Hyperlipidemia/ja: Difference between revisions
Created page with "=== ナイアシン ===" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Created page with "ナイアシン、またはビタミンB<sub>3</sub>の作用機序はよくわかっていないが、LDLコレステロールとトリグリセリドを減少させ、HDLコレステロールを増加させることが示されている。 最も一般的な副作用は、二次的な皮膚血管拡張による紅潮である。この作用はプロスタグランジンによって媒介され、同時にaspirin/ja..." |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 242: | Line 242: | ||
=== ナイアシン === | === ナイアシン === | ||
ナイアシン、またはビタミンB<sub>3</sub>の作用機序はよくわかっていないが、LDLコレステロールとトリグリセリドを減少させ、HDLコレステロールを増加させることが示されている。 最も一般的な副作用は、二次的な[[skin/ja|皮膚]][[vasodilation/ja|血管拡張]]による紅潮である。この作用は[[prostaglandin/ja|プロスタグランジン]]によって媒介され、同時に[[aspirin/ja|アスピリン]]を服用することで減少させることができる。 | |||
< | <span id="Bile_acid_binding_resins"></span> | ||
=== | === 胆汁酸結合樹脂=== | ||
[[colestipol/ja|コレスチポール]]、[[cholestyramine/ja|コレスチラミン]]、[[colesevelam/ja|コレスベラム]]などの[[bile acid/ja|胆汁酸]]結合性の[[resin/ja|樹脂]]は、胆汁酸を結合して排泄を増加させることで機能する。これらはLDLコレステロールを減少させるのに有用である。最も一般的な副作用は腹部膨満感と下痢である。 | |||
[[ | |||
< | <span id="Sterol_absorption_inhibitors"></span> | ||
=== | === ステロール吸収阻害剤 === | ||
[[ezetimibe/ja|エゼチミブ]]などの腸管[[sterol/ja|ステロール]]吸収阻害薬は、[[gastrointestinal wall/ja|消化管壁]]の[[transport protein/ja|輸送タンパク質]]である[[NPC1L1/ja|NPC1L1]]を標的とすることにより、消化管におけるコレステロールの吸収を低下させることで機能する。その結果、LDLコレステロールが減少する。 | |||
== 予防{{Anchor|Prevention}} == | == 予防{{Anchor|Prevention}} == | ||
Latest revision as of 21:33, 13 April 2024
| 高脂血症 | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 高リポ蛋白血症、高脂血症 |
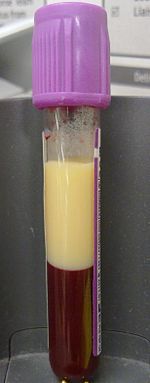 | |
| EDTAを入れたバキュテイナーに高脂血症の血液を4ml採取する。 遠心分離せずに4時間放置すると、脂質は上部の画分に分離した。 | |
| Specialty | 循環器学 |
| Differential diagnosis | 高トリグリセリド血症 |
高脂血症とは、血液中の脂質(例えば、脂肪、トリグリセリド、コレステロール、リン脂質)またはリポ蛋白のいずれかまたはすべての値が異常に高いことである。高脂血症という用語は、検査所見そのものを指し、その所見をもたらす様々な後天的または遺伝的障害を包括する用語としても用いられる。高脂血症は脂質異常症のサブセットであり、高コレステロール血症のスーパーセットである。高脂血症は通常慢性であり、血中脂質値をコントロールするために継続的な医薬品が必要である。
脂質(水に溶けない分子)はタンパク質の中に輸送される。カプセルに入って輸送される。そのカプセル、すなわちリポタンパク質の大きさによって密度が決まる。リポタンパク質の密度とそれが含むアポリポタンパク質の種類は、粒子の運命と代謝への影響を決定する。
高脂血症は一次性高脂血症と二次性高脂血症に分けられる。一次性高脂血症は通常、遺伝的原因(受容体タンパク質の変異など)によるものであり、二次性高脂血症は糖尿病などの他の基礎的原因によって生じる。脂質およびリポ蛋白の異常は一般集団によくみられ、アテローム性動脈硬化症への影響から心血管系疾患の修正可能な危険因子とみなされている。さらに、急性膵炎の素因となる型もある。
分類
高脂血症は、基本的に、特定の遺伝子異常によって引き起こされる家族性(原発性とも呼ばれる)と、血漿脂質およびリポ蛋白代謝の変化をもたらす他の基礎疾患に起因する後天性(続発性とも呼ばれる)に分類される。また、高脂血症は特発性、すなわち原因が明らかでない場合もある。
高脂血症は、高コレステロール血症、高トリグリセリド血症、またはその両方の複合高脂血症のどのタイプの脂質が上昇するかによっても分類される。リポ蛋白(a)の上昇も高脂血症の一種に分類される。
家族性(一次性)
家族性高脂血症は、電気泳動または超遠心機でのリポ蛋白のパターンに基づくFredrickson分類に従って分類される。後に世界保健機関(WHO)によって採用された。これはHDLを直接的に説明するものではなく、また、これらの状態のいくつかに部分的に関与している可能性のある異なる遺伝子を区別するものでもない。
| 高リポ 蛋白血症 |
OMIM/ja | 症状 | 欠陥 | リポ蛋白質の増加 | 主な症状 | 治療 | 血清の外観 | 推定有病率 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I型 | a | 238600 | Buerger-Gruetz症候群または家族性高カイロミクロン血症 | lipoprotein lipase/jaの減少 (LPL) | Chylomicrons/ja | Acute pancreatitis/ja, lipemia retinalis/ja, 発疹性皮膚黄色腫症, hepatosplenomegaly/ja | 食事管理 | クリーミーなトップ層 | 100万分の1 |
| b | 207750 | 家族性アポ蛋白CII欠損症 | 変化したApoC2 | ||||||
| c | 118830 | 血中のLPL阻害 | |||||||
| II型 | a | 143890 | Familial hypercholesterolemia/ja | LDL receptor/ja欠乏症 | LDL/ja | Xanthelasma/ja, arcus senilis/ja, 腱黄色腫 | Bile acid sequestrant/ja, statin/ja, ナイアシン | クリア | ヘテロ接合体は500人に1人 |
| b | 144250 | 家族性複合高脂血症 | LDL receptor/jaの減少とApoBの増加 | LDL/jaとVLDL/ja | スタチン, ナイアシン, fibrate/ja | 濁っている | 100人に1人 | ||
| III型 | 107741 | Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia/ja | Apo E 2合成の欠陥 | IDL | 結節性黄色腫および手掌黄色腫 | フィブラート, スタチン | 濁っている | 1万人に1人 | |
| IV型 | 144600 | Familial hypertriglyceridemia/ja | VLDLの産生が増加し、排泄が減少する。 | VLDL | トリグリセリド値が高いと膵炎を引き起こす可能性がある。 | フィブラート, ナイアシン, スタチン | 濁っている | 100人に1人 | |
| V型 | 144650 | VLDL産生が増加し、LDLが減少する。 | VLDLとカイロミクロン | ナイアシン, フィブラート | 上層はクリーミーで、下層は濁っている。 | ||||

I型
I型高リポ蛋白血症にはいくつかの病型がある:
- リポ蛋白リパーゼ欠乏症(Ia型)、リポ蛋白リパーゼ(LPL)の欠乏またはアポリポ蛋白C2の変化により、脂肪酸を消化管から肝臓に移行させる粒子であるカイロミクロンが上昇する。
- 家族性アポ蛋白CII欠乏症(Ib型)は、リポ蛋白リパーゼ活性化因子の欠乏によって起こる。
- 循環リポ蛋白リパーゼ阻害剤によるカイロミクロン血症(Ic型)
I型高リポ蛋白血症は通常、小児期に発疹性黄色腫と腹部疝痛を呈する。合併症としては、網膜静脈閉塞症、急性膵炎、脂肪症、臓器腫大、網膜脂肪血症などがある。
II型
高リポ蛋白血症II型は、主にLDLコレステロールに加えてトリグリセリド値の上昇が起こるかどうかによって、IIa型とIIb型にさらに分類される。
IIa型
これは、19番染色体上のLDL受容体遺伝子(人口の0.2%)またはApoB遺伝子(0.2%)のいずれかの変異の結果として、散発性(食事要因による)、多遺伝性、または真に家族性の場合がある。家族型は、腱黄色腫、肝斑、および早発性の心血管疾患を特徴とする。 この疾患の発生率は、ヘテロ接合体では約500人に1人、ホモ接合体では100万人に1人である。
HLPIIaは、LDL粒子が取り込まれない(Apo B受容体がない)ために血中のLDLコレステロール濃度が上昇することを特徴とするまれな遺伝性疾患である。しかし、この病態は様々な高リポ蛋白血症の中で2番目に多い疾患であり、ヘテロ接合体素因を持つ個体は500人に1人、ホモ接合体素因を持つ個体は100万人に1人である。これらの患者は、黄色腫(皮膚の下に脂肪が黄色く沈着し、しばしば眼球の鼻の部分に現れる)、腱様黄色腫、結節性黄色腫、若年性円弧腫(高齢者によくみられる眼の白化)、動脈瘤、跛行、そしてもちろんアテローム性動脈硬化症などの独特な身体的特徴を呈することがある。これらの人の検査所見では、血清総コレステロール値が正常値の2〜3倍で、LDLコレステロールも増加しているが、トリグリセリド値とVLDL値は正常範囲である。
HLPIIa患者を管理するためには、特にHDLコレステロール値が30 mg/dL未満で、LDL値が160 mg/dLを超える場合は、抜本的な対策を講じる必要があるかもしれない。このような人に適切な食事は、総脂肪を総カロリーの30%以下に減らし、一価不飽和脂肪:多価不飽和脂肪:飽和脂肪の比率を1:1:1にすることである。コレステロールは300 mg/日未満に減らし、動物性食品を避け、食物繊維の摂取量を20g/日以上に増やし、水溶性食物繊維を6g/日摂取する。運動はHDLを増加させるので、推進すべきである。このような人の全体的な予後は、コントロールされず治療を受けていない場合、最悪のシナリオでは20歳までに死亡する可能性があるが、正しい医学的介入を受けながら慎重な食生活を心がければ、10年ごとに黄色腫の発生率が増加し、アキレス腱炎や動脈硬化の促進が見られるようになる。
IIb型
VLDL値が高いのは、トリグリセリド、アセチル-CoA、B-100合成の増加などの基質の過剰生産によるものである。また、LDLのクリアランスの低下によっても起こる。集団における有病率は10%である。
- 家族性複合高リポ蛋白血症 (FCH)
- ライソゾーム酸性リパーゼ欠乏症(しばしばコレステリルエステル貯蔵症と呼ばれる)。
- 二次性複合高リポ蛋白血症(通常メタボリックシンドロームの診断基準となっている。)
III型
この型は、カイロミクロンおよびIDL(中間密度リポ蛋白)の高値に起因する。この型の最も一般的な原因はApoEの存在である。E2/E2遺伝子型の存在である。コレステロールを多く含むVLDL(β-VLDL)が原因である。その有病率は約10,000人に1人と推定されている。
高コレステロール血症(通常8〜12mmol/L)、高トリグリセリド血症(通常5〜20mmol/L)、正常ApoB濃度、2種類の皮膚徴候(手掌黄色腫または皮膚のしわのオレンジ色変色、肘と膝の結節性黄色腫)を伴う。心血管系疾患と末梢血管疾患の早期発症が特徴である。高脂血症はApoE受容体の機能異常の結果として起こる。ApoE受容体は通常、カイロミクロン残渣とIDLの循環からのクリアランスに必要である。レセプターの欠損により、血液中のカイロミクロン残渣とIDLの濃度が正常より高くなる。受容体の欠損は常染色体劣性突然変異または多型である。
IV型
家族性高トリグリセリド血症は常染色体優性遺伝で、人口の約1%にみられる。
この型はトリグリセリド値が高いことによる。他のリポ蛋白の値は正常か少し増加している。
治療には食事療法、フィブラート、ナイアシンなどがある。スタチンは、トリグリセリド値を低下させる場合、フィブラートよりも優れているわけではない。
V型
高リポ蛋白血症Ⅴ型は、家族性混合型高リポ蛋白血症または混合型高リポ蛋白血症としても知られ、Ⅰ型に非常によく似ているが、カイロミクロンに加えてVLDLが高い。
また、耐糖能異常や高尿酸血症とも関連している。
医学的には、複合型高脂血症(または貧血)(「多型高リポ蛋白血症」とも呼ばれる)は、LDLおよびトリグリセリド濃度の上昇を特徴とする高コレステロール血症(コレステロール値の上昇)の一般的な発症形態であり、しばしばHDLの低下を伴う。リポ蛋白電気泳動法(現在ではほとんど行われていない検査)では、高リポ蛋白血症IIB型として示される。最も一般的な遺伝性脂質異常症で、約200人に1人の割合で発症する。実際、60歳までに冠動脈性心疾患を発症する人のほぼ5人に1人がこの疾患を持っている。 トリグリセリド値の上昇(>5 mmol/L)は一般に、動脈硬化を引き起こしやすいリポ蛋白の一種である超低密度リポ蛋白(VLDL)の増加によるものである。
両疾患とも、ペルオキシソーム増殖因子活性化受容体(PPAR)、特にPPARαに作用して遊離脂肪酸産生を減少させるフィブラート薬物で治療される。 スタチン系薬物、特に合成スタチン系薬物(アトルバスタチン、ロスバスタチン)は、LDL受容体発現の増加によりLDLの肝での再取り込みを増加させることにより、LDL値を低下させることができる。
分類不能の家族型
これらの未分類型は極めてまれである:
後天性(二次性)
後天性高脂血症(二次性リポ蛋白異常症とも呼ばれる)はしばしば原発性高脂血症を模倣し、同様の結果をもたらすことがある。後天性高脂血症は、早期アテローム性動脈硬化症のリスクを増大させたり、著明な高トリグリセリド血症を伴う場合には、膵炎や他のカイロミクロン血症症候群の合併症を引き起こしたりする。後天性高脂血症の最も一般的な原因は以下の通りである:
- 糖尿病
- サイアザイド系利尿薬、β遮断薬、エストロゲンなどの薬物の使用である。
後天性高脂血症の原因となる他の疾患には、以下のようなものがある:
可能であれば基礎疾患の治療、または原因となる薬物の中止は、通常、高脂血症の改善につながる。
高脂血症のもう一つの後天的な原因として、常にこのカテゴリーに含まれるわけではないが、食後高脂血症がある。
プレゼンテーション
心血管疾患との関係
高脂血症はアテローム性動脈硬化症の素因となる。アテローム性動脈硬化症は、動脈壁内に脂質、コレステロール、カルシウム、線維性プラークが蓄積することである。この蓄積は血管を狭くし、心臓の筋肉への血流と酸素を減少させる。時間が経つにつれて脂肪沈着物が蓄積し、臓器や組織が適切に機能するのに十分な血液が供給されなくなるまで動脈を硬化させ狭くする。 心臓に血液を供給する動脈が影響を受けると、狭心症(胸痛)を起こすことがある。動脈の完全な閉塞は心筋細胞の梗塞を引き起こし、心臓発作としても知られる。血栓が脳への血流を遮断すると、動脈に脂肪が蓄積して脳卒中を引き起こすこともある。
スクリーニング
20歳以上の成人は、4~6年ごとにコレステロールの検査を受けるべきである。血清中の低比重リポ蛋白(LDL)コレステロール、高比重リポ蛋白(HDL)コレステロール、およびトリグリセリドの値は、プライマリケアにおいて脂質パネルを用いて一般的に検査される。リポ蛋白およびトリグリセリドの定量値は、フラミンガムリスクスコア、ACC/AHAアテローム性動脈硬化性心血管疾患リスク推定因子、および/またはレイノルズリスクスコアなどのモデル/計算機による心血管系疾患リスク層別化に寄与する。これらのモデル/計算機は、家族歴(心臓病および/または高血中コレステロール)、年齢、性別、Body-Mass-Index、病歴(糖尿病、高コレステロール、心臓病)、高感度CRP値、冠動脈カルシウムスコア、および足関節上腕血圧指数も考慮することができる。心血管系の層別化はさらに、将来の心血管系疾患のリスクを減少させるためにどのような医薬品介入が必要かを決定する。
総コレステロール
LDLとHDLの合計量。総コレステロールが240mg/dLを超えると異常であるが、医薬品への介入はLDLとHDLの値の内訳によって決定される。
LDLコレステロール
一般に「悪玉コレステロール」として知られるLDLは、心血管疾患のリスク増大と関連している。LDLコレステロールはコレステロール粒子を全身に運搬し、動脈壁に蓄積して動脈を硬く狭くする。LDLコレステロールは体内で自然に生成されるが、飽和脂肪酸、トランス脂肪酸、コレステロールの多い食事を摂るとLDL値が上昇する。LDL値の上昇は、糖尿病、高血圧、高中性脂肪血症、動脈硬化と関連している。空腹時脂質パネルでは、LDLが160mg/dLを超えると異常である。
HDLコレステロール
HDLは "善玉コレステロール "としても知られ、心血管系疾患のリスク低下と関連している。HDLコレステロールは、体内の他の部位にあるコレステロールを肝臓に運び、体外に排出する。HDLコレステロールは、タバコの使用、肥満、運動不足、高トリグリセリド血症、糖尿病、高炭水化物食、医薬品の副作用(ベータ遮断薬、アンドロゲンステロイド、コルチコステロイド、黄体ホルモン、サイアザイド系利尿薬、レチノイン酸誘導体、経口エストロゲンなど)、遺伝的異常(変異エストロゲンなど)など、後天的または遺伝的要因によって影響を受けることがある。 など)、遺伝子異常(ApoA-I、LCAT、ABC1の変異)などがある。低値は40mg/dL未満と定義される。
トリグリセリド
トリグリセリド値は、心血管疾患および/またはメタボリックシンドロームの独立した危険因子である。検査前の食物摂取により、最大20%上昇することがある。正常値は150mg/dL未満と定義される。境界域高値は150~199mg/dLと定義される。高値は200~499mg/dLである。500mg/dLを超えると非常に高値と定義され、膵炎と関連し、医薬品による治療が必要となる。
スクリーニング開始年齢
高脂血症のスクリーニングを開始する年齢について、医療機関のコンセンサスは得られていない。CDCは、9~11歳の間に1回、17~21歳の間にもう1回、成人後は4~6年ごとにコレステロール検査を行うことを推奨している。早期の心臓発作や心臓病の家族歴がある人や、子供に肥満や糖尿病がある場合には、医師はより頻繁なスクリーニングを勧めることがある。USPSTFは、35歳以上の男性と45歳以上の女性にスクリーニングを受けるよう推奨している。NCE-ATPⅢでは、20歳以上のすべての成人にスクリーニングを受けることを推奨している。 しかし、CHDまたはそれに相当するリスク(例えば、急性冠症候群、心臓発作の既往、安定型または非安定型狭心症、一過性脳虚血発作、アテローム性動脈硬化症由来の末梢動脈疾患、冠動脈またはその他の動脈血行再建術)がある場合には、スクリーニングを行うべきである。
スクリーニングの頻度
20歳以上の成人は4~6年ごとにコレステロールの検査を受けるべきであり、ほとんどの検診ガイドラインでは5年ごとの検査を推奨している。USPSTFは、心血管疾患リスクスコアを用いて判断されるCHDリスクが高い人に対しては、頻度を増やすことを推奨している。
管理
高脂血症の管理には、正常体重の維持、身体活動の増加、精製炭水化物および単糖の摂取の減少が含まれる。心血管疾患、190mg/dLを超えるLDLコレステロールまたは糖尿病などの重大な危険因子を有する一部の人の治療には、処方薬物が使用されることがある。一般的な医薬品治療はスタチンである。
HMG-CoA還元酵素阻害薬
ロバスタチン、アトルバスタチン、フルバスタチン、プラバスタチン、シンバスタチン、ロスバスタチン、ピタバスタチンなどのHMG-CoA還元酵素の競合的阻害薬は、コレステロールの前駆体分子であるメバロン酸の合成を阻害する。この医薬品クラスは、上昇したLDLコレステロールを減少させるのに特に効果的である。主な副作用には、トランスアミナーゼの上昇やミオパシーがある。
線維酸誘導体
ゲムフィブロジルやフェノフィブラートなどの線維酸誘導体は、ペルオキシソーム増殖因子活性化受容体-αの活性化を介して脂肪組織の脂肪分解を増加させることによって機能する。これらの薬剤は、人によってはVLDL-超低比重リポ蛋白とLDLを減少させる。 主な副作用には、発疹、消化器系の不調、ミオパシー、トランスアミナーゼの増加などがある。
ナイアシン
ナイアシン、またはビタミンB3の作用機序はよくわかっていないが、LDLコレステロールとトリグリセリドを減少させ、HDLコレステロールを増加させることが示されている。 最も一般的な副作用は、二次的な皮膚血管拡張による紅潮である。この作用はプロスタグランジンによって媒介され、同時にアスピリンを服用することで減少させることができる。
胆汁酸結合樹脂
コレスチポール、コレスチラミン、コレスベラムなどの胆汁酸結合性の樹脂は、胆汁酸を結合して排泄を増加させることで機能する。これらはLDLコレステロールを減少させるのに有用である。最も一般的な副作用は腹部膨満感と下痢である。
ステロール吸収阻害剤
エゼチミブなどの腸管ステロール吸収阻害薬は、消化管壁の輸送タンパク質であるNPC1L1を標的とすることにより、消化管におけるコレステロールの吸収を低下させることで機能する。その結果、LDLコレステロールが減少する。
予防
禁煙、飽和脂肪とアルコールの摂取量を減らすこと、過剰な体重を減らすこと、果物、野菜、全粒穀物を中心とした塩分控えめの食事を摂ることは、血中コレステロールを減らすのに役立つ。
こちらも参照
- List of xanthoma variants associated with hyperlipoproteinemia subtypes/ja
- Combined hyperlipidemia/ja