> ( [[lung/ja|肺]]内; 低 CO<sub>2</sub> 濃度)|{{EquationRef|2}}}} | |||
{{NumBlk|:| <chem>CO2{} + H2O <-[\text{Carbonic anhydrase}] H2CO3</chem> ( | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 09:23, 22 February 2024

| Part of a series on |
| Biochemistry/ja |
|---|
 |
酵素 (/ˈɛnzaɪmz/) は、化学反応を促進することによって生物学的触媒として働くタンパク質である。 酵素が作用する分子は基質と呼ばれ、酵素は基質を生成物として知られる異なる分子に変換する。細胞内のほとんどすべての代謝過程は、生命を維持するのに十分な速さで起こるために酵素触媒を必要とする。 代謝経路は、個々のステップを触媒する酵素に依存している。酵素の研究は酵素学と呼ばれ、擬似酵素分析の分野では、進化の過程で一部の酵素が生物学的触媒作用を遂行する能力を失っていることを認識している。このことはしばしばアミノ酸配列や特異な「擬触媒」特性に反映されている。
酵素は5,000種類以上の生化学反応を触媒することが知られている。他の生体触媒は触媒RNA分子で、リボザイムと呼ばれる。酵素の特異性は、そのユニークな立体構造に由来する。

すべての触媒と同様に、酵素はその活性化エネルギーを下げることによって反応速度を増加させる。一部の酵素は、基質から生成物への変換を何百万倍も速くすることができる。極端な例としては、オロチジン5'-リン酸脱炭酸酵素があり、この酵素を用いると、通常なら数百万年かかる反応が数ミリ秒で起こるようになる。化学的には、酵素は他の触媒と同様であり、化学反応で消費されることはなく、反応の平衡を変化させることもない。酵素は他のほとんどの触媒と異なり、はるかに特異的である。酵素活性は他の分子によって影響を受けることがある: 阻害剤は酵素活性を減少させる分子であり、活性化剤は活性を増加させる分子である。多くの治療薬物や毒物は酵素阻害剤である。酵素の活性は最適な温度とpH以外では著しく低下し、多くの酵素は過剰な熱にさらされると(永久的に)変性し、その構造と触媒特性を失う。
酵素の中には、例えば抗生物質の合成など、商業的に利用されているものもある。生物学的洗濯粉に含まれる酵素は衣服についたタンパク質やデンプン、脂肪の汚れを分解し、肉軟化剤に含まれる酵素はタンパク質をより小さな分子に分解して肉を噛み砕きやすくする。
語源と歴史

17世紀後半から18世紀初頭までに、胃分泌物による肉の消化と、植物抽出物と唾液によるデンプンの糖への変換は知られていたが、これらが起こるメカニズムは特定されていなかった。
フランスの化学者Anselme Payenは1833年に初めて酵素であるジアスターゼを発見した。その数十年後、酵母による糖のアルコールへの発酵を研究していたルイ・パスツールは、この発酵は「発酵物」と呼ばれる酵母細胞内に含まれる生命力によって引き起こされると結論づけた。彼は「アルコール発酵は酵母細胞の生命と組織に関連した行為であり、細胞の死や腐敗に関連した行為ではない」と書いた。
1877年、ドイツの生理学者Wilhelm Kühne(1837-1900)が初めて酵素という用語を使用し、from Ancient Greek ἔνζυμον (énzymon) 'イーストで捏ねる'このプロセスを説明した。
1897年にエドゥアルド・ブフナーが酵母エキスの研究に関する最初の論文を提出した。彼はベルリン大学での一連の実験において、混合物中に生きた酵母細胞が存在しなくても、酵母エキスによって砂糖が発酵することを発見した。彼はショ糖の発酵をもたらす酵素を「ザイマーゼ」と名付けた。1907年、彼は「無細胞発酵の発見」によりノーベル化学賞を受賞した。ブフナーの例に倣い、酵素は通常、それらが行う反応に従って命名される。接尾辞-aseは基質の名前と組み合わされる(例えば、ラクターゼは乳糖を切断する酵素である)、あるいは反応の種類に組み合わされる(例えば、DNAポリメラーゼはDNAポリマーを形成する)。
酵素の生化学的な正体は、1900年代初頭にはまだ不明であった。多くの科学者は酵素活性がタンパク質と関連していることを観察していたが、他の科学者(ノーベル賞受賞者のリチャード・ウィルシュテッターなど)は、タンパク質は真の酵素の単なるキャリアであり、タンパク質それ自体は触媒作用ができないと主張していた。1926年、ジェームズ・B・サムナーはウレアーゼという酵素が純粋なタンパク質であることを示し、それを結晶化させた。1937年にはカタラーゼという酵素も同様に結晶化させた。純粋なタンパク質が酵素になりうるという結論は、消化酵素ペプシン(1930年)、トリプシン、キモトリプシンの研究を行ったジョン・ハワード・ノースロップとウェンデル・メレディス・スタンリーによって決定的に示された。これら3人の科学者は1946年にノーベル化学賞を受賞した。
酵素が結晶化できることが発見されると、最終的にはX線結晶構造解析によってその構造を解明することができるようになった。これが最初に行われたのはリゾチームで、涙や唾液、卵白に含まれ、いくつかのバクテリアの被膜を消化する酵素である。その構造はデイヴィッド・チルトン・フィリップスが率いるグループによって解明され、1965年に発表された。このリゾチームの高分解能構造は、構造生物学の分野の始まりであり、酵素がどのように働くのかを原子レベルの詳細さで理解しようとする努力の始まりであった。
分類と命名法
酵素は主に2つの基準で分類することができる:アミノ酸配列の類似性(したがって進化的関係)と酵素活性である。
酵素活性。酵素の名前は多くの場合、その基質または触媒する化学反応に由来し、語尾に-aseが付く。例えば、ラクターゼ、アルコールデヒドロゲナーゼ、DNAポリメラーゼなどである。同じ化学反応を触媒する異なる酵素はアイソザイムと呼ばれる。
国際生化学分子生物学連合は、酵素の命名法であるEC番号(「酵素委員会」の意)を開発した。 各酵素は "EC "の後に、酵素活性の階層(非常に一般的なものから非常に特異的なものまで)を表す4つの番号のシーケンスで記述される。つまり、最初の数字はそのメカニズムに基づいて酵素を大まかに分類し、他の数字はより特異性を高めていく。
トップレベルの分類は以下の通りである:
- EC 1の酸化還元酵素:酸化/還元反応を触媒する。
- EC 2, 転移酵素:官能基(メチル基やリン酸基など)を転移する。
- EC 3, ヒドロラーゼ:様々な結合の加水分解を触媒する
- EC 4, リアーゼ:加水分解と酸化以外の方法で様々な結合を切断する
- EC 5, イソメラーゼ:1分子内の異性体化変化を触媒する
- EC 6, リガーゼ:2つの分子を共有結合で結合させる。
- EC 7, トランスロカーゼ:膜を介したイオンや分子の移動、または膜内での分離を触媒する。
これらのセクションは、基質、生成物、化学機構などの他の特徴によって細分化される。酵素は4つの数値で完全に指定される。例えば、ヘキソキナーゼ(EC 2.7.1.1)は、アルコール基(EC 2.7.1)を含む分子であるヘキソース糖にリン酸基(EC 2.7)を付加する転移酵素(EC 2)である。
配列類似性。ECカテゴリーは配列の類似性を反映しない。例えば、全く同じ反応を触媒する同じEC番号の2つのリガーゼが、全く異なる配列を持つことがある。酵素はその機能とは無関係に、他のタンパク質と同様に、配列の類似性によって数多くのファミリーに分類されている。これらのファミリーは、Pfamのような何十種類ものタンパク質やタンパク質ファミリーのデータベースに記録されている。
非相同同機能酵素。同じ酵素活性を持つ非相同酵素は非相同同機能酵素と呼ばれている。遺伝子の水平転移によって、これらの遺伝子が無関係な生物種、特に細菌に広がり、同じ機能を持つ内在性遺伝子と置き換わる可能性がある。
構造

酵素は一般に球状タンパク質であり、単独で、あるいはより大きな複合体の中で作用する。アミノ酸の配列が構造を決定し、それが酵素の触媒活性を決定する。構造は機能を決定するが、構造のみから新しい酵素活性を予測することはまだできない。酵素の構造は、加熱されたり化学的変性剤にさらされたりするとアンフォールディング(変性)する。その結果、温泉のような火山性環境に生息するバクテリアの酵素は、高温で機能する能力を持つため、産業界で珍重され、酵素触媒反応を非常に高い速度で行うことができる。
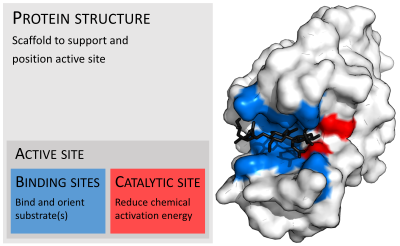
酵素は通常、基質よりもはるかに大きい。その大きさは、4-オキサロクロトン酸トートメラーゼの単量体のわずか62アミノ酸残基から、動物の脂肪酸合成酵素の2,500残基以上まで様々である。これらの構造のうち、触媒反応に直接関与しているのはごく一部(2-4アミノ酸程度)である。この触媒部位は、1つ以上の結合部位の隣に位置し、残基が基質を方向付ける。触媒部位と結合部位は一緒になって酵素の活性部位を構成する。酵素構造の残りの大部分は、活性部位の正確な方向と動態を維持する役割を果たしている。
酵素の中には、触媒反応に直接関与するアミノ酸を持たないものもある。その代わりに、酵素には触媒補因子を結合・配向させる部位が存在する。酵素の構造にはアロステリック部位が含まれることもあり、そこでは低分子の結合によって立体構造変化が起こり、活性が増減する。
リボザイムと呼ばれるRNAベースの生物学的触媒が少数存在し、これらも単独で、あるいはタンパク質と複合体となって作用する。これらの中で最も一般的なものはリボソームであり、タンパク質と触媒RNA成分の複合体である。
メカニズム
基質結合
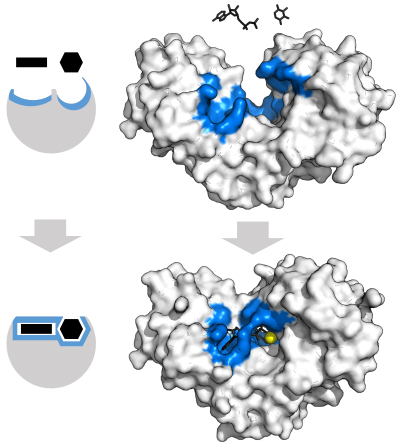
酵素は化学反応を触媒する前に、基質と結合しなければならない。酵素は通常、結合する基質と触媒される化学反応に関して非常に特異的である。特異性は、相補的な形状、電荷、親水性/疎水性特性を持つポケットを基質に結合させることで達成される。したがって酵素は、非常に類似した基質分子を化学選択性、位置選択性、立体特異性に区別することができる。
最も高い特異性と正確性を示す酵素のいくつかは、ゲノムのコピーと発現に関与している。これらの酵素の中には、「プルーフリーディング」機構を持つものがある。ここでは、DNAポリメラーゼなどの酵素が第一段階で反応を触媒し、第二段階で生成物が正しいかどうかをチェックする。この2段階のプロセスにより、高忠実度の哺乳類ポリメラーゼでは、平均エラー率は1億回の反応で1エラー以下となる。アミノアシルtRNA合成酵素とリボソームがある。
逆に、酵素の多様性を示す酵素もあり、広範な特異性を持ち、生理学的に適切な様々な基質に作用する。多くの酵素は、偶然に(すなわち中立)生じた小さな副次的活性を有しており、それが新しい機能を進化的に選択する出発点となっている可能性がある。
"鍵と錠"モデル
1894年、酵素の特異性を説明するために、Emil Fischerは、酵素と基質が互いにぴったりはまる特定の相補的な幾何学的形状を持っていると提唱した。これはしばしば「鍵と錠」モデルと呼ばれる。この初期のモデルでは、酵素の特異性は説明できるが、酵素が達成する遷移状態の安定化は説明できない。
誘導適合モデル
1958年、Daniel Koshlandは"鍵と錠"モデルの修正を提案した:酵素はどちらかというと柔軟な構造であるため、活性部位は基質が酵素と相互作用する際に、基質との相互作用によって絶えず再形成される。その結果、基質は単純に硬い活性部位に結合するのではなく、活性部位を構成するアミノ酸側鎖は、酵素が触媒機能を発揮できるような正確な位置に成形される。グリコシダーゼなどの場合、基質分子も活性部位に入るとわずかに形を変える。活性部位は基質が完全に結合するまで変化し続け、その時点で最終的な形状と電荷分布が決定される。 誘導された適合は、コンフォメーション校正機構を介して、競合やノイズの存在下での分子認識の忠実度を高める可能性がある。
触媒作用
酵素はいくつかの方法で反応を促進することができるが、そのどれもが活性化エネルギー(ΔG‡、ギブス自由エネルギー)を低下させる。
- 遷移状態を安定化させる:
- 遷移状態と相補的な電荷分布を持つ環境を作り、エネルギーを下げる。
- 代替反応経路を提供する:
- 基質と一時的に反応して共有結合中間体を形成し、より低エネルギーの遷移状態を提供する。
- 基質の基底状態を不安定化する:
- 結合した基質を遷移状態の形に変形させ、遷移状態に到達するのに必要なエネルギーを低下させる。
- 基質を生産的な配置に配向させ、反応のエントロピー変化を減少させる(この機構の触媒反応への寄与は比較的小さい)。
酵素はこれらの機構のいくつかを同時に用いることがある。例えば、トリプシンのようなプロテアーゼは、触媒三重鎖を用いて共有結合触媒反応を行い、オキシアニオンホールを用いて遷移状態の電荷蓄積を安定化させ、配向した水基質を用いて加水分解を完了させる。
動力学
つまり、個々のアミノ酸残基、タンパク質ループや二次構造の単位を形成する残基のグループ、あるいはタンパク質ドメイン全体など、酵素の構造の一部の動きである。 これらの運動は、平衡で互いに変換しあう、わずかに異なる構造のコンフォーメーションアンサンブルを生み出す。このアンサンブル内の異なる状態は、酵素の機能の異なる側面に関連しているかもしれない。
例えば、酵素ジヒドロ葉酸還元酵素の異なるコンフォーメーションは、触媒サイクルの基質結合、触媒反応、補酵素放出、生成物放出の各ステップと関連しており、触媒共鳴理論と一致している。
基質提示
基質提示とは、酵素が基質から離れて隔離されるプロセスのことである。酵素は核や細胞質内の基質から離れた細胞膜に隔離される。あるいは膜内では、酵素は脂質ラフトに隔離され、無秩序領域にある基質から遠ざかる。酵素が放出されると基質と混合する。あるいは、酵素を活性化するために、酵素を基質の近くに封じ込めることもできる。例えば、酵素は可溶性で、活性化すると細胞膜の脂質に結合し、細胞膜の分子に作用する。
アロステリック・モジュレーション
アロステリック部位とは、活性部位とは異なる酵素上のポケットのことで、細胞環境中の分子と結合する。これらの分子は、酵素のコンフォメーションやダイナミクスの変化を引き起こし、それが活性部位に伝達され、酵素の反応速度に影響を与える。このようにして、アロステリック相互作用は酵素を阻害することも活性化することもできる。酵素の代謝経路の上流または下流の代謝産物とのアロステリック相互作用はフィードバック制御を引き起こし、経路の残りの部分を通るフラックスに応じて酵素の活性を変化させる。
補因子=

酵素の中には、完全な活性を示すために追加の成分を必要としないものもある。また、活性を示すために補酵素と呼ばれる非タンパク質分子が結合している必要があるものもある。補因子は無機性(例えば、金属イオンや鉄-硫黄クラスターなど)、または有機化合物(例えば、フラビンやヘムなど)である。例えば、金属イオンは活性部位内の求核種を安定化させるのに役立つ。有機補酵素には、反応中に酵素の活性部位から放出される補酵素と、酵素に強固に結合している補欠基がある。有機補酵素基は共有結合することができる(例えば、ピルビン酸カルボキシラーゼなどの酵素ではビオチン)。
補因子を含む酵素の例は炭酸脱水酵素で、活性部位の一部として結合した亜鉛補酵素を用いる。これらの強固に結合したイオンや分子は通常活性部位に存在し、触媒反応に関与する。例えば、フラビンやヘムの補酵素はしばしば酸化還元反応に関与する。
補因子を必要とするが、補酵素が結合していない酵素はアポ酵素またはアポタンパク質と呼ばれる。酵素と活性に必要な補酵素を合わせてホロ酵素(またはハロ酵素)と呼ぶ。ホロ酵素という用語は、DNAポリメラーゼのような複数のタンパク質サブユニットを含む酵素にも適用できる。ここでいうホロ酵素とは、活性に必要なすべてのサブユニットを含む完全な複合体のことである。
補酵素
補酵素は小さな有機分子で、酵素に緩く結合していることもあれば、きつく結合していることもある。補酵素は、ある酵素から別の酵素へ化学基を輸送する。例えば、NADH、NADPH、アデノシン三リン酸(ATP)などがある。フラビンモノヌクレオチド(FMN)、フラビンアデニンジヌクレオチド(FAD)、チアミンピロリン酸(TPP)、テトラヒドロ葉酸(THF)など、いくつかの補酵素はビタミンに由来する。これらの補酵素は体内で合成de novoすることができず、近縁の化合物(ビタミン)は食事から摂取しなければならない。運ばれる化学グループには以下のものがある:
- NADまたはNADP+によって運ばれるヒドリドイオン(H-)
- アデノシン三リン酸によって運ばれるリン酸基
- コエンザイムAによって運ばれるアセチル基
- 葉酸によって運ばれるホルミル基、メテニル基、メチル基、および
- S-アデノシルメチオニンによって運ばれるメチル基
補酵素は酵素の作用の結果として化学的に変化するため、補酵素を多くの異なる酵素に共通する特殊な基質、すなわち第二基質と考えることは有用である。例えば、約1000種類の酵素が補酵素NADHを使用することが知られている。
補酵素は通常継続的に再生され、その濃度は細胞内で定常レベルに維持される。例えば、NADPHはペントースリン酸経路を通じて再生され、S-アデノシルメチオニンはメチオニンアデノシルトランスフェラーゼによって再生される。この継続的な再生は、少量の補酵素が非常に集中的に使用されることを意味する。例えば、人体は毎日自分の体重分のATPを消費している。
熱力学
すべての触媒と同様、酵素は反応の化学平衡の位置を変えることはない。酵素の存在下では、反応は酵素がない場合と同じ方向に進むが、より速く進むだけである。例えば、炭酸脱水酵素は反応物の濃度に応じて、どちらの方向にも反応を触媒する:
-
( 組織内; 高 CO2 濃度)
(1)
-
( 肺内; 低 CO2 濃度)
(2)
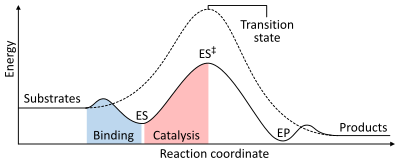
The rate of a reaction is dependent on the activation energy needed to form the transition state which then decays into products. Enzymes increase reaction rates by lowering the energy of the transition state. First, binding forms a low energy enzyme-substrate complex (ES). Second, the enzyme stabilises the transition state such that it requires less energy to achieve compared to the uncatalyzed reaction (ES‡). Finally the enzyme-product complex (EP) dissociates to release the products.
Enzymes can couple two or more reactions, so that a thermodynamically favorable reaction can be used to "drive" a thermodynamically unfavourable one so that the combined energy of the products is lower than the substrates. For example, the hydrolysis of ATP is often used to drive other chemical reactions.
Kinetics
Enzyme kinetics is the investigation of how enzymes bind substrates and turn them into products. The rate data used in kinetic analyses are commonly obtained from enzyme assays. In 1913 Leonor Michaelis and Maud Leonora Menten proposed a quantitative theory of enzyme kinetics, which is referred to as Michaelis–Menten kinetics. The major contribution of Michaelis and Menten was to think of enzyme reactions in two stages. In the first, the substrate binds reversibly to the enzyme, forming the enzyme-substrate complex. This is sometimes called the Michaelis–Menten complex in their honor. The enzyme then catalyzes the chemical step in the reaction and releases the product. This work was further developed by G. E. Briggs and J. B. S. Haldane, who derived kinetic equations that are still widely used today.
Enzyme rates depend on solution conditions and substrate concentration. To find the maximum speed of an enzymatic reaction, the substrate concentration is increased until a constant rate of product formation is seen. This is shown in the saturation curve on the right. Saturation happens because, as substrate concentration increases, more and more of the free enzyme is converted into the substrate-bound ES complex. At the maximum reaction rate (Vmax) of the enzyme, all the enzyme active sites are bound to substrate, and the amount of ES complex is the same as the total amount of enzyme.
Vmax is only one of several important kinetic parameters. The amount of substrate needed to achieve a given rate of reaction is also important. This is given by the Michaelis–Menten constant (Km), which is the substrate concentration required for an enzyme to reach one-half its maximum reaction rate; generally, each enzyme has a characteristic KM for a given substrate. Another useful constant is kcat, also called the turnover number, which is the number of substrate molecules handled by one active site per second.
The efficiency of an enzyme can be expressed in terms of kcat/Km. This is also called the specificity constant and incorporates the rate constants for all steps in the reaction up to and including the first irreversible step. Because the specificity constant reflects both affinity and catalytic ability, it is useful for comparing different enzymes against each other, or the same enzyme with different substrates. The theoretical maximum for the specificity constant is called the diffusion limit and is about 108 to 109 (M−1 s−1). At this point every collision of the enzyme with its substrate will result in catalysis, and the rate of product formation is not limited by the reaction rate but by the diffusion rate. Enzymes with this property are called catalytically perfect or kinetically perfect. Example of such enzymes are triose-phosphate isomerase, carbonic anhydrase, acetylcholinesterase, catalase, fumarase, β-lactamase, and superoxide dismutase. The turnover of such enzymes can reach several million reactions per second. But most enzymes are far from perfect: the average values of and are about and , respectively.
Michaelis–Menten kinetics relies on the law of mass action, which is derived from the assumptions of free diffusion and thermodynamically driven random collision. Many biochemical or cellular processes deviate significantly from these conditions, because of macromolecular crowding and constrained molecular movement. More recent, complex extensions of the model attempt to correct for these effects.
Inhibition
Enzyme reaction rates can be decreased by various types of enzyme inhibitors.
Types of inhibition
Competitive
A competitive inhibitor and substrate cannot bind to the enzyme at the same time. Often competitive inhibitors strongly resemble the real substrate of the enzyme. For example, the drug methotrexate is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which catalyzes the reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate. The similarity between the structures of dihydrofolate and this drug are shown in the accompanying figure. This type of inhibition can be overcome with high substrate concentration. In some cases, the inhibitor can bind to a site other than the binding-site of the usual substrate and exert an allosteric effect to change the shape of the usual binding-site.
Non-competitive
A non-competitive inhibitor binds to a site other than where the substrate binds. The substrate still binds with its usual affinity and hence Km remains the same. However the inhibitor reduces the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme so that Vmax is reduced. In contrast to competitive inhibition, non-competitive inhibition cannot be overcome with high substrate concentration.
Uncompetitive
An uncompetitive inhibitor cannot bind to the free enzyme, only to the enzyme-substrate complex; hence, these types of inhibitors are most effective at high substrate concentration. In the presence of the inhibitor, the enzyme-substrate complex is inactive. This type of inhibition is rare.
Mixed
A mixed inhibitor binds to an allosteric site and the binding of the substrate and the inhibitor affect each other. The enzyme's function is reduced but not eliminated when bound to the inhibitor. This type of inhibitor does not follow the Michaelis–Menten equation.
Irreversible
An irreversible inhibitor permanently inactivates the enzyme, usually by forming a covalent bond to the protein. Penicillin and aspirin are common drugs that act in this manner.
Functions of inhibitors
In many organisms, inhibitors may act as part of a feedback mechanism. If an enzyme produces too much of one substance in the organism, that substance may act as an inhibitor for the enzyme at the beginning of the pathway that produces it, causing production of the substance to slow down or stop when there is sufficient amount. This is a form of negative feedback. Major metabolic pathways such as the citric acid cycle make use of this mechanism.
Since inhibitors modulate the function of enzymes they are often used as drugs. Many such drugs are reversible competitive inhibitors that resemble the enzyme's native substrate, similar to methotrexate above; other well-known examples include statins used to treat high cholesterol, and protease inhibitors used to treat retroviral infections such as HIV. A common example of an irreversible inhibitor that is used as a drug is aspirin, which inhibits the COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes that produce the inflammation messenger prostaglandin. Other enzyme inhibitors are poisons. For example, the poison cyanide is an irreversible enzyme inhibitor that combines with the copper and iron in the active site of the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase and blocks cellular respiration.
Factors affecting enzyme activity
As enzymes are made up of proteins, their actions are sensitive to change in many physio chemical factors such as pH, temperature, substrate concentration, etc.
The following table shows pH optima for various enzymes.
| Enzyme | Optimum pH | pH description |
|---|---|---|
| Pepsin | 1.5–1.6 | Highly acidic |
| Invertase | 4.5 | Acidic |
| Lipase (stomach) | 4.0–5.0 | Acidic |
| Lipase (castor oil) | 4.7 | Acidic |
| Lipase (pancreas) | 8.0 | Alkaline |
| Amylase (malt) | 4.6–5.2 | Acidic |
| Amylase (pancreas) | 6.7–7.0 | Acidic-neutral |
| Cellobiase | 5.0 | Acidic |
| Maltase | 6.1–6.8 | Acidic |
| Sucrase | 6.2 | Acidic |
| Catalase | 7.0 | Neutral |
| Urease | 7.0 | Neutral |
| Cholinesterase | 7.0 | Neutral |
| Ribonuclease | 7.0–7.5 | Neutral |
| Fumarase | 7.8 | Alkaline |
| Trypsin | 7.8–8.7 | Alkaline |
| Adenosine triphosphate | 9.0 | Alkaline |
| Arginase | 10.0 | Highly alkaline |
Biological function
Enzymes serve a wide variety of functions inside living organisms. They are indispensable for signal transduction and cell regulation, often via kinases and phosphatases. They also generate movement, with myosin hydrolyzing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to generate muscle contraction, and also transport cargo around the cell as part of the cytoskeleton. Other ATPases in the cell membrane are ion pumps involved in active transport. Enzymes are also involved in more exotic functions, such as luciferase generating light in fireflies. Viruses can also contain enzymes for infecting cells, such as the HIV integrase and reverse transcriptase, or for viral release from cells, like the influenza virus neuraminidase.
An important function of enzymes is in the digestive systems of animals. Enzymes such as amylases and proteases break down large molecules (starch or proteins, respectively) into smaller ones, so they can be absorbed by the intestines. Starch molecules, for example, are too large to be absorbed from the intestine, but enzymes hydrolyze the starch chains into smaller molecules such as maltose and eventually glucose, which can then be absorbed. Different enzymes digest different food substances. In ruminants, which have herbivorous diets, microorganisms in the gut produce another enzyme, cellulase, to break down the cellulose cell walls of plant fiber.
Metabolism

Several enzymes can work together in a specific order, creating metabolic pathways. In a metabolic pathway, one enzyme takes the product of another enzyme as a substrate. After the catalytic reaction, the product is then passed on to another enzyme. Sometimes more than one enzyme can catalyze the same reaction in parallel; this can allow more complex regulation: with, for example, a low constant activity provided by one enzyme but an inducible high activity from a second enzyme.
Enzymes determine what steps occur in these pathways. Without enzymes, metabolism would neither progress through the same steps and could not be regulated to serve the needs of the cell. Most central metabolic pathways are regulated at a few key steps, typically through enzymes whose activity involves the hydrolysis of ATP. Because this reaction releases so much energy, other reactions that are thermodynamically unfavorable can be coupled to ATP hydrolysis, driving the overall series of linked metabolic reactions.
Control of activity
There are five main ways that enzyme activity is controlled in the cell.
Regulation
Enzymes can be either activated or inhibited by other molecules. For example, the end product(s) of a metabolic pathway are often inhibitors for one of the first enzymes of the pathway (usually the first irreversible step, called committed step), thus regulating the amount of end product made by the pathways. Such a regulatory mechanism is called a negative feedback mechanism, because the amount of the end product produced is regulated by its own concentration. Negative feedback mechanism can effectively adjust the rate of synthesis of intermediate metabolites according to the demands of the cells. This helps with effective allocations of materials and energy economy, and it prevents the excess manufacture of end products. Like other homeostatic devices, the control of enzymatic action helps to maintain a stable internal environment in living organisms.
Post-translational modification
Examples of post-translational modification include phosphorylation, myristoylation and glycosylation. For example, in the response to insulin, the phosphorylation of multiple enzymes, including glycogen synthase, helps control the synthesis or degradation of glycogen and allows the cell to respond to changes in blood sugar. Another example of post-translational modification is the cleavage of the polypeptide chain. Chymotrypsin, a digestive protease, is produced in inactive form as chymotrypsinogen in the pancreas and transported in this form to the stomach where it is activated. This stops the enzyme from digesting the pancreas or other tissues before it enters the gut. This type of inactive precursor to an enzyme is known as a zymogen or proenzyme.
Quantity
Enzyme production (transcription and translation of enzyme genes) can be enhanced or diminished by a cell in response to changes in the cell's environment. This form of gene regulation is called enzyme induction. For example, bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics such as penicillin because enzymes called beta-lactamases are induced that hydrolyse the crucial beta-lactam ring within the penicillin molecule. Another example comes from enzymes in the liver called cytochrome P450 oxidases, which are important in drug metabolism. Induction or inhibition of these enzymes can cause drug interactions. Enzyme levels can also be regulated by changing the rate of enzyme degradation. The opposite of enzyme induction is enzyme repression.
Subcellular distribution
Enzymes can be compartmentalized, with different metabolic pathways occurring in different cellular compartments. For example, fatty acids are synthesized by one set of enzymes in the cytosol, endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi and used by a different set of enzymes as a source of energy in the mitochondrion, through β-oxidation. In addition, trafficking of the enzyme to different compartments may change the degree of protonation (e.g., the neutral cytoplasm and the acidic lysosome) or oxidative state (e.g., oxidizing periplasm or reducing cytoplasm) which in turn affects enzyme activity. In contrast to partitioning into membrane bound organelles, enzyme subcellular localisation may also be altered through polymerisation of enzymes into macromolecular cytoplasmic filaments.
Organ specialization
In multicellular eukaryotes, cells in different organs and tissues have different patterns of gene expression and therefore have different sets of enzymes (known as isozymes) available for metabolic reactions. This provides a mechanism for regulating the overall metabolism of the organism. For example, hexokinase, the first enzyme in the glycolysis pathway, has a specialized form called glucokinase expressed in the liver and pancreas that has a lower affinity for glucose yet is more sensitive to glucose concentration. This enzyme is involved in sensing blood sugar and regulating insulin production.
Involvement in disease


Since the tight control of enzyme activity is essential for homeostasis, any malfunction (mutation, overproduction, underproduction or deletion) of a single critical enzyme can lead to a genetic disease. The malfunction of just one type of enzyme out of the thousands of types present in the human body can be fatal. An example of a fatal genetic disease due to enzyme insufficiency is Tay–Sachs disease, in which patients lack the enzyme hexosaminidase.
One example of enzyme deficiency is the most common type of phenylketonuria. Many different single amino acid mutations in the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, which catalyzes the first step in the degradation of phenylalanine, result in build-up of phenylalanine and related products. Some mutations are in the active site, directly disrupting binding and catalysis, but many are far from the active site and reduce activity by destabilising the protein structure, or affecting correct oligomerisation. This can lead to intellectual disability if the disease is untreated. Oral administration of enzymes can be used to treat some functional enzyme deficiencies, such as pancreatic insufficiency and lactose intolerance.
Another way enzyme malfunctions can cause disease comes from germline mutations in genes coding for DNA repair enzymes. Defects in these enzymes cause cancer because cells are less able to repair mutations in their genomes. This causes a slow accumulation of mutations and results in the development of cancers. An example of such a hereditary cancer syndrome is xeroderma pigmentosum, which causes the development of skin cancers in response to even minimal exposure to ultraviolet light.
Evolution
Similar to any other protein, enzymes change over time through mutations and sequence divergence. Given their central role in metabolism, enzyme evolution plays a critical role in adaptation. A key question is therefore whether and how enzymes can change their enzymatic activities alongside. It is generally accepted that many new enzyme activities have evolved through gene duplication and mutation of the duplicate copies although evolution can also happen without duplication. One example of an enzyme that has changed its activity is the ancestor of methionyl aminopeptidase (MAP) and creatine amidinohydrolase (creatinase) which are clearly homologous but catalyze very different reactions (MAP removes the amino-terminal methionine in new proteins while creatinase hydrolyses creatine to sarcosine and urea). In addition, MAP is metal-ion dependent while creatinase is not, hence this property was also lost over time. Small changes of enzymatic activity are extremely common among enzymes. In particular, substrate binding specificity (see above) can easily and quickly change with single amino acid changes in their substrate binding pockets. This is frequently seen in the main enzyme classes such as kinases.
Artificial (in vitro) evolution is now commonly used to modify enzyme activity or specificity for industrial applications (see below).
Industrial applications
Enzymes are used in the chemical industry and other industrial applications when extremely specific catalysts are required. Enzymes in general are limited in the number of reactions they have evolved to catalyze and also by their lack of stability in organic solvents and at high temperatures. As a consequence, protein engineering is an active area of research and involves attempts to create new enzymes with novel properties, either through rational design or in vitro evolution. These efforts have begun to be successful, and a few enzymes have now been designed "from scratch" to catalyze reactions that do not occur in nature.
| Application | Enzymes used | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Biofuel industry | Cellulases | Break down cellulose into sugars that can be fermented to produce cellulosic ethanol. |
| Ligninases | Pretreatment of biomass for biofuel production. | |
| Biological detergent | Proteases, amylases, lipases | Remove protein, starch, and fat or oil stains from laundry and dishware. |
| Mannanases | Remove food stains from the common food additive guar gum. | |
| Brewing industry | Amylase, glucanases, proteases | Split polysaccharides and proteins in the malt. |
| Betaglucanases | Improve the wort and beer filtration characteristics.:545 | |
| Amyloglucosidase and pullulanases | Make low-calorie beer and adjust fermentability. | |
| Acetolactate decarboxylase (ALDC) | Increase fermentation efficiency by reducing diacetyl formation. | |
| Culinary uses | Papain | Tenderize meat for cooking. |
| Dairy industry | Rennin | Hydrolyze protein in the manufacture of cheese. |
| Lipases | Produce Camembert cheese and blue cheeses such as Roquefort. | |
| Food processing | Amylases | Produce sugars from starch, such as in making high-fructose corn syrup. |
| Proteases | Lower the protein level of flour, as in biscuit-making. | |
| Trypsin | Manufacture hypoallergenic baby foods. | |
| Cellulases, pectinases | Clarify fruit juices. | |
| Molecular biology | Nucleases, DNA ligase and polymerases | Use restriction digestion and the polymerase chain reaction to create recombinant DNA. |
| Paper industry | Xylanases, hemicellulases and lignin peroxidases | Remove lignin from kraft pulp. |
| Personal care | Proteases | Remove proteins on contact lenses to prevent infections. |
| Starch industry | Amylases | Convert starch into glucose and various syrups. |
See also
Further reading
|
|
External links
 Media related to Enzymes at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Enzymes at Wikimedia Commons
| この記事は、クリエイティブ・コモンズ・表示・継承ライセンス3.0のもとで公表されたウィキペディアの項目Enzyme/ja(8 February 2024編集記事参照)を素材として二次利用しています。 Lua error in Module:Itemnumber at line 91: attempt to concatenate local 'qid' (a nil value). |



