Thiamine/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "チアミンとその代謝物(2-メチル-4-アミノ-5-ピリミジンカルボン酸、4-メチル-チアゾール-5-酢酸など)は主に尿中に排泄される。" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "===干渉=== 食品中のチアミンの生物学的利用能は、様々な方法で阻害される可能性がある。保存料として食品に添加される亜硫酸塩は、チアミンをメチレン橋で攻撃し、チアゾール環からピリミジン環を切断する。この反応の速度は酸性条件下で増大する。チアミンは、魚介類やその他の食品に含まれる熱分解性のthiaminase/ja|..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 280: | Line 280: | ||
チアミンとその代謝物(2-メチル-4-アミノ-5-ピリミジンカルボン酸、4-メチル-チアゾール-5-酢酸など)は主に尿中に排泄される。 | チアミンとその代謝物(2-メチル-4-アミノ-5-ピリミジンカルボン酸、4-メチル-チアゾール-5-酢酸など)は主に尿中に排泄される。 | ||
===干渉=== | |||
食品中のチアミンの[[bioavailability/ja|生物学的利用能]]は、様々な方法で阻害される可能性がある。保存料として食品に添加される[[Sulfite/ja|亜硫酸塩]]は、チアミンをメチレン橋で攻撃し、チアゾール環からピリミジン環を切断する。この反応の速度は酸性条件下で増大する。チアミンは、魚介類やその他の食品に含まれる熱分解性の[[thiaminase/ja|チアミナーゼ]]によって分解される。アフリカのカイコ、''[[Anaphe venata/ja|Anaphe venata]]'の蛹はナイジェリアの伝統的な食べ物である。摂取するとチアミン欠乏症になる。古い文献によると、タイでは発酵させた未調理の魚を摂取するとチアミン欠乏症になるが、魚を食べるのを控えるか、加熱すると欠乏症が回復したと報告されている。反芻動物では、腸内細菌がチアミンとチアミナーゼを合成する。細菌のチアミナーゼは細胞表面酵素であり、活性化される前に細胞膜から解離しなければならない;解離は反芻動物では[[acidosis/ja|酸性条件下]]で起こりうる。[[dairy cattle/ja|乳牛]]では、穀物の過剰給与により亜急性ルーミナルアシドーシスが起こり、ルーミナル細菌チアミナーゼの放出が増加し、チアミン欠乏症が起こる。 | |||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 19 February 2024
 | |
 チアミン陽イオンの骨格式とボール&スティックモデル | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈθaɪ.əmɪn/ THY-ə-min |
| Other names | ビタミンB1, アノイリン, チアミン |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | by mouth, IV, IM |
| Drug class | vitamin/ja |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 3.7% to 5.3% (チアミン塩酸塩) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
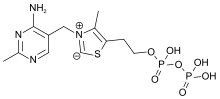
| Formula | C12H17N4OS+ |
| Molar mass | 265.36 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
チアミン(thiamin、vitamin B1)は、ビタミンの一種で、必須微量栄養素の一つである。食品中に含まれるほか、栄養補助食品や医薬品として商業的に合成されている。チアミンのリン酸化型は、グルコースやアミノ酸の分解など、いくつかの代謝反応に必要である。
チアミンの食物源としては、全粒穀物、豆類、肉や魚がある。穀物加工はビタミン含有量の多くを除去するため、多くの国では穀物や小麦粉はチアミンで強化されている。サプリメントや医薬品は、チアミン欠乏症やそれに起因する脚気やウェルニッケ脳症などの障害を治療・予防するために利用できる。また、メープルシロップ尿症やリー症候群の治療にも用いられる。サプリメントや医薬品は通常口から摂取されるが、点滴や筋肉注射で投与されることもある。
チアミンサプリメントは一般的に忍容性が高い。注射で反復投与する場合、アナフィラキシーを含むアレルギー反応が起こることがある。チアミンは世界保健機関(WHO)の必須医薬品リストに掲載されている。チアミンはジェネリック医薬品として、また一部の国では非処方の栄養補助食品として入手可能である。
定義
チアミンはビタミンB群の一つであり、ビタミンB1としても知られている。陽イオンであり、通常は塩化物として供給される。塩として供給される。水、メタノール、グリセロールには可溶性であるが、極性の低い有機溶媒には実質的に溶解しない。体内ではチアミンは誘導体を形成することができる;その中で最もよく特徴付けられるのはチアミンピロリン酸(TPP)であり、糖とアミノ酸の異化における補酵素である。
化学構造はアミノピリミジンとチアゾリウム環がメチレン架橋で結合したものである。チアゾールはメチルおよびヒドロキシエチル側鎖で置換されている。チアミンは酸性のpHでは安定であるが、アルカリ溶液や熱にさらされると不安定になる。メイラード型反応では強く反応する。酸化により蛍光誘導体チオクロムを生成し、生体試料中のビタミン量を測定することができる。
欠乏
チアミン欠乏による疾患としては、脚気、ウェルニッケ・コルサコフ症候群、視神経症、リー病、アフリカ季節性運動失調症(またはナイジェリア季節性運動失調症)、および中枢性小脳脊髄融解症がよく知られている。症状には倦怠感、体重減少、過敏性、錯乱などがある。
欧米諸国では、慢性アルコール中毒が欠乏症の危険因子である。また、高齢者、HIV/AIDSまたは糖尿病の患者、肥満手術を受けた者も危険である。さまざまな程度のチアミン欠乏症が利尿薬の長期使用と関連している。
生物学的機能

5種類の天然チアミンリン酸誘導体が知られている:チアミン一リン酸(ThMP)、チアミンピロリン酸(TPP)、チアミン三リン酸(ThTP)、アデノシンチアミン二リン酸(AThDP)、アデノシンチアミン三リン酸(AThTP)。これらは多くの細胞プロセスに関与している。最もよく知られているのはTPPで、糖とアミノ酸の異化における補酵素である。その役割はよく知られているが、チアミンとその誘導体の非補酵素作用は、その機構を用いないタンパク質との結合によって実現されている可能性がある。一リン酸については、チアミンが細胞内で二リン酸および三リン酸に変換される際の中間体としての役割以外、生理学的な役割は知られていない。
チアミンピロリン酸塩
チアミンピロリン酸(TPP)は、チアミン二リン酸(ThDP)とも呼ばれ、極性反転が起こる代謝反応などに補酵素として関与する。その合成は酵素チアミン・ジホスホキナーゼによって、チアミン+ATP→TPP+AMP(EC 2.7.6.2)という反応に従って触媒される。TPPは、2-オキソ酸(α-ケト酸)の脱水素化(脱炭酸とそれに続くコエンザイム Aとの共役)を触媒するいくつかの酵素の補酵素である。補酵素としてのTPPの作用機序は、イリドを形成する能力に依存している。例えば、以下のようなものがある:
- ほとんどの種に存在する
- いくつかの種に存在する:
- ピルビン酸脱炭酸酵素(酵母にある)
- さらにいくつかのバクテリアl酵素がある
酵素トランスケトラーゼ、ピルビン酸デヒドロゲナーゼ(PDH)、2-オキソグルタル酸デヒドロゲナーゼ(OGDH)は糖質代謝において重要である。PDHは解糖とクエン酸サイクルを結びつける。OGDHはクエン酸サイクルにおいて、2-オキソグルタル酸(α-ケトグルタル酸)からスクシニル-CoAおよびCO2への全体的な変換を触媒する。OGDHによって触媒される反応はクエン酸サイクルの律速段階である。細胞質酵素トランスケトラーゼは、ペントース糖であるデオキシリボースとリボースの生合成の主要な経路であるペントースリン酸経路の中心である。ミトコンドリアのPDHとOGDHは、細胞の主要なエネルギー伝達分子であるアデノシン三リン酸(ATP)の生成をもたらす生化学的経路の一部である。神経系では、PDHはミエリンと神経伝達物質アセチルコリンの合成にも関与している。
=== チアミン三リン酸===

ThTPは哺乳類やその他の動物の神経細胞におけるクロライド・チャンネルの活性化に関与しているが、その役割はよくわかっていない。ThTPはバクテリア、菌類、植物でも見つかっており、他の細胞での役割も示唆している。大腸菌では、アミノ酸飢餓に対する反応に関与している。
アデノシン誘導体
AThDPは脊椎動物の肝臓に少量存在するが、その役割は未知のままである。
AThTPは大腸菌に存在し、炭素飢餓の結果として蓄積する。この細菌では、AThTPは全チアミンの最大20%を占めることがある。また、酵母や高等植物の根、動物組織にも少ない量ではあるが存在する。
Medical uses
During pregnancy, thiamine is sent to the fetus via the placenta. Pregnant women have a greater requirement for the vitamin than other adults, especially during the third trimester. Pregnant women with hyperemesis gravidarum are at an increased risk of thiamine deficiency due to losses when vomiting. In lactating women, thiamine is delivered in breast milk even if it results in thiamine deficiency in the mother.
チアミンはミトコンドリア膜の発達だけでなく、シナプス膜の機能にも重要である。また、欠乏は乳児の脳の発達を妨げ、乳幼児突然死症候群の原因である可能性も示唆されている。
食事に関する推奨事項
| 米国医学アカデミー | |
| 年齢層 | RDA (mg/日) |
|---|---|
| 幼児 0–6ヶ月 | 0.2* |
| 幼児 6–12ヶ月 | 0.3* |
| 1–3歳 | 0.5 |
| 4–8歳 | 0.6 |
| 9–13歳 | 0.9 |
| 女性 14–18歳 | 1.0 |
| 男性 14歳以上 | 1.2 |
| 女性 19歳以上 | 1.1 |
| 妊娠中/授乳中の女性 14–50 | 1.4 |
| * RDAはまだ確立されていないため、乳幼児にとって十分な摂取量である | |
| 欧州食品安全機関 | |
| 年齢層 | 十分な摂取量 (mg/MJ) |
| 7ヶ月以上のすべての人 | 0.1 |
| 米国医学アカデミーも欧州食品安全機関も、チアミンの耐容上限摂取量を決定していない。 | |
米国医学アカデミーは、1998年にチアミンの推定平均必要量(EAR)と推奨食事許容量(RDA)を更新した。14歳以上の女性および男性のチアミンのEARは、それぞれ0.9 mg/日および1.1 mg/日であり、RDAはそれぞれ1.1および1.2 mg/日である。RDAはEARよりも高く設定されているが、これは必要量が平均よりも多い人に適切な摂取量を提供するためである。妊娠中および授乳中の女性のRDAは1.4 mg/日である。生後12ヵ月までの乳児の場合、適量摂取量(AI)は0.2~0.3 mg/日であり、1~13歳の子供の場合、RDAは0.5~0.9 mg/日と年齢とともに増加する。
欧州食品安全機関(EFSA)は、この一連の情報を食事摂取基準値と呼び、RDAの代わりに人口摂取基準値(PRI)、EARの代わりに平均所要量を用いている。女性(妊娠中または授乳中を含む)、男性、子供の場合、PRIは食事中のエネルギー1メガジュール(MJ)あたり0.1 mgのチアミンである。1MJ=239kcalに換算すると、2390キロカロリーを消費する成人は、1.0 mgのチアミンを摂取していることになる。これは米国のRDAより若干低い。
米国医学アカデミーもEFSAも、チアミンの上限摂取量を設定していない。高用量摂取による有害作用に関するヒトのデータがないからである。
安全性
チアミンは経口投与の場合、一般的に忍容性が高く、毒性はない。アレルギー反応、吐き気、昏睡、協調運動障害などである。
ラベル表示
米国の食品および栄養補助食品の表示目的上、1食あたりの摂取量は1日当たりの摂取量(Daily Value)のパーセンテージで表される。2016年5月27日以降、デイリーバリューはRDAに合わせて1.2 mgとなっている。
摂取源
チアミンは、レンズ豆、エンドウ豆、全粒穀物、豚肉、ナッツ類など、加工食品や全食品に幅広く含まれている。典型的な1日分の妊婦用ビタミン剤には、約1.5 mgのチアミンが含まれている。
食品強化
加工によってビタミンの含有量が低下するため、小麦、米、トウモロコシなどの穀物食品の強化が義務づけられたり推奨されたりしている国もある。2022年2月現在、北アフリカとサハラ以南のアフリカを中心とする59カ国が、小麦、米、トウモロコシにチアミンまたはチアミン一硝酸塩の食品強化を義務付けている。規定量は2.0~10.0mg/kgである。さらに18カ国が自主的な強化プログラムを実施している。例えば、インド政府は、マイダ(白)とアタ(全粒粉)の小麦粉に3.5 mg/kgを推奨している。
合成
生合成
チアミンの生合成は細菌、一部の原生動物、植物、菌類で行われる。チアゾール部分とピリミジン部分は別々に生合成され、次にチアミン-リン酸合成酵素の作用によってThMPを形成するために結合される。
ピリミジン環系は、S-アデノシルメチオニンを補酵素として用いる鉄-硫黄タンパク質のラジカルSAMスーパーファミリーの酵素であるホスホメチルピリミジン合成酵素(ThiC)によって触媒される反応で形成される。
出発物質は5-アミノイミダゾールリボチドであり、このリボチドはラジカル中間体を経て転位反応を受け、青、緑、赤のフラグメントを生成物に取り込む。
チアゾール環は、チアゾール合成酵素(EC 2.8.1.10)によって触媒される反応で形成される。最終的な前駆体は、1-デオキシ-D-キシルロース5-リン酸、2-イミノ酢酸、そしてThiSと呼ばれる硫黄キャリアタンパク質である。酵素活性部位で環の全成分をまとめるためには、さらにThiGというタンパク質も必要である。

ThMPを形成する最終段階は、チアゾール中間体の脱炭酸を伴う。この中間体は、ホスホメチルピリミジンのピロリン酸誘導体と反応し、それ自体がキナーゼであるホスホメチルピリミジンキナーゼの産物である。
生合成経路は生物によって異なる。大腸菌や他の腸内細菌科では、ThMPはチアミン-リン酸キナーゼによって補酵素TPPにリン酸化される(ThMP + ATP → TPP + ADP)。ほとんどの細菌と真核生物では、ThMPはチアミンに加水分解された後、チアミンジホスホキナーゼによってTPPにピロリン酸化される(チアミン + ATP → TPP + AMP)。
生合成経路はリボスイッチによって制御されている。細胞内に十分なチアミンが存在する場合、チアミンは経路に必要な酵素のmRNAに結合し、その翻訳を阻害する。チアミンが存在しなければ阻害は起こらず、生合成に必要な酵素は生成される。特異的なリボスイッチであるTPPリボスイッチは、真核生物と原核生物の両方に見られる唯一の既知のリボスイッチである。
実験室での合成
1936年の最初の全合成では、3-エトキシプロパン酸エチルをギ酸エチルで処理して中間体ジカルボニル化合物を得、これをアセトアミジンと反応させると置換ピリミジンを形成した。その水酸基のアミノ基への変換は求核芳香族置換によって行われ、まずオキシ塩化リンを用いて塩化誘導体に変換し、続いてアンモニアで処理した。次にエトキシ基を臭化水素酸を用いてブロモ誘導体に変換した。最終段階では、4-メチル-5-(2-ヒドロキシエチル)チアゾールを用いたアルキル化反応でチアミン(二臭化物塩として)が生成した。
工業的合成

[[[Merck & Co.|メルク社]]は1936年の実験室規模の合成を応用し、1937年にラーウェイでチアミンを製造できるようにした。しかし、1937年に初めて発表された中間体であるグレウジアミン(5-(アミノメチル)-2-メチル-4-ピリミジナミン)を用いた代替ルートがホフマン・ラ・ロシュによって研究され、競争力のある製造プロセスが続いた。ジアミンへの効率的なルートは引き続き注目されている。欧州経済領域では、チアミンはREACH規則に登録されており、年間100トンから1,000トンが製造または輸入されている。
合成類似体
多くのビタミンB1類似体、例えばベンフォチアミン、フルスルチアミン、スルブチアミンはチアミンの合成誘導体である。ほとんどは、チアミンと比較して吸収を改善することを意図した形態として、1950年代と1960年代に日本で開発された。一部の国では、糖尿病性神経障害またはその他の健康状態の治療のための薬物または非処方栄養補助食品としての使用が承認されている。
吸収、代謝および排泄
小腸上部では、食物中のチアミンリン酸エステルがアルカリホスファターゼ酵素によって加水分解される。低濃度では、吸収過程は担体を介する。高濃度では、吸収は受動拡散経由でも起こる。能動輸送はアルコール摂取や葉酸欠乏症によって阻害されることがある。
血清中のチアミンの大部分はタンパク質、主にアルブミンと結合している。血液中の総チアミンのおよそ90%は赤血球中にある。チアミン結合タンパク質と呼ばれる特異的な結合タンパク質がラット血清で同定されており、チアミンの組織分布に重要なホルモン制御キャリアタンパク質であると考えられている。血液や他の組織の細胞によるチアミンの取り込みは、能動輸送と受動拡散を介して起こる。遺伝子SLC19A2およびSLC19A3によってコードされるトランスポータータンパク質のファミリーの2つのメンバーは、チアミン輸送が可能である。いくつかの組織では、チアミンの取り込みと分泌はNa+依存性トランスポーターと経細胞プロトン勾配によって媒介されるようである。
ヒトのチアミン貯蔵量は約25~30 mgで、骨格筋、心臓、脳、肝臓、腎臓に最も多く存在する。ThMPおよび遊離(リン酸化されていない)チアミンは、血漿、牛乳、脳脊髄液、および推定ではすべての細胞外液に存在する。高度にリン酸化された形態のチアミンとは異なり、ThMPと遊離チアミンは細胞膜を通過することができる。カルシウムとマグネシウムは体内のチアミンの分布に影響を与えることが示されており、マグネシウム欠乏はチアミン欠乏を悪化させることが示されている。ヒトの組織中のチアミン含量は他の生物種よりも少ない。
チアミンとその代謝物(2-メチル-4-アミノ-5-ピリミジンカルボン酸、4-メチル-チアゾール-5-酢酸など)は主に尿中に排泄される。
干渉
食品中のチアミンの生物学的利用能は、様々な方法で阻害される可能性がある。保存料として食品に添加される亜硫酸塩は、チアミンをメチレン橋で攻撃し、チアゾール環からピリミジン環を切断する。この反応の速度は酸性条件下で増大する。チアミンは、魚介類やその他の食品に含まれる熱分解性のチアミナーゼによって分解される。アフリカのカイコ、Anaphe venata'の蛹はナイジェリアの伝統的な食べ物である。摂取するとチアミン欠乏症になる。古い文献によると、タイでは発酵させた未調理の魚を摂取するとチアミン欠乏症になるが、魚を食べるのを控えるか、加熱すると欠乏症が回復したと報告されている。反芻動物では、腸内細菌がチアミンとチアミナーゼを合成する。細菌のチアミナーゼは細胞表面酵素であり、活性化される前に細胞膜から解離しなければならない;解離は反芻動物では酸性条件下で起こりうる。乳牛では、穀物の過剰給与により亜急性ルーミナルアシドーシスが起こり、ルーミナル細菌チアミナーゼの放出が増加し、チアミン欠乏症が起こる。
From reports on two small studies conducted in Thailand, chewing slices of areca nut wrapped in betel leaves and chewing tea leaves reduced food thiamine bioavailability by a mechanism that may involve tannins.
Bariatric surgery for weight loss is known to interfere with vitamin absorption. A meta-analysis reported that 27% of people who underwent bariatric surgeries experience vitamin B1 deficiency.
History
Thiamine was the first of the water-soluble vitamins to be isolated. The earliest observations in humans and in chickens had shown that diets of primarily polished white rice caused beriberi, but did not attribute it to the absence of a previously unknown essential nutrient.
In 1884, Takaki Kanehiro, a surgeon general in the Imperial Japanese Navy, rejected the previous germ theory for beriberi and suggested instead that the disease was due to insufficiencies in the diet. Switching diets on a navy ship, he discovered that replacing a diet of white rice only with one also containing barley, meat, milk, bread, and vegetables, nearly eliminated beriberi on a nine-month sea voyage. However, Takaki had added many foods to the successful diet and he incorrectly attributed the benefit to increased protein intake, as vitamins were unknown at the time. The Navy was not convinced of the need for such an expensive program of dietary improvement, and many men continued to die of beriberi, even during the Russo-Japanese war of 1904–5. Not until 1905, after the anti-beriberi factor had been discovered in rice bran (removed by polishing into white rice) and in barley bran, was Takaki's experiment rewarded. He was made a baron in the Japanese peerage system, after which he was affectionately called "Barley Baron".
The specific connection to grain was made in 1897 by Christiaan Eijkman, a military doctor in the Dutch East Indies, who discovered that fowl fed on a diet of cooked, polished rice developed paralysis that could be reversed by discontinuing rice polishing. He attributed beriberi to the high levels of starch in rice being toxic. He believed that the toxicity was countered in a compound present in the rice polishings. An associate, Gerrit Grijns, correctly interpreted the connection between excessive consumption of polished rice and beriberi in 1901: He concluded that rice contains an essential nutrient in the outer layers of the grain that is removed by polishing. Eijkman was eventually awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1929, because his observations led to the discovery of vitamins.
In 1910, a Japanese agricultural chemist of Tokyo Imperial University, Umetaro Suzuki, isolated a water-soluble thiamine compound from rice bran, which he named aberic acid. (He later renamed it Orizanin.) He described the compound as not only an anti-beriberi factor, but also as being essential to human nutrition; however, this finding failed to gain publicity outside of Japan, because a claim that the compound was a new finding was omitted in translation of his publication from Japanese to German. In 1911 a Polish biochemist Casimir Funk isolated the antineuritic substance from rice bran (the modern thiamine) that he called a "vitamine" (on account of its containing an amino group). However, Funk did not completely characterize its chemical structure. Dutch chemists, Barend Coenraad Petrus Jansen and his closest collaborator Willem Frederik Donath, went on to isolate and crystallize the active agent in 1926, whose structure was determined by Robert Runnels Williams, in 1934. Thiamine was named by the Williams team as a portmanteau of "thio" (meaning sulfur-containing) and "vitamin". The term "vitamin" coming indirectly, by way of Funk, from the amine group of thiamine itself (although by this time, vitamins were known to not always be amines, for example, vitamin C). Thiamine was also synthesized by the Williams group in 1936.
Sir Rudolph Peters, in Oxford, used pigeons to understand how thiamine deficiency results in the pathological-physiological symptoms of beriberi. Pigeons fed exclusively on polished rice developed opisthotonos, a condition characterized by head retraction. If not treated, the animals died after a few days. Administration of thiamine after opisthotonos was observed led to a complete cure within 30 minutes. As no morphological modifications were seen in the brain of the pigeons before and after treatment with thiamine, Peters introduced the concept of a biochemical-induced injury. In 1937, Lohmann and Schuster showed that the diphosphorylated thiamine derivative, TPP, was a cofactor required for the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate.
- Some contributors to the discovery of thiamine
外部リンク
- "Thiamine". Drug Information Portal. US National Library of Medicine.