Translations:Riboflavin/16/en
Synthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis takes place in bacteria, fungi and plants, but not animals. The biosynthetic precursors to riboflavin are ribulose 5-phosphate and guanosine triphosphate. The former is converted to L-3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate while the latter is transformed in a series of reactions that lead to 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil. These two compounds are then the substrates for the penultimate step in the pathway, catalysed by the enzyme lumazine synthase in reaction EC 2.5.1.78.
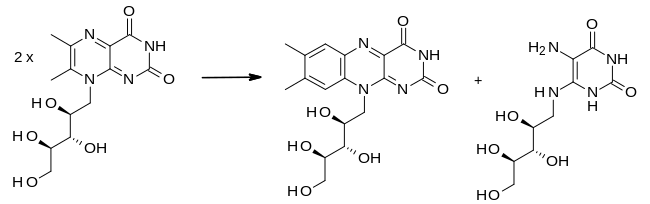
In the final step of the biosynthesis, two molecules of 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine are combined by the enzyme riboflavin synthase in a dismutation reaction. This generates one molecule of riboflavin and one of 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino) uracil. The latter is recycled to the previous reaction in the sequence.
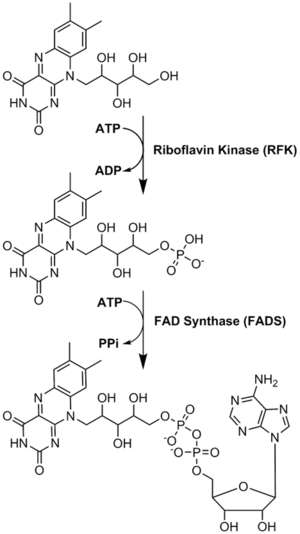
Conversions of riboflavin to the cofactors FMN and FAD are carried out by the enzymes riboflavin kinase and FAD synthetase acting sequentially.