Inulin/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "==糸球体濾過率の計算== {{Anchor|Calculation of glomerular filtration rate}} イヌリンは糸球体で完全に濾過されるが、尿細管では分泌も再吸収もされないというユニークな性質を持つ。イヌリンのこの性質により、イヌリンのクリアランスを糸球体濾過率(GFR)の非常に正確な指標として臨床的に使用することができる..." Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "イヌリンは水溶性食物繊維で、水溶性、不溶性、レジスタントスターチを含む3種類の食物繊維のうちの1つである。水溶性食物繊維は水に溶けてゲル状になる。水溶性食物繊維の中には、血中コレステロール値やブドウ糖値を下げる働きがあるものもある。" |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
イヌリンと[[para-aminohippuric acid/ja|パラアミノ吉草酸]](PAH)の特性を対比することは有益である。PAHはイヌリンと同じように、糸球体で血漿から部分的に濾過され、尿細管では再吸収されない。PAHはイヌリンと異なり、糸球体を迂回してネフロンの尿細管細胞に入ったPAHの一部は([[peritubular capillaries/ja|尿細管周囲毛細血管]]を経由して)完全に分泌される。したがって、PAHの腎クリアランスは、経験的に(1-[[hematocrit/ja|ヘマトクリット]])×[[renal blood flow/ja|腎血流量]]である腎血漿流量(RPF)の計算に有用である。注意すべき点は、PAHのクリアランスは、腎臓の尿形成に関わる部分へのRPFのみを反映しているため、実際のRPFを約10%過小評価することである。 | イヌリンと[[para-aminohippuric acid/ja|パラアミノ吉草酸]](PAH)の特性を対比することは有益である。PAHはイヌリンと同じように、糸球体で血漿から部分的に濾過され、尿細管では再吸収されない。PAHはイヌリンと異なり、糸球体を迂回してネフロンの尿細管細胞に入ったPAHの一部は([[peritubular capillaries/ja|尿細管周囲毛細血管]]を経由して)完全に分泌される。したがって、PAHの腎クリアランスは、経験的に(1-[[hematocrit/ja|ヘマトクリット]])×[[renal blood flow/ja|腎血流量]]である腎血漿流量(RPF)の計算に有用である。注意すべき点は、PAHのクリアランスは、腎臓の尿形成に関わる部分へのRPFのみを反映しているため、実際のRPFを約10%過小評価することである。 | ||
イヌリンまたはシニストリンによるGFRの測定は、依然として[[Gold standard (test)/ja|ゴールドスタンダード]]と考えられている。しかし、現在では、GFRの近似値である、より単純な他の測定法に取って代わられている。これらの測定法は、[[EDTA/ja|EDTA]]、[[iohexol/ja|イオヘキソール]]、[[cystatin C/ja|シスタチンC]]、[[125I/ja|<sup>125</sup>I]]-[[iothalamate/ja|イオサラーム酸]](放射性イオサラーム酸ナトリウム)、クロム放射性同位元素[[chromium-51/ja|<sup>51</sup>Cr]](EDTAでキレート)、[[creatinine/ja|クレアチニン]]などの基質のクリアランスを伴うもので、慢性腎臓病患者の大規模コホートでその有用性が確認されている。 | |||
イヌリンとクレアチニンは、尿中濃度と血清中濃度を用いて計算される。しかし、クレアチニンとは異なり、イヌリンは天然には体内に存在しない。これはイヌリンの利点(注入量がわかるため)であり、欠点(注入が必要なため)でもある。 | |||
==''生体内''での代謝== | |||
{{Anchor|Metabolism ''in vivo''}} | |||
イヌリンはヒトの[[enzyme/ja|酵素]]である[[ptyalin/ja|プチアリン]]と[[amylase/ja|アミラーゼ]]には消化されない。アミラーゼはデンプンの消化に適応している。その結果、[[digestive system/ja|消化器系]]の大部分をそのまま通過する。大腸でのみ、細菌がイヌリンを[[metabolism/ja|代謝]]し、大量の[[carbon dioxide/ja|二酸化炭素]]、[[hydrogen/ja|水素]]、[[methane/ja|メタン]]を放出する。イヌリンを含む食品は、特にイヌリンに慣れていない人にとっては、かなり[[Flatulence/ja|ガス]]が出やすくなる。 | |||
イヌリンは水溶性食物繊維で、[[soluble fiber/ja|水溶性]]、[[insoluble fiber/ja|不溶性]]、[[resistant starch/ja|レジスタントスターチ]]を含む3種類の食物繊維のうちの1つである。水溶性食物繊維は水に溶けてゲル状になる。水溶性食物繊維の中には、血中コレステロール値やブドウ糖値を下げる働きがあるものもある。 | |||
イヌリンは通常の[[digestion/ja|消化]]では[[monosaccharide/ja|単糖類]]に分解されないため、血糖値を上昇させず、糖尿病の管理に役立つ可能性がある。イヌリンは[[Gut (zoology)/ja|腸]]内細菌の増殖も促進する。イヌリンは消化されずに[[stomach/ja|胃]]や[[duodenum/ja|十二指腸]]を通過するため、腸内[[bacterial flora/ja|細菌叢]]が非常に利用しやすい。そのため、レジスタントスターチやその他の発酵性炭水化物と似ている。 | |||
伝統的な食事には、イヌリンやフラクトオリゴ糖を1日20g以上含むものもある。チワワン砂漠の先史時代の狩猟採集民の食事には、1日あたり135gのイヌリン型フルクタンが含まれていたと推定されている。チコリ、ニンニク、[[leek/ja|ネギ]]など、イヌリンやフラクトオリゴ糖を多く含む食品は、何世紀にもわたって「健康増進剤」とされてきた。 | |||
2013年の時点では、プレバイオティクスのマーケティングにおける健康強調表示を許可した規制当局はなかった。イヌリンの健康効果は小規模な臨床試験で研究されており、膨満感や鼓腸などの胃腸への悪影響、[[Triglyceride/ja|トリグリセリド値]]や[[fatty liver/ja|脂肪肝]]の発症に影響を与えないこと、[[travelers' diarrhea/ja|旅行者下痢]]の予防に役立つ可能性があること、思春期のカルシウム吸収を高めるのに役立つ可能性があることなどが示されていた。 | |||
==天然の供給源== | |||
{{Anchor|Natural sources}} | |||
イヌリンを多く含む植物には以下のようなものがある: | |||
* [[Agave]] ('' | * [[Agave/ja]] (''リュウゼツラン''属) | ||
* [[Banana]] | * [[Banana/ja]]と[[Cooking plantain/ja|オオバコ]] ([[Musaceae/ja]]) | ||
* [[Burdock]] (''Arctium lappa'') | * [[Burdock/ja]] (''Arctium lappa'') | ||
* [[Camassia| | * [[Camassia/ja|カマス]] (''カマッシア''属) | ||
* [[Chicory]] (''Cichorium intybus'') | * [[Chicory/ja]] (''Cichorium intybus'') | ||
* [[Echinacea| | * [[Echinacea/ja|コーンフラワー]] (''[[Echinacea/ja]]'' 属) | ||
* [[Costus]] (''Saussurea lappa'') | * [[Costus/ja]] (''Saussurea lappa'') | ||
* [[Dandelion]] (''Taraxacum officinale'') | * [[Dandelion/ja]] (''Taraxacum officinale'') | ||
* [[Elecampane]] (''Inula helenium'') | * [[Elecampane/ja]] (''Inula helenium'') | ||
* [[Garlic]] (''Allium sativum'') | * [[Garlic/ja]] (''Allium sativum'') | ||
* [[Globe artichoke]] (''Cynara scolymus'', ''Cynara cardunculus'' | * [[Globe artichoke/ja]] (''Cynara scolymus'', ''Cynara cardunculus'' 変種 ''scolymus'') | ||
* [[Jerusalem artichoke]] (''Helianthus tuberosus'') | * [[Jerusalem artichoke/ja]] (''Helianthus tuberosus'') | ||
* [[Jicama]] (''Pachyrhizus erosus'') | * [[Jicama/ja]] (''Pachyrhizus erosus'') | ||
* [[Leopard's bane]] (''[[Arnica montana]]'') | * [[Leopard's bane/ja]] (''[[Arnica montana/ja]]'') | ||
* [[Mugwort]] | * [[Mugwort/ja]] 根 (''[[Artemisia vulgaris/ja]]'') | ||
* [[Onion]] (''Allium cepa'') | * [[Onion/ja]] (''Allium cepa'') | ||
* [[Wild yam]] (''[[Dioscorea]]'' | * [[Wild yam/ja]] (''[[Dioscorea/ja]]'' 属) | ||
* ''[[Yacón]]'' (''Smallanthus sonchifolius'') | * ''[[Yacón/ja]]'' (''Smallanthus sonchifolius'') | ||
{{carbohydrates/ja}} | |||
{{carbohydrates}} | |||
[[Category:Dietary fiber]] | [[Category:Dietary fiber]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:31, 27 November 2023
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| C6nH10n+2O5n+1 | |
| Molar mass | Polymer; depends on n |
| Pharmacology | |
| V04CH01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
イヌリン(English: Inulin)は多くの種類の植物が生産する天然多糖類の一群で、工業的にはチコリから抽出されることが多い。イヌリンは、フルクタンとして知られる食物繊維の一群に属する。イヌリンは、一部の植物がエネルギーを貯蔵する手段として利用し、通常、根や根茎に含まれている。イヌリンを合成し貯蔵するほとんどの植物は、デンプンのような他の形態の炭水化物を貯蔵しない。米国では2018年、食品医薬品局はイヌリンを、製造された食品の栄養価を向上させるために使用される食物繊維成分として承認した。イヌリンを用いて腎機能を測定することは、糸球体濾過量を推定する他の手段と比較するための「ゴールドスタンダード」である。
起源と歴史
イヌリンは、リュウゼツラン、小麦、タマネギ、バナナ、ニンニク、アスパラガス、エルサレム・アーティチョーク、チコリなど、36,000種以上の植物に含まれる天然の貯蔵炭水化物である。これらの植物にとって、イヌリンはエネルギー備蓄として、また耐寒性を調節するために利用されている。イヌリンは水に溶けるため、浸透圧活性である。ある種の植物は、加水分解によってイヌリン分子の重合度を変えることで、細胞の浸透圧ポテンシャルを変えることができる。炭水化物の総量を変えずに浸透圧ポテンシャルを変えることで、植物は冬の寒さや乾燥に耐えることができる。
イヌリンは1804年、ドイツの科学者ヴァレンティン・ローズによって発見された。彼はイヌラヘレニウムの根から沸騰水抽出によって「特異な物質」を発見した。1920年代、J.アーバインはイヌリンの分子構造を研究するためにメチル化などの化学的方法を用い、この新しいアンヒドロフラクトースの単離方法を考案した。1930年代、腎尿細管の研究において、研究者たちは尿細管に導入された後、再吸収も分泌もされないバイオマーカーとなる物質を探した。A.N.リチャーズは、その高分子量と酵素に対する抵抗性からイヌリンを導入した。イヌリンは腎臓の糸球体濾過率を測定するために使用される。
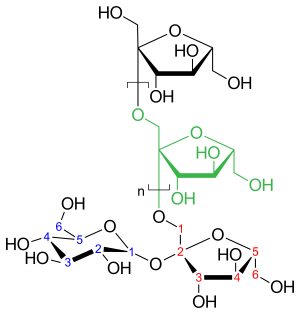
化学構造と特性
イヌリンはフルクトースポリマーの異種集合体である。鎖末端のグルコシル部分と繰り返しのフルクトシル部分からなり、これらはβ(2,1)結合で結ばれている。標準的なイヌリンの重合度(DP)は2〜60である。製造工程でDPが10以下のフラクションを除去した後、残った製品が高性能イヌリンとなる。DPが10より低い画分を短鎖のフラクトオリゴ糖とみなし、より長鎖の分子だけをイヌリンと呼ぶ論文もある。
β(2,1)結合のため、イヌリンはヒトの消化器系では酵素によって消化されず、カロリー値の低減、食物繊維、プレバイオティクス効果といった機能的特性に寄与している。また、色や匂いもなく、食品の官能特性にはほとんど影響を与えない。オリゴフルクトースの甘味度はショ糖の35%で、甘味のプロファイルは砂糖に似ている。標準的なイヌリンはわずかに甘いが、高機能イヌリンは甘くない。溶解性は古典的な繊維よりも高い。液体と十分に混合すると、イヌリンはゲルを形成し、脂肪に似た白いクリーム状の構造を形成する。不溶性のサブミクロン結晶イヌリン粒子からなるその三次元ゲルネットワークは、大量の水を固定化し、その物理的安定性を保証する。また、フォームやエマルションの安定性を向上させることができる。
用途
収穫と抽出
チコリの根は、イヌリンの商業生産のための主な抽出源である。イヌリンの抽出プロセスは、テンサイから砂糖を得るのと似ている。収穫後、チコリの根をスライスし、洗浄した後、溶媒(熱水またはエタノール)に浸し、イヌリンを分離、精製し、噴霧乾燥する。イヌリンはスクロースから合成することもできる。
加工食品
イヌリンは、米国食品医薬品局(FDA)から、長鎖イヌリンを含むGRAS(generally recognized as safe:一般に安全と認められる)として、異議なしステータスを取得した。21世紀初頭、加工食品にイヌリンが使用されるようになったのは、製造に適応しやすいという特性もあった。製造された食品の食物繊維価値を高める成分としてFDAに認可されている。その風味は、淡白なものからほのかに甘いもの(砂糖/ショ糖の約10%の甘さ)まで幅広い。砂糖、脂肪、小麦粉の代わりに使用できる。イヌリンは炭水化物(デンプン、砂糖)の食物エネルギーの25~35%を含むので、これは有利である。イヌリンは、万能食材であることに加え、腸内細菌の増殖を促進する一方で、カルシウムの吸収を高め、場合によってはマグネシウムの吸収を促進することで、栄養学的な利点をもたらす。チコリのイヌリンは、カルシウム吸収率の低い若い女性や若い男性のカルシウム吸収率を高めることが報告されている。栄養学的には、水溶性食物繊維の一種と考えられ、プレバイオティクスに分類されることもある。逆に、大腸で急速に発酵してガスを発生させる炭水化物の一種であるFODMAPとみなされることもある。FODMAPは人によっては消化不良を引き起こすが、腸内細菌叢に好ましい変化をもたらす可能性があり、大腸の健康維持に貢献する。
イヌリンは、体内でフルクタン類を処理する能力が限られているため、血糖値への影響はほとんどなく、メタボリックシンドロームなど血糖値に関連する病気の管理に利用できる可能性がある。
医薬品
イヌリンとその類似体であるシニストリンは、糸球体濾過量(GFR)を測定することによって腎機能を測定するのに使用される。GFRとは、単位時間当たりに腎(腎臓)の糸球体毛細血管からボーマン嚢に濾過される液体の量である。
イヌリンはGFR測定のゴールドスタンダードであるが、検査には費用がかかり、実施も難しいため、実際にはほとんど使用されていない。イヌリンを注入するために静脈(IV)アクセスが必要であり、また4時間かけて患者から最大12回の血液サンプルを採取する必要がある。ヒトの糸球体濾過率を測定するためには、最初に大量のイヌリンを注射し、その後、尿中の損失を補う速度でイヌリンを一定量注入し、血漿中の濃度を適度に一定に保つ。米国では、GFRの推定にはクレアチニンクリアランスがより広く用いられている。
2017年に行われた低~中程度の質の臨床試験研究のシステマティックレビューでは、イヌリン型フルクタンによる栄養補給が、心血管疾患のバイオマーカーである低比重コレステロールの血中濃度を低下させることが示された。
食事療法と副作用
イヌリン食物繊維ダイエットの副作用は、通常、敏感な人に起こる可能性がある:
- 鼓腸、腹部膨満感、腹鳴、腹鳴、けいれんなどの腸の不快感
- 下痢
- 炎症 - イヌリンは腸や肺にアレルギーに関連したタイプの炎症を引き起こす可能性がある。
- アナフィラキシー性アレルギー反応(まれ)- イヌリンはGFR検査に使用され、いくつかの孤立した症例ではアレルギー反応を引き起こし、おそらく食物アレルギー反応と関連している。
産業利用
非加水分解イヌリンは、糖化と発酵の同時プロセスで直接エタノールに変換することもでき、イヌリンを多く含む作物を燃料用エタノールに変換する可能性がある。
生化学
イヌリンは主にフルクトース単位(フルクタン)からなるポリマーで、通常、末端にグルコースを持つ。イヌリンのフルクトースユニットはβ(2→1)グリコシド結合で結合している。分子はほとんど直鎖状であり、分岐しているものは数パーセントしかない。一般に、植物イヌリンは2〜70個、時には200個ものフルクトースユニットを含むが、10個以下のユニットはフルクトオリゴ糖と呼ばれ、最も単純なものは1-ケストースで、2個のフルクトースユニットと1個のグルコースユニットを持つ。バクテリアのイヌリンはより高度に分岐しており(15%以上分岐)、数十から数百のサブユニットのオーダーを含んでいる。
イヌリンは次のように命名される。nはフルクトース残基の数、pyはピラノシルの略称である:
- 末端にグルコースを持つイヌリンは、α-D-グルコピラノシル-[β-D-フルクトフラノシル](n-1)-D-フルクトフラノシドと呼ばれ、GpyFnと略される。
- グルコースを含まないイヌリンはβ-D-フルクトピラノシル-[D-フルクトフラノシル](n-1)-D-フルクトフラノシドであり、FpyFnと略される。
イヌリンを加水分解すると、重合度(DP)が10以下のオリゴマーであるフルクトオリゴ糖が得られる。
糸球体濾過率の計算
イヌリンは糸球体で完全に濾過されるが、尿細管では分泌も再吸収もされないというユニークな性質を持つ。イヌリンのこの性質により、イヌリンのクリアランスを糸球体濾過率(GFR)の非常に正確な指標として臨床的に使用することができる - GFRとは、ボーマン嚢に濾過される血漿の遠心性細動脈からの割合をml/minで測定したものである。
イヌリンとパラアミノ吉草酸(PAH)の特性を対比することは有益である。PAHはイヌリンと同じように、糸球体で血漿から部分的に濾過され、尿細管では再吸収されない。PAHはイヌリンと異なり、糸球体を迂回してネフロンの尿細管細胞に入ったPAHの一部は(尿細管周囲毛細血管を経由して)完全に分泌される。したがって、PAHの腎クリアランスは、経験的に(1-ヘマトクリット)×腎血流量である腎血漿流量(RPF)の計算に有用である。注意すべき点は、PAHのクリアランスは、腎臓の尿形成に関わる部分へのRPFのみを反映しているため、実際のRPFを約10%過小評価することである。
イヌリンまたはシニストリンによるGFRの測定は、依然としてゴールドスタンダードと考えられている。しかし、現在では、GFRの近似値である、より単純な他の測定法に取って代わられている。これらの測定法は、EDTA、イオヘキソール、シスタチンC、125I-イオサラーム酸(放射性イオサラーム酸ナトリウム)、クロム放射性同位元素51Cr(EDTAでキレート)、クレアチニンなどの基質のクリアランスを伴うもので、慢性腎臓病患者の大規模コホートでその有用性が確認されている。
イヌリンとクレアチニンは、尿中濃度と血清中濃度を用いて計算される。しかし、クレアチニンとは異なり、イヌリンは天然には体内に存在しない。これはイヌリンの利点(注入量がわかるため)であり、欠点(注入が必要なため)でもある。
生体内での代謝
イヌリンはヒトの酵素であるプチアリンとアミラーゼには消化されない。アミラーゼはデンプンの消化に適応している。その結果、消化器系の大部分をそのまま通過する。大腸でのみ、細菌がイヌリンを代謝し、大量の二酸化炭素、水素、メタンを放出する。イヌリンを含む食品は、特にイヌリンに慣れていない人にとっては、かなりガスが出やすくなる。
イヌリンは水溶性食物繊維で、水溶性、不溶性、レジスタントスターチを含む3種類の食物繊維のうちの1つである。水溶性食物繊維は水に溶けてゲル状になる。水溶性食物繊維の中には、血中コレステロール値やブドウ糖値を下げる働きがあるものもある。
イヌリンは通常の消化では単糖類に分解されないため、血糖値を上昇させず、糖尿病の管理に役立つ可能性がある。イヌリンは腸内細菌の増殖も促進する。イヌリンは消化されずに胃や十二指腸を通過するため、腸内細菌叢が非常に利用しやすい。そのため、レジスタントスターチやその他の発酵性炭水化物と似ている。
伝統的な食事には、イヌリンやフラクトオリゴ糖を1日20g以上含むものもある。チワワン砂漠の先史時代の狩猟採集民の食事には、1日あたり135gのイヌリン型フルクタンが含まれていたと推定されている。チコリ、ニンニク、ネギなど、イヌリンやフラクトオリゴ糖を多く含む食品は、何世紀にもわたって「健康増進剤」とされてきた。
2013年の時点では、プレバイオティクスのマーケティングにおける健康強調表示を許可した規制当局はなかった。イヌリンの健康効果は小規模な臨床試験で研究されており、膨満感や鼓腸などの胃腸への悪影響、トリグリセリド値や脂肪肝の発症に影響を与えないこと、旅行者下痢の予防に役立つ可能性があること、思春期のカルシウム吸収を高めるのに役立つ可能性があることなどが示されていた。
天然の供給源
イヌリンを多く含む植物には以下のようなものがある:
- Agave/ja (リュウゼツラン属)
- Banana/jaとオオバコ (Musaceae/ja)
- Burdock/ja (Arctium lappa)
- カマス (カマッシア属)
- Chicory/ja (Cichorium intybus)
- コーンフラワー (Echinacea/ja 属)
- Costus/ja (Saussurea lappa)
- Dandelion/ja (Taraxacum officinale)
- Elecampane/ja (Inula helenium)
- ニンニク (Allium sativum)
- Globe artichoke/ja (Cynara scolymus, Cynara cardunculus 変種 scolymus)
- Jerusalem artichoke/ja (Helianthus tuberosus)
- Jicama/ja (Pachyrhizus erosus)
- Leopard's bane/ja (Arnica montana/ja)
- Mugwort/ja 根 (Artemisia vulgaris/ja)
- Onion/ja (Allium cepa)
- Wild yam/ja (Dioscorea/ja 属)
- Yacón/ja (Smallanthus sonchifolius)
