Latest revision as of 13:48, 5 April 2024
Definition
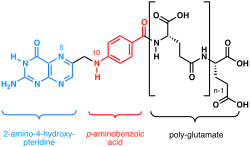 Chemical structure of the folate family
Chemical structure of the folate family
Folate (vitamin B9) refers to the many forms of folic acid and its related compounds, including tetrahydrofolic acid (the active form), methyltetrahydrofolate (the primary form found in blood), methenyltetrahydrofolate, folinic acid, folacin, and pteroylglutamic acid. Historic names included L. casei factor, vitamin Bc and vitamin M.
