Translations:Vitamin D/11/en
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Biology
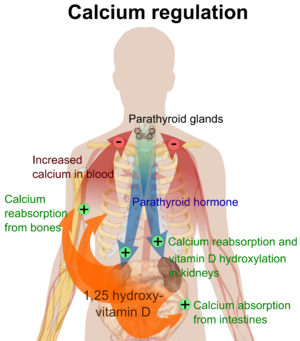
The active vitamin D metabolite calcitriol mediates its biological effects by binding to the vitamin D receptor (VDR), which is principally located in the nuclei of target cells. The binding of calcitriol to the VDR allows the VDR to act as a transcription factor that modulates the gene expression of transport proteins (such as TRPV6 and calbindin), which are involved in calcium absorption in the intestine. The vitamin D receptor belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily of steroid/thyroid hormone receptors, and VDRs are expressed by cells in most organs, including the brain, heart, skin, gonads, prostate and breast.