Vitamin D/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "米国の医学研究所(IOM)の報告書にはこう書かれている: 「がん、心血管系疾患と高血圧、および糖尿病とメタボリックシンドローム、転倒と身体能力、免疫機能と自己免疫疾患、感染症、神経心理学的機能、および子癇前症に関する結果は、カ..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "=== あらゆる原因による死亡率 === ビタミンD<sub>3</sub>の補充は、高齢者の死亡リスクの減少につながることが暫定的に判明しているが、その効果は顕著ではなく、サプリメントの摂取を推奨するほど確実なものでもない。その他のビタミンD(ビタミンD<sub>2</sub>、アルファカルシドール、カルシトリオール)には、死亡リスクに対する有益な効果はないよ..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
米国の[[Institute of Medicine/ja|医学研究所]](IOM)の報告書にはこう書かれている: 「がん、[[cardiovascular disease/ja|心血管系疾患]]と[[hypertension/ja|高血圧]]、および[[diabetes/ja|糖尿病]]とメタボリックシンドローム、転倒と身体能力、免疫機能と[[autoimmune disorder/ja|自己免疫疾患]]、感染症、神経心理学的機能、および[[preeclampsia/ja|子癇前症]]に関する結果は、カルシウムまたはビタミンDのどちらかの摂取量と確実に関連づけることができず、しばしば矛盾していた。一部の研究者は、IOMの勧告はあまりにも断定的であり、骨の健康に関連するビタミンDの血中濃度を計算する際に数学的な間違いを犯したと主張している。IOM委員会のメンバーは、自分たちは "食事勧告の標準的な手順 "を使用し、報告書はデータにしっかりと基づいていると主張している。 | 米国の[[Institute of Medicine/ja|医学研究所]](IOM)の報告書にはこう書かれている: 「がん、[[cardiovascular disease/ja|心血管系疾患]]と[[hypertension/ja|高血圧]]、および[[diabetes/ja|糖尿病]]とメタボリックシンドローム、転倒と身体能力、免疫機能と[[autoimmune disorder/ja|自己免疫疾患]]、感染症、神経心理学的機能、および[[preeclampsia/ja|子癇前症]]に関する結果は、カルシウムまたはビタミンDのどちらかの摂取量と確実に関連づけることができず、しばしば矛盾していた。一部の研究者は、IOMの勧告はあまりにも断定的であり、骨の健康に関連するビタミンDの血中濃度を計算する際に数学的な間違いを犯したと主張している。IOM委員会のメンバーは、自分たちは "食事勧告の標準的な手順 "を使用し、報告書はデータにしっかりと基づいていると主張している。 | ||
=== あらゆる原因による死亡率 === | |||
=== | ビタミンD<sub>3</sub>の補充は、高齢者の死亡リスクの減少につながることが暫定的に判明しているが、その効果は顕著ではなく、サプリメントの摂取を推奨するほど確実なものでもない。その他のビタミンD(ビタミンD<sub>2</sub>、アルファカルシドール、カルシトリオール)には、死亡リスクに対する有益な効果はないようである。血中濃度が高いことは死亡リスクの低下と関連しているようであるが、補充によってこのような利益が得られるかどうかは不明である。ビタミンDは過剰でも欠乏でも、機能異常と早期老化を引き起こすようである。血清カルシフェジオール濃度と全死因死亡率との関係は "U字型"であり、カルシフェジオール濃度が高くても低くても、死亡率は中等度に比べて上昇する。ビタミンDによる害は、白人集団よりも黒人集団の方がビタミンD濃度が低い場合に起こるようである。 | ||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | <div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | ||
Revision as of 19:38, 29 January 2024
| Vitamin D/ja | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
 コレカルシフェロール (D3) | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | Calciferols |
| Use | Rickets/ja, osteoporosis/ja, ビタミン D 欠乏症 |
| ATC code | A11CC |
| Biological target | ビタミン D 受容体 |
| Clinical data | |
| Drugs.com | MedFacts Natural Products |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D014807 |
| Legal status | |
ビタミンDは脂溶性 セコステロイドの一群である。カルシウム、マグネシウム、リン酸塩の腸管吸収を増加させ、他の多くの生物学的作用を担う。ヒトにおいて、このグループの最も重要な化合物はビタミンD3(コレカルシフェロール)とビタミンD2(エルゴカルシフェロール)である。
ビタミンDの主な天然供給源は、皮膚の表皮下層におけるコレカルシフェロールの合成であり、日光暴露(具体的にはUVB放射)またはUVBランプによるUVB光の光化学反応によって得られる。コレカルシフェロールとエルゴカルシフェロールは、食事やサプリメントから摂取することができる。米国やその他の国では、牛乳や植物由来の代用乳にビタミンDが強化されており、朝食用シリアルにもビタミンDが配合されている。紫外線を浴びたキノコ類は、有用な量のビタミンD2を含んでいる。一般に食事療法では、ビタミンDをすべて口から摂取することを想定している。なぜなら、人々の日光浴の程度はさまざまであり、皮膚がんのリスクを考慮すると、安全な日光浴の量に関する推奨は不確かだからである。
食事から摂取したビタミンDも、皮膚で合成されたビタミンDも、生物学的には不活性である。ビタミンDは2つのタンパク質酵素ヒドロキシル化によって活性化され、1つ目は肝臓で、2つ目は腎臓で合成される。ビタミンDは日光を十分に浴びればほとんどの哺乳類で十分な量を合成することができるため、必須栄養素ではなく、厳密にはビタミンではない。その代わりにホルモンとみなすことができ、ビタミンDプロホルモンの活性化によって活性型であるカルシトリオールが生成され、これが複数の場所にある核内受容体を介して効果を発揮する。
コレカルシフェロールは肝臓でカルシフェジオール(25-ヒドロキシコレカルシフェロール)に変換され、エルゴカルシフェロールは25-ヒドロキシエルゴカルシフェロールに変換される。これら2つのビタミンD代謝産物(25-ヒドロキシビタミンDまたは25(OH)Dと呼ばれる)は、血清中で測定され、その人のビタミンDの状態を決定する。カルシフェジオールは、腎臓と免疫系細胞の一部でさらに水酸化され、生物学的に活性なビタミンDであるカルシトリオール(1,25-ジヒドロキシコレカルシフェロール)を形成する。カルシトリオールはホルモンとして血液中を循環し、カルシウムとリン酸の濃度を調節し、骨の健全な成長とリモデリングを促進する主要な役割を担っている。カルシトリオールには他にも、細胞増殖、神経筋・免疫機能、炎症抑制などの作用がある。
ビタミンDはカルシウムの恒常性および代謝において重要な役割を担っている。その発見は、くる病(骨軟化症の小児型)の子どもたちに欠乏している食事性物質を見つける努力によるものであった。ビタミンDのサプリメントは、骨軟化症やくる病の治療や予防のために投与される。ビタミンDが不足している人に対するビタミンD補給の他の健康効果に関する証拠は一貫していない。死亡率に対するビタミンD補給の効果は明らかではないが、あるメタアナリシスでは、高齢者における死亡率のわずかな減少が認められている。高リスク群におけるくる病や骨軟化症の予防を除けば、ビタミンD補給による筋骨格系や全身の健康への恩恵はわずかであろう。
タイプ
| 名称 | 化学組成 | 構造 |
|---|---|---|
| ビタミン D1 | エルゴカルシフェロールとルミステロールの分子化合物の混合物、1:1 | |
| ビタミン D2 | エルゴカルシフェロール (エルゴステロールから作られる) | 
|
| ビタミン D3 | コレカルシフェロール
(皮膚の7-デヒドロコレステロールから作られる) |

|
| ビタミン D4 | 22-ジヒドロエルゴカルシフェロール | 
|
| ビタミン D5 | シトカルシフェロール
(7-デヒドロコレステロールから作られる) |

|
ビタミンDにはいくつかの形態(ビタマー)が存在する。ビタミンD2またはエルゴカルシフェロールとビタミンD3またはコレカルシフェロールである。添え字のないビタミンDは、D2またはD3のいずれか、あるいは両方を指し、カルシフェロールとして総称される。
ビタミンD2は1931年に化学的に特徴づけられた。1935年、ビタミンD3の化学構造が定義され、7-デヒドロコレステロールの紫外線照射から生じることが示された。1981年にビタミンDの化学的命名法が推奨されたが、別の名称が一般的に使用されている。
化学的には、ビタミンDの様々な形はセコステロイド、つまりステロイド環の結合の1つが切れたステロイドである。ビタミンD2とビタミンD3の構造の違いは、炭素22と23の間にある二重結合を含む側鎖にあり、ビタミンD2では炭素24上にメチル基がある。多くのビタミンD類似体が合成されている。
生物学
活性型ビタミンD代謝物であるカルシトリオールは、主に標的細胞の核に存在するビタミンD受容体(VDR)に結合することにより、その生物学的作用を媒介する。VDRへのカルシトリオールの結合により、VDRは、腸でのカルシウム吸収に関与する輸送タンパク質(TRPV6やカルビンディンなど)の遺伝子発現を調節する転写因子として働く。ビタミンD受容体はステロイド/甲状腺ホルモン受容体の核内受容体スーパーファミリーに属し、VDRは脳、心臓、皮膚、生殖腺、前立腺、乳房などほとんどの器官の細胞で発現している。
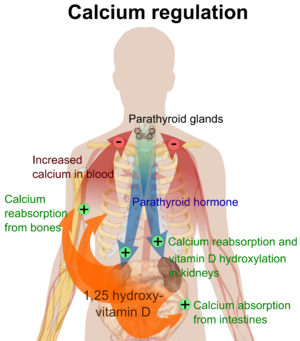
腸、骨、腎臓、副甲状腺細胞におけるVDRの活性化は、(副甲状腺ホルモンとカルシトニンの助けを借りて)血液中のカルシウムとリンの濃度を維持し、骨の量を維持する。
ビタミンDの最も重要な役割のひとつは、腸におけるカルシウム吸収の促進、破骨細胞数の増加による骨吸収の促進、骨形成のためのカルシウムおよびリン酸レベルの維持、および血清カルシウムレベルを維持するための副甲状腺ホルモンの適切な機能によって、骨格カルシウムバランスを維持することである。ビタミンDの欠乏は体内のミネラル代謝を変化させるため、ビタミンD欠乏症は骨密度の低下(骨粗鬆症)や骨折のリスクを高める。したがって、ビタミンDは骨吸収の強力な刺激因子としての役割を通じて、骨リモデリングにも重要である。
VDRは細胞増殖と分化を制御している。ビタミンDは免疫系にも影響を及ぼし、VDRは単球や活性化T、B細胞など、いくつかの白血球に発現している。試験管内では、ビタミンDは副腎髄質細胞のチロシン水酸化酵素遺伝子の発現を増加させる、 また、神経栄養因子、一酸化窒素合成酵素、グルタチオンの合成に影響を与える。
ビタミンD受容体の発現は加齢とともに減少する。
欠乏症
ビタミンDが不十分な食事と不十分な日光浴はビタミンD欠乏症を引き起こし、血中25(OH)D濃度が12 ng/mL(30 nmol/liter)未満である場合をビタミンD欠乏症、血中25(OH)D濃度が12-20 ng/mL(30-50 nmol/liter)である場合をビタミンD欠乏症と定義する。ヨーロッパの先進国を含め、世界中で推定10億人の成人がビタミンD不足または欠乏状態にある。先進国では稀な疾患であるが、小児における重度のビタミンD欠乏症は、成長期の骨が軟化し弱くなり、くる病と呼ばれる状態を引き起こす。
ビタミンDの欠乏は、高齢者では世界的にみられ、小児や成人では依然として一般的である。欠乏すると、骨のミネラル化が損なわれ、骨に損傷が生じ、小児ではくる病、成人では骨軟化症などの骨軟化性疾患につながる。日光浴を避けると、血中カルシフェジオール(25-ヒドロキシビタミンD)が低下する。ビタミンDが不足すると、食事から摂取したカルシウムの吸収率が通常の割合(60~80%)から15%にまで低下する。
温帯気候に住む肌の黒い人は、ビタミンD濃度が低いことがわかっている。肌の黒い人は、皮膚のメラニンがビタミンDの合成を妨げるため、ビタミンDを作る効率が低いのだ。ビタミンD欠乏症は、米国のヒスパニック系やアフリカ系アメリカ人に多く、冬になるとレベルが著しく低下する。これは、皮膚中のメラニンが日光暴露から皮膚を守る働きをするためである。
骨の健康
くる病
小児疾患のひとつであるくる病は、成長が阻害され、柔らかく、弱く、変形した長骨が特徴である。くる病は通常、生後3ヵ月から18ヵ月の間に発症する。北米やその他の欧米諸国では症例が報告され続けており、主に母乳で育てられた乳児や皮膚の色が濃い乳児にみられる。この疾患は、カルシウムやリンの欠乏、ビタミンDの欠乏によって引き起こされる弓脚を特徴とする。21世紀には、アフリカ、アジア、中東の低所得国や、偽性ビタミンD欠乏性くる病などの遺伝的疾患を持つ人に多く見られる。
母親のビタミンD欠乏は、出生前から明らかな骨疾患を引き起こし、出生後は骨質の障害を引き起こす可能性がある。栄養性くる病は、ナイジェリアのように年間を通じて日照量の多い国にも存在し、ビタミンD欠乏がなくても発症する。
イギリスでは現在、くる病や骨軟化症はまれであるが、いくつかの移民コミュニティでは、西洋の衣服を着て日中屋外に十分出ているように見える女性も骨軟化症患者として含まれていた。肌が黒く、日光に当たる機会が少なくても、肉、魚、卵を多く摂取する西洋の雑食パターンから外れない限り、くる病は発症しなかった。くる病の食事危険因子には、動物性食品を控えることが含まれる。
母乳にはビタミンDが少なく、社会的慣習や気候条件が十分な日光浴を妨げるためである。ナイジェリア、南アフリカ、バングラデシュのような日照時間の長い国では、年長の幼児や小児にくる病がみられるが、その原因は、乳製品へのアクセスが限られている穀類中心の食生活に特徴的な、食事からのカルシウム摂取量の低さにあるとされている。
くる病はかつて、アメリカ国民の間で公衆衛生上の大きな問題となっていた。デンバーでは、1920年代後半に500人の子供のほぼ3分の2が軽度のくる病であった。20世紀のアメリカ人の食事に占める動物性タンパク質の割合が増加し、比較的少量のビタミンDを強化した牛乳の消費量が増えたことで、くる病の患者数が劇的に減少した。また、米国とカナダでは、ビタミンD強化乳、乳児用ビタミン剤、ビタミン補助食品により、脂肪吸収不良の子供たちのくる病の大部分を根絶することができた。
骨軟化症と骨粗鬆症
骨軟化症は、ビタミンDの欠乏に起因する成人の疾患である。この疾患の特徴は、骨が軟化し、背骨が曲がり、近位筋力が低下し、骨がもろくなり、骨折のリスクが高まることである。骨軟化症は、カルシウムの吸収を低下させ、骨からのカルシウム喪失を増加させるため、骨折の危険性を増大させる。骨軟化症は通常、25-ヒドロキシビタミンD値が約10 ng/mL未満の場合にみられる。骨軟化症の影響は慢性的な筋骨格系の痛みの一因であると考えられているが慢性痛を有する人のビタミンD濃度が低いという説得力のある証拠や、ビタミンD補充が慢性非特異的筋骨格痛を緩和するという証拠はない。骨軟化症は骨粗鬆症に進行し、骨密度が低下して骨がもろくなり、骨折の危険性が高まる。骨粗鬆症は、カルシウムおよび/またはビタミンDの不足による長期的な影響である可能性があり、後者はカルシウムの吸収を低下させることで寄与する。
サプリメントの使用
ビタミンDの補給は、くる病の予防や治療に確実な方法である。一方、ビタミンDの補給が非骨格系の健康に及ぼす影響は不明である。あるレビューでは、高齢者における死亡率の暫定的な減少以外に、非骨格系疾患の発生率に対するビタミンD補給の効果は認められなかった。ビタミンDサプリメントは、心筋梗塞、脳卒中または脳血管疾患、がん、骨折または膝変形性関節症の転帰を変化させない。
米国の医学研究所(IOM)の報告書にはこう書かれている: 「がん、心血管系疾患と高血圧、および糖尿病とメタボリックシンドローム、転倒と身体能力、免疫機能と自己免疫疾患、感染症、神経心理学的機能、および子癇前症に関する結果は、カルシウムまたはビタミンDのどちらかの摂取量と確実に関連づけることができず、しばしば矛盾していた。一部の研究者は、IOMの勧告はあまりにも断定的であり、骨の健康に関連するビタミンDの血中濃度を計算する際に数学的な間違いを犯したと主張している。IOM委員会のメンバーは、自分たちは "食事勧告の標準的な手順 "を使用し、報告書はデータにしっかりと基づいていると主張している。
あらゆる原因による死亡率
ビタミンD3の補充は、高齢者の死亡リスクの減少につながることが暫定的に判明しているが、その効果は顕著ではなく、サプリメントの摂取を推奨するほど確実なものでもない。その他のビタミンD(ビタミンD2、アルファカルシドール、カルシトリオール)には、死亡リスクに対する有益な効果はないようである。血中濃度が高いことは死亡リスクの低下と関連しているようであるが、補充によってこのような利益が得られるかどうかは不明である。ビタミンDは過剰でも欠乏でも、機能異常と早期老化を引き起こすようである。血清カルシフェジオール濃度と全死因死亡率との関係は "U字型"であり、カルシフェジオール濃度が高くても低くても、死亡率は中等度に比べて上昇する。ビタミンDによる害は、白人集団よりも黒人集団の方がビタミンD濃度が低い場合に起こるようである。
Bone health
In general, no good evidence supports the commonly held belief that vitamin D supplements can help prevent osteoporosis. Its general use for prevention of this disease in those without vitamin D deficiency is thus likely not needed. For older people with osteoporosis, taking vitamin D with calcium may help prevent hip fractures, but it also slightly increases the risk of stomach and kidney problems. A study found that supplementation with 800 IU or more daily, in those older than 65 years was "somewhat favorable in the prevention of hip fracture and non-vertebral fracture". The effect is small or none for people living independently. Low serum vitamin D levels have been associated with falls, and low bone mineral density. Taking extra vitamin D, however, does not appear to change the risk.
Athletes who are vitamin D deficient are at an increased risk of stress fractures and/or major breaks, particularly those engaging in contact sports. The greatest benefit with supplementation is seen in athletes who are deficient (25(OH)D serum levels <30 ng/mL), or severely deficient (25(OH)D serum levels <25 ng/mL). Incremental decreases in risks are observed with rising serum 25(OH)D concentrations plateauing at 50 ng/mL with no additional benefits seen in levels beyond this point.
A 2020 Cochrane systematic review has found limited evidence that vitamin D plus calcium, but not independently can improve healing in children with nutritional rickets, but the evidence was not conclusive for reducing fractures.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required manufacturers to declare the amount of vitamin D on nutrition facts labels, as "nutrients of public health significance", since May 2016. By a proposed deadline extension, some manufacturers had until 1 July 2021, to comply.
Cancer
Potential associations have been found between low vitamin D levels and the risk of developing several types of cancer. Meta-analyses of observational studies have found reduced risk of cancer incidence related to vitamin D intake and 25(OH)D levels, particularly for colorectal cancer, although the strength of the associations was classified as weak. While randomized controlled trials have not confirmed that vitamin D supplements reduce the risk of cancer incidence, the relative risk of cancer deaths was lower by up to 16% in several meta-analyses.
Cardiovascular disease
Vitamin D supplementation is not associated with a reduced risk of stroke, cerebrovascular disease, myocardial infarction, or ischemic heart disease. Supplementation does not lower blood pressure in the general population.
Immune system
Infectious diseases
In general, vitamin D functions to activate the innate and dampen the adaptive immune systems with antibacterial, antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects. Low levels of vitamin D appear to be a risk factor for tuberculosis, and historically it was used as a treatment.
Vitamin D supplementation in low doses (400 to 1000 IU/day) may slightly decrease the overall risk of acute respiratory tract infections. The benefits were found in young children and adolescents (ages 1 up to 16 years) and were not confirmed with higher doses (>1000 IU per day or more). Vitamin D supplementation substantially reduces the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations of COPD in people with baseline 25(OH)D levels under 25nmol/L, but not in those with less severe deficiency.
Asthma
Vitamin D supplementation does not help prevent asthma attacks or alleviate their symptoms.
Inflammatory bowel disease
Low levels of vitamin D are associated with two major forms of human inflammatory bowel disease: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Deficiencies in vitamin D have been linked to the severity of the case of inflammatory bowl disease, however, whether vitamin D deficiency causes inflammatory bowl disease or is a symptom of the disease is not clear.
There is some evidence that vitamin D supplementation therapy for people with inflammatory bowel disease may be associated with improvements in scores for clinical inflammatory bowel disease activity and biochemical markers. Vitamin D treatment may be associated with less frequent relapse of symptoms in IBD. It is not clear if this treatment improves the person's quality of life or what the clinical response to vitamin D treatment. The ideal treatment regime and dose of vitamin D therapy has not been well enough studied.
Other conditions
Diabetes
A meta-analysis reported that vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced the risk of type 2 diabetes for non-obese people with prediabetes. Another meta-analysis reported that vitamin D supplementation significantly improved glycemic control [homeostatic model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)], hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C), and fasting blood glucose (FBG) in individuals with type 2 diabetes. In prospective studies, high versus low level of vitamin D was respectively associated with significant decrease in risk of type 2 diabetes, combined type 2 diabetes and prediabetes, and prediabetes. A 2011 Cochrane systematic review examined one study that showed vitamin D together with insulin maintained levels of fasting C-peptide after 12 months better than insulin alone. However, it is important to highlight that the studies available to be included in this review presented considerable flaws in quality and design.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
A meta-analysis of observational studies showed that children with ADHD have lower vitamin D levels, and that there was a small association between low vitamin D levels at the time of birth and later development of ADHD. Several small, randomized controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation indicated improved ADHD symptoms such as impulsivity and hyperactivity.
Depression
Clinical trials of vitamin D supplementation for depressive symptoms have generally been of low quality and show no overall effect, although subgroup analysis showed supplementation for participants with clinically significant depressive symptoms or depressive disorder had a moderate effect.
Cognition and dementia
A systematic review of clinical studies found an association between low vitamin D levels with cognitive impairment and a higher risk of developing Alzheimer's disease. However, lower vitamin D concentrations are also associated with poor nutrition and spending less time outdoors. Therefore, alternative explanations for the increase in cognitive impairment exist and hence a direct causal relationship between vitamin D levels and cognition could not be established.
Schizophrenia
Trials have demonstrated lower vitamin D levels are highly prevalent in people with schizophrenia, particularly those with acute episodes.
Pregnancy
Low levels of vitamin D in pregnancy are associated with gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia, and small (for gestational age) infants. Although taking vitamin D supplements during pregnancy raises blood levels of vitamin D in the mother at term, the full extent of benefits for the mother or baby is unclear. Pregnant women who take an adequate amount of vitamin D during gestation may experience a lower risk of pre-eclampsia and positive immune effects. Vitamin D supplementation is also likely to reduce the risk of gestational diabetes, undersized babies and of their poor rate of growth. Pregnant women often do not take the recommended amount of vitamin D.
Weight loss
Though hypothesized that vitamin D supplementation may be an effective treatment for obesity apart from calorie restriction, one systematic review found no association of supplementation with body weight or fat mass. A 2016 meta-analysis found that circulating vitamin D status was improved by weight loss, indicating that fat mass may be inversely associated with blood levels of vitamin D.
Allowable health claims
Governmental regulatory agencies stipulate for the food and dietary supplement industries certain health claims as allowable as statements on packaging.
European Food Safety Authority
- normal function of the immune system
- normal inflammatory response
- normal muscle function
- reduced risk of falling in people over age 60
US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- "Adequate calcium and vitamin D, as part of a well balanced diet, along with physical activity, may reduce the risk of osteoporosis."
- "Adequate calcium and regular exercise may help to achieve strong bones in children and adolescents and may reduce the risk of osteoporosis in older adults. An adequate intake of vitamin D is also necessary."
Other possible agencies with claim guidance: Japan FOSHU and Australia-New Zealand.
Dietary intake
| United Kingdom | ||
| Age group | Intake (μg/day) | Maximum intake (μg/day) |
|---|---|---|
| Breast-fed infants 0–12 months | 8.5 – 10 | 25 |
| Formula-fed infants (<500 mL/d) | 10 | 25 |
| Children 1 – 10 years | 10 | 50 |
| Children >10 and adults | 10 | 100 |
| United States | ||
| Age group | RDA (IU/day) | (μg/day) |
| Infants 0–6 months | 400* | 10 |
| Infants 6–12 months | 400* | 10 |
| 1–70 years | 600 | 15 |
| Adults > 70 years | 800 | 20 |
| Pregnant/Lactating | 600 | 15 |
| Age group | Tolerable upper intake level (IU/day) | (μg/day) |
| Infants 0–6 months | 1,000 | 25 |
| Infants 6–12 months | 1,500 | 37.5 |
| 1–3 years | 2,500 | 62.5 |
| 4–8 years | 3,000 | 75 |
| 9+ years | 4,000 | 100 |
| Pregnant/lactating | 4,000 | 100 |
| Canada | ||
| Age group | RDA (IU) | Tolerable upper intake (IU) |
| Infants 0–6 months | 400* | 1,000 |
| Infants 7–12 months | 400* | 1,500 |
| Children 1–3 years | 600 | 2,500 |
| Children 4–8 years | 600 | 3,000 |
| Children and adults 9–70 years | 600 | 4,000 |
| Adults > 70 years | 800 | 4,000 |
| Pregnancy & lactation | 600 | 4,000 |
| Australia and New Zealand | ||
| Age group | Adequate Intake (μg) | Upper Level of Intake (μg) |
| Infants 0–12 months | 5* | 25 |
| Children 1–18 years | 5* | 80 |
| Adults 19–50 years | 5* | 80 |
| Adults 51–70 years | 10* | 80 |
| Adults > 70 years | 15* | 80 |
| European Food Safety Authority | ||
| Age group | Adequate Intake (μg) | Tolerable upper limit (μg) |
| Infants 0–12 months | 10 | 25 |
| Children 1–10 years | 15 | 50 |
| Children 11–17 years | 15 | 100 |
| Adults | 15 | 100 |
| Pregnancy & Lactation | 15 | 100 |
| * Adequate intake, no RDA/RDI yet established | ||
Recommended levels
Various institutions have proposed different recommendations for the amount of daily intake of vitamin D. These vary according to precise definition, age, pregnancy or lactation, and the extent assumptions are made regarding skin synthesis of vitamin D. Conversion: 1 μg (microgram) = 40 IU (international unit).
United Kingdom
The UK National Health Service (NHS) recommends that people at risk of vitamin D deficiency, breast-fed babies, formula-fed babies taking less than 500 ml/day, and children aged 6 months to 4 years, should take daily vitamin D supplements throughout the year to ensure sufficient intake. This includes people with limited skin synthesis of vitamin D, who are not often outdoors, are frail, housebound, living in a care home, or usually wearing clothes that cover up most of the skin, or with dark skin, such as having an African, African-Caribbean or south Asian background. Other people may be able to make adequate vitamin D from sunlight exposure from April to September. The NHS and Public Health England recommend that everyone, including those who are pregnant and breastfeeding, consider taking a daily supplement containing 10 μg (400 IU) of vitamin D during autumn and winter because of inadequate sunlight for vitamin D synthesis.
United States
The dietary reference intake for vitamin D issued in 2010 by the Institute of Medicine (IoM) (renamed National Academy of Medicine in 2015), superseded previous recommendations which were expressed in terms of adequate intake. The recommendations were formed assuming the individual has no skin synthesis of vitamin D because of inadequate sun exposure. The reference intake for vitamin D refers to total intake from food, beverages and supplements, and assumes that calcium requirements are being met. The tolerable upper intake level (UL) is defined as "the highest average daily intake of a nutrient that is likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects for nearly all persons in the general population." Although ULs are believed to be safe, information on the long-term effects is incomplete and these levels of intake are not recommended for long-term consumption.
For US food and dietary supplement labeling purposes, the amount in a serving is expressed as a percent of Daily Value (%DV). For vitamin D labeling purposes, 100% of the daily value was 400 IU (10 μg), but in May 2016, it was revised to 800 IU (20 μg) to bring it into agreement with the recommended dietary allowance (RDA). Compliance with the updated labeling regulations was required by 1 January 2020 for manufacturers with US$10 million or more in annual food sales, and by 1 January 2021 for manufacturers with lower volume food sales. A table of the old and new adult daily values is provided at Reference Daily Intake.
Canada
Health Canada published recommended dietary intakes (DRIs) and tolerable upper intake levels (ULs) for vitamin D based on the jointly commissioned and funded Institute of Medicine 2010 report.
Australia and New Zealand
Australia and New Zealand published nutrient reference values including guidelines for dietary vitamin D intake in 2006.
European Union
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in 2016 reviewed the current evidence, finding the relationship between serum 25(OH)D concentration and musculoskeletal health outcomes is widely variable. They considered that average requirements and population reference intakes values for vitamin D cannot be derived, and that a serum 25(OH)D concentration of 50 nmol/L was a suitable target value. For all people over the age of 1, including women who are pregnant or lactating, they set an adequate intake of 15 μg/day (600 IU).
The EFSA reviewed safe levels of intake in 2012, setting the tolerable upper limit for adults at 100 μg/day (4000 IU), a similar conclusion as the IOM.
The Swedish National Food Agency recommends a daily intake of 10 μg (400 IU) of vitamin D3 for children and adults up to 75 years, and 20 μg (800 IU) for adults 75 and older.
Non-government organisations in Europe have made their own recommendations. The German Society for Nutrition recommends 20 μg. The European Menopause and Andropause Society recommends postmenopausal women consume 15 μg (600 IU) until age 70, and 20 μg (800 IU) from age 71. This dose should be increased to 100 μg (4,000 IU) in some patients with very low vitamin D status or in case of co-morbid conditions.
Sources
Although vitamin D is present naturally in only a few foods, it is commonly added as a fortification in manufactured foods. In some countries, staple foods are artificially fortified with vitamin D.
Natural sources
| Animal sources | |||
| Source | IU/g | Irregular | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooked egg yolk | 0.7 | 44 IU for a 61g egg | |
| Beef liver, cooked, braised | 0.5 | ||
| Fish liver oils, such as cod liver oil | 100 | 450 IU per teaspoon (4.5 g) | |
| Fatty fish species | |||
| Salmon, pink, cooked, dry heat | 5.2 | ||
| Mackerel, Pacific and jack, mixed species, cooked, dry heat | 4.6 | ||
| Tuna, canned in oil | 2.7 | ||
| Sardines, canned in oil, drained | 1.9 | ||
| Fungal sources | |||
| Source | μg/g | IU/g | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cladonia arbuscula (lichen), thalli, dry | vitamin D3 | 0.67–2.04 | 27–82 |
| vitamin D2 | 0.22–0.55 | 8.8–22 | |
| Agaricus bisporus (common mushroom): D2 + D3 | |||
| Portobello | Raw | 0.003 | 0.1 |
| Exposed to ultraviolet light | 0.11 | 4.46 | |
| Crimini | Raw | 0.001 | 0.03 |
| Exposed to ultraviolet light | 0.32 | 12.8 | |
In general, vitamin D3 is found in animal source foods, particularly fish, meat, offal, egg and dairy. Vitamin D2 is found in fungi and is produced by ultraviolet irradiation of ergosterol. The vitamin D2 content in mushrooms and Cladina arbuscula, a lichen, increases with exposure to ultraviolet light, and is stimulated by industrial ultraviolet lamps for fortification. The United States Department of Agriculture reports D2 and D3 content combined in one value.
Food fortification
Manufactured foods fortified with vitamin D include some fruit juices and fruit juice drinks, meal replacement energy bars, soy protein-based beverages, certain cheese and cheese products, flour products, infant formulas, many breakfast cereals, and milk.
In 2016 in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) amended food additive regulations for milk fortification, stating that vitamin D3 levels not exceed 42 IU vitamin D per 100 g (400 IU per US quart) of dairy milk, 84 IU of vitamin D2 per 100 g (800 IU per quart) of plant milks, and 89 IU per 100 g (800 IU per quart) in plant-based yogurts or in soy beverage products. Plant milks are defined as beverages made from soy, almond, rice, among other plant sources intended as alternatives to dairy milk.
While some studies have found that vitamin D3 raises 25(OH)D blood levels faster and remains active in the body longer, others contend that vitamin D2 sources are equally bioavailable and effective as D3 for raising and sustaining 25(OH)D.
Food preparation
Vitamin D content in typical foods is reduced variably by cooking. Boiled, fried and baked foods retained 69–89% of original vitamin D.
Recommended serum levels

Recommendations on recommended 25(OH)D serum levels vary across authorities, and vary based on factors like age. US labs generally report 25(OH)D levels in ng/mL. Other countries often use nmol/L. One ng/mL is approximately equal to 2.5 nmol/L.
A 2014 review concluded that the most advantageous serum levels for 25(OH)D for all outcomes appeared to be close to 30 ng/mL (75 nmol/L). The optimal vitamin D levels are still controversial and another review concluded that ranges from 30 to 40 ng/mL (75 to 100 nmol/L) were to be recommended for athletes. Part of the controversy is because numerous studies have found differences in serum levels of 25(OH)D between ethnic groups; studies point to genetic as well as environmental reasons behind these variations. Supplementation to achieve these standard levels could cause harmful vascular calcification.
A 2012 meta-analysis showed that the risk of cardiovascular diseases increases when blood levels of vitamin D are lowest in a range of 8 to 24 ng/mL (20 to 60 nmol/L), although results among the studies analyzed were inconsistent.
In 2011 an IOM committee concluded a serum 25(OH)D level of 20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L) is needed for bone and overall health. The dietary reference intakes for vitamin D are chosen with a margin of safety and 'overshoot' the targeted serum value to ensure the specified levels of intake achieve the desired serum 25(OH)D levels in almost all persons. No contributions to serum 25(OH)D level are assumed from sun exposure and the recommendations are fully applicable to people with dark skin or negligible exposure to sunlight. The Institute found serum 25(OH)D concentrations above 30 ng/mL (75 nmol/L) are "not consistently associated with increased benefit". Serum 25(OH)D levels above 50 ng/mL (125 nmol/L) may be cause for concern. However, some people with serum 25(OH)D between 30 and 50 ng/mL (75 nmol/L-125 nmol/L) will also have inadequate vitamin D.
Excess
Vitamin D toxicity is rare. It is caused by supplementing with high doses of vitamin D rather than sunlight. The threshold for vitamin D toxicity has not been established; however, according to some research, the tolerable upper intake level (UL) is 4,000 IU/day for ages 9–71 (100 μg/day), while other research concludes that, in healthy adults, sustained intake of more than 50,000 IU/day (1250 μg) can produce overt toxicity after several months and can increase serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels to 150 ng/mL and greater. Those with certain medical conditions, such as primary hyperparathyroidism, are far more sensitive to vitamin D and develop hypercalcemia in response to any increase in vitamin D nutrition, while maternal hypercalcemia during pregnancy may increase fetal sensitivity to effects of vitamin D and lead to a syndrome of intellectual disability and facial deformities.
Idiopathic infantile hypercalcemia is caused by a mutation of the CYP24A1 gene, leading to a reduction in the degradation of vitamin D. Infants who have such a mutation have an increased sensitivity to vitamin D and in case of additional intake a risk of hypercalcaemia. The disorder can continue into adulthood.
A review published in 2015 noted that adverse effects have been reported only at 25(OH)D serum concentrations above 200 nmol/L.
Published cases of toxicity involving hypercalcemia in which the vitamin D dose and the 25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels are known all involve an intake of ≥40,000 IU (1,000 μg) per day.
Those who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult a doctor before taking a vitamin D supplement. The FDA advised manufacturers of liquid vitamin D supplements that droppers accompanying these products should be clearly and accurately marked for 400 international units (1 IU is the biological equivalent of 25 ng cholecalciferol/ergocalciferol). In addition, for products intended for infants, the FDA recommends the dropper hold no more than 400 IU. For infants (birth to 12 months), the tolerable upper limit (maximum amount that can be tolerated without harm) is set at 25 μg/day (1,000 IU). One thousand micrograms per day in infants has produced toxicity within one month. After being commissioned by the Canadian and American governments, the Institute of Medicine (IOM) November 30, 2010現在[update], has increased the tolerable upper limit (UL) to 2,500 IU per day for ages 1–3 years, 3,000 IU per day for ages 4–8 years and 4,000 IU per day for ages 9–71+ years (including pregnant or lactating women).
Calcitriol itself is auto-regulated in a negative feedback cycle, and is also affected by parathyroid hormone, fibroblast growth factor 23, cytokines, calcium, and phosphate.
A study published in 2017 assessed the prevalence of high daily intake levels of supplemental vitamin D among adults ages 20+ in the United States, based on publicly available NHANES data from 1999 through 2014. Its data shows the following:
- Over 18% of the population exceeds the NIH daily recommended allowance (RDA) of 600–800 IU, by taking over 1000 IU, which suggests intentional supplement intake.
- Over 3% of the population exceeds the NIH daily tolerable upper intake level (UL) of 4000 IU, above which level the risk of toxic effects increases.
- The percentage of the population taking over 1000 IU/day, as well as the percentage taking over 4000 IU/day, have both increased since 1999, according to trend analysis.
Effect of excess
Vitamin D overdose causes hypercalcemia, which is a strong indication of vitamin D toxicity – this can be noted with an increase in urination and thirst. If hypercalcemia is not treated, it results in excess deposits of calcium in soft tissues and organs such as the kidneys, liver, and heart, resulting in pain and organ damage.
The main symptoms of vitamin D overdose are hypercalcemia including anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. These may be followed by polyuria, polydipsia, weakness, insomnia, nervousness, pruritus and ultimately kidney failure. Furthermore, proteinuria, urinary casts, azotemia, and metastatic calcification (especially in the kidneys) may develop. Other symptoms of vitamin D toxicity include intellectual disability in young children, abnormal bone growth and formation, diarrhea, irritability, weight loss, and severe depression.
Vitamin D toxicity is treated by discontinuing vitamin D supplementation and restricting calcium intake. Kidney damage may be irreversible. Exposure to sunlight for extended periods of time does not normally cause vitamin D toxicity. The concentrations of vitamin D precursors produced in the skin reach an equilibrium, and any further vitamin D produced is degraded.
Biosynthesis
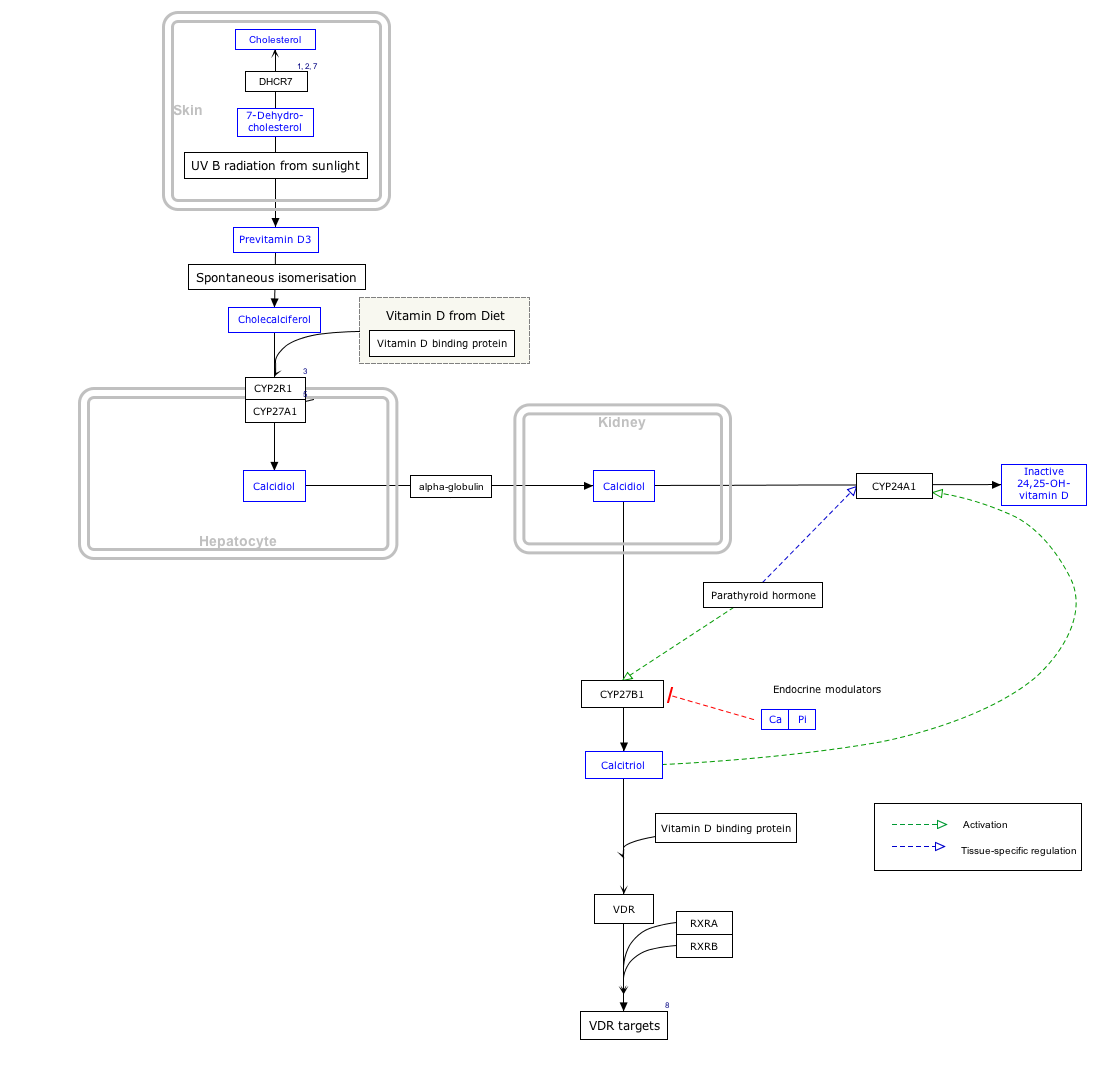
Synthesis of vitamin D in nature is dependent on the presence of UV radiation and subsequent activation in the liver and in the kidneys. Many animals synthesize vitamin D3 from 7-dehydrocholesterol, and many fungi synthesize vitamin D2 from ergosterol.
Interactive pathway
Click on icon in lower right corner to open.
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- ↑ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
Photochemistry


The transformation that converts 7-dehydrocholesterol to vitamin D3 occurs in two steps. First, 7-dehydrocholesterol is photolyzed by ultraviolet light in a 6-electron conrotatory ring-opening electrocyclic reaction; the product is previtamin D3. Second, previtamin D3 spontaneously isomerizes to vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) in an antarafacial sigmatropic [1,7] hydride shift. At room temperature, the transformation of previtamin D3 to vitamin D3 in an organic solvent takes about 12 days to complete. The conversion of previtamin D3 to vitamin D3 in the skin is about 10 times faster than in an organic solvent.
The conversion from ergosterol to vitamin D2 follows a similar procedure, forming previtamin D2 by photolysis, which isomerizes to vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol). The transformation of previtamin D2 to vitamin D2 in methanol has a rate comparable to that of previtamin D3. The process is faster in white button mushrooms.
Synthesis in the skin

Vitamin D3 is produced photochemically from 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin of most vertebrate animals, including humans. The precursor of vitamin D3, 7-dehydrocholesterol is produced in relatively large quantities. 7-Dehydrocholesterol reacts with UVB light at wavelengths of 290–315 nm. These wavelengths are present in sunlight, as well as in the light emitted by the UV lamps in tanning beds (which produce ultraviolet primarily in the UVA spectrum, but typically produce 4% to 10% of the total UV emissions as UVB, some tanning beds can use only separate UVB light bulbs specifically for vitamin D production). Exposure to light through windows is insufficient because glass almost completely blocks UVB light.
Adequate amounts of vitamin D can be produced with moderate sun exposure to the face, arms and legs (for those with the least melanin), averaging 5–30 minutes twice per week, or approximately 25% of the time for minimal sunburn. The darker the skin on the Fitzpatrick scale and the weaker the sunlight, the more minutes of exposure are needed. It also depends on parts of body exposed, all three factors affect minimal erythema dose (MED). Vitamin D overdose from UV exposure is impossible: the skin reaches an equilibrium where the vitamin D degrades as fast as it is created.
The skin consists of two primary layers: the inner layer called the dermis, and the outer, thinner epidermis. Vitamin D is produced in the keratinocytes of two innermost strata of the epidermis, the stratum basale and stratum spinosum, which also are able to produce calcitriol and express the VDR.
Evolution
Vitamin D can be synthesized only by a photochemical process. Its production from sterols would have started very early in the evolution of life around the origin of photosynthesis, possibly helping to prevent DNA damage by absorbing UVB, making vitamin D an inactive end product. The familiar vitamin D endocrine machinery containing vitamin D receptor (VDR), various CYP450 enzymes for activation and inactivation, and a vitamin D binding protein (DBP) is found in vertebrates only. Primitive marine vertebrates are thought to absorb calcium from the ocean into their skeletons and eat plankton rich in vitamin D, although the function in those without a calcified cartilage is unclear. Phytoplankton in the ocean (such as coccolithophore and Emiliania huxleyi) have been photosynthesizing vitamin D for more than 500 million years.
Land vertebrates required another source of vitamin D other than plants for their calcified skeletons. They had to either ingest it or be exposed to sunlight to photosynthesize it in their skin. Land vertebrates have been photosynthesizing vitamin D for more than 350 million years.
In birds and fur-bearing mammals, fur or feathers block UV rays from reaching the skin. Instead, vitamin D is created from oily secretions of the skin deposited onto the feathers or fur, and is obtained orally during grooming. However, some animals, such as the naked mole-rat, are naturally cholecalciferol-deficient, as serum 25-OH vitamin D levels are undetectable. Dogs and cats are practically incapable of vitamin D synthesis due to high activity of 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase, but get vitamin D from prey animals.
Industrial synthesis
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is produced industrially by exposing 7-dehydrocholesterol to UVB and UVC light, followed by purification. The 7-dehydrocholesterol is a natural substance in fish organs, especially the liver, in wool grease (lanolin) from sheep and in some plants, like lichen (Cladonia rangiferina). Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is produced in a similar way using ergosterol from yeast or mushrooms as a starting material.
Mechanism of action
Metabolic activation


Vitamin D is carried via the blood to the liver, where it is converted into the prohormone calcifediol. Circulating calcifediol may then be converted into calcitriol – the biologically active form of vitamin D – in the kidneys.
Whether synthesized in the skin or ingested, vitamin D is hydroxylated in the liver at position 25 (upper right of the molecule) to form 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (calcifediol or 25(OH)D). This reaction is catalyzed by the microsomal enzyme vitamin D 25-hydroxylase, the product of the CYP2R1 human gene, and expressed by hepatocytes. Once made, the product is released into the plasma, where it is bound to an α-globulin carrier protein named the vitamin D-binding protein.
Calcifediol is transported to the proximal tubules of the kidneys, where it is hydroxylated at the 1-α position (lower right of the molecule) to form calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, 1,25(OH)2D). The conversion of calcifediol to calcitriol is catalyzed by the enzyme 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1-alpha-hydroxylase, which is the product of the CYP27B1 human gene. The activity of CYP27B1 is increased by parathyroid hormone, and also by low calcium or phosphate. Following the final converting step in the kidney, calcitriol is released into the circulation. By binding to vitamin D-binding protein, calcitriol is transported throughout the body, including to the intestine, kidneys, and bones. Calcitriol is the most potent natural ligand of the vitamin D receptor, which mediates most of the physiological actions of vitamin D. In addition to the kidneys, calcitriol is also synthesized by certain other cells, including monocyte-macrophages in the immune system. When synthesized by monocyte-macrophages, calcitriol acts locally as a cytokine, modulating body defenses against microbial invaders by stimulating the innate immune system.
Inactivation
The activity of calcifediol and calcitriol can be reduced by hydroxylation at position 24 by vitamin D3 24-hydroxylase, forming secalciferol and calcitetrol, respectively.
Difference between substrates
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) share a similar mechanism of action as outlined above. Metabolites produced by vitamin D2 are named with an er- or ergo- prefix to differentiate them from the D3-based counterparts (sometimes with a chole- prefix).
- Metabolites produced from vitamin D2 tend to bind less well to the vitamin D-binding protein.
- Vitamin D3 can alternatively be hydroxylated to calcifediol by sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1), but vitamin D2 cannot.
- Ergocalciferol can be directly hydroxylated at position 24 by CYP27A1. This hydroxylation also leads to a greater degree of inactivation: the activity of calcitriol decreases to 60% of original after 24-hydroxylation, whereas ercalcitriol undergoes a 10-fold decrease in activity on conversion to ercalcitetrol.
It is disputed whether these differences lead to a measurable drop in efficacy (see § Food fortification).
Intracellular mechanisms
Calcitriol enters the target cell and binds to the vitamin D receptor in the cytoplasm. This activated receptor enters the nucleus and binds to vitamin D response elements (VDRE) which are specific DNA sequences on genes. Transcription of these genes is stimulated and produces greater levels of the proteins which mediate the effects of vitamin D.
Some reactions of the cell to calcitriol appear to be too fast for the classical VDRE transcription pathway, leading to the discovery of various non-genomic actions of vitamin D. The membrane-bound PDIA3 likely serves as an alternate receptor in this pathway. The classical VDR may still play a role.
History
Vitamin D was discovered in 1922 following on from previous research. American researchers Elmer McCollum and Marguerite Davis in 1914 discovered a substance in cod liver oil which later was called "vitamin A". British doctor Edward Mellanby noticed dogs that were fed cod liver oil did not develop rickets and concluded vitamin A, or a closely associated factor, could prevent the disease. In 1922, Elmer McCollum tested modified cod liver oil in which the vitamin A had been destroyed. The modified oil cured the sick dogs, so McCollum concluded the factor in cod liver oil which cured rickets was distinct from vitamin A. He called it vitamin D because he thought it was the fourth vitamin to be named. It was not initially realized that vitamin D can be synthesized by humans (in the skin) through exposure to UV light, and therefore is technically not a vitamin, but rather can be considered to be a hormone.
In 1925, it was established that when 7-dehydrocholesterol is irradiated with light, a form of a fat-soluble substance is produced (now known as D3). Alfred Fabian Hess stated: "Light equals vitamin D." Adolf Windaus, at the University of Göttingen in Germany, received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1928 for his work on the constitution of sterols and their connection with vitamins. In 1929, a group at NIMR in Hampstead, London, were working on the structure of vitamin D, which was still unknown, as well as the structure of steroids. A meeting took place with J.B.S. Haldane, J.D. Bernal, and Dorothy Crowfoot to discuss possible structures, which contributed to bringing a team together. X-ray crystallography demonstrated the sterol molecules were flat, not as proposed by the German team led by Windaus. In 1932, Otto Rosenheim and Harold King published a paper putting forward structures for sterols and bile acids which found immediate acceptance. The informal academic collaboration between the team members Robert Benedict Bourdillon, Otto Rosenheim, Harold King, and Kenneth Callow was very productive and led to the isolation and characterization of vitamin D. At this time, the policy of the Medical Research Council was not to patent discoveries, believing the results of medical research should be open to everybody. In the 1930s, Windaus clarified further the chemical structure of vitamin D.
In 1923, American biochemist Harry Steenbock at the University of Wisconsin demonstrated that irradiation by ultraviolet light increased the vitamin D content of foods and other organic materials. After irradiating rodent food, Steenbock discovered the rodents were cured of rickets. Using US$300 of his own money, Steenbock patented his invention. His irradiation technique was used for foodstuffs, most notably for milk. By the expiration of his patent in 1945, rickets had been all but eliminated in the US.
In 1969, a specific binding protein for vitamin D called the vitamin D receptor was identified. Shortly thereafter, the conversion of vitamin D to calcifediol and then to calcitriol, the biologically active form, was confirmed. The photosynthesis of vitamin D3 in skin via previtamin D3 and its subsequent metabolism was described in 1980.
Research
There is conflicting evidence about the benefits of interventions with vitamin D. Supplementation of between 800 and 1,000 IU is safe, but higher levels leading to blood levels of more than 50 ng/mL (125 nmol/L) may cause adverse effects.
The US Office of Dietary Supplements established a Vitamin D Initiative over 2004–18 to track current research and provide education to consumers. As of 2022, the role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of diabetes, glucose intolerance, hypertension, multiple sclerosis, and other medical conditions remains under preliminary research.
Some preliminary studies link low vitamin D levels with disease later in life. One meta-analysis found a decrease in mortality in elderly people. Another meta-analysis covering over 350,000 people concluded that vitamin D supplementation in unselected community-dwelling individuals does not reduce skeletal (total fracture) or non-skeletal outcomes (myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, stroke, cerebrovascular disease, cancer) by more than 15%, and that further research trials with similar design are unlikely to change these conclusions. As of 2022, there is insufficient evidence for an effect of vitamin D supplementation on the risk of cancer. A 2019 meta-analysis found a small increase in risk of stroke when calcium and vitamin D supplements were taken together.
COVID-19
2022年9月、米国国立衛生研究所は、COVID-19の予防や治療のためにビタミンDサプリメントを使用することに賛成または反対を推奨する十分な証拠がないとしている。英国国立医療技術評価機構(NICE)は、COVID-19の予防または治療のためだけにビタミンDサプリメントを人々に提供することを推奨していない。両機関とも、骨や筋肉の健康など他の理由によるビタミンD補給については、以前から確立されている推奨を継続するよう勧告している。両団体は、パンデミック期間中は日光浴の量が減るため、より多くの人がサプリメントを必要とするかもしれないと指摘している。
ビタミンD欠乏とCOVID-19の有害転帰との関連については、複数の研究のシステマティックレビューやメタアナリシスで述べられている。約200万人の成人を含む76の観察研究のデータを用いた最も大規模な解析では、ビタミンD欠乏または不足はCOVID-19に感染しやすく、重症のCOVID-19に罹患しやすく、オッズ比はそれぞれ1.5と1.9と有意に増加したが、これらの所見は偏りと異質性のリスクが高かった。死亡率は2倍高かったが、この解析はあまり頑健ではなかった。COVID-19の人は健康な人に比べて25(OH)D値が低い傾向があることを報告したそのうちの1つでは、健康上の転帰との関連については、研究の質が低いことや逆因果の可能性によって限界があると述べている。
ビタミンDまたはカルシフェジオールの経口補給の効果に関する3件の研究のメタアナリシスでは、補給なしの場合と比較して集中治療室(ICU)入室率が低い(オッズ比:0.36)が、死亡率には変化がないことが示された。COVID-19の治療に対するビタミンD補充が有効であるというエビデンスは非常に不確かである。彼らは、主に補充戦略、ビタミンD製剤(1つはカルシフェジオールを使用)、治療前の状態、報告された転帰が異なるため、対象となった3つの研究には臨床的、方法論的にかなりの異質性があることを発見した。別のメタアナリシスでは、カルシフェジオールの補充はICU入室を予防する効果があるかもしれないが、COVID-19患者における高用量のビタミンDの使用は確かなエビデンスに基づくものではないとしている。